A-Level OCR Biology A: 4.1 Communicable diseases
Disease
A condition that impairs the normal functions of the body
Pathogen
A microorganism that causes disease
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Disease
A condition that impairs the normal functions of the body
Pathogen
A microorganism that causes disease
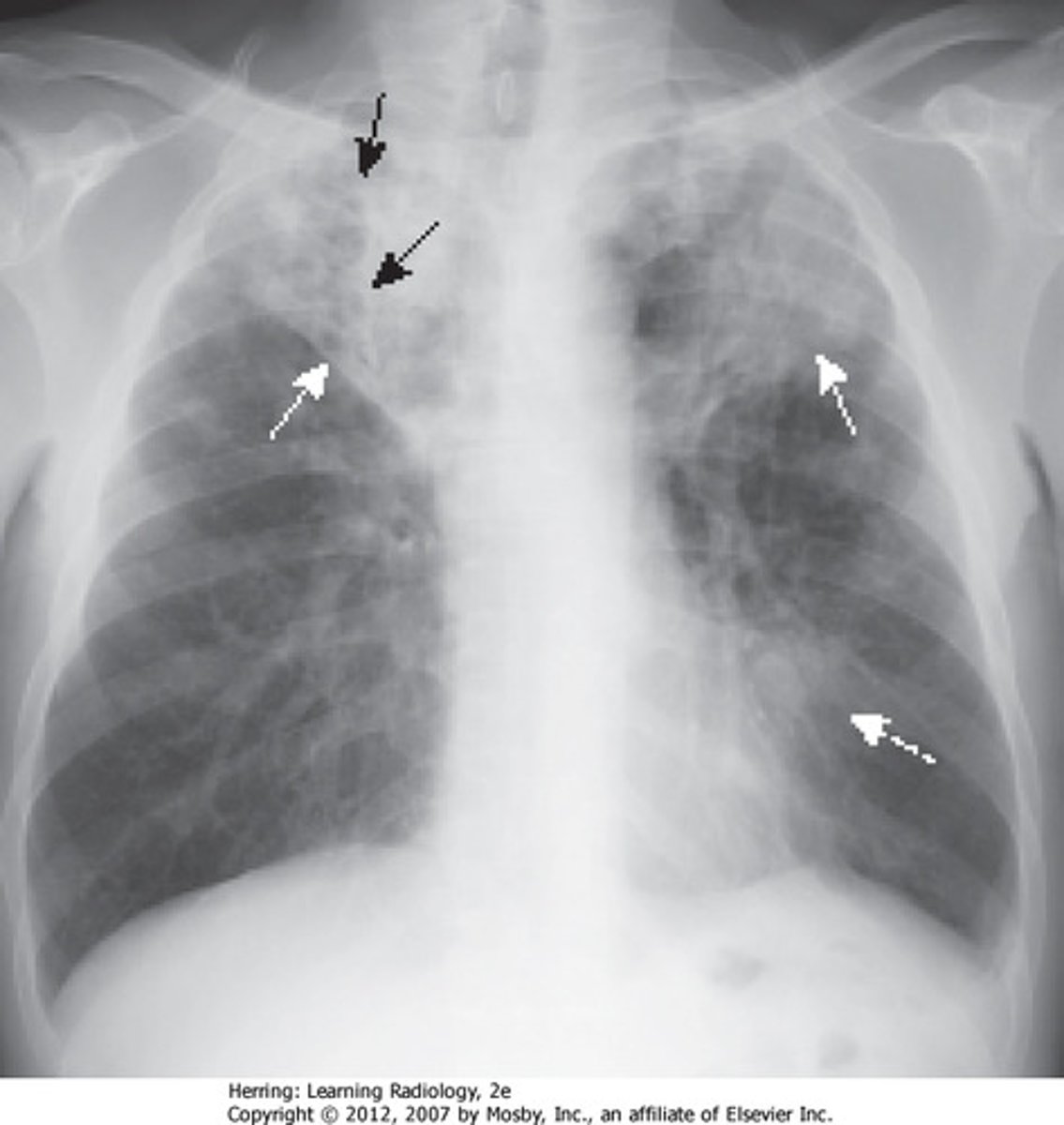
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
A bacterial infectious disease that affects humans and cattle
- Kills cells and tissues, mainly the lungs
- Has thick cell wall
- Diagnosed with x-ray
- Transmitted through airborne droplets
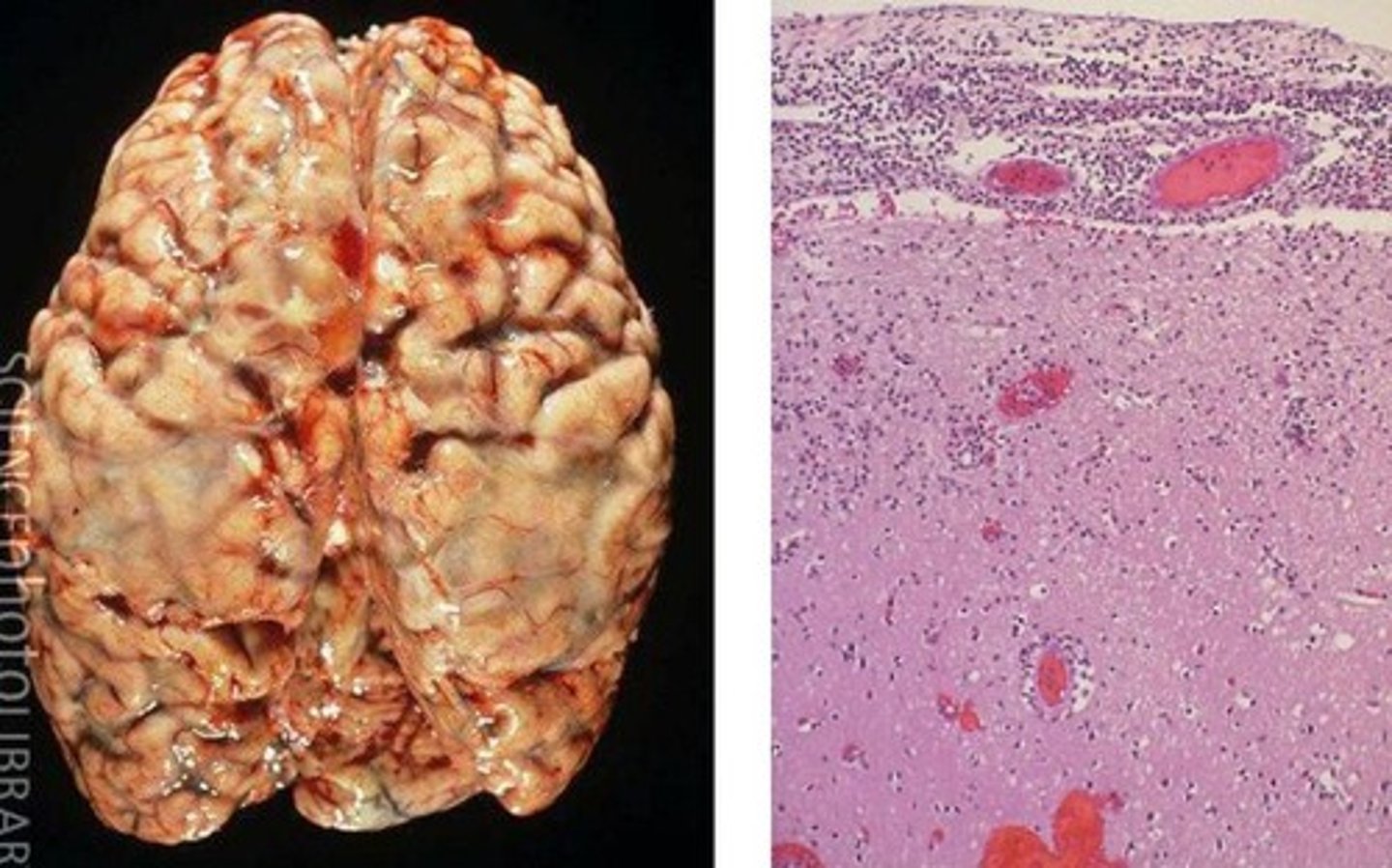
Meningitis
A bacterial infectious disease that affects humans.
- Infects the membrane around brain & spinal cord (meninges), causing brain and nerve damage
- Diagnosed with blood test or lumbar puncture
- Treated with antibiotics
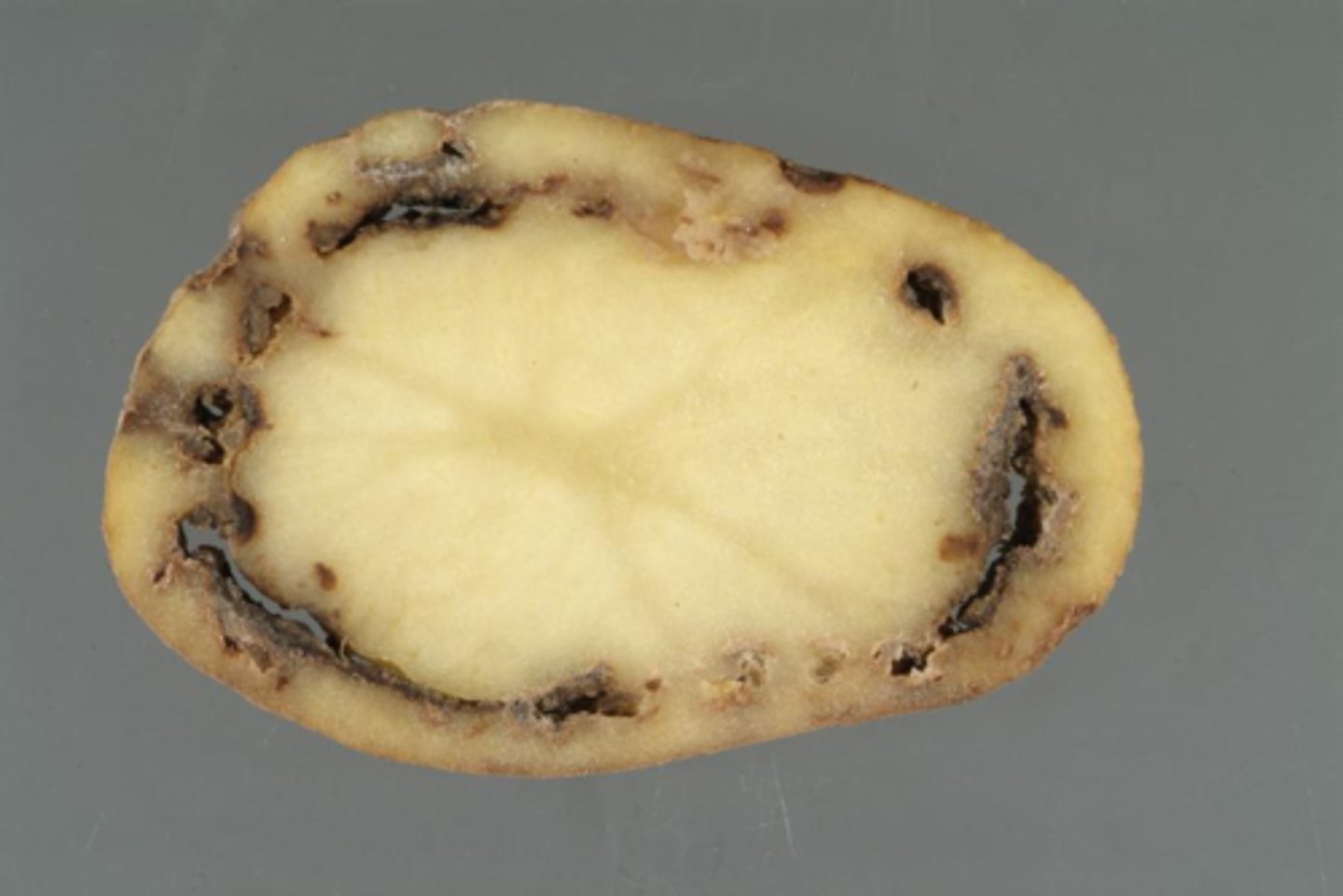
Ring rot
A bacterial infectious disease that affects plants
- Rots vascular tissue and wilts foliage
- Diagnosed via observation
- Prevent through proper hygiene and avoiding waste
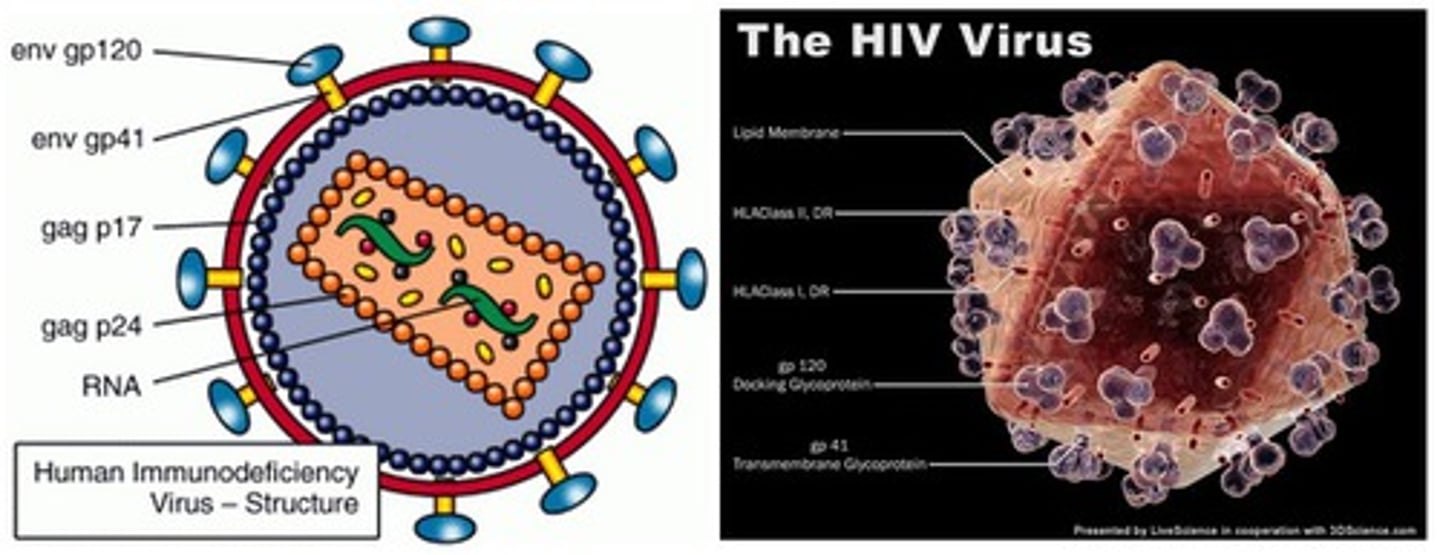
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
A viral infectious disease that affects humans.
- Enters T-lymphocytes, compromising the immune system
- Diagnosed through blood / saliva test
- STI, passed through body fluids
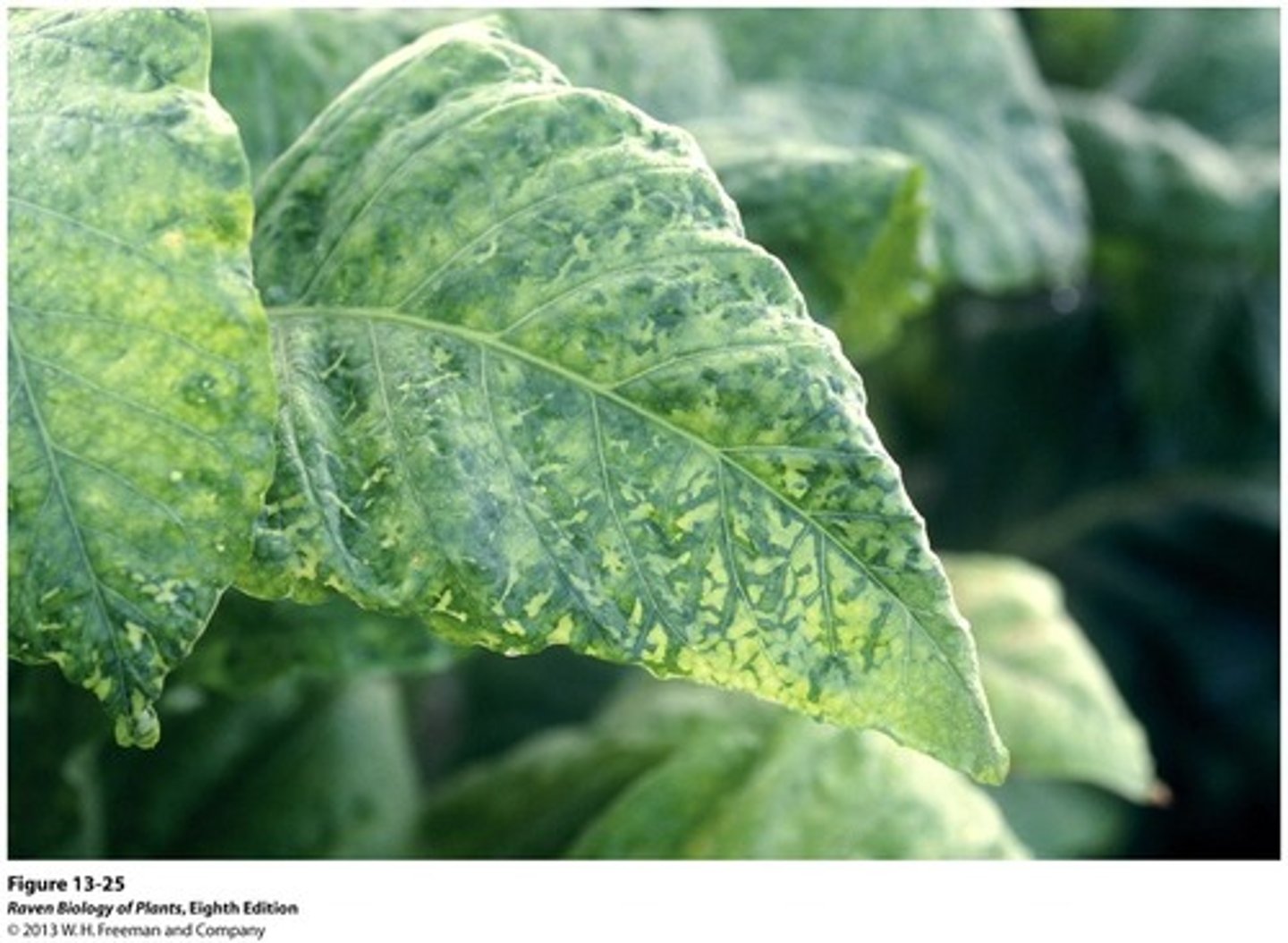
Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV)
A viral infectious disease that affects plants.
