First 5 Units of SCIENCE FINALS
1/508
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
509 Terms
What is the difference in shape between a concave and convex lens?
Convex flexes outward, Concave bends(caves) inwards.
What type of lens magnifies the objects?
Convex
What is light? In what form does it travel?
A form of electromagnetic radiation. It travels in the form of a wave.
What is reflection?
When light bounces of a (opaque) surface.
What is refraction?
When light is bent as it travels through a material.
What is absorption?
When the energy from the light wave is absorbed by the material.
What is color?
A form of electromagnetic radiation on the electromagnetic spectrum
What is a pigment? Do pigments absorb and/or reflect the color you see?
Pigment is a color found in substances that absorbs and reflects different wavelengths of light. A red shirt will absorb blue and yellow radiation, and reflect back to the person looking at the shirt.
f you wanted to see more area and objects around you, you would look through what type of lens?
Concave
Does sunlight have color? Can you provide an example to prove your point?
Sunlight contains all the colors in the electromagnetic spectrum. If you have a prism like Sir Isaac Newton, you can separate all the colors from sunlight. Or you can simply observe the beautiful creating that is a rainbow, where water droplets refract and separate the sunlight into its many colors.
What is the opposite of opaque?
Transparent
Light that appears bent as it passes through a material is…
Refracted
When lights energy is transferred to a material it is….
Absorbed
Light that bounces off an object is…..
Reflected
A pigment will…
Absorb light
What part of the human eye controls the amount of light entering?
The iris
What protects the front of the eyeball?
The cornea
The image that enters the eye is projected onto the …which uses light sensitive cells (rods and cones) to create the image.
Retina
When the iris shrinks to let less light in, less light enters the …
Pupil
The image on the retina is analyzed by the brain after it passes through the …
Optic nerve
The bundle of fibers that carries visual messages from the retina is the ...
Optic nerve
What does the retina contain which allows you to see color in your vision?
Cones
What type of lens is found in the human eye?
Convex
What structure does a cow and cat eye possess, that is not found in a human eye?
Tapetum
What advantage does a tapetum give animals that have it in their eyes?
Better night vision
Can dust in a room get into your eye?
No, but it can touch your cornea, which might cause pain.
What structures would allow or prevent objects from entering your eye?
The cornea.
What parts of the human eye provide structural support? (two)
The sclera (white) and the vitreous humour (clear)
What part of the eye is responsible for night vision?
Rods in the retina
Why don’t you see color when it’s really dark?
Cones are not as sensitive as rods, and need more light to function.
Can the lens of a human eye change shape?
Yes: The lens of a human eye is stretched by muscles attached to it. When the muscles relax, the lens flattens out, and you can see distant objects. When the muscles contract, the lens returns to normal shape, enabling you to see closer objects. This is why it is more tiring to look at close objects (because the muscles have to contract).
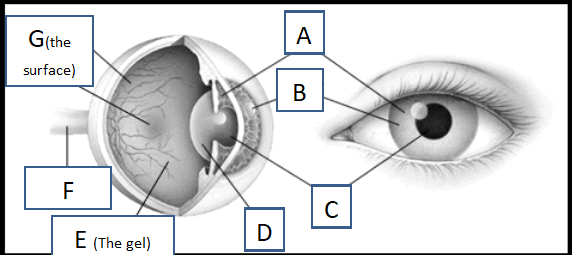
Label the parts of the eye.
A. Iris
B. Cornea
C. Pupil
D. Lens
E. Vitreous Humour
F. Optic Nerve
G. Retina
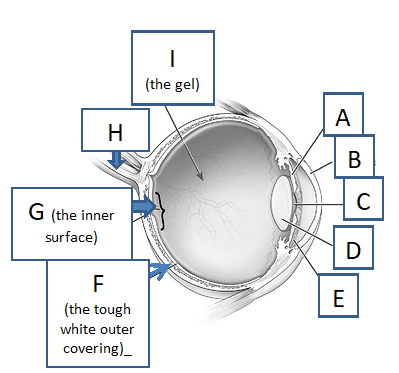
Label the parts of the eye. (don’t include A)
B. Cornea
C. Pupil
D. Lens
E. Iris
F. Sclera
G. Retina
H. Optic Nerve
I. Vitreous Humour
What is the magnification of the ocular/eyepiece?
10x
What is the magnification of the low power objective on our microscopes?
4x
What is the overall magnification equation?
multiple the ocular (10x) X objective
What 2 parts do you use when carrying a microscope?
Arm and base
What 2 parts are used for focusing the specimen?
The coarse and fine adjustment.
Is the coarse or fine adjustment not used in medium or high power?
You should never use the coarse adjustment in medium or high power, because you might crack the slide.
What part of a microscope allows you to change the magnification?
The nosepiece allows you to change the objective lens and the overall magnification.
What part controls the amount of light passing through the specimen?
Diaphragm
If the ocular is 10x and the low power is 6x, what is the overall magnification?
60x
When would you use a stereo microscope instead of a compound microscope?
When you are dissecting or need a 3-dimensional view of the specimen.
What are the steps for making a proper wet mounted slide?
Place a drop of water on the slide
Place the specimen on the drop of water
Place a drop of water on the specimen
Lower the cover slip on a 45 degree angle
What are the steps for making a stained slide?
Place a drop of stain on the left edge of the cover slip
Place the flat edge of a paper towel on the right edge of the cover slip
Why do you lower the cover slip on a 45 degree angle?
To remove air bubbles, and not damage the specimen
Under which magnification is the field of view larger? (low, medium, or high)
The field of view is larger (you see more) in low power.
