11Bio - Cell membranes
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
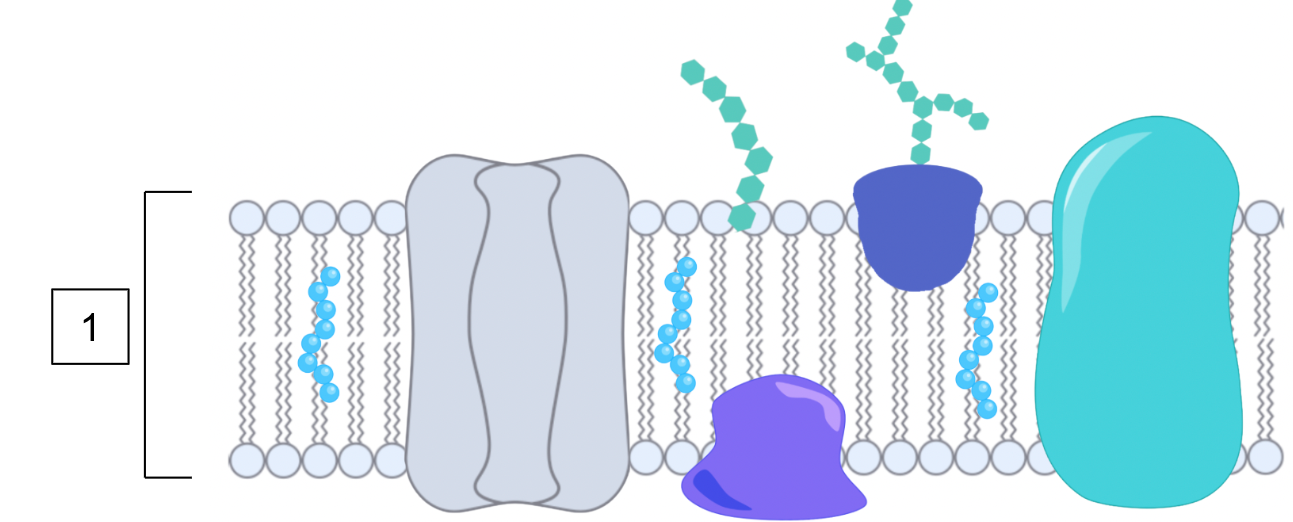
List all the structures in the cell membrane
Phospholipid bilayer
Cholesterol
Transport protein
Integral protein
Peripheral protein
Glycolipid
Glycoprotein
What are the properties of the phospholipid bilayer?
Hydrophobic (water-hating) fatty acid tails
Due to the presence of these hydrophobic tails, only small uncharged molecules can diffuse freely through phosopholipid bilayers
Charged molecules, such as ions, are unable to diffuse through a phospholipid bilayer regardless of size
Hydrophillic (water-loving) head
Attracted to water molecules due to its polar nature and negative charge - allows the head to interact with the aqueous environment both and in and out the cell
What are proteins?
Proteins are the other major component of cell membranes, making up 25-75% of the mass of the various cell membranes.
Proteins carry out the specific functions of different cell membranes
Act as transporters, enzymes, receptors and structural components
What are the two types of proteins found in the cell membrane?
Peripheral proteins
more loosely attached to the phospholipid bilayer
act as enzymes
attaching the membrane to the cytoskeleton, providing structural support and maintaining cell shape
Integral proteins
their potential to cross the membrane are often involved in transportation (e.g. glucose) across the membrane, signalling molecules and providing structural support
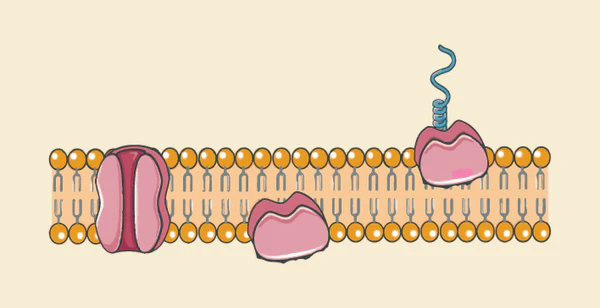
What are the classifications of protein functions?