- Causes dark mosaic patterns on leaves, preventing photosynthesis
- Diagnosed through observation (stunted growth, etc)
- Prevent through weeding and disinfecting tools

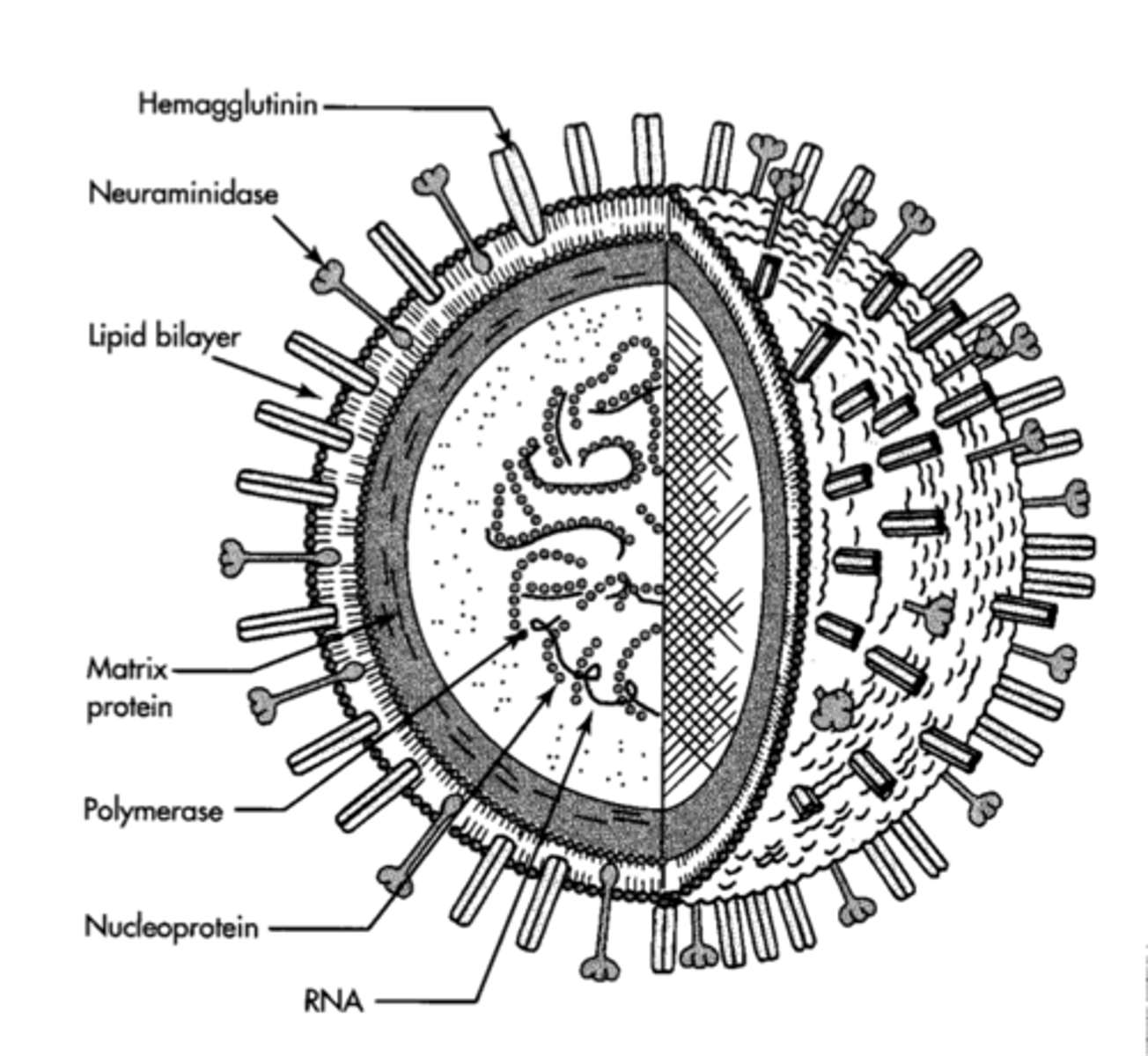
Influenza
A viral infectious disease that affects animals.
- Attacks the respiratory system, causing muscle pains and headaches
- Diagnosed via observation, or blood test
- Treated with antiviral drugs
- Caused the Spanish flu pandemic, killing at least 40 million
- High degree of genetic mutations means a new vaccine needs developing each year
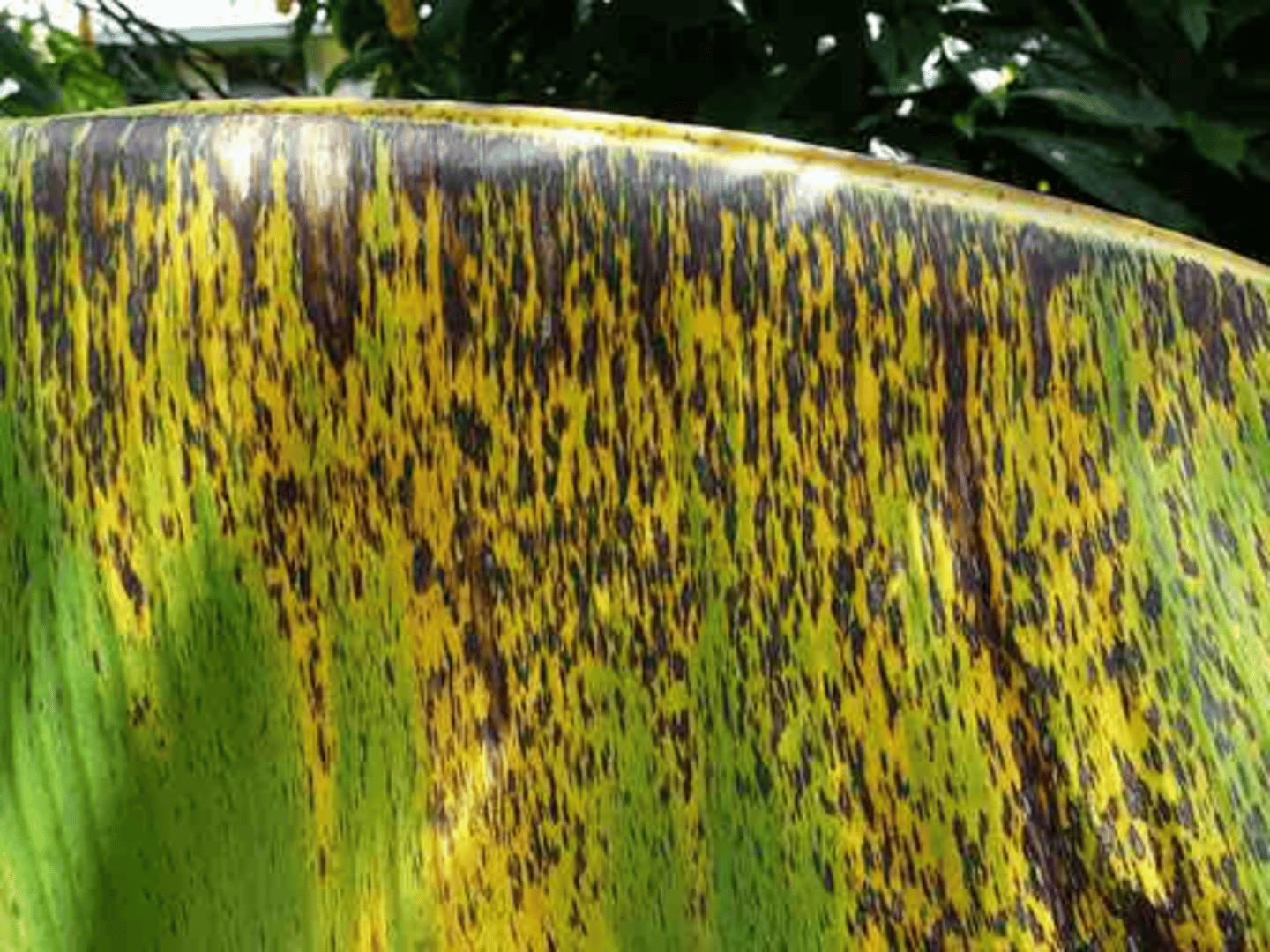
Black sigatoka
Fungal infectious disease that affects bananas.
- Causes leaf spots, reducing photosynthesis
- Diagnosed through lower yield of fruit
- Treated with fungicide

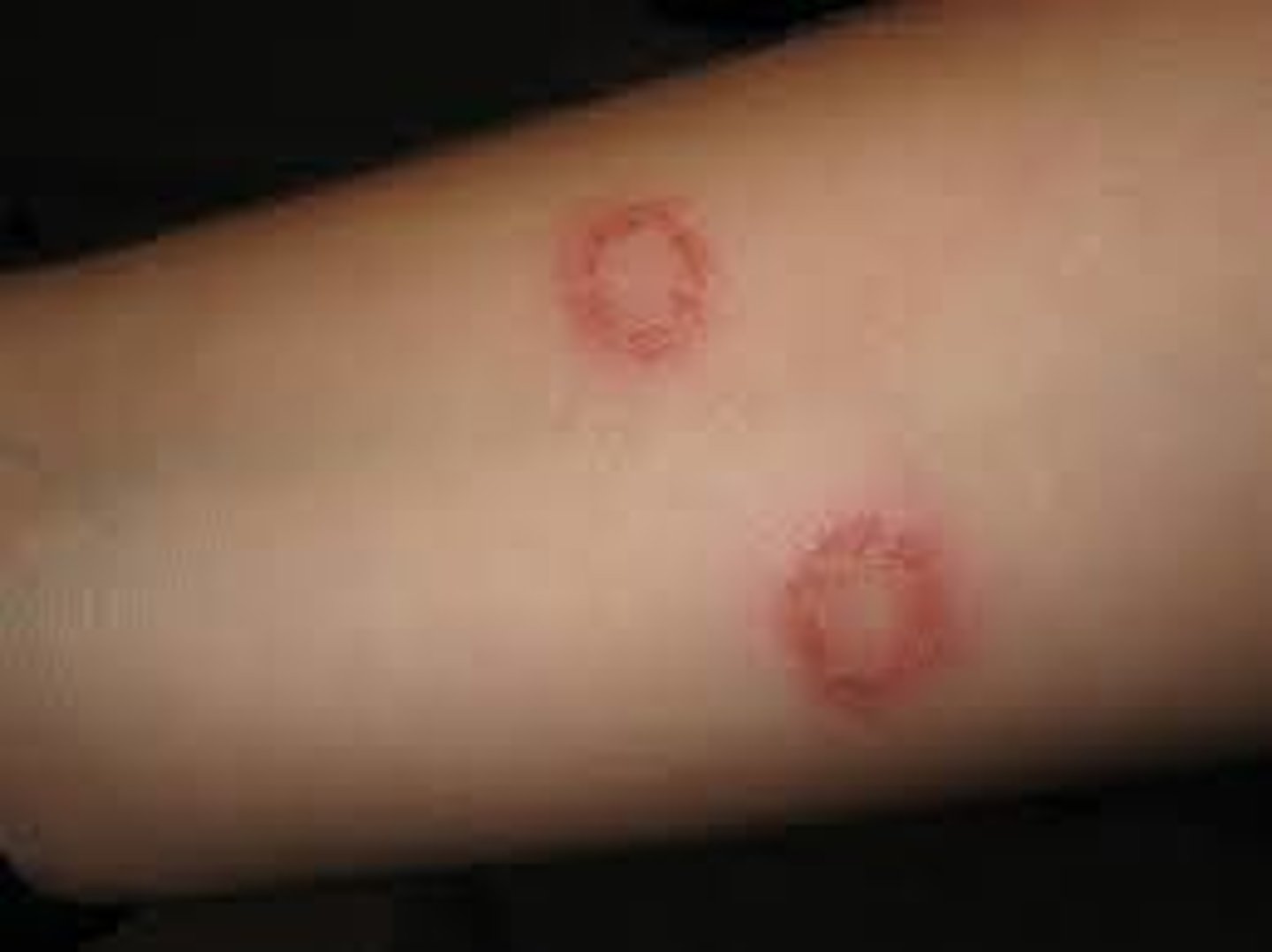
Ringworm
A fungal infectious disease that affects cattle.
- Causes growth of fungus under skin, leading to rash
- Diagnosed through observation
- Treated with antifungal cream
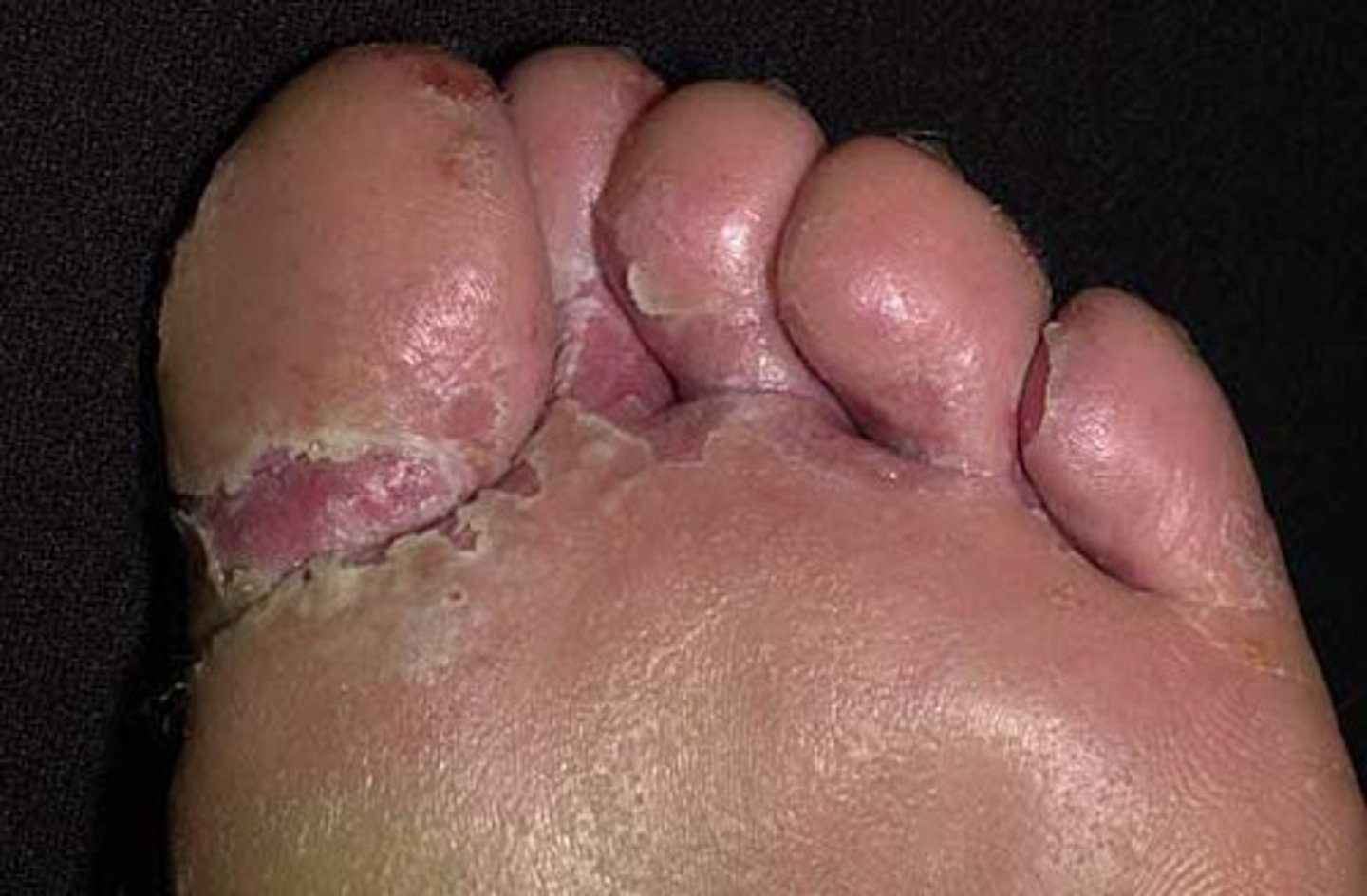
Athlete's foot
A fungal infectious disease that affects humans
- Lives in damp areas on feet
- Diagnosed through observation
- Prevented through hygiene and drying feet properly
Blight
A protist infectious disease that affects tomatoes and potatoes.