What part of the microscope has the same function as the iris in your eye?
Both the iris and the diaphragm change size to control the amount of light going through.
How many oculars does a stereo microscope have?
2 Oculars
How many oculars does a compound microscope have?
1 Ocular
The field of view is 6 millimeters across in high power. 1 millimeter is equal to 1000 micrometers. How many micrometers is the field of view in high power?
6000 micrometers
If 3 cells fit across the microscope in high power, how big is each cell in millimeters? (field of view is 6 mm)
2mm
You see 10 cells under low power, which has a field of view = 5mm. What is the size of each individual cell?
0.5mm
How would the letter T look under a microscope?
It would look upside-down.
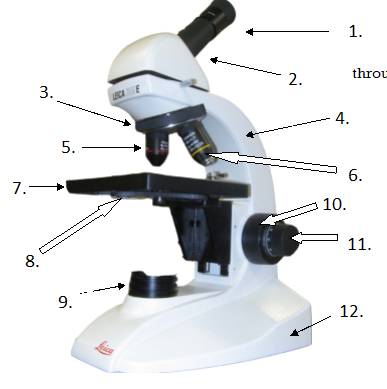
Label the microscope.
Eyepiece or Ocular
2. Body Tube
3. Nosepiece
4. Arm
5. Low power objective
6. High power objective
7. Stage
8. Diaphragm
9. Light Source
10. Coarse Adjustment
11. Fine Adjustment
12. Base
You are given a microscope with a low power field of view of 4mm. When looking through the ocular (eyepiece) you can see that 2 cells fit across the field of view. What is the size of the cells?
2mm
You are given a slide of a plant cell to observe under high power magnification. You count approximately 8 of them in the field of view under high power. If the field of view under high power is 2mm, how big is each cell?
0.25mm
What are the 2 types of observations? (give an example of each)
Quantitative and qualitative
If I give 5 students broccoli and 5 students sour patch kids, then the students given broccoli will do better on the next test, because sugar negatively affects their attention span (Hypothesis, Theory, or Law?)
Hypothesis
A ball thrown into the air will fall down every time because of gravity (Hypothesis, Theory, or Law?)
Law (The Law of Gravitational Attraction)
Billions of years ago the universe was condensed into a single point, and is currently expanding every day since. There is evidence to support this; however, it cannot be definitively confirmed.
The Big Bang Theory
What is the responding variable?
The dependent variable
What is the manipulated variable (what the research manipulates or changes)?
The independent variable
What is your proposed explanation for a problem or an observation?
Inference
What is the same for both the experimental and control group?
Everything except the (independent) variable.
What is the same about an inference and a prediction?
They both reasoning and are based on evidence or observations.
What is the difference between an inference and a prediction?
An inference describes something current, a prediction describes something in the future that hasn’t happened.
How are the 2 words related: Observation and Theory
An observation taken during an experiment will prove or disprove a theory.
How are the 2 words related: Theory and Law
A theory that is proven beyond all doubt will become a law.
What are the three parts of a Hypothesis?
If, then, and because
What is respiration?
The release of chemical energy in cells.
What type of reproduction involves 1 parent?
Asexual reproduction
Which type of reproduction combines the DNA of both parents?
Sexual reproduction
Organisms that are made up of one cell are…
Unicellular
Organisms that are made up of more than one cell are…
Multicellular
If your breakfast consisted on hydrogen sulfide, you would be a…
Chemotroph
Organisms that perform which type of reproduction typically have less offspring?
Sexual
Trees, mosses, and stromatolites are…. (autotroph, heterotroph, or chemotroph?)
Autotrophs
Humans are… (autotroph, heterotroph, or chemotroph?)
Heterotroph
Autotroph
An organism that makes its own food for energy
Heterotroph
An organism that eats other organisms for energy
Chemotroph
An organism that gets energy from chemicals
The first living organisms over 3 billion years ago were… (unicellular or multicellular?)
Unicellular
The specialization of cells to have different functions of is known as…
Development
The specialization of cells to have different functions would be found in… (what organism?)
Humans
The development of mosquitoes from larvae in shallow pools of water is known as…
Metamorphosis
True or False: all organisms experience growth
True
More offspring are possible in species with… (internal/external development?)
External development
What are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system responsible for cell communication?
Hormones
What organisms get heat from respiration? (warm or cold blooded?)
Warm-Blooded
A nervous system transports electrical messages in the form of …
(nerve) impulses
Which of the following would be considered autotrophs?
o Warm-blooded animals
o Cold-blooded animals
o Plants
o Snottites
Plants
Touching a hot plate is a
o Good idea
o Stimulus
o Response
o Homeostasis
Stimulus (you screaming in pain would be the response)
You didn’t listen and burned your fingers touching the hotplate. The message sent through your body of this painful stimulus travels through your …
Neurons
Respiration in humans occurs in…
Every cell
Light entering you eye is a…
Stimulus
The light entering your eye is converted to impulses as it travels through your…
Nervous system
How are growth and development different?
Growth is when an organism increases in size. Development does not require an increase in size, but the specialization of cells for specific tasks within the organism.
What type of organism does more respiration: a warm-blooded or cold-blooded organism? Why?
A warm-blooded organism does more respiration to produce enough heat to help regulate (homeostasis) their internal temperature.
How is growth and development different in unicellular and multicellular organisms?
Unicellular organisms cannot have specialization of cells (development) for specific tasks because they are only made of one cell. Humans have many cells with specific tasks: neurons for sending messages, muscles cells for movement, etc… In a unicellular organism, the one cells performs all the functions needed for survival.