Transport
transports needed compounds into the cell that aren’t permeable acorss the membrane
faciltated diffusion
active transport
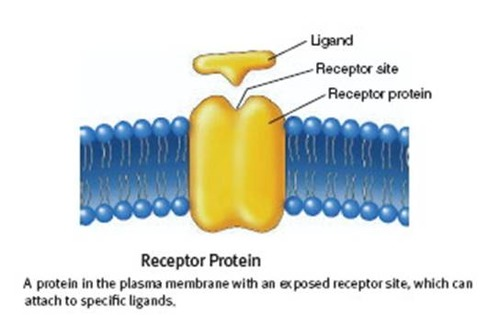
Receptor
detect hormones, neurotransmitters or other messages from outside the cell
helps the cell know what to do: grow, divide, or stop
coordinate with other cells
Adhesion
the tendency of unlike molecules cells sticking together
form tissues and organs
clotting for a wound
Recognition
allows cells to distinguish between their own cells and foreign cells
ensures proper immune system function so white blood cells can identify the difference between pathogens (viruses, bacteria) your own cells
What is the function of the phospholipid bilayer?
Phospholipid bilayer
Forms the membrane’s basic structure
Selective permeaability - allows small, non-polar and lipid-soluble substances (e.g. gases) to pass through. Barrier to water-soluble substances, large molecules and ions
Fluidity - enables cell movement, needed for cell divide or white blood cells enfulfing pathogens
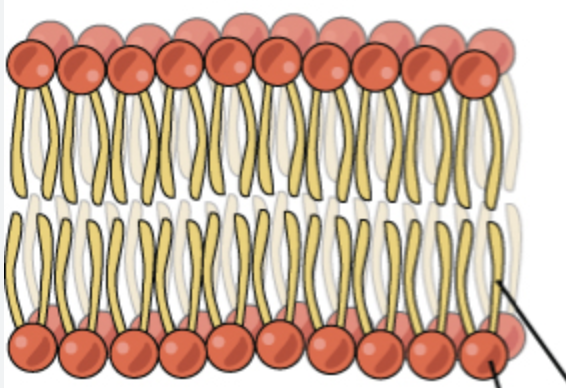
What is this?
Phospholipid bilayer
What is the function of cholesterol?
Cholesterol
Maintains fluidity and stability (structure) of the membrane in hot and cold temperatures
cholesterol’s rigid structure interacts with the phospholipid fatty acid tails, restricting their movement and preventing the membrane from becoming too fluid at high temp
at lower temp, cholesterol prevents fatty acids from packing together too tightly and becoming rigid
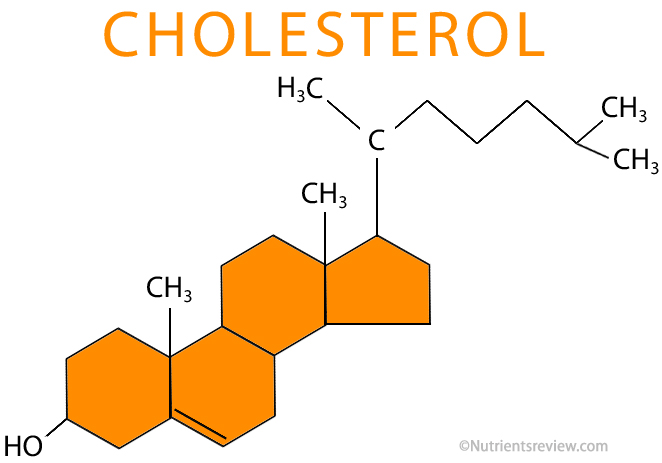
What is this?