- Affects leaves and tubers
- Spread through air and water
- Diagnosed through brown patches on leaves
- Treated with fungicide and disinfecting tools
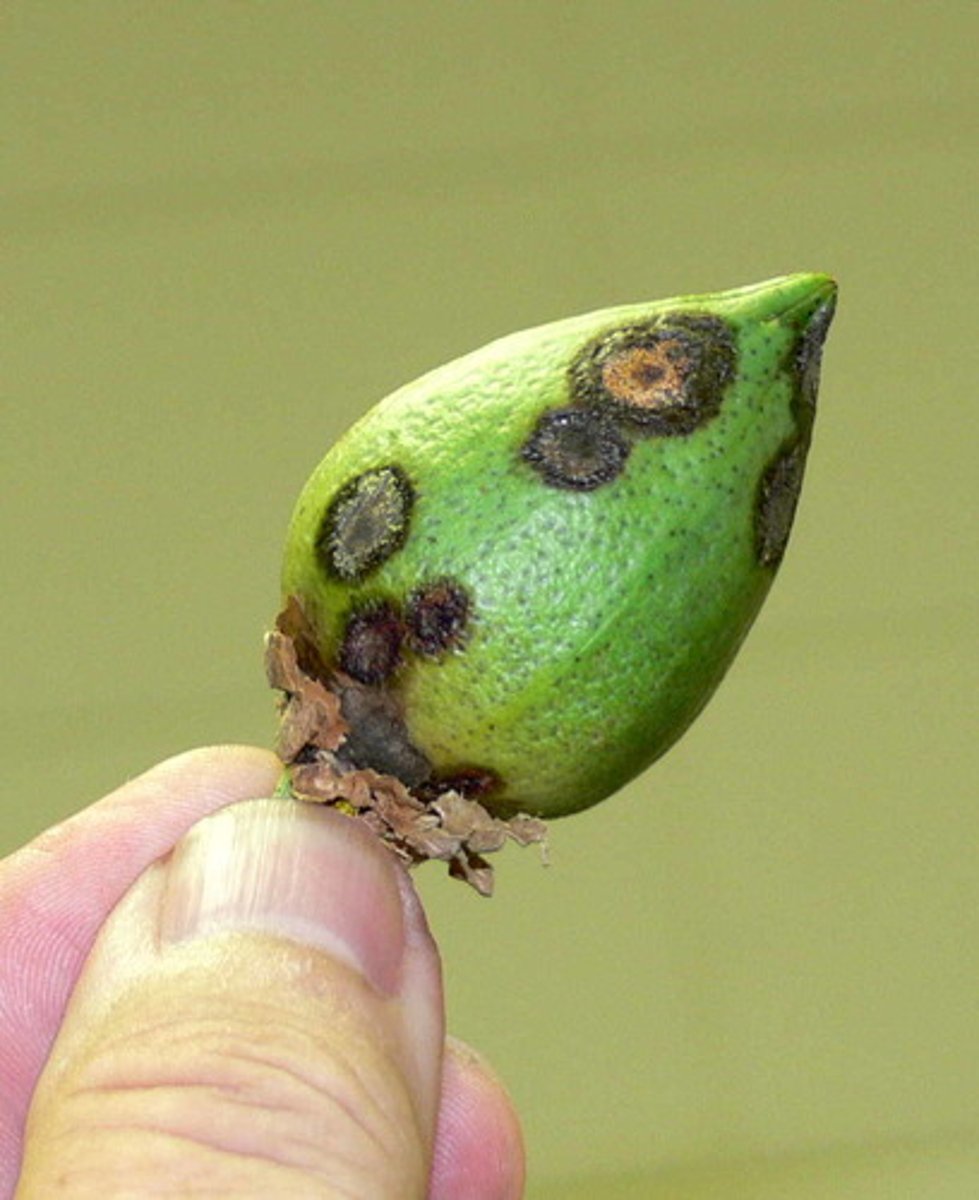

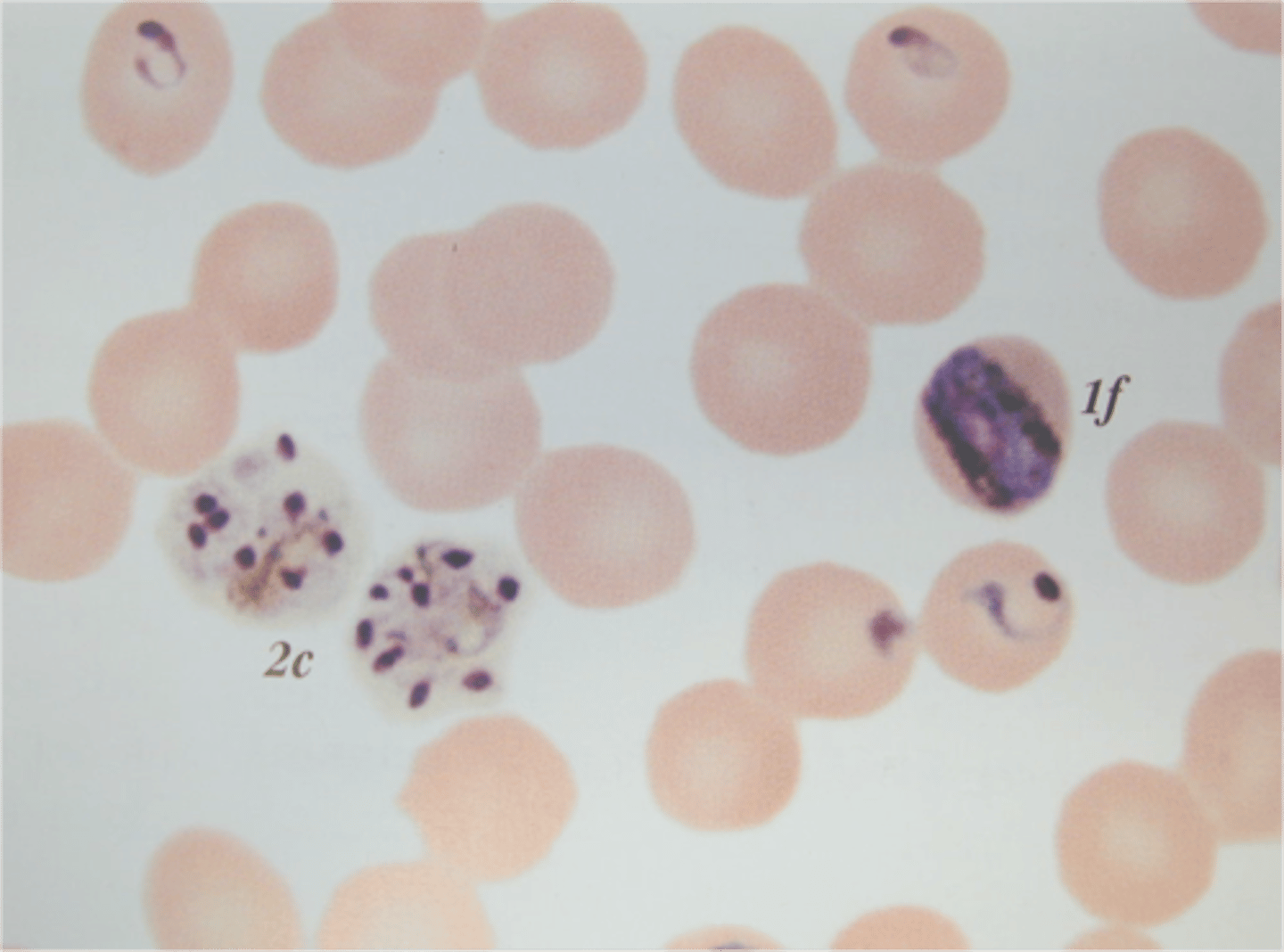
Malaria
A protist infectious disease that affects animals.
- Parasite that causes headaches and fever, possibly leading to coma and death
- Diagnosed through observation of symptoms / blood tests
- Treated with chloroquine phosphate, ACT's and antimalarial drugs
- Uses mosquitoes as vector
- Disease of poverty
- Targets liver cells (hepatocytes) and bursts them
- Then targets erythrocytes and bursts them, leading to lack of oxygen and fatigue
Direct transmission
When a disease is transmitted directly from one organism to another.
- Airborne
- Droplet infection
- Infected body fluids
- Touch
Indirect transmission
When a disease is transmitted via an intermediary
- Spores
- Vectors
Factors affecting direct transmission
- Overcrowding
- Ventilation
- Hygiene
- Public health
- Poverty
- Education
- Climate
Passive defence
A defence against pathogens or predators that is constantly in action, but requires little to no action or input
Active defence
A defence against pathogens or predators that is only activated when a threat is identified and requires active input
Physical defence
A defence against pathogens or pathogens that is constantly active and mainly acts to prevent the entrance of pathogens
Chemical defence
A defence against pathogens or predators that is based around chemicals or compounds
Bark
The hard outer layer of some plants that is difficult to chew and impermeable to pathogens

Waxy cuticle
The outer layer of a leaf that acts as a physical plant defence.
Prevents water from collecting on cell surfaces, preventing the conditions required by pathogens
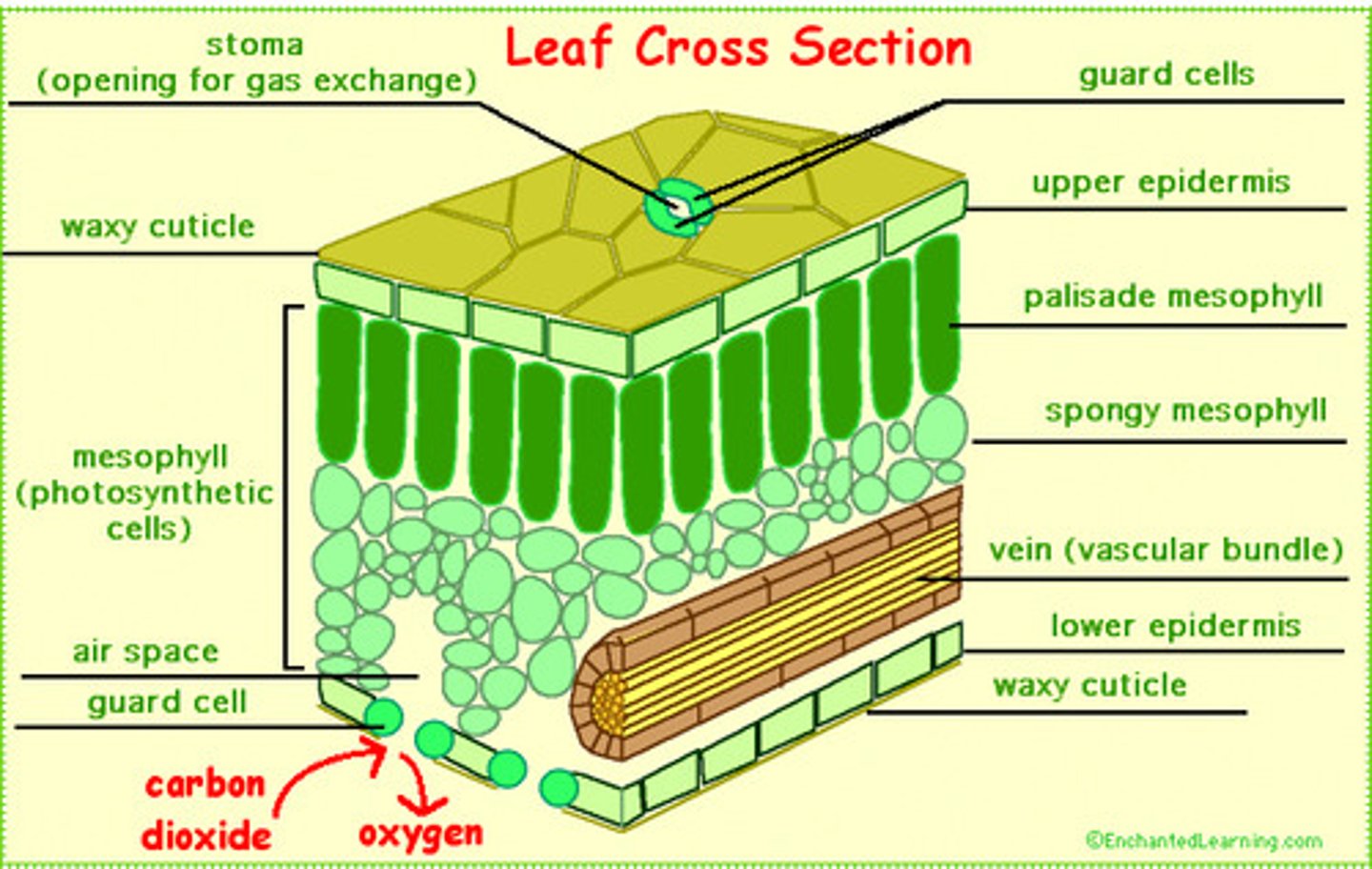
Callose
A physical plant defence that is a polysaccharide deposited in sieve tube elements to block the phloem, preventing the spread of infection around the plant
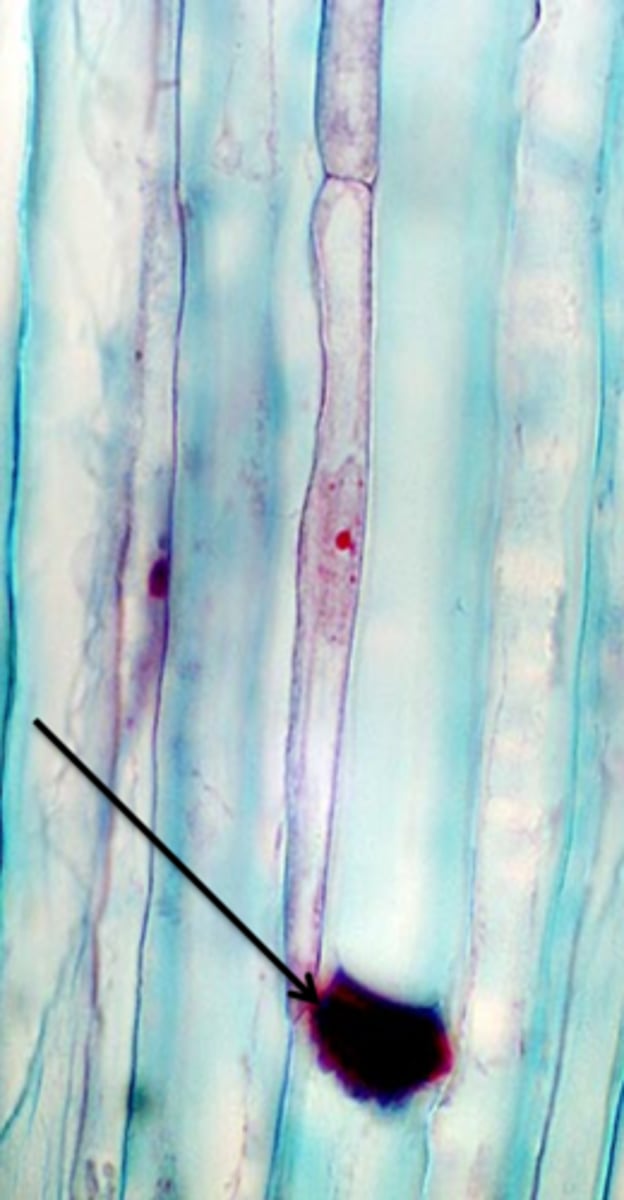
Cellulose
A physical plant defence that acts as a tough and strong polymer used to reinforce cell walls, providing strength
