Monetary Policy
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is monetary policy?
Changes to the base rate of interest, money supply and exchange rates
What is expansionary monetary policy?
Used to increase AD
Low interest rates
Fewer restrictions on the money supply
What is Contractionary Monetary Policy?
Used to decrease AD
High Interest Rates
Greater restrictions on the money supply
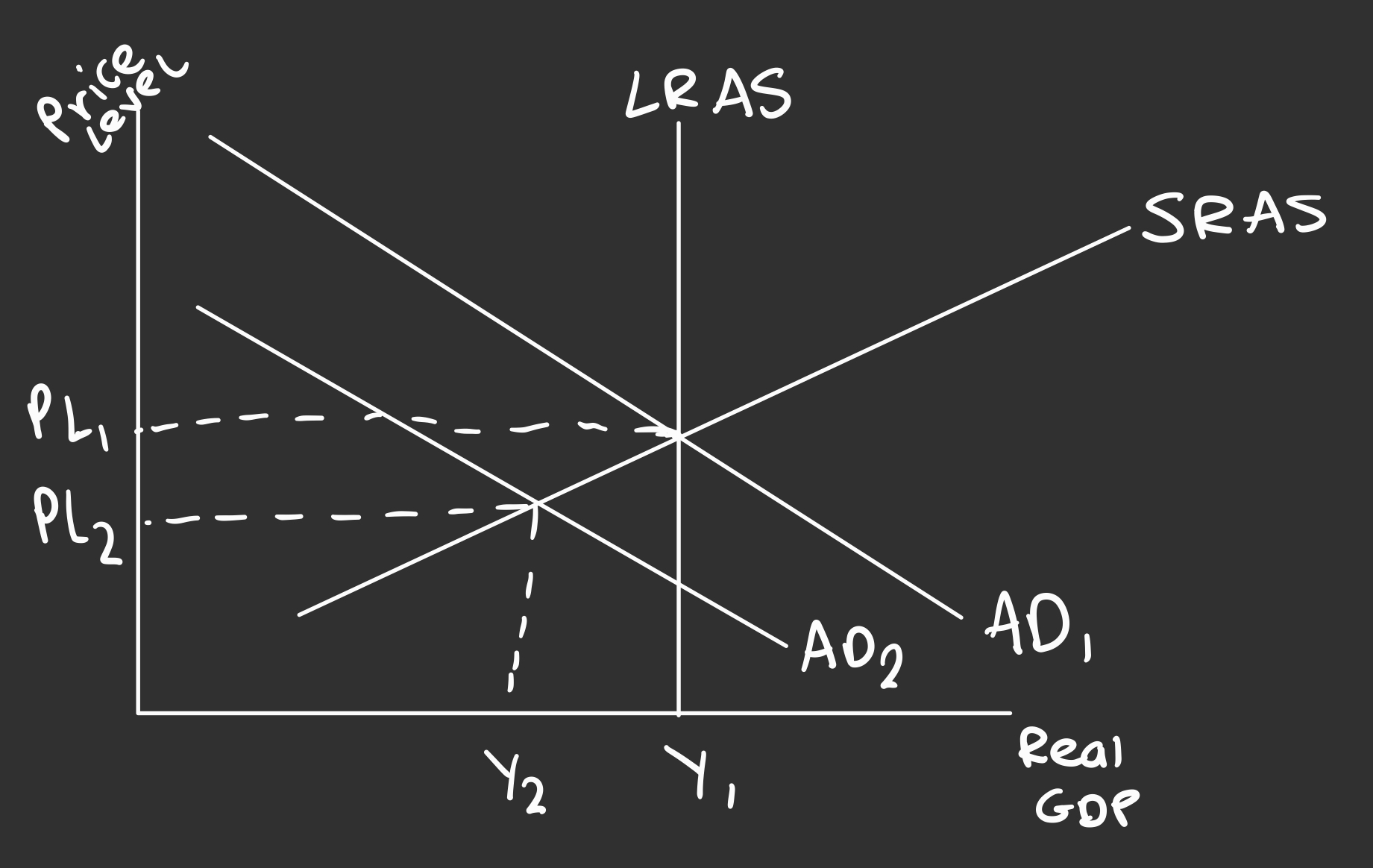
What is a diagram for contractionary fiscal policy?
Increasing interest rates, should decrease AD, reducing inflation
Negative multiplier effect could lead to a further fall in AD
What is the multiplier effect?