Cholesterol
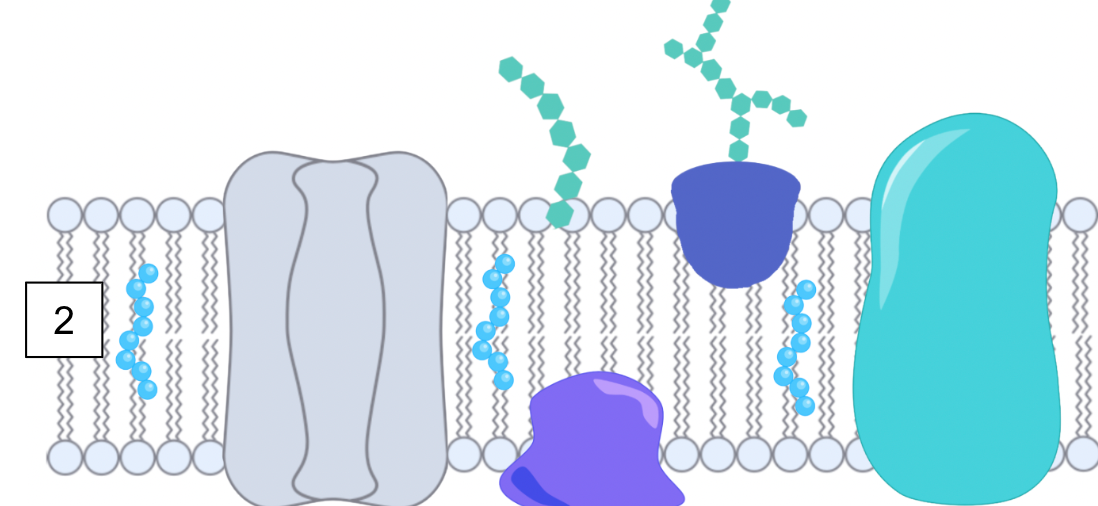
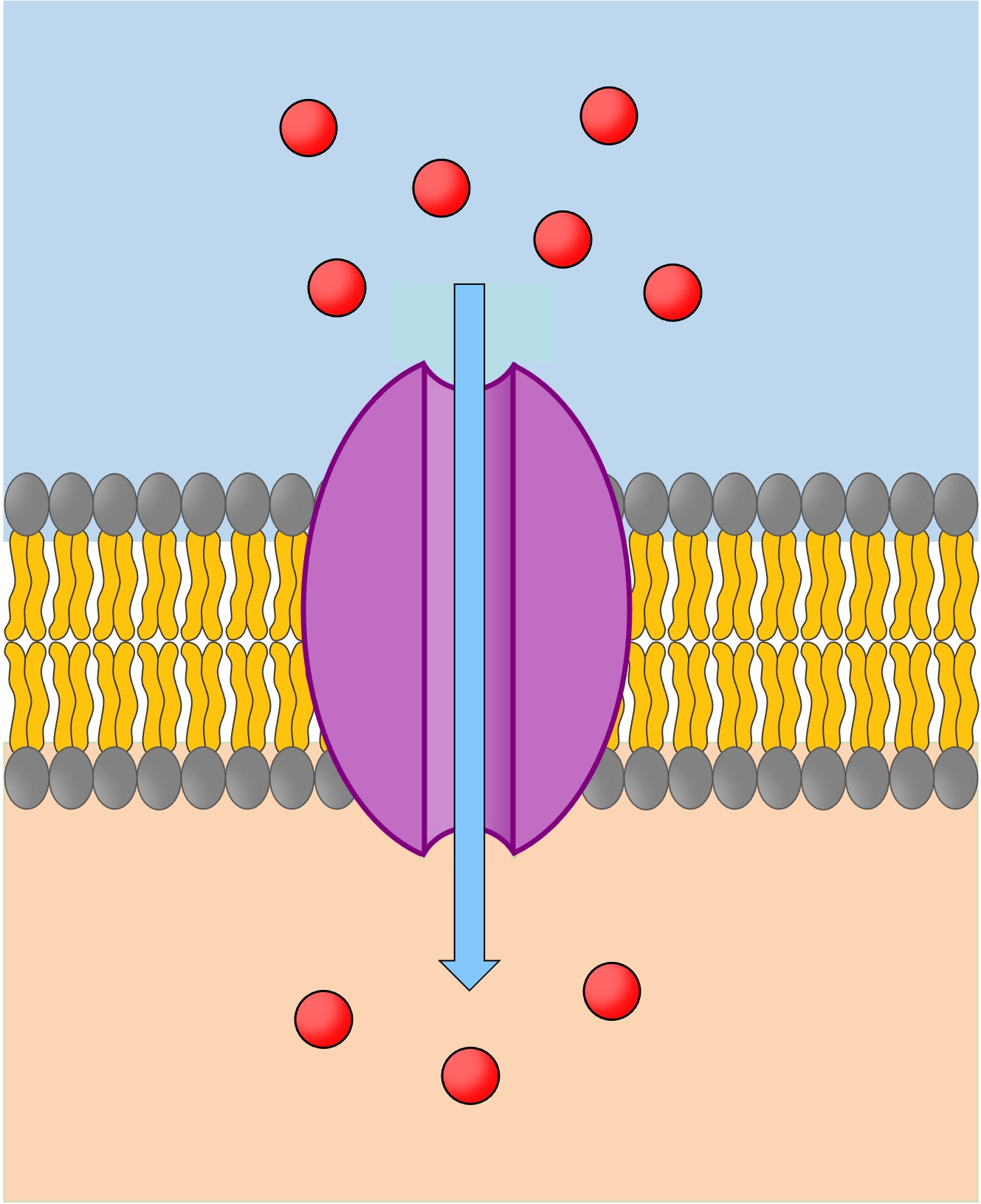
What is the function of the channel (transport) protein?
