Chapter 12 ENDOCRINE
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Exocrine glands
Glands that secrete products into ducts.
Endocrine glands
Ductless glands that secrete hormones.
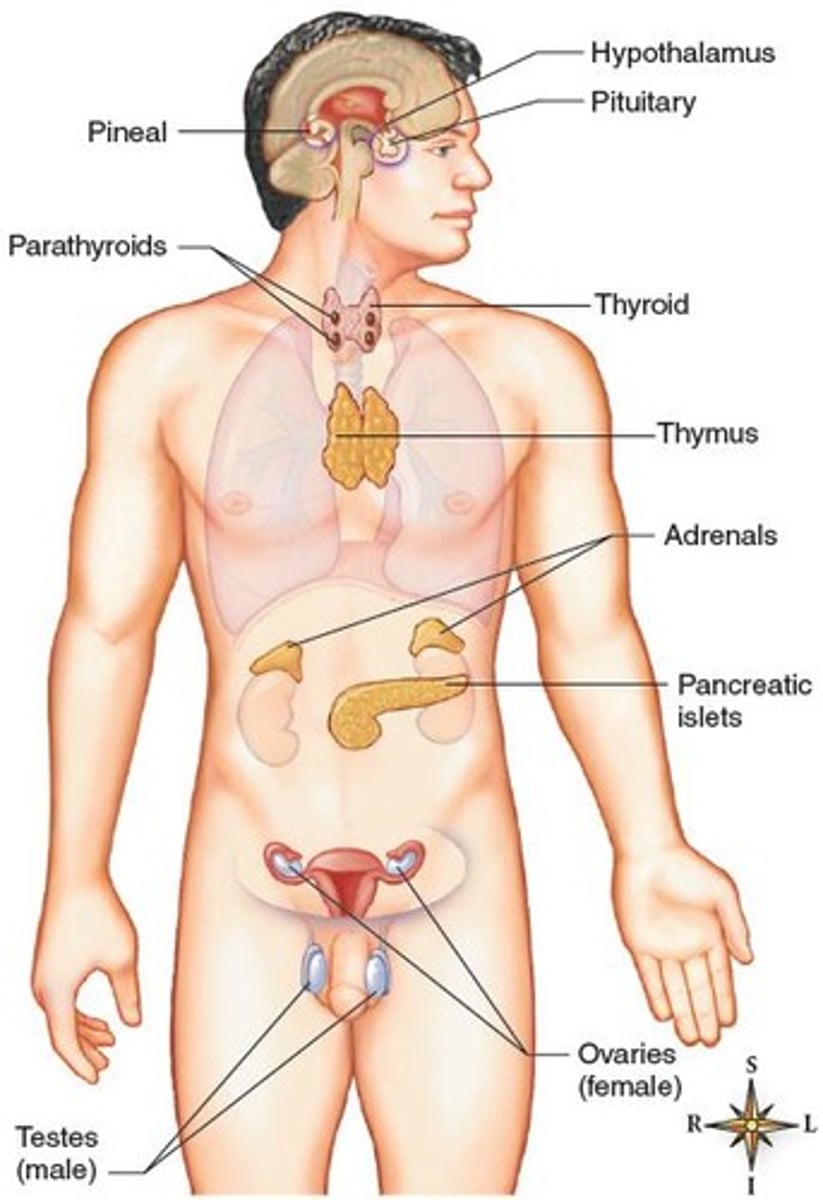
Hormones
Chemical substances regulating target cell activity.
Target cells
Cells affected by hormones in target organs.
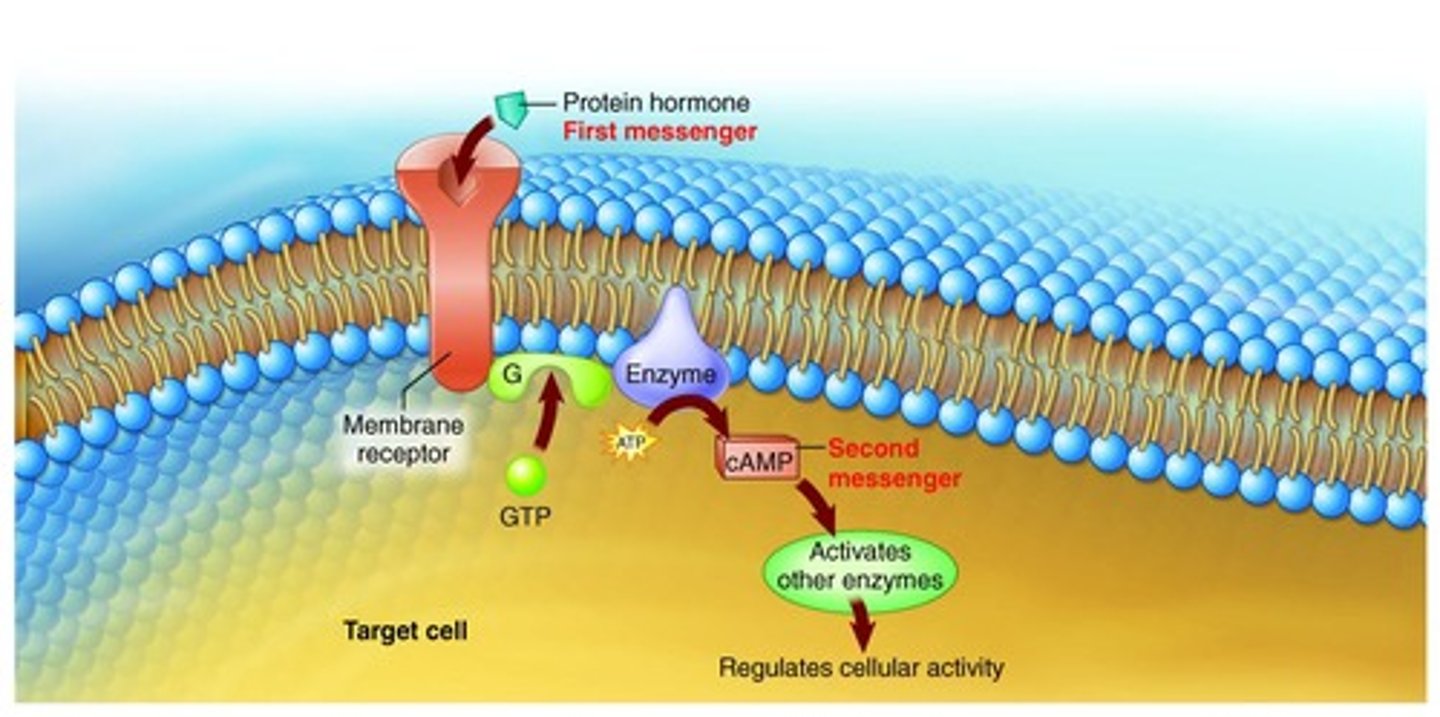
Nonsteroid hormones
First messengers binding to cell membrane receptors.