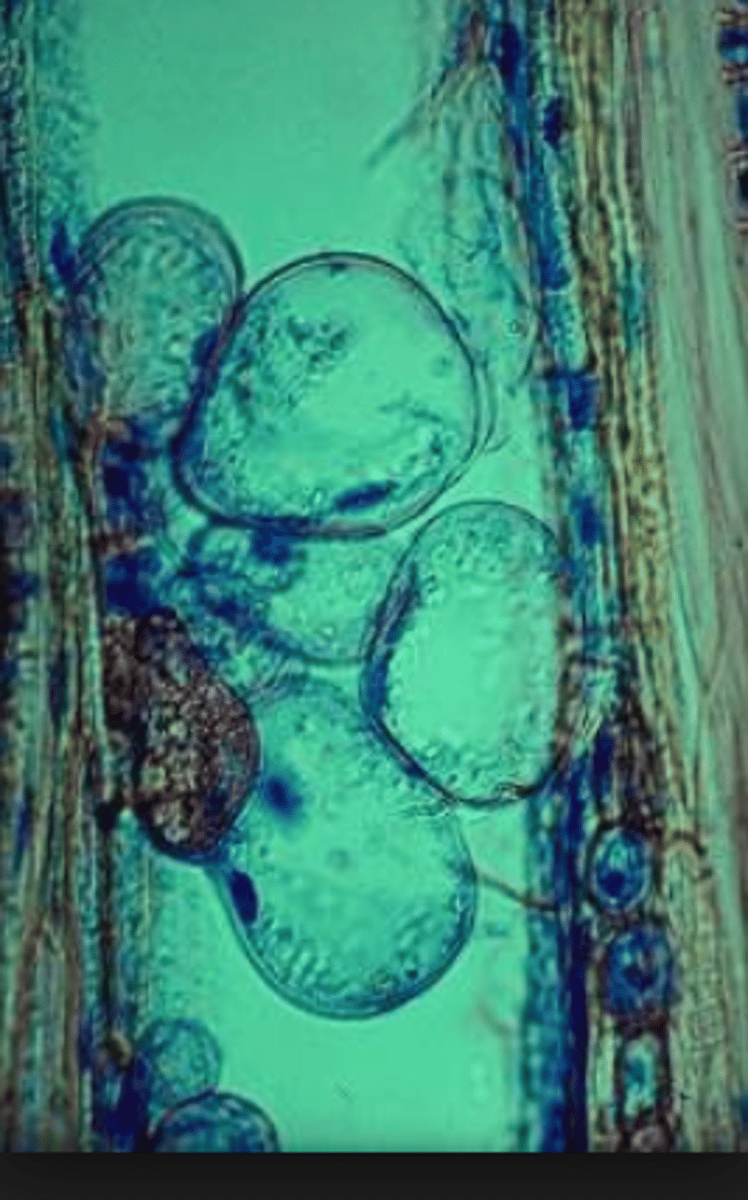
Tylose
A physical plant defence that forms a swelling that fills xylem vessels, preventing the flow of water, stopping the spread of infection. Also contains anti-pathogen chemicals
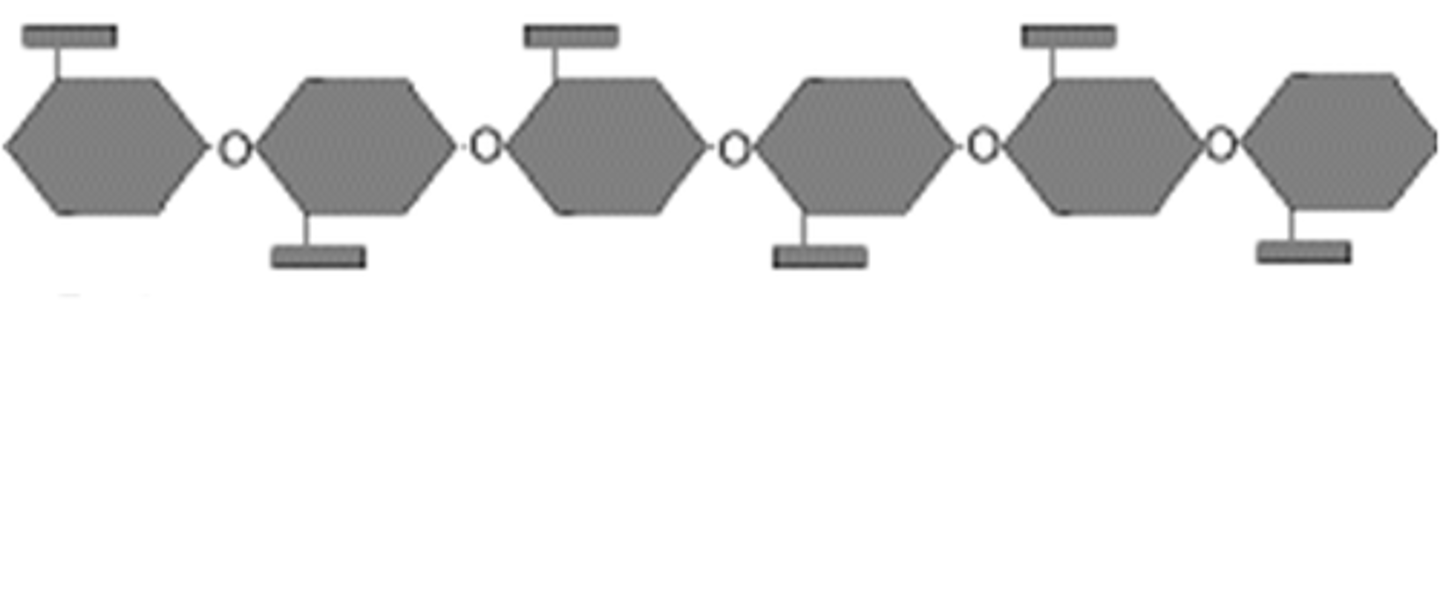
Lignin
A physical plant defence that is a polymer which hardens cell walls by strengthening it, killing the cell. Waterproof and indigestible
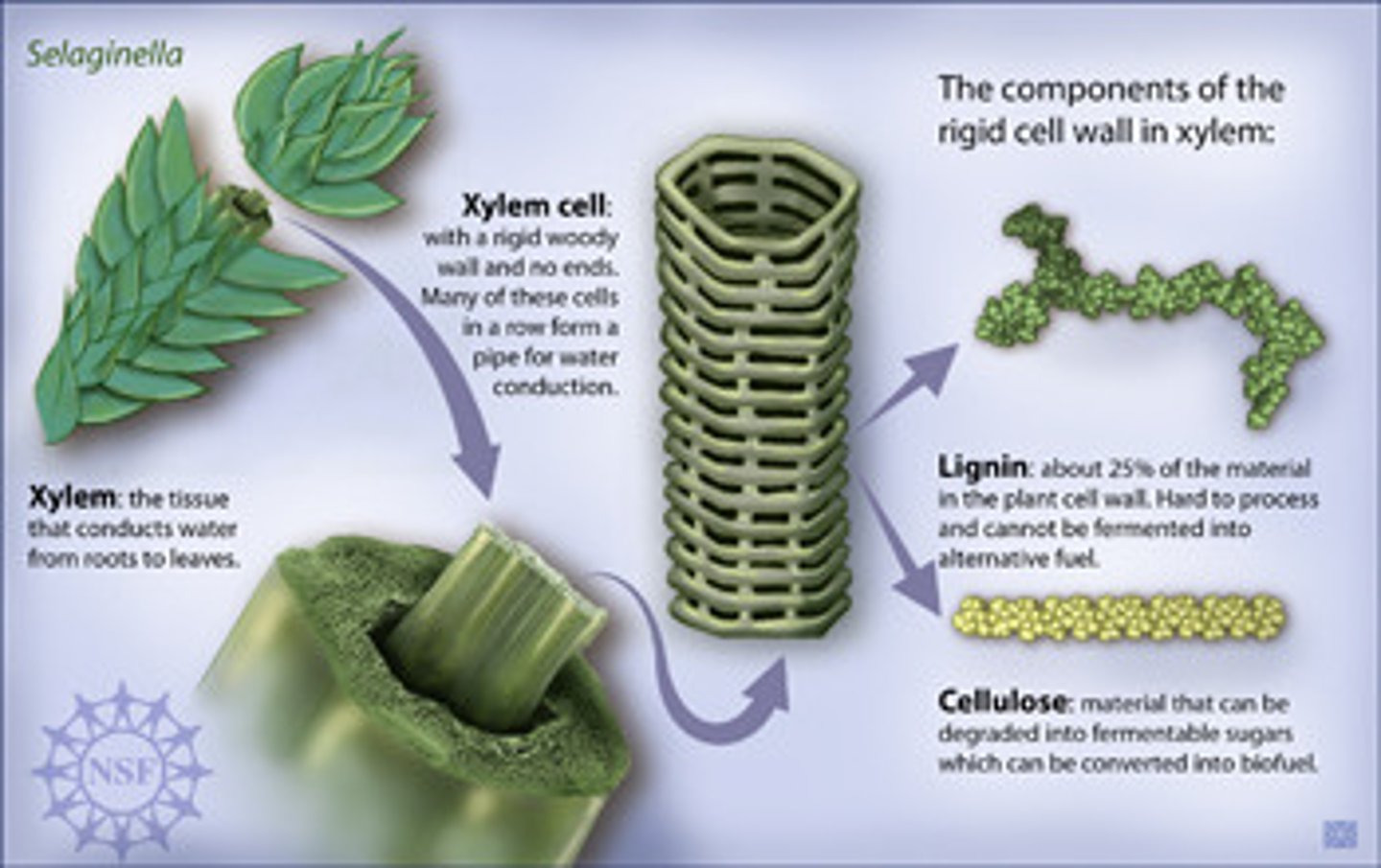
Stomatal closure
The act of guard cells closing the stomata, preventing the entrance of pathogens
Terpenoids
A chemical plant defence that are antibacterial and antifungal essential oils
Phenols
Chemical plant defence
Chemicals that deactivate salivary proteins and digestive enzymes from insects, also toxic to the insect if consumed
Defensins
Chemical plant defence
Small cysteine-rich proteins that are anti-microbial by interfering with the plasma membrane of pathogens, inhibits iron transport channels
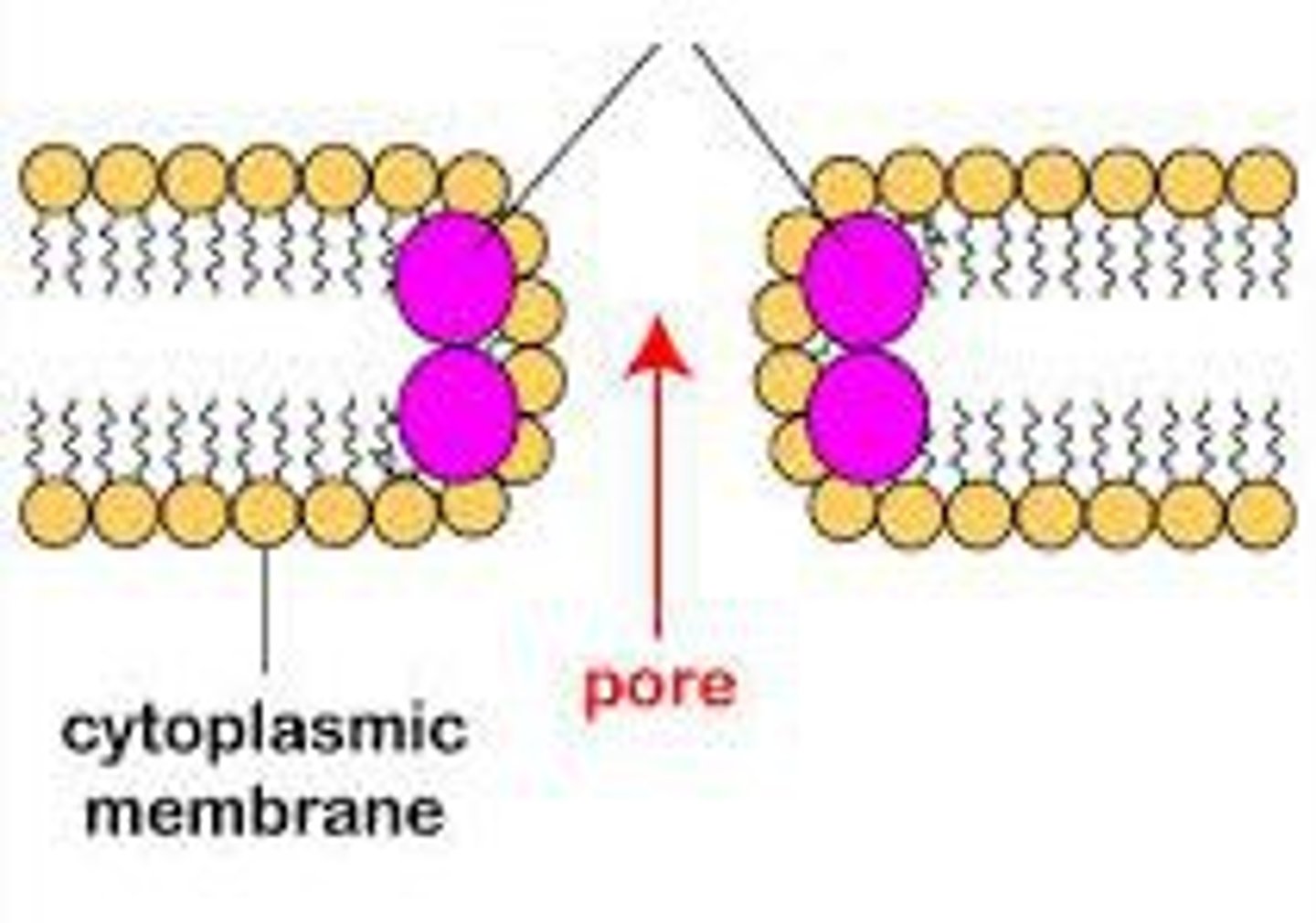
Hydrolytic enzymes
Chemical plant defences
Found between cells
Chitinases - Breaks down chitin in fungal cell walls
Glucanases - Hydrolyse glycosidic bonds in glucans
Lysozyme - Degrades bacterial cell walls
Alkaloids
Chemical plant defence
Nitrogen-containing compounds that taste bitter and can control enzyme reactions. Reduces damage from pathogens that enter after herbivore grazing
E.g. caffeine, nicotine, cocaine
Necrosis
Cell suicide of a few cells to save the rest of the plant. Limits the spread of pathogens by cutting their supply of water and nutrients.
Caused by intracellular enzymes activated by injury
Canker
A sunken necrotic lesion in the woody tissue. Causes death of the cambium tissue
Primary defence
The first line of defence against pathogens. Prevent the pathogens accessing the body
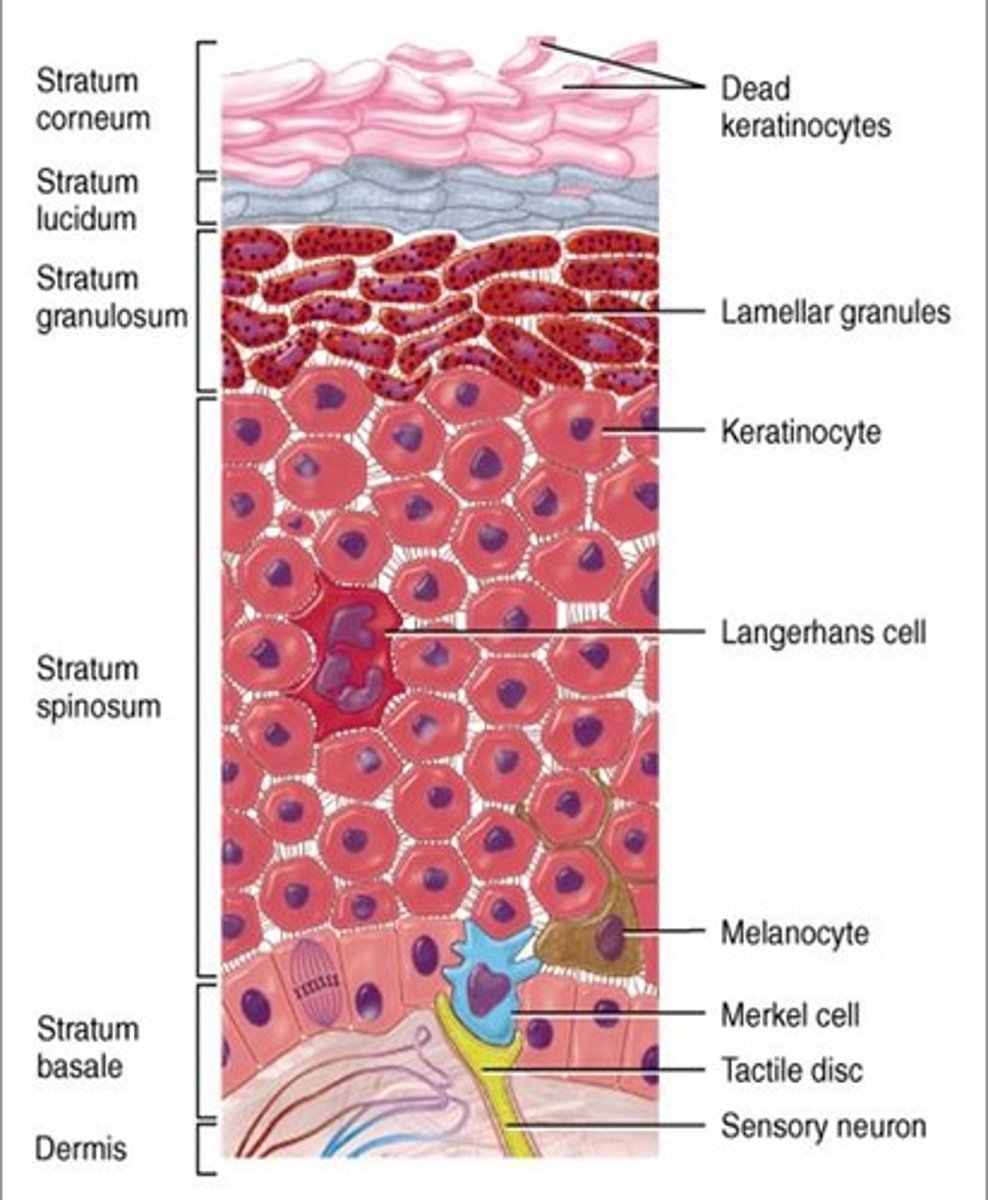
Skin
The main primary defence of the body.
A layer of epidermis, topped by keratinocytes covering the exterior of the whole body
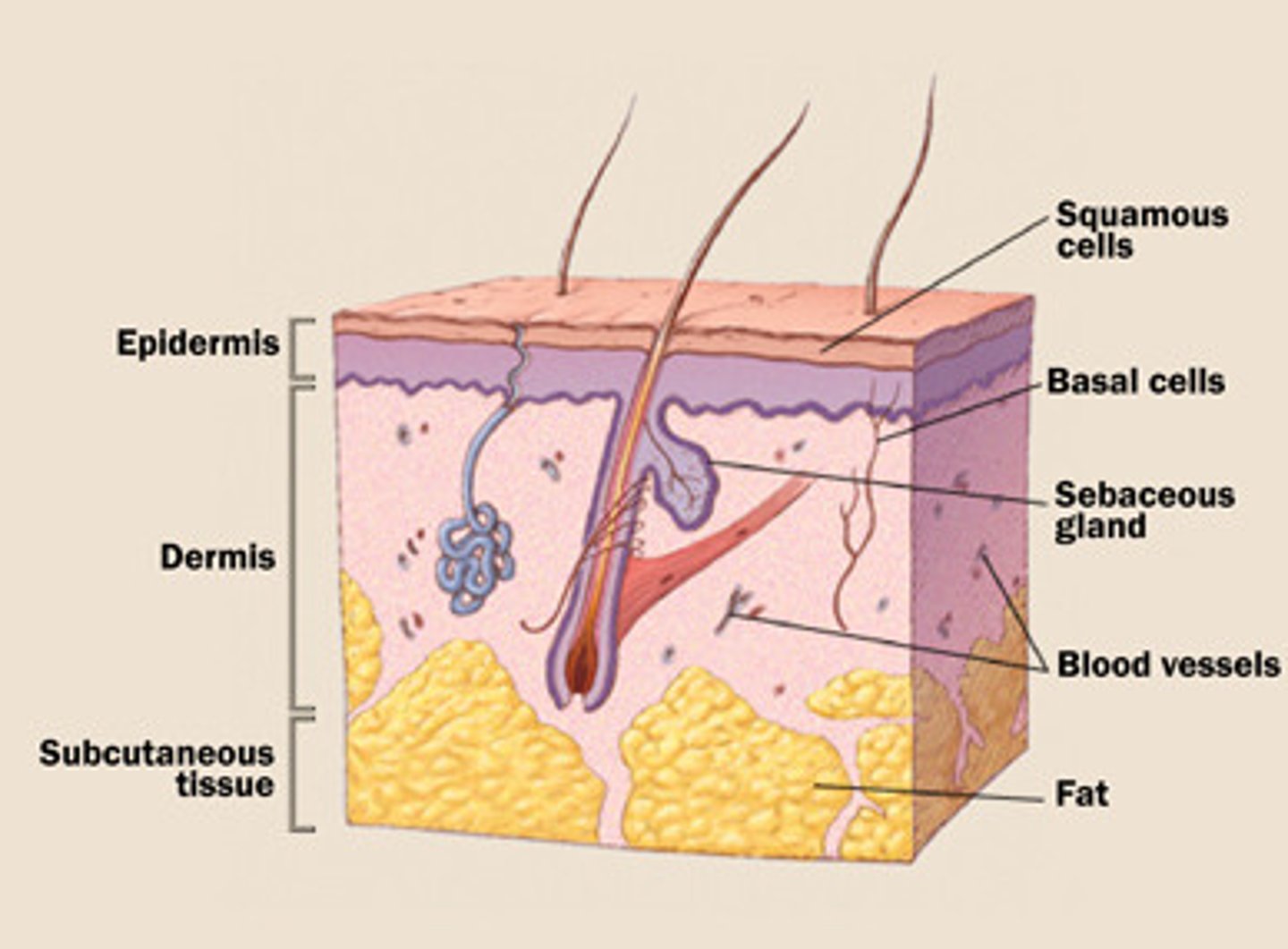
Keratinocytes
Epidermal cells that form the very outer layer of skin.
Cytoplasm has been replaced by keratin, therefore the cell is dead.