Channel protein
Creates hydrophillic pores to transports specific compounds into the cell that AREN’T PERMEABLE across the membrane
Facilitated diffusion (high → low concentration)
Active transport (low → high concentration)
Allows larger molecules (e.g. glucose), ions and polar substances to move across the membrane
What is this?
Channel protein
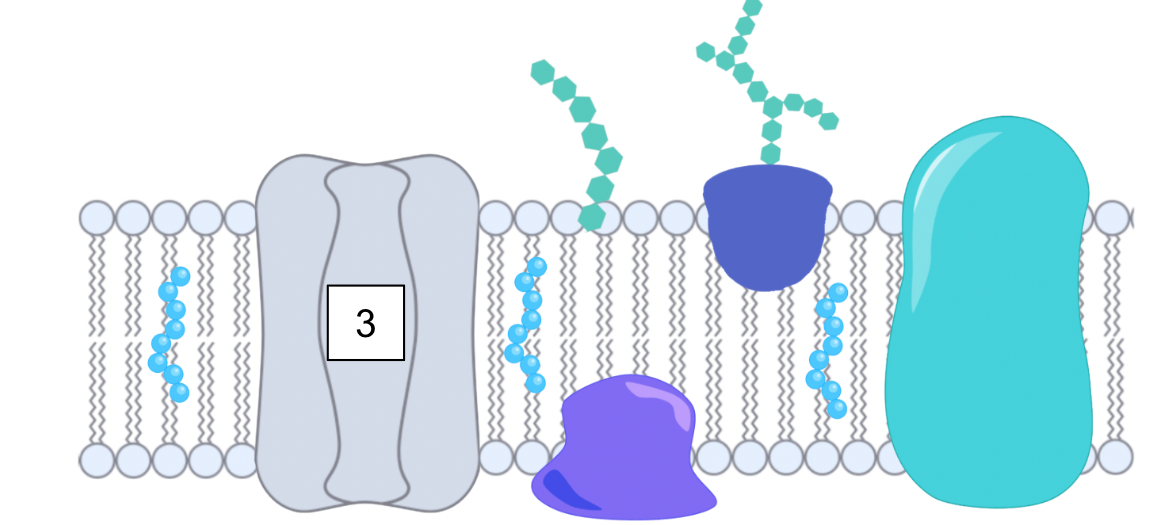
What is the function of integral (receptor) proteins?
Integral proteins
Detects hormones, neutransmitters, or other messages from outside the cell
Receptors on the outer part of the protein detect signals and communicate messages to proteins inside the cell
Helps the cell know what to do: grow, divide or stop
What is this?