An initial increase in AD, e.g. through extra government spending, will lead to a further increase in AD.
e.g.
If the gov spends £1B on building new hospitals
Construction workers earn more
So spend more on restaurants, shops etc
Shop owners earn more and the cycle continues
Why do higher interest rates reduce AD?
Cost to borrow money increases, so consumption falls
Reward of holding money increases, so there are more savers and less spenders
Investment by firms falls, as it is more expensive to borrow and fund the investment
Gov spending falls, as cost for government to borrow money increases
What does contractionary monetary policy depend on?
Size of the reduction in AD depends on all components of AD
Time lag, new IR don’t come into effect for around 18 months
The wage rises from reduction in economic growth may eventually cancel out the fall in AD
Wage rises from fall in economic growth could cause cost-push inflation
What are other ways to reduce inflation instead of increasing interest rates?
Increasing taxes - reducing AD
Reduced government spending - reducing AD
Increasing immigration- increases productivity and LRAS
What happens to inflation if the money supply increases?
Inflation falls, as banks raise interest rates
becomes harder to borrow and spending falls
firms lower their prices
What happens to inflation if the money supply increases?
Inflation rises as banks decrease interest rates
Borrowing increases, so consumption and AD increases
Firms raise prices to maximise profits
What happens to interest rates if the reserve requirement is increased?
Commercial banks hold more money with the bank, reducing the money supply
Commercial banks have to raise interest rates to maintain profits
What happens to interest rates if the reserve requirement is increased?
Commercial banks hold less money with the central bank, increasing money supply
Commercial banks reduce interest rates to attract borrowers
What happens to interest rates if the BoE increases the base rate?
More expensive for commercial banks to borrow
Pass on this cost to consumers through increasing interest rates
What happens to interest rates if the BoE reduces the base rate?
Cheaper for commercial banks to borrow, so they can borrow more
Money supply increases, so commercial banks reduce interest rates to attract borrowers
How does Quantitative Easing reduce interest rates?
Central bank buys government bonds from commercial banks
Commercial banks have more money available to loan, so money supply increases
Commercial banks reduce interest rates in order to attract borrowers
Spending increases, boosting AD
Why may monetary policy become ineffective in order to get out of a recession?
Due to liquidity traps
What are liquidity traps?
When interest rates or close to or at zero, and the central bank is unable to stimulate AD
Why do Liquidity traps occur?
Preference for saving
Consumers may not be confident about the future, so look to save rather than borrow money to spend, no matter how low the interest rates are
Deflation
If prices are continually falling, people hold money as it is increasing in value and will buy more in the future
Balance Sheet Recession
Firms and consumers may have high levels of existing debt
Low interest rates encourages them to pay off debt now
Therefore they don’t take on new debt by borrowing
Illustrate a liquidity trap diagram
Illustrate the loanable funds theory
Why is supply of loanable funds upwards sloping?
Why is demand for loanable funds downwards sloping?
What is the loanable funds theory?
Interest rates are set by savers and borrowers
EVALUATE the impact of Expansionary monetary policy on macroeconomic objectives
Economic Growth
Reducing interest rates increases spending
AD increases, and AS then increases (so total output or GDP rises)
Low and Stable Inflation
Increasing money supply will reduce interest rates, which will increase borrowing and AD so firms raise prices
BUT IF THERE’S A LIQUIDITY TRAP ANY CHANGE TO MONEY SUPPLY IS INEFFECTIVE
Unemployment
Unemployment will fall as spending and borrowing increases when interest rates are low
Firms require more workers to meet this demand increase
Stable Current account on balance of payments
Inflation increases price levels
If exports get more expensive, foreign demand falls
Demand for imports rises as they’re cheaper
Current account on balance of payments becomes unstable
EVALUATE the impact of contractionary monetary policy on macroeconomic objectives
Economic Growth
Increases IR reduces borrowing and spending
AD falls, so firms reduce their supply, reducing total output and GDP
Low and Stable Inflation
Higher IR reduce spending, so inflation may fall
But if consumer and business confidence is high, they may continue to borrow and spend
Unemployment
Higher IR reduces spending and AD
Workers aren’t needed as no pressure to increase supply
Unemployment rises
Stable Current Account on Balance of Payments
Current account position worsens
Currency becomes stronger, so exports are more expensive
IR are high so households don’t spend on imports
Why does the currency appreciate due to contractionary monetary policy?
As interest rates increase, foreign investment rises, so demand for currency increases, making it stronger