Anat Lecture 2
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Structure is…
Function
Tissue is composed of.
cell + ECM
groups of similar cells that carry out a common function
tissues
epithelial tissue
>covers body surfaces (skin, body cavities, and internal lining of body cavities),
>Acts a shield protector
epithelial tissue (epithelia) function include:
protection, sensation, absorption, and secretion
classification of epithelial tissue
>shape of cells,
>number of layers,
What is histology hierarchy?
Cell > Tissues > Organs > Organ Systens
What are the four types of Tissue?
1)Epithelial tissue
2)Connective tissue
3)Muscle Tissue
4)Nervous Tissue
True or False: The extracellular matrix (ECM) is living material.
False – it is non-living material secreted by cells.
What are the two main types of epithelial tissue? Give an example of each.
Membranous (ex: skin, stomach lining).
Glandular (ex: sweat glands, thyroid).
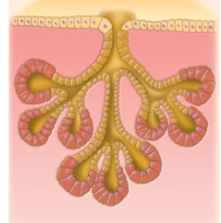
Exocrine glands:
>Secrete substances via ducts, onto surfaces, or into cavities.
>unicellular or multicellular
Endocrine glands:
>Secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
>target can be far or close
>ductless
epithelial tissue composition?
Cells > ECM
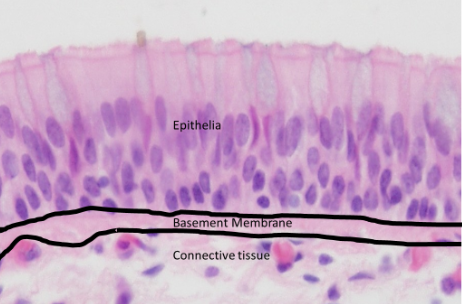
Q11. Why are epithelia considered avascular?
A: They contain no blood vessels; nutrients diffuse from the lumen or underlying connective tissue.
What covers the endocrine system?
endocrine glands
Goblet cells
<only unicellular exocrine gland
>Produce mucus
Exocrine gland multicellular
Continuation of epithelial sheet that invaginates into connective tissue
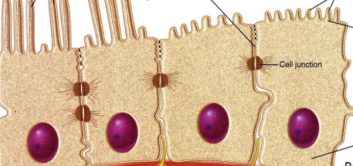
Q12. What is the function of the basement membrane?
Anchors epithelial cells, provides support, and separates epithelium from connective tissue.
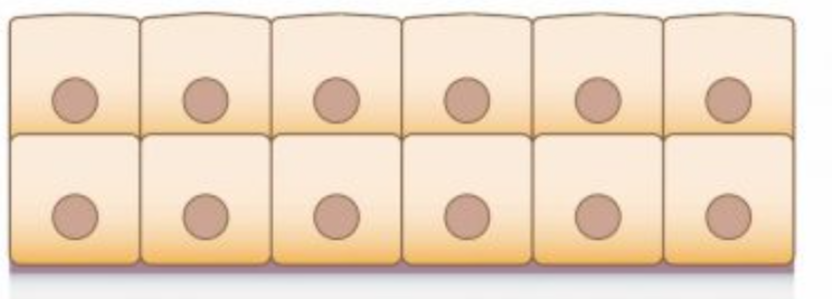
simple
1 layer

Stratified
Multiple layers
Pseudostratified
Appears multi-layered but all touch basement membrane, although not all cells reach the apical surface.
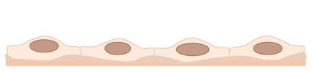
Squamous
> Flat > wider >tall, > oval nuclei |
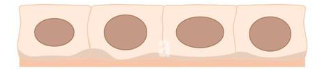
Cuboidal
>Cube-shaped
>round nuclei
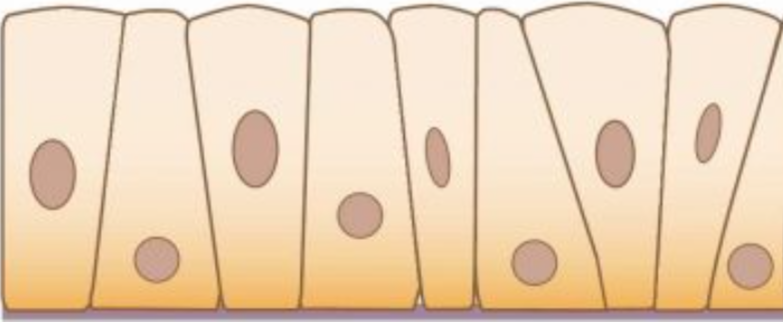
Columnar
>Tall > Width
>oval nuclei near base

Transitional
Stretches, umbrella cells, urinary tract only |
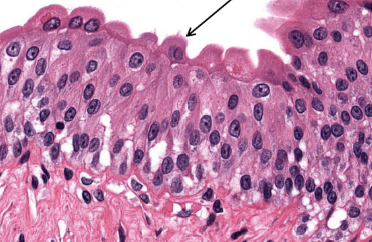
Move mucus/particles
Cilia
Simple Squamous Function
Diffusion, Filtration |
ex (lung, vessels, kideny)
Stratified Squamous Function
Protection
(mouth, skin, vagina)
Simple Cuboidal
Absorption, Secretion
(kidney ovary)
Simple Columnar
Absorption, Secretion |
(digestive tract, uterus)
Pseudostratified Columnar
>Protection and Mucus
>all cells touch basement membrane w/ Cicala on top
>WILL HAVE GOBLET CELLS
>unique to respiratory tract
Transitional
>Stretch
>Umbrella cells in urinary tract
Glandular epithelium
>glands
>endocrine and exocrine
membranous epithelium
>acts a lining
>cover body cavities, stomach etc
Cells in Epithelia are held by what?
Tight junctions