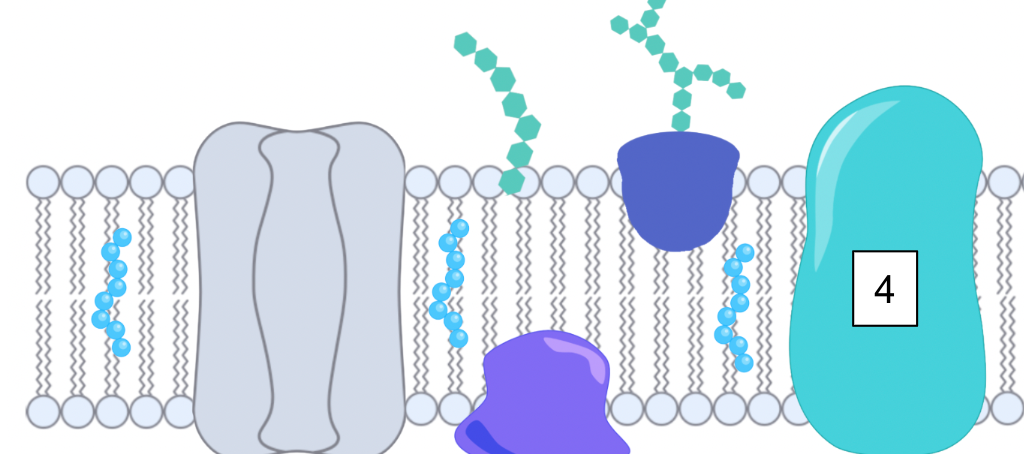
Integral protein
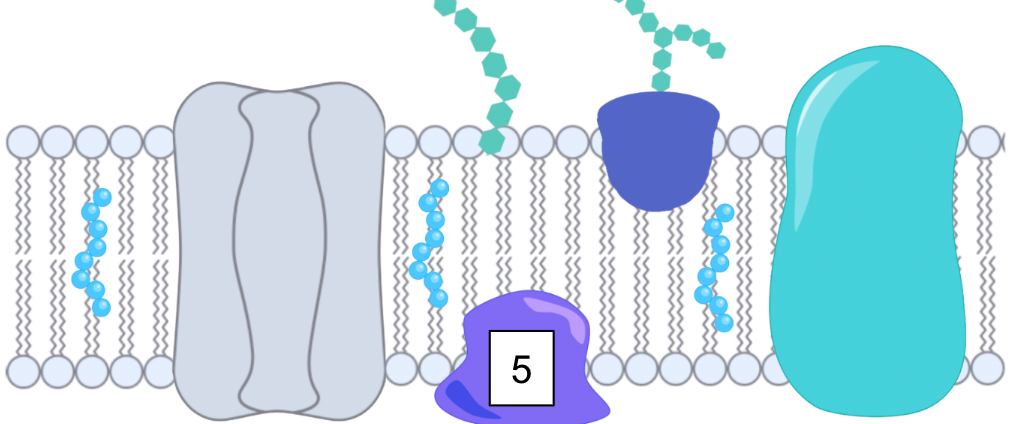
What is the function of the peripheral protein?
Peripheral proteins
Attached to the membrane’s surface, either inside or outside, but does not cross it
Inside membrane - recieves messages from integral protein and passes them to the cell
Outside membrane - involved in adhesion (cells sticking together)
Forms tissues and organs
Clotting for a wound
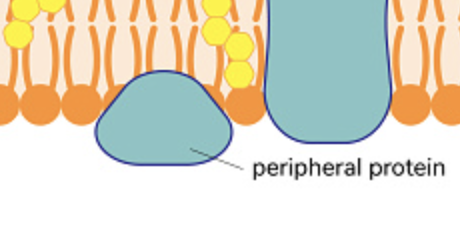
What is this?
Peripheral protein
