Astronomy Unit 2: The Sun
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
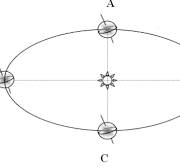
What season is this shown at letter A?
Fall
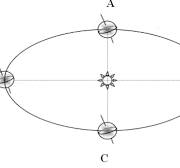
What season is shown at letter B?
Summer
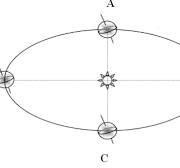
What season is shown at letter C?
Spring
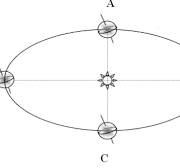
What season is shown at letter D?
Winter
Where do the most direct rays strike the Earth during winter?
The Tropic of Capricorn
Where do the most direct rays strike the Earth during spring?
At the Equator
Where do the most direct rays strike Earth during the summer?
The Tropic of Cancer
Where do the most direct rays strike the Earth during the fall?
The Equator
How does daylight change with the seasons?
Earth’s axial tilt causes different hemishperes to recieve different amounts of sunlight at different times of the year
What is the angle of solar noon altitude during the winter?
23 degrees
What is the angle of solar noon altitude during the spring and fall?
47 degrees
What is the angle of solar noon altitude during the summer?
70 degrees
What is the effect of the angle of the sun on solar radiation and daylight hours?
It causes the changing of the seasons
Where is the location of sunrise and sunset?
The sun rises in the east and sets in the west
How does the axial tilt of the Earth cause changes in the apparent path of the sun?
Different hemishperes are angled towards the sun at different times of the year
What is the reason for the seasons?
The Earth’s axial tilt causes different areas to receive different amounts of sunlight
What type of star is the sun?
A yellow dwarf star
How big is the sun compared to Earth?
About 109 times bigger than Earth
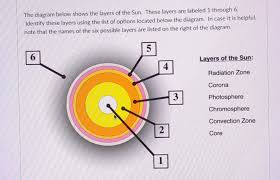
What layer of the sun is #1?
The core
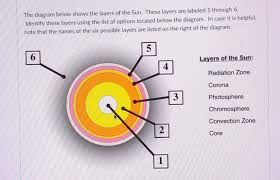
What layer of the sun is #2?
Radiative Zone

What layer of the sun is #3?
Convective Zone
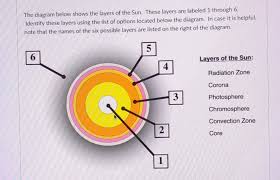
What layer of the sun is #4?
Photosphere

What layer of the sun is #5?
Chromosphere
What layer of the sun is #6?
Corona
What is the sun’s energy source and what occurs during this process?
Nuclear Fusion
Why do thermonuclear reactions only occurs in the sun’s core?
It’s the only place with high enough temperatures and pressure for nuclear fusion to happen
How does energy move through the radiative and convection zones?
Energy moves from the radiative zone as photons and is transported by the movement of plasma in the convective zone
How does the density change through the layers of the sun?
Decreases dramatically from the core to the surface of the sun
How does the temperature change through the layers of the sun?
Decreases from the core out to the visible surface but rapidly increases in the sun’s atmosphere
Sunspot:
Result from the interaction of the sun’s surface plasma with it’s magnetic field
Solar Flare:
High magnetic fields in sunspot regions cause explosions
Prominence:
A large loop of plasma that is released into space and held together by the sun’s magnetic field
CME:
Plasma that explodes back into space from the sun
How are sunspots different from the surrounding photosphere?
They are regions of intense magnetic fields that are cooler and darker
How do magnetic fields and differential rotation cause the formation of sunspots?
When the sun’s magnetic field lines twist and break through the surface, creating intense magnetism
How does the location of sunspots change during a solar cycle?
Sunspots migrate from high latitudes towards the equator
How are sunspots, solar flares, prominences, and CME’s related?
They are related to intense magnetism on the sun
Why should solar flares and coronal mass ejection s be a concern for businesses that use telecommunication satellites?
Solar weather can damage power grids and create long-lasting blackouts; they can also disrupt satellite communications
What causes auroras?
When the energy from a solar storm reaches Earth, charged particles interact with air molecules to create aurora