Produced at the base of the epidermis, and over 30 days works there way up to the outer layer
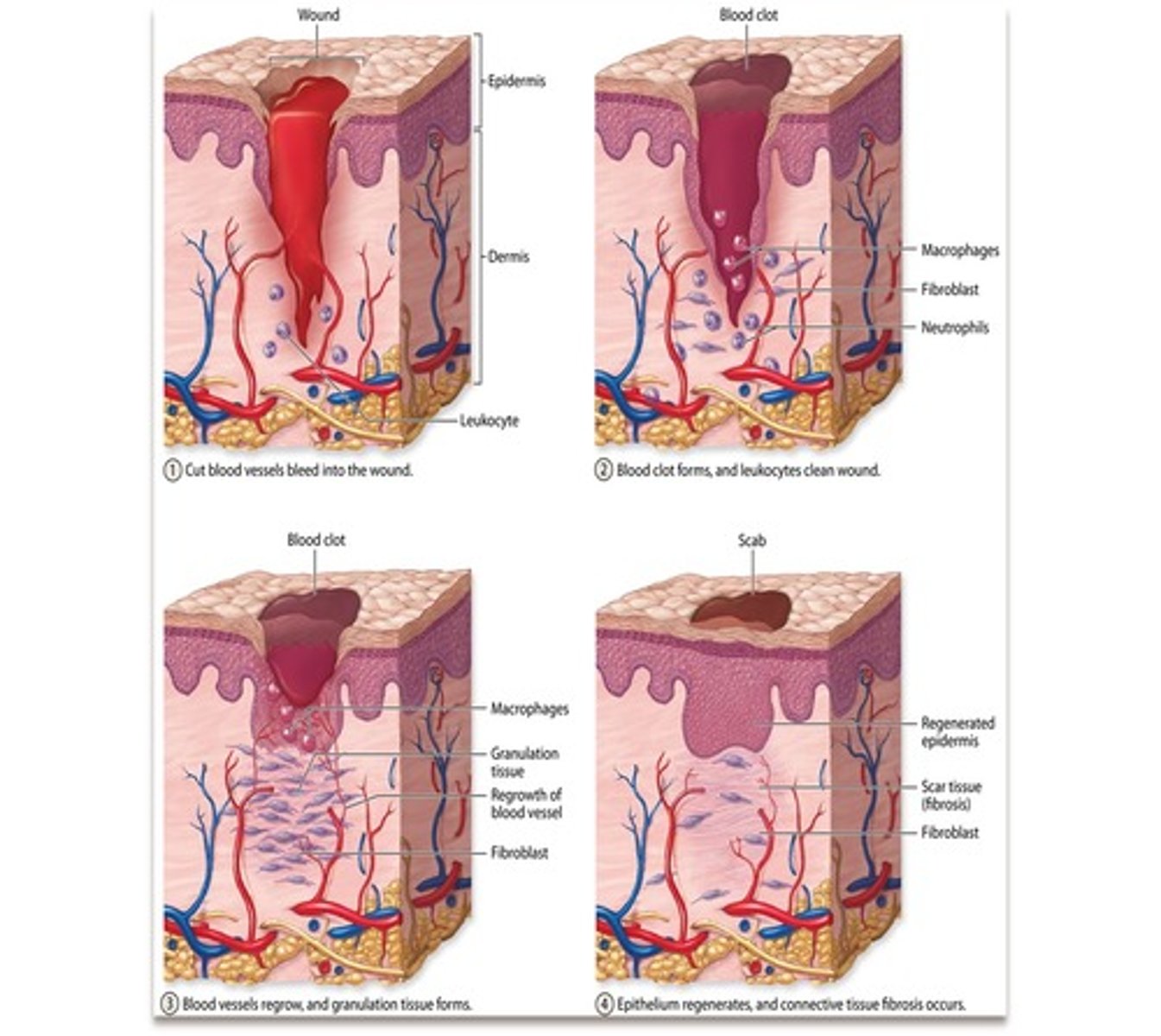
Blood clot
A solid that was once flowed as liquid blood.
Mesh of fibrin fibres
Used as a temporary seal at abrasions on the skin until it can be repaired.
Caused by at least 12 factors that cause an enzyme cascade
Dries to form a scab

Skin repair
1. Skin surface damaged
2. Exposure of platelets to damaged blood vessel triggers enzyme cascade that causes a blood clot to form
3. Blood clot seals abrasion
4. As it dries it shrinks, forming a scab and drawing the 2 sides of the injury together
5. Deposition of collagen begins the processing of repairing the skin
6. Stem cells differentiate into skin cells and blood vessel cells
7. Scab is released when skin is repaired
Mucous membrane
Primary defence that protects openings in the body
- Found in respiratory tract, nose, genitals, mouth
- Traps pathogens
- May contain antimicrobial enzymes
- Released from mucus-secreting glands and goblet cells
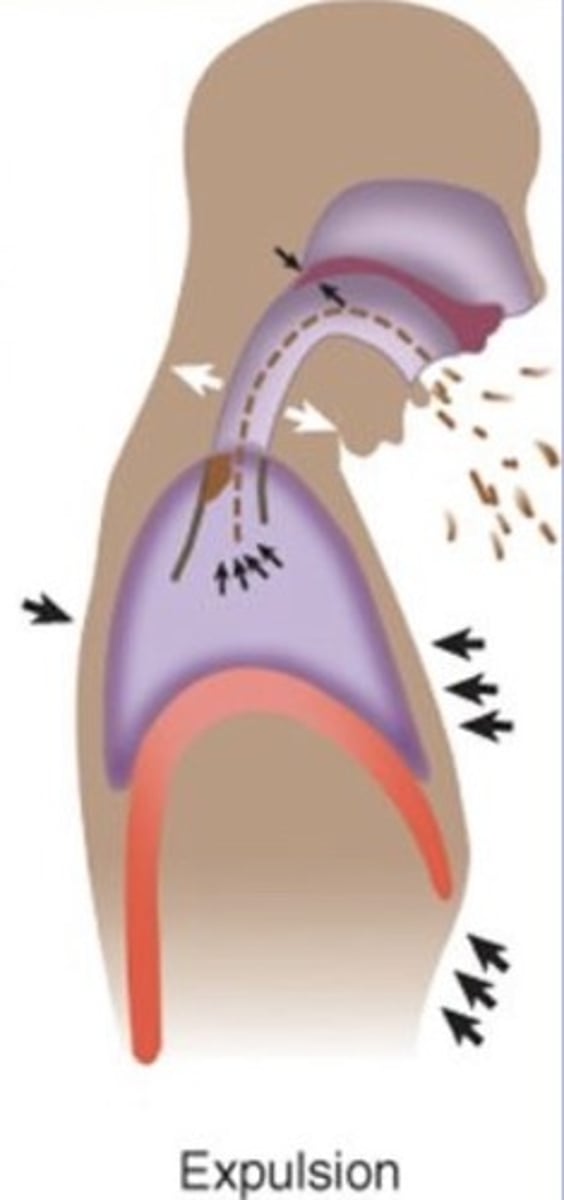
Expulsive reflexes
Primary defence to expel any irritants in exposed areas
- E.g. coughing, sneezing, vomiting
Inflammation
Damaged tissue release histamine that cause vasodilation of blood vessels to ensure more immune cells reach the infection site.
This increases the amount of tissue fluid, causing this
Eyes
Protected by antibodies and enzymes in tear fluid
Ears
Protected by a lining of wax, which traps pathogens
Female reproductive system
Protected by:
- Mucus plug acting as a seal to the cervix
- Acidic conditions in the vagina to kill pathogens
Secondary defence
The immune response whereby immune cells attempt to kill any pathogens in the body
- Divided between non-specific (phagocytes) and specific (lymphocytes)
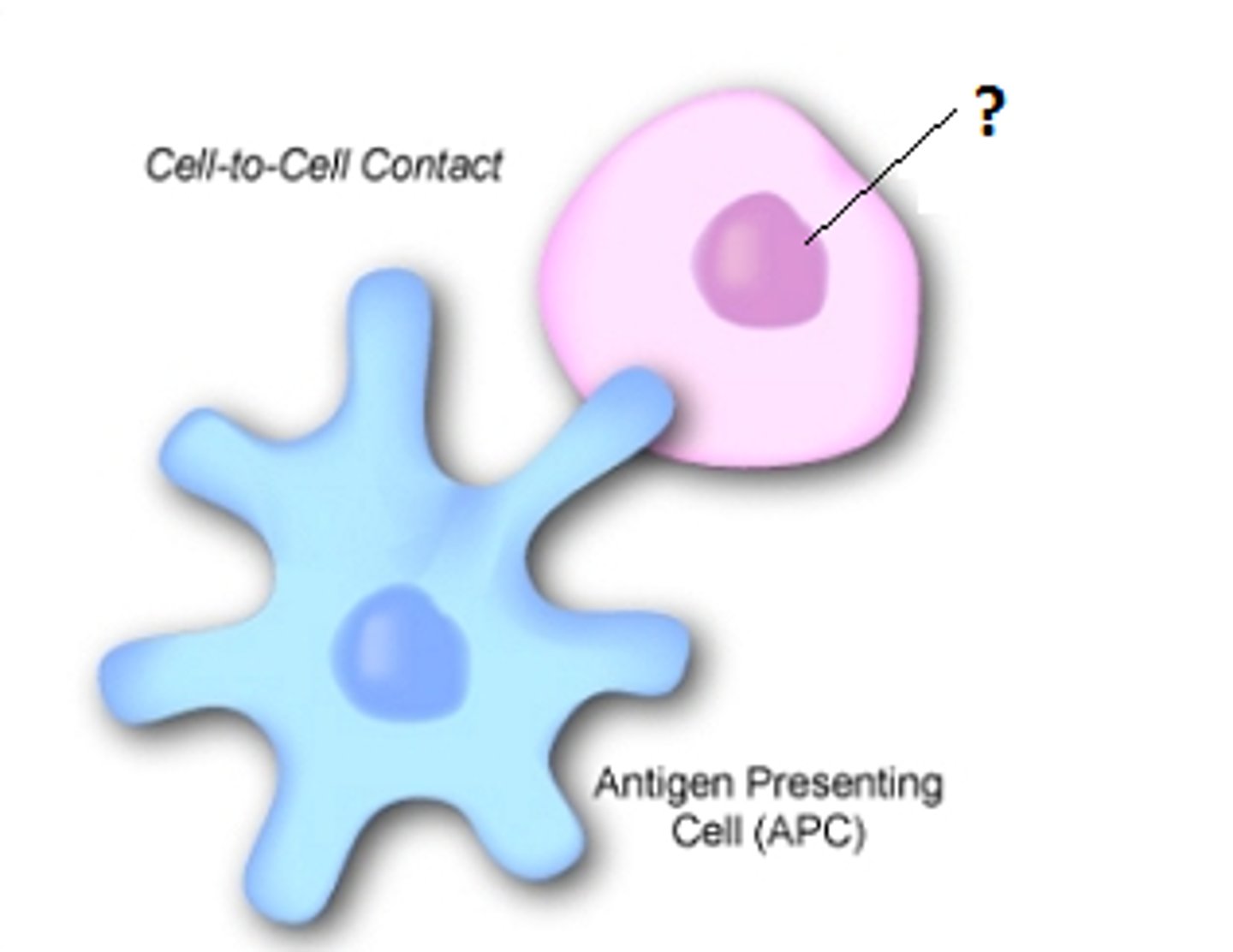
Antigen presenting cell
A cell that isolates and presents an antigen so that other immune cells can recognise it
Cytokines
Hormone cell signallers that trigger the immune response
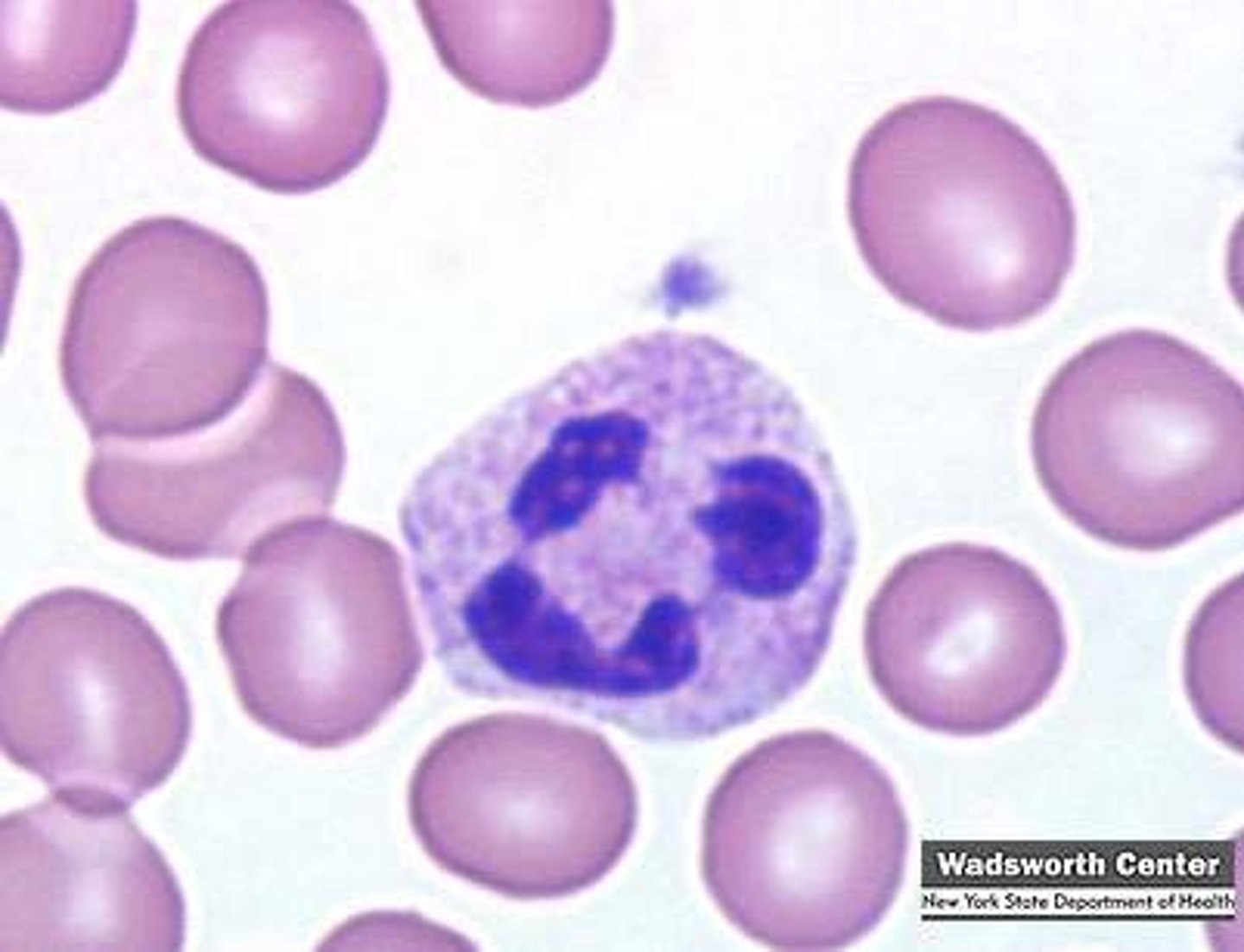
Neutrophil
A immune cell that undergoes phagocytosis on foreign material
Opsonin
Antibodies that bind to the antigen of a pathogen, allowing phagocytes to bind
- Some are specific, others non-specific
- Can neutralise the pathogen
- Identify pathogens to phagocytes
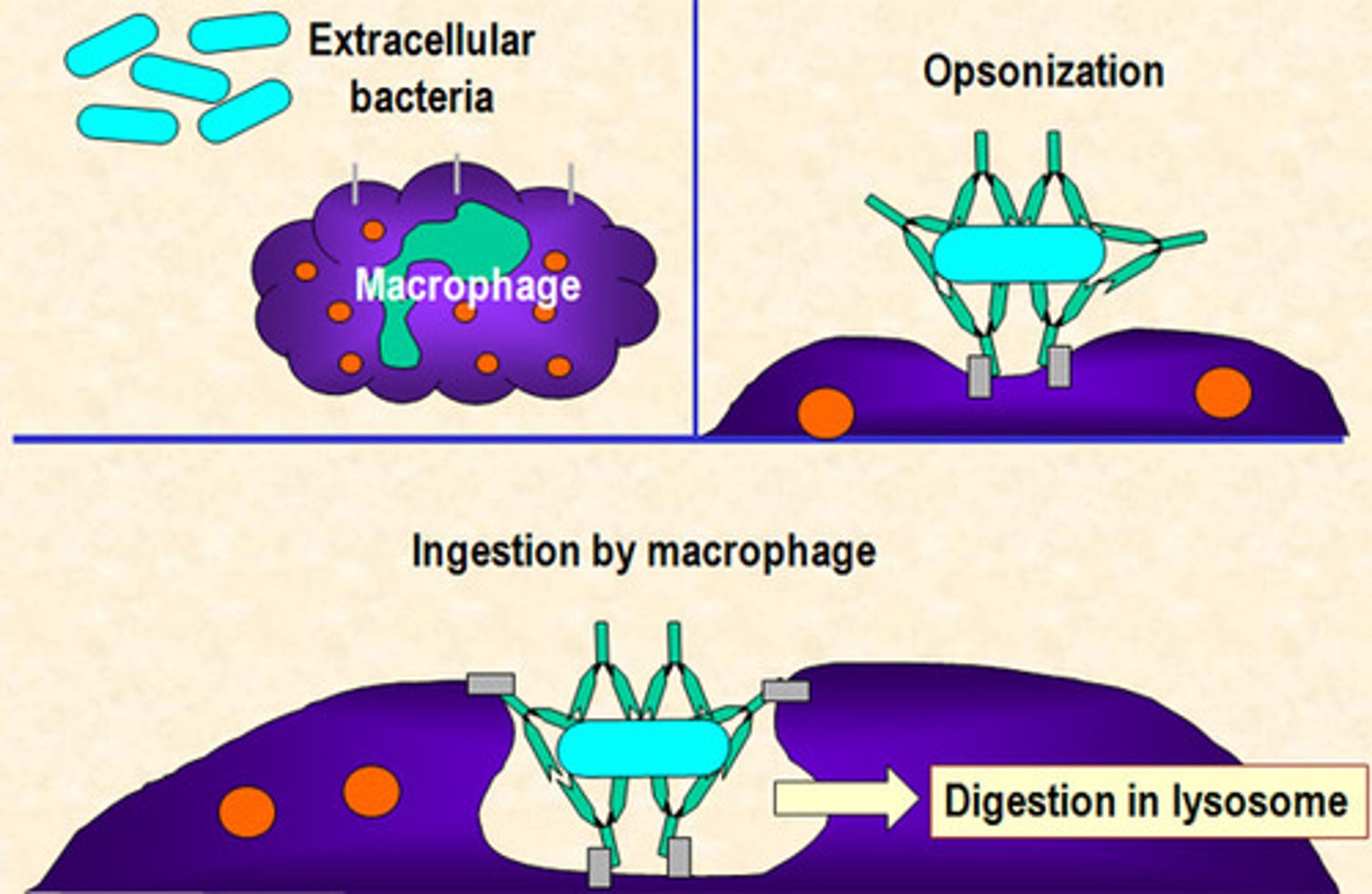
Antigen
A protein on the outside of a pathogen that identifies it
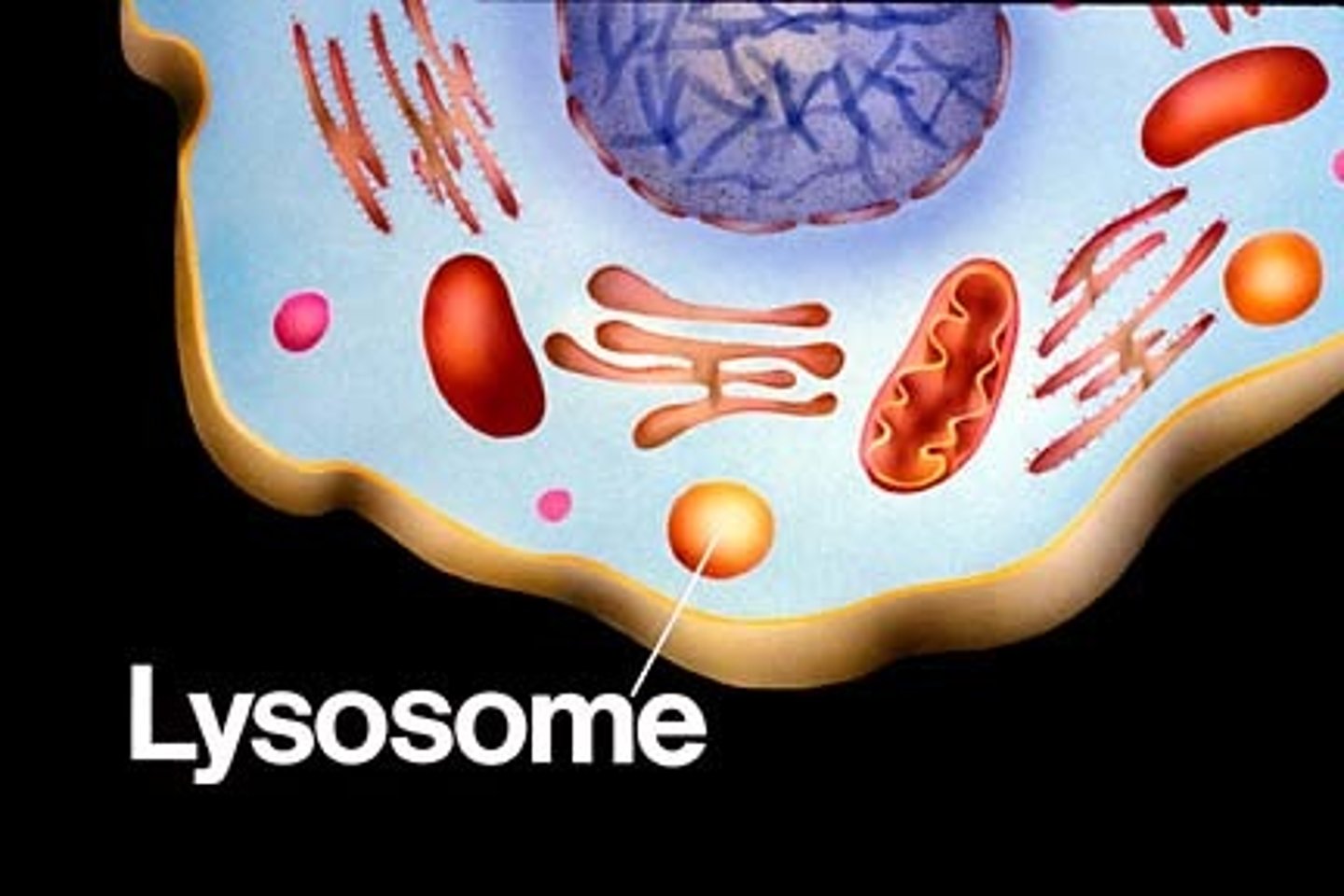