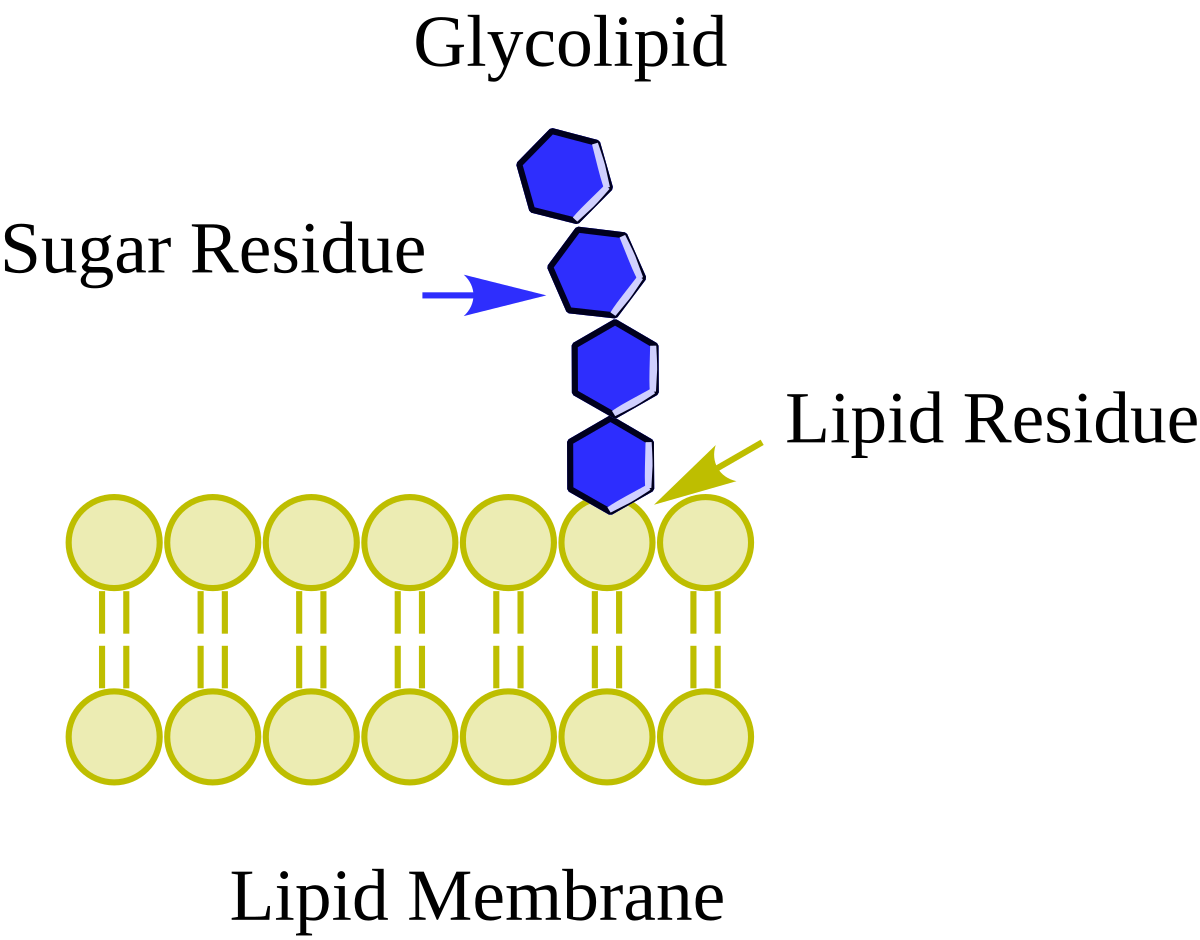
What is the function of the glycolipid?
Glycolipid protein
Glycolipid: a lipid (fat molecule) with one or more sugar chains (carbohydrates) attached. This lipid part anchors it to the membrane
Sugar chain - cell recognition
What is the function of the glycoprotein?
Glycoprotein
Glycoprotein: proteins that have sugar chains (carbohydrates) attached to them
Protein - helps with adhesion
Sugar chain - helps with recognition
What are these
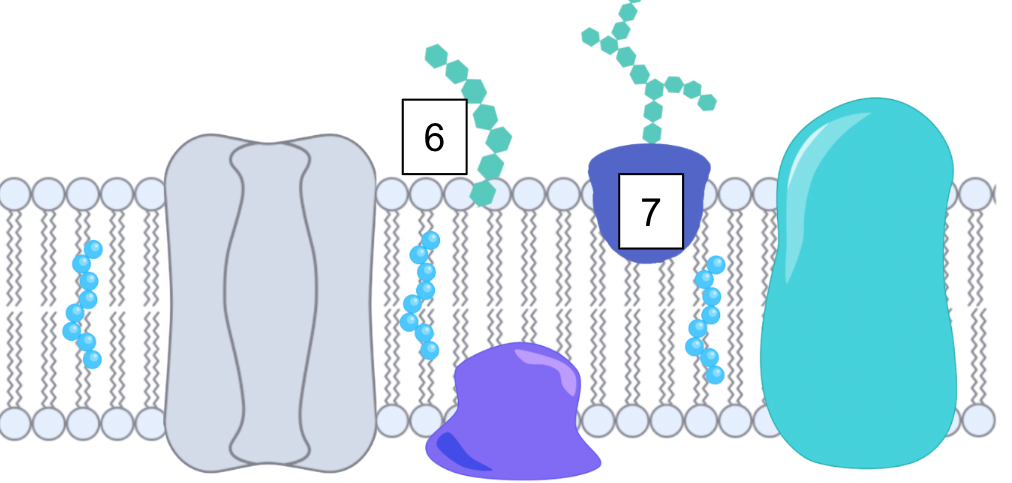
Glycolipid
Glycoprotein