Phagocytosis
1. Neutrophils bind to opsonin, which is attached to a pathogen
2. The pathogen is engulfed, forming a phagosome
3. Lysosomes fuse to the phagosome (forming a phagolysosome), releasing lytic enzymes that digest it
4. The digested products are either absorbed or released
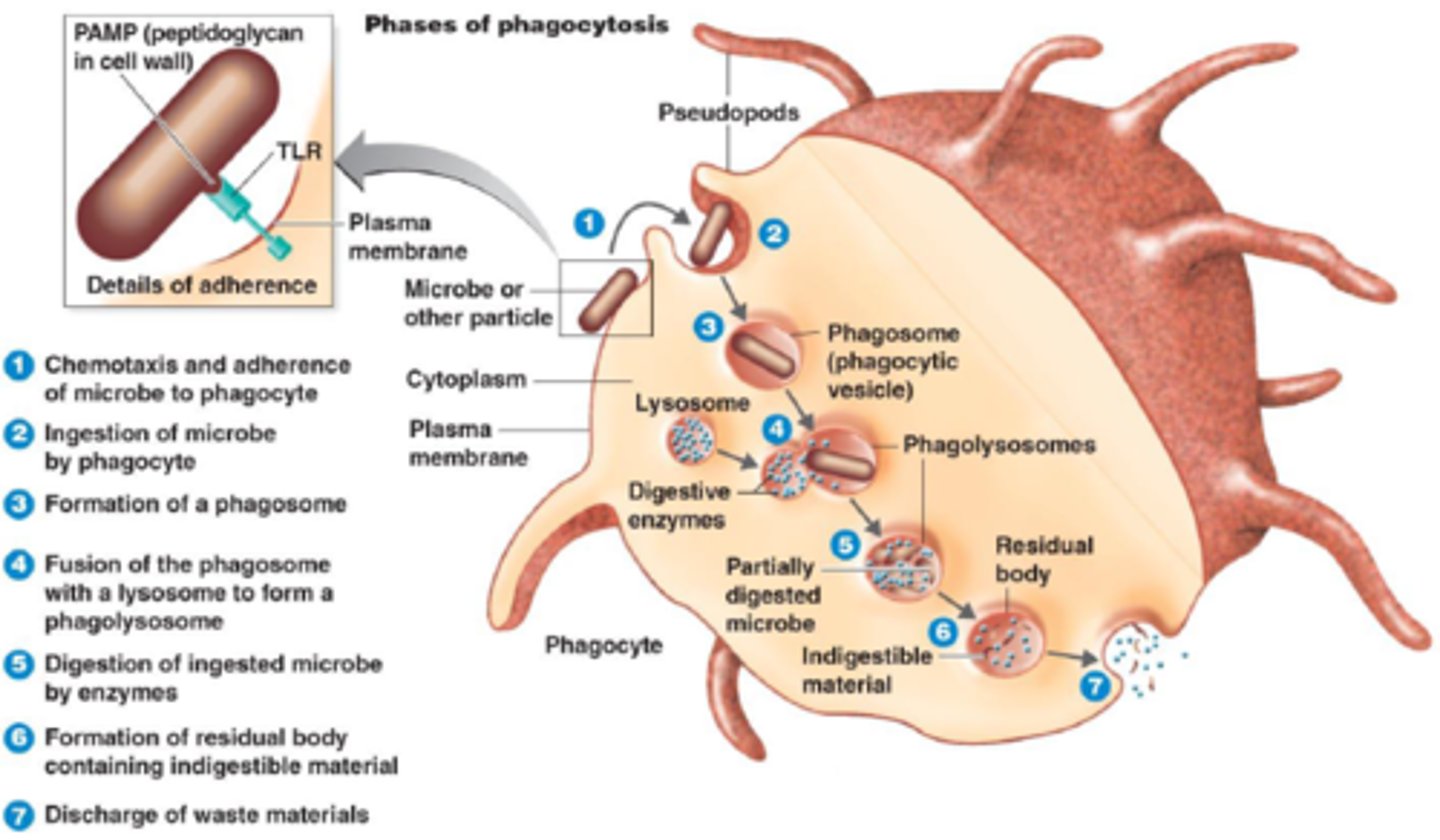
Phagosome
Intracellular vesicle containing material taken up by phagocytosis, often a pathogen
Macrophage
Matured monocytes
- Engulfs pathogens by phagocytosis, then isolates its antigen and becomes an antigen-presenting cell
- Then moves around the body until coming into contact with the corresponding lymphocytes
Phagocytes specialisations
- Receptors on the membrane to bind to opsonin or antigens
- Lobed nucleus, allowing the cell to squeeze into narrow spaces
- Cytoskeleton so the cell can easily change shape
- Many lysosomes containing lysine
- Many mitochondria
- Many ribosomes to synthesise enzymes
B lymphocyte
A type of lymphocyte that matures in the bone marrow and can connect directly to the antigens on the surface of the pathogen
- Can detect free antigens in the blood stream
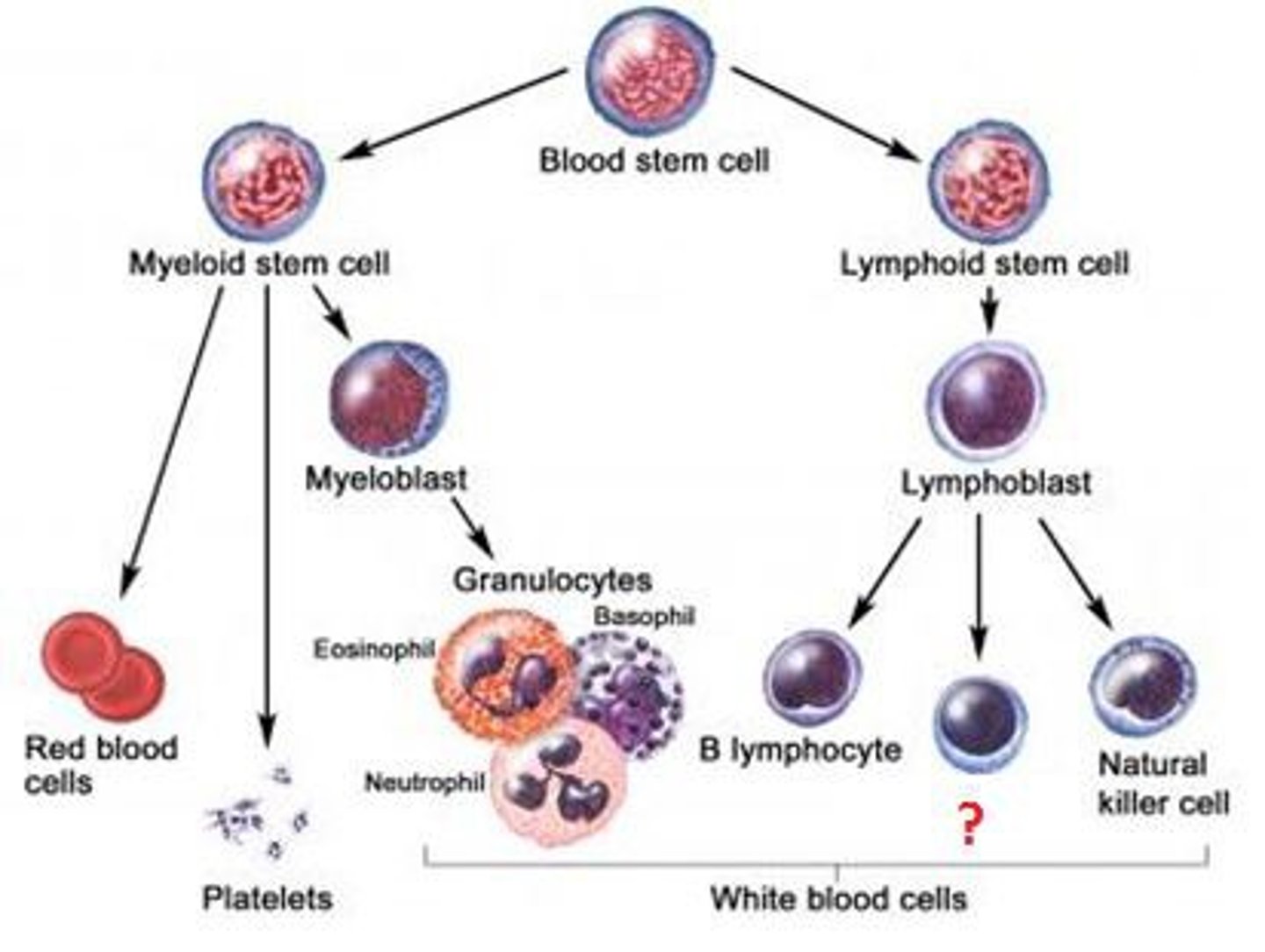
T lymphocyte
A type of lymphocyte that matures in the thymus and can connect to antigens on the surface of infected body cells
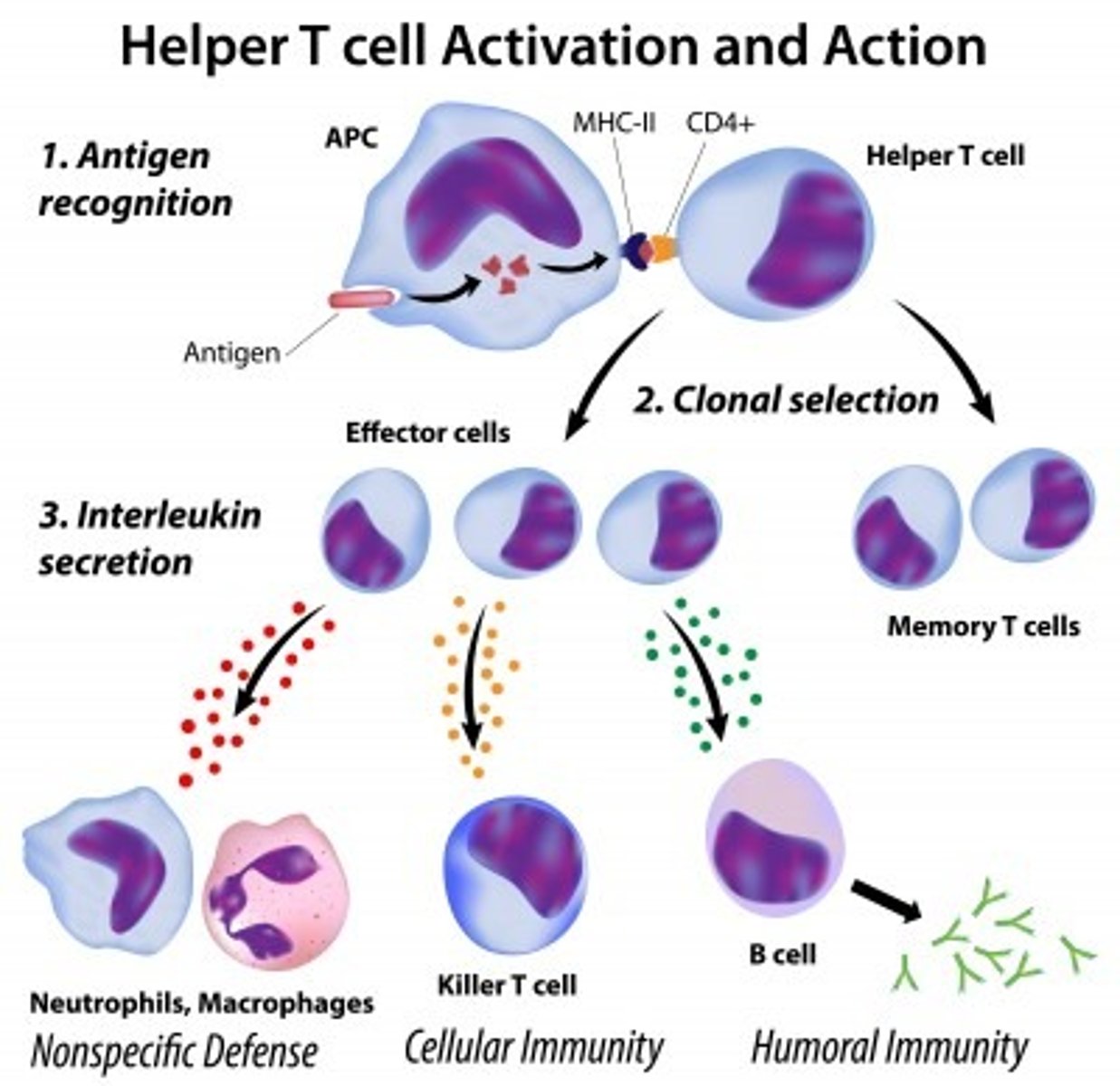
T helper cells
A type of T lymphocyte that releases cytokines to stimulate B cells and phagocytosis by phagocytes
T killer cells
A type of T lymphocyte that attack and kill any cell displaying the foreign antigen
T memory cells
A type of T lymphocyte that provides long term immunity by 'remembering the antigen'
T regulator cells
A type of T lymphocyte that deactivate the immune system once the threat has been eliminated.
Prevents autoimmunity
Plasma cell
A type of B lymphocyte that manufacture and release antibodies
B memory cells
A type of B lymphocyte that acts as immunological memory for a number of years
Cell signalling
The complex system of communication between cells. Based off the transmission of hormones and their receptors
Monokines
Released by macrophages.
- Attract neutrophils
- Stimulate differentiation of B cells
Interleukins
Released by macrophages and T cells
- Stimulates clonal expansion
- Stimulates differentiation of lymphocytes
Interferon
Released by many cells
- Inhibits virus replication
- Stimulates T killer cells
Autoimmune disease
A disease when cells that react to our own antigens aren't deleted before birth.
Causes the immune system to attack body cells
E.g. arthritis, lupus
Arthritis
An autoimmune disease where antibodies attack membranes around the joints, causing painful inflammation
Lupus
An autoimmune disease where antibodies attack proteins in the nuclei of cells, causing painful swelling all over the body
Specific immune response
1. Infection
2. Presentation of antigens
3. Clonal selection
4. Proliferation
5. Differentiation
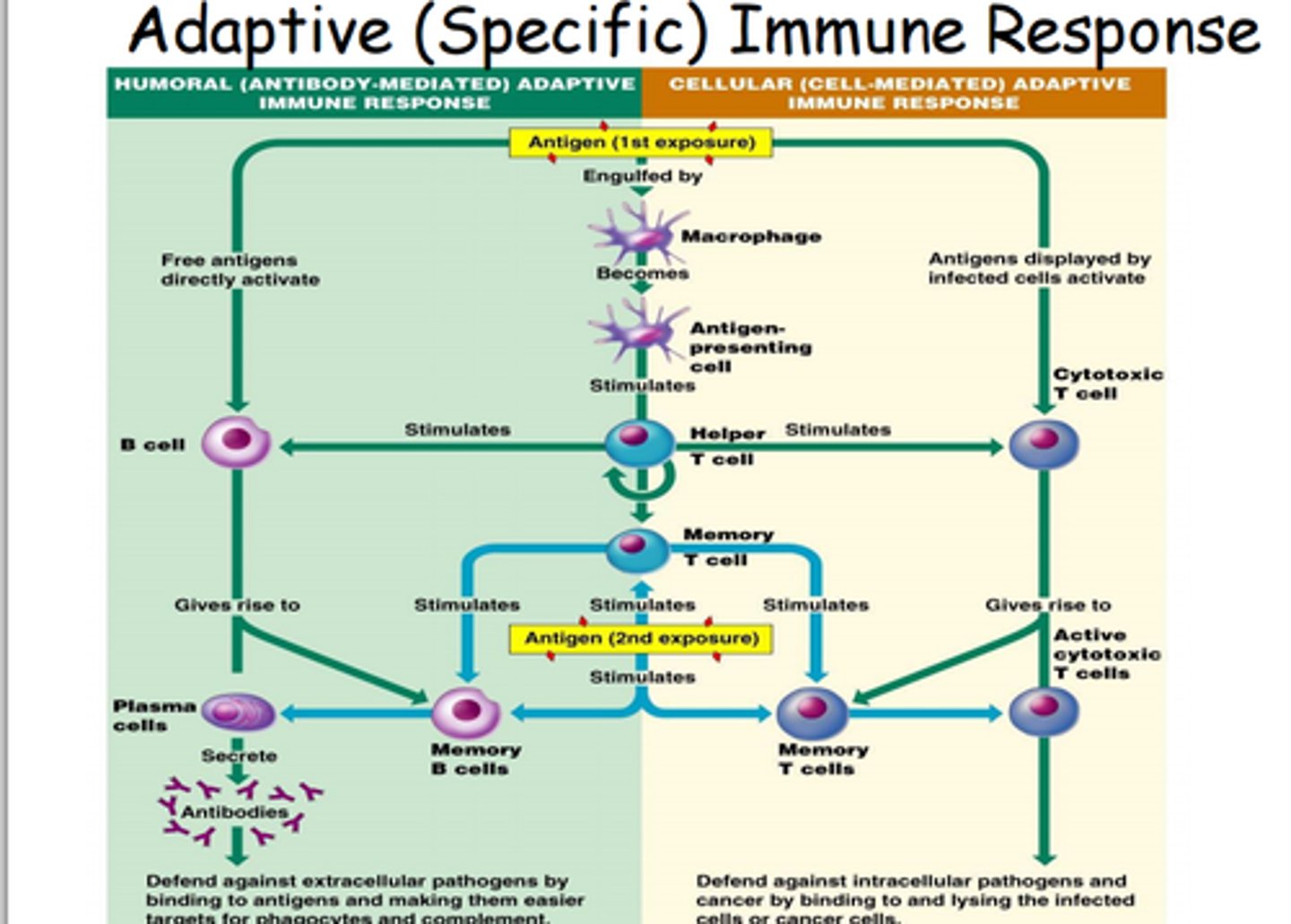
Infection
The 1st stage of the specific immune response
The pathogen invades the body, bypassing the primary defences, and begins to reproduce
Presentation of antigens
The 2nd stage of specific immune response
- Antigens are detected by macrophages and presented to the rest of the immune cells (non-specific response)
OR
- Antigens infect a body cell, which is detected by T and B lymphocytes (specific response)
OR
- Free antigens in the bloodstream is detected by B cells (specific response)
Clonal selection
The 3rd stage of specific immune system
Selection of a specific T or B cell to respond to a specific antigen
Lymphocytes, with the specific antibodies are produced in the bone marrow, T cells mature in the thymus, B cells mature in the bone marrow
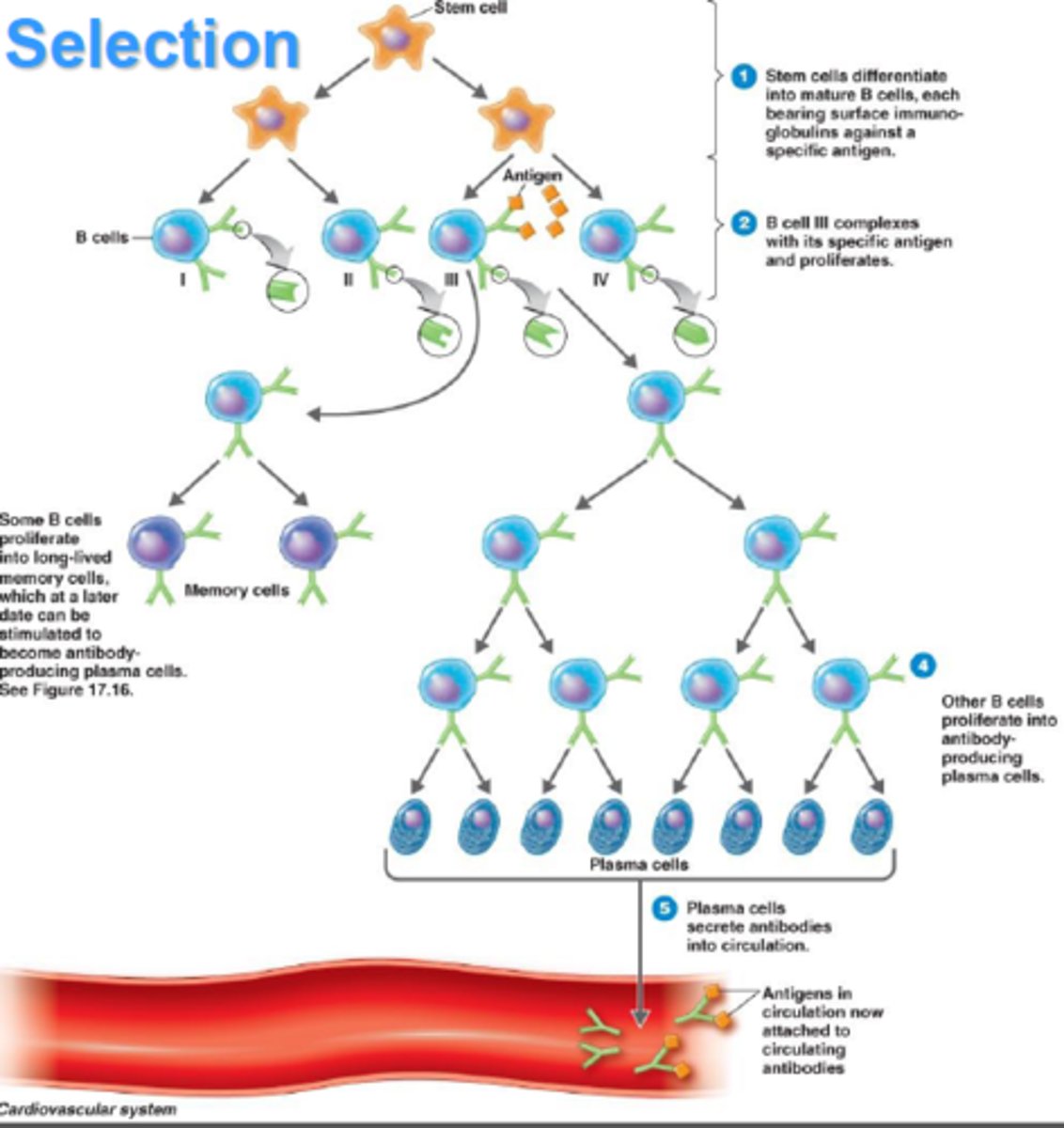
Proliferation
The 4th stage of specific immune response
The lymphocytes divide by mitosis to produce enough numbers to effectively combat the infection
Differentiation
The 5th stage of specific immune response
- T cells differentiate into Tk, Th and Tm cells
- Th cells release interleukins to stimulate B cell differentiation
- B cells differentiate into plasma and Bm cells
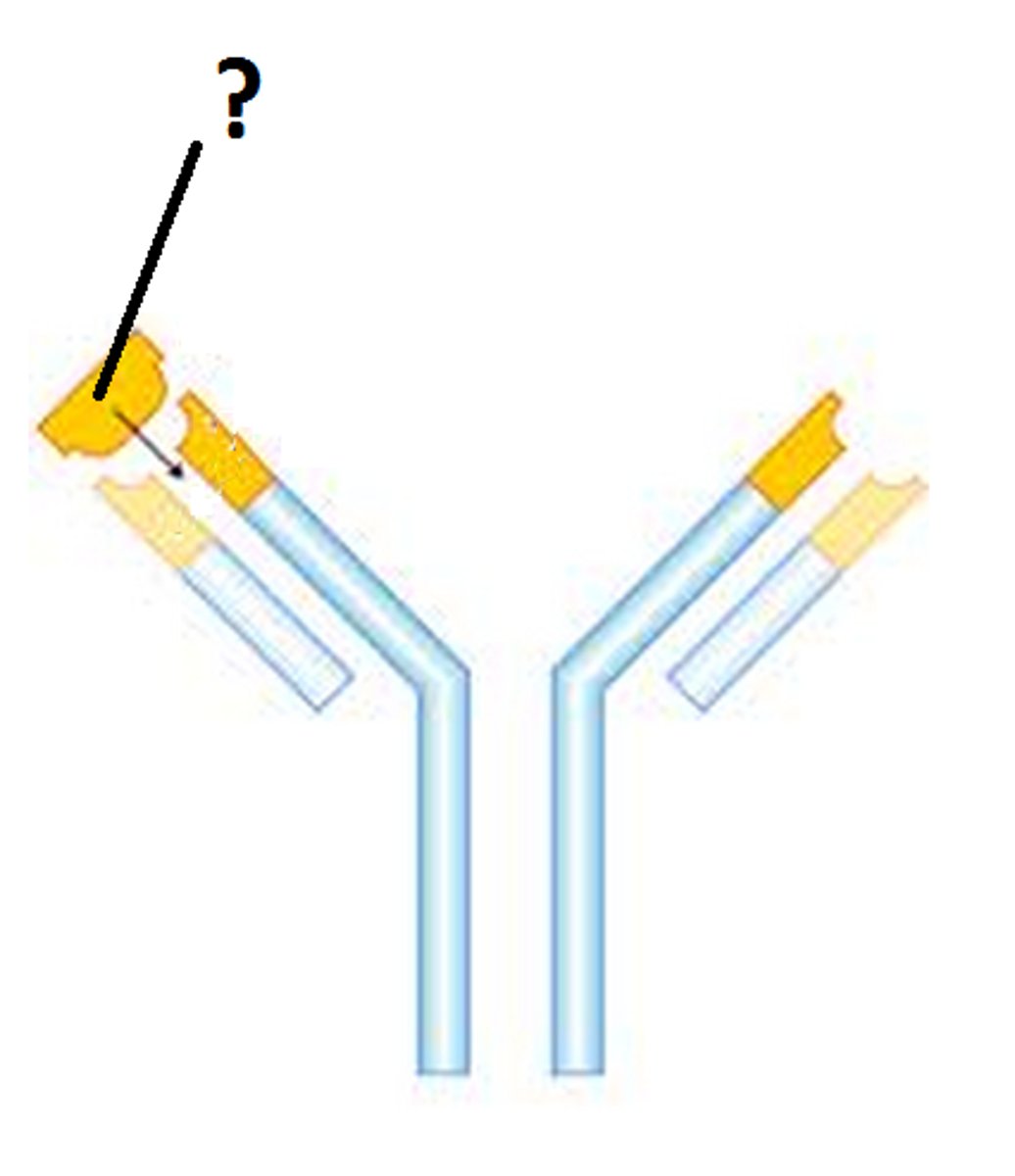
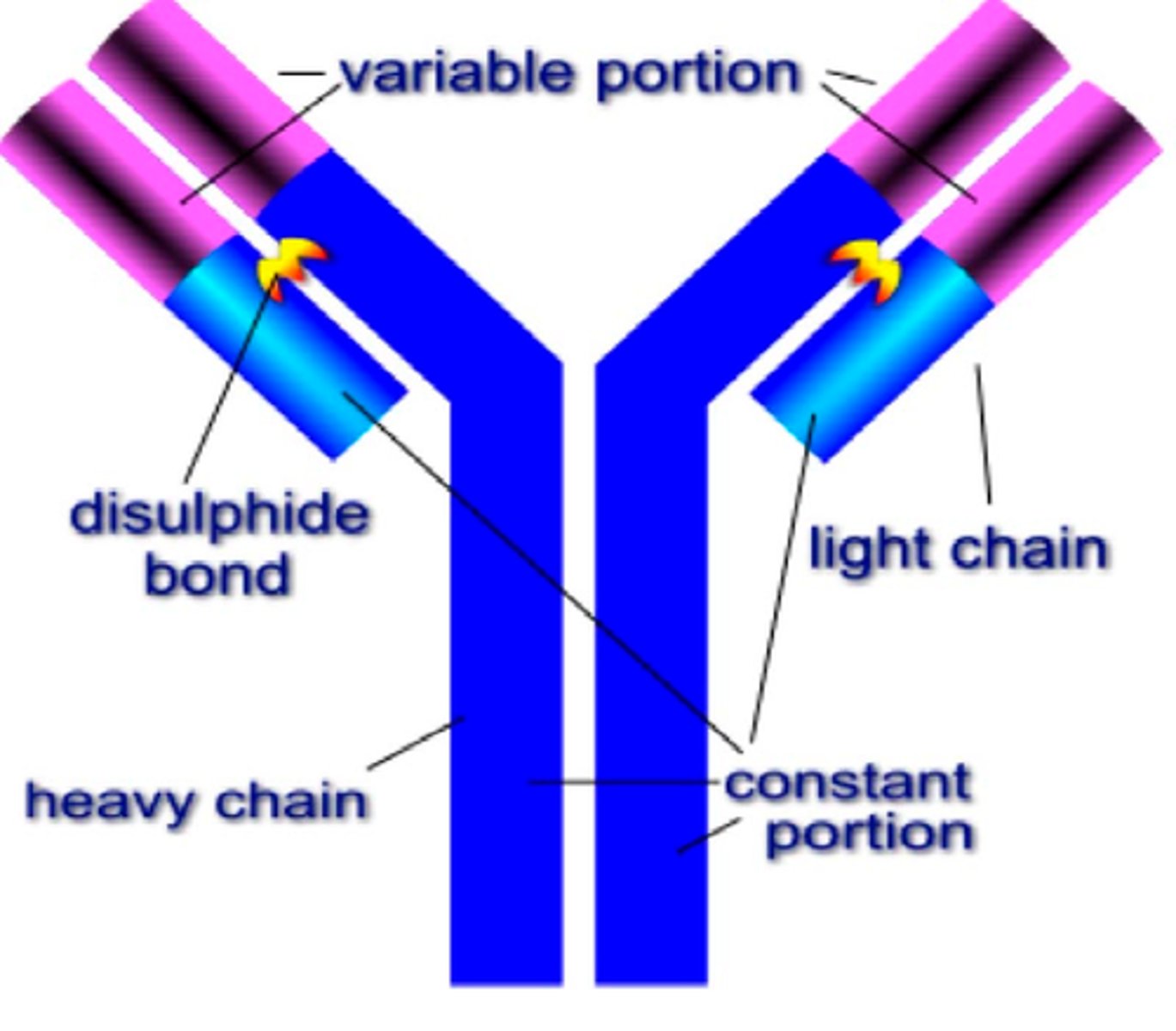
Antibody
A protein produced by immune cells that counters antigens.
- An immunoglobulin
- Y shape
- Consists of 4 polypeptide chains, 2 light and 2 heavy
- Disulfide bridges hold chains together
- Hinge region allow flexibility
- Variable region has specific shape
- Constant region is the same for all antibodies
- Contains site for binding to phagocytes
Immunoglobulin
A complex protein produced by plasma cells that is specific to a certain antigen
E.g. antibody
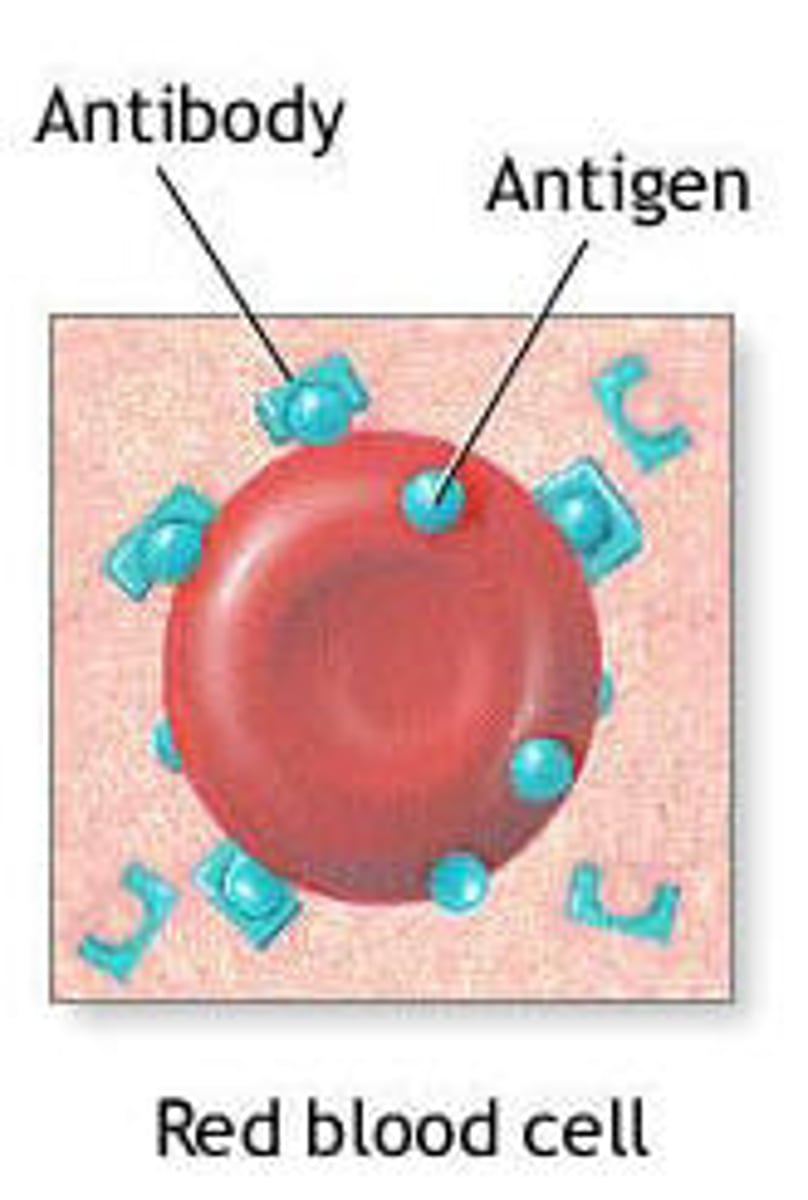
Agglutinin
An antibody with 2 identical binding sites, allowing for clumping of pathogens
- Prevents pathogens from infecting cells
- Allows phagocytes to more easily identify
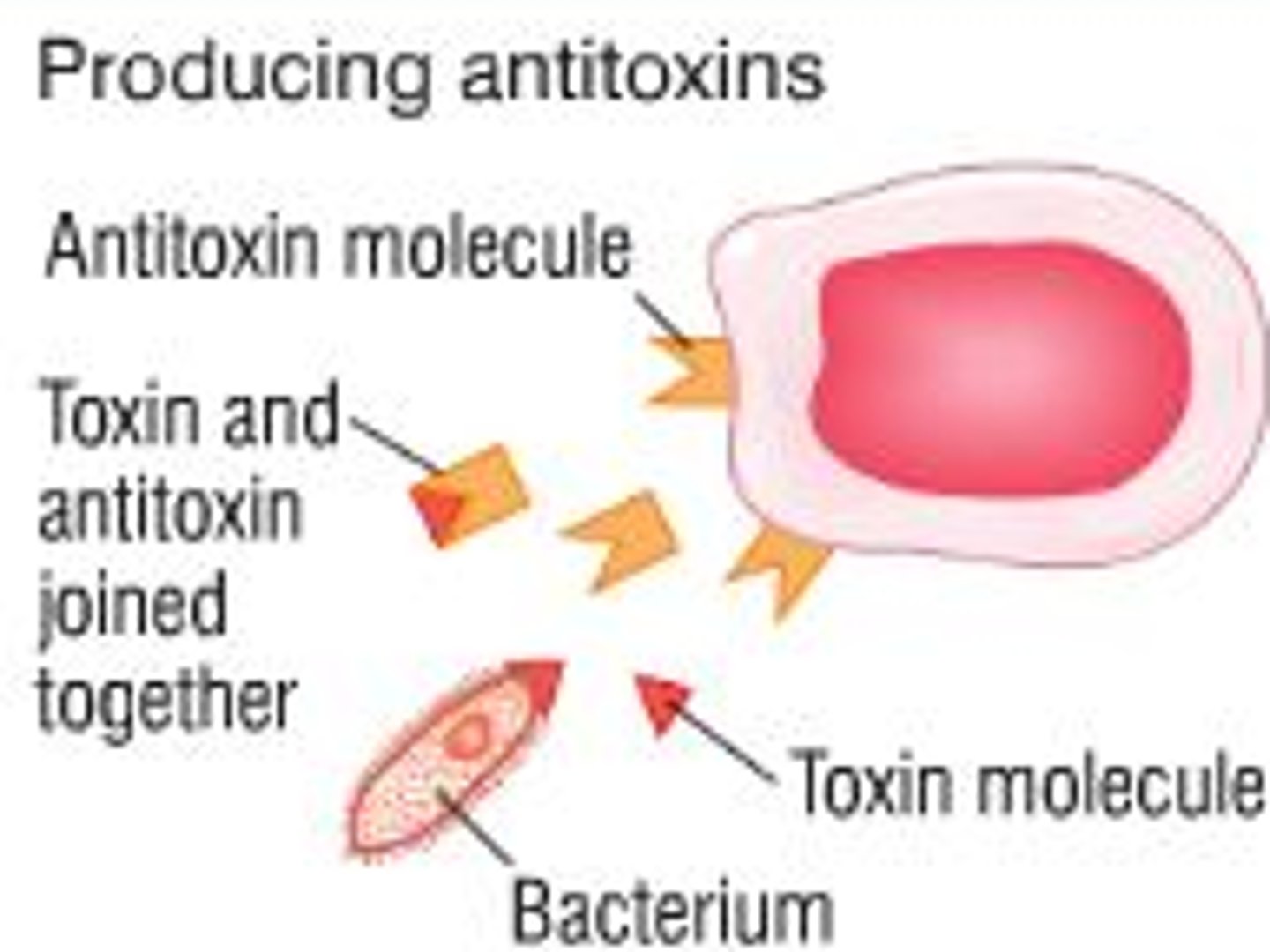
Anti-toxin
An antibody that binds to molecules released by pathogens, neutralising any harmful substances
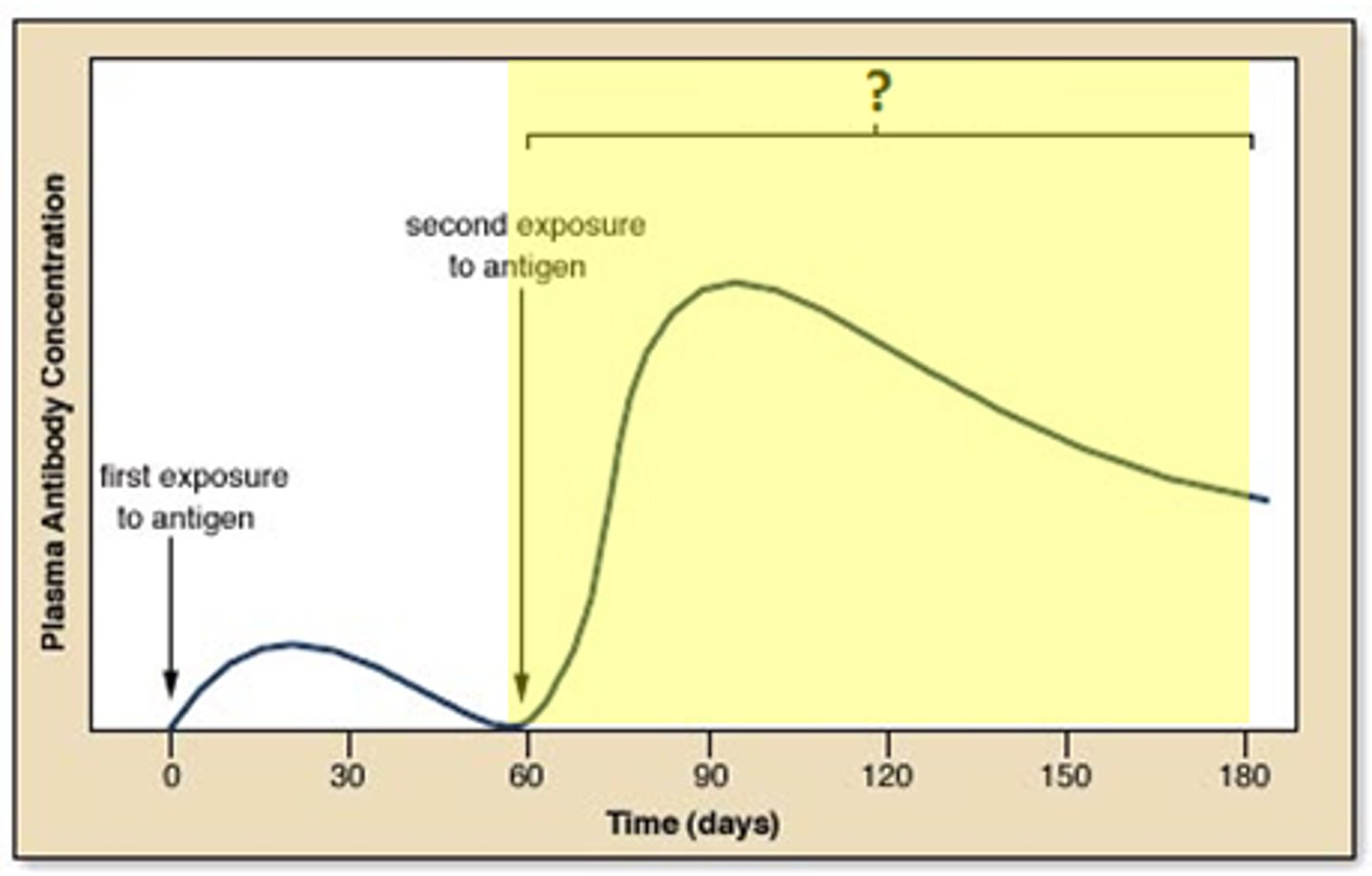
Primary immune response
The bodies response to a pathogen it has never encountered before.
Very slow, taking a few days to produce enough antibodies to respond to the infection
Secondary immune response
The bodies response to a pathogen it has encountered before, or been vaccinated against
- T and B memory cells quickly identify the antigens and produce antibodies, eliminating the infection often before you even develop symptoms
Vaccination
An injection that initiates the primary immune response to ensure that a person has increased immunity to a pathogens. Boosters sometimes have to be given
Types:
Live organisms - Usually a less dangerous form of the pathogen. E.g. cowpox creates immunity to smallpox
Weakened organism - Has the antigens but can't cause damage. E.g. Measles, TB
Dead pathogen - Typhoid, cholera
Antigens - The antigens from the pathogen, but not the pathogen itself. E.g. Hepatitis B
Toxoid - A harmless form of a toxin. E.g. tetanus
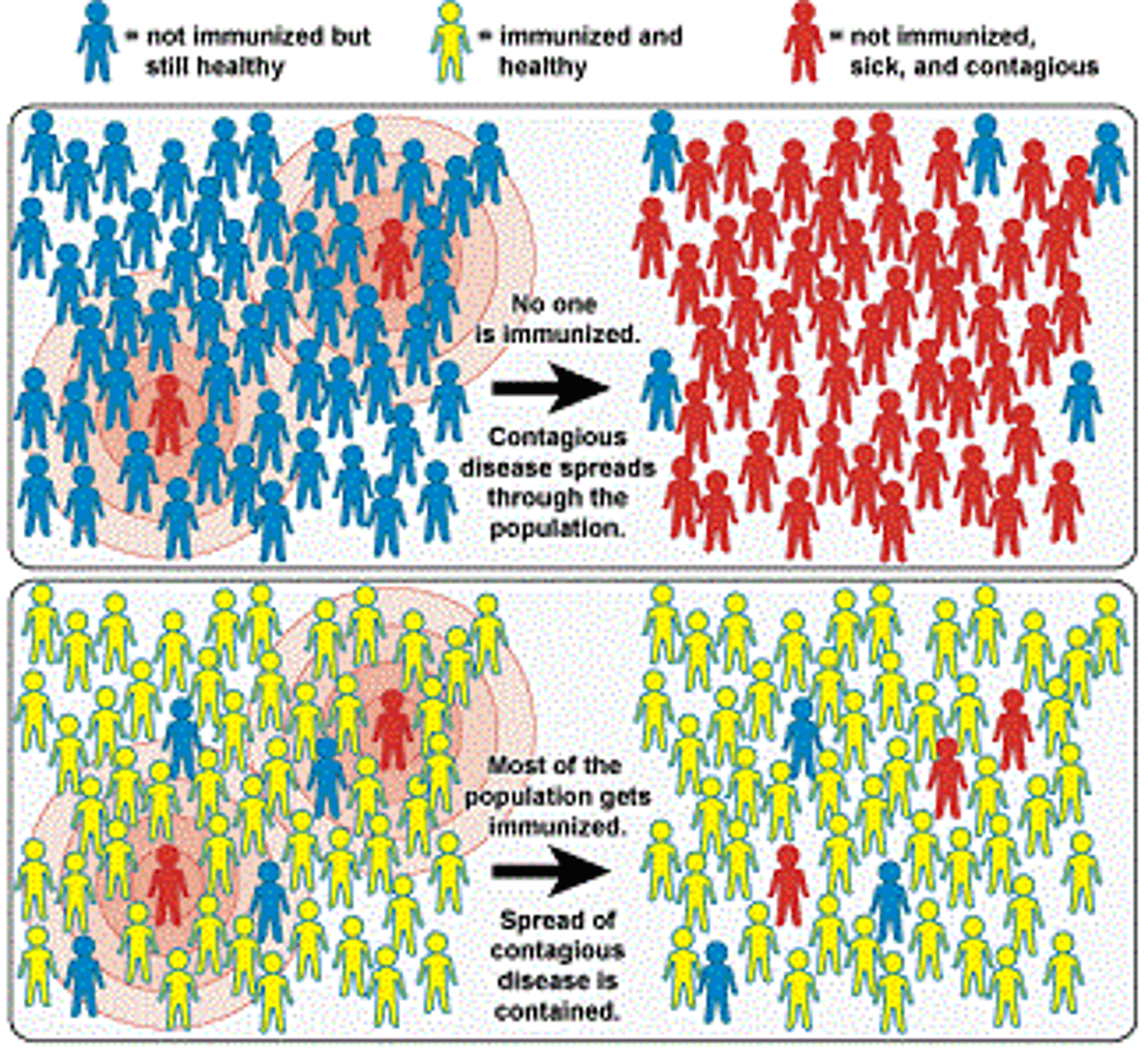
Herd vaccination
When a large proportion of a community has been vaccinated and is immune, the chance of an infected person coming into contact with someone who isn't immune is low, and therefore it can't be spread
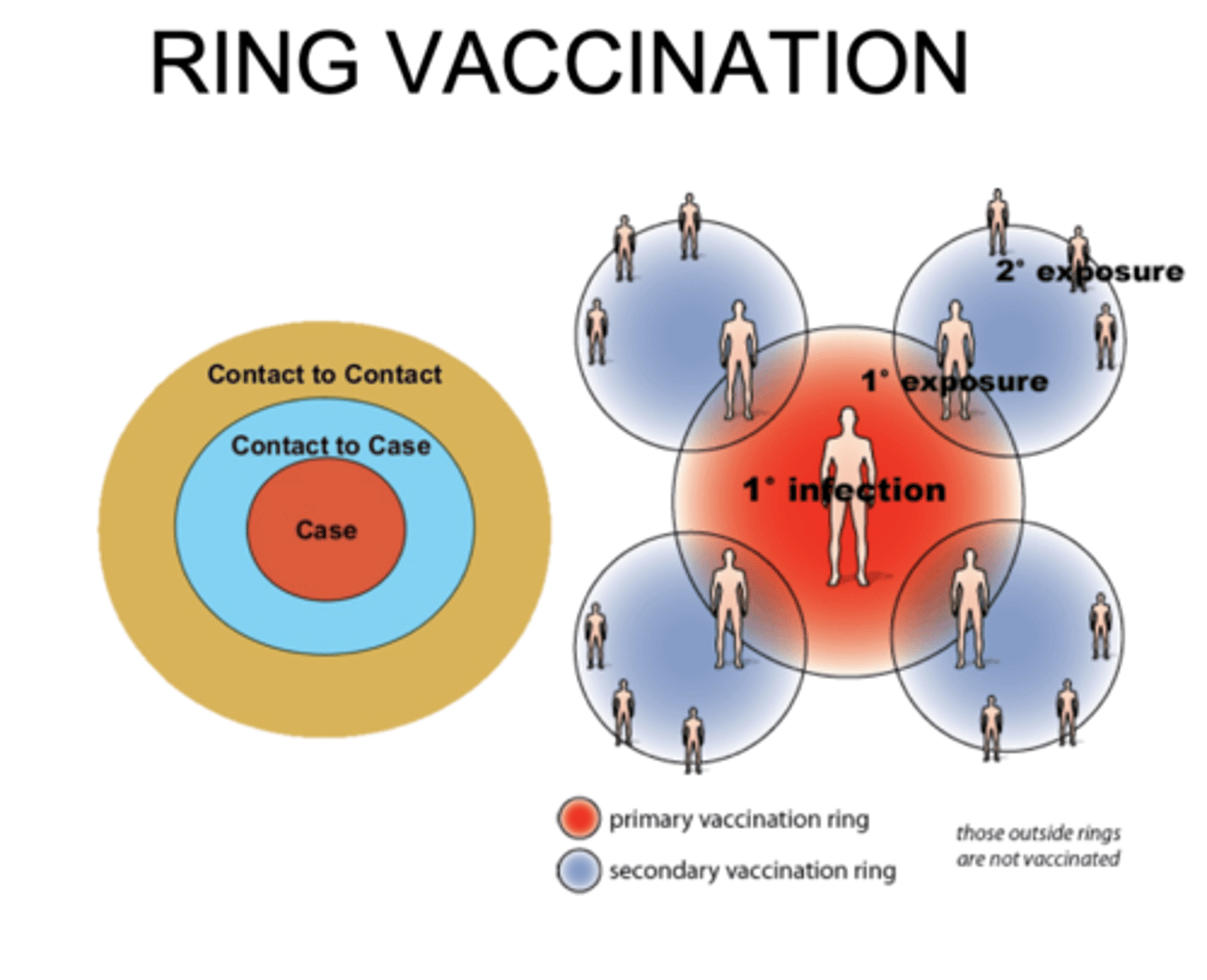
Ring vaccination
Involves vaccinating all the people who have been in contact with the infected person
Genetic mutation
If this happens to a pathogen, then the vaccine may no longer be effective if the immune system can't recognise the new antigens.
Renders the vaccine useless
Natural immunity
Immunity achieved through normal life processes
Artificial immunity
Immunity achieved through medical intervention
Passive immunity
Immunity achieved by transferring antibodies from one person to another
E.g. vaccine, breast feeding
- No exposure to antigen
- Protection is immediate
- Protection is short-term
- Memory cells aren't produced
Active immunity
When the immune system is activated and manufactures its own antibodies
- Requires exposure to antigen
- Takes a while for protection to develop
- Protection is long-term
- Memory cells are produced
Active natural immunity
Immunity provided by antibodies made in the immune system as a result of infection
Active artificial immunity
Immunity provided by antibodies made in the immune system as a result of vaccination
Passive natural immunity
Antibodies provided by the placenta or breast milk from mother to child. Makes the child immune to any disease that the mother is immune to
Passive artificial immunity
Immunity provided by injection of antibodies produced by another individual. E.g. Hepatitis
Need of new drugs
- New diseases are being found
- Still diseases with no known cures
- Microbes are mutating to become resistant to existing drugs
Antibiotic
A chemical which prevents the growth of microorganisms. Can be used against bacteria (antibacterial) or fungi (antifungal)
Penicillin
The first antibiotic discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928.
- Discovered by accident
- Popularised by Florey and Chain in the lead up to WW2
Traditional remedies
Drugs often based on plants and have been used for centuries. Relied upon by up to 80% of the world's population
Morphine - Used since Neolithic times (10,000-4500 BC). Reduces nerve actions, preventing pain
Willow-bark extract - Led to the development of aspirin and ibuprofen
Personalised medicine
The development of designer drugs based on an individual's genome.
Synthetic medicine
The development of molecules that mimic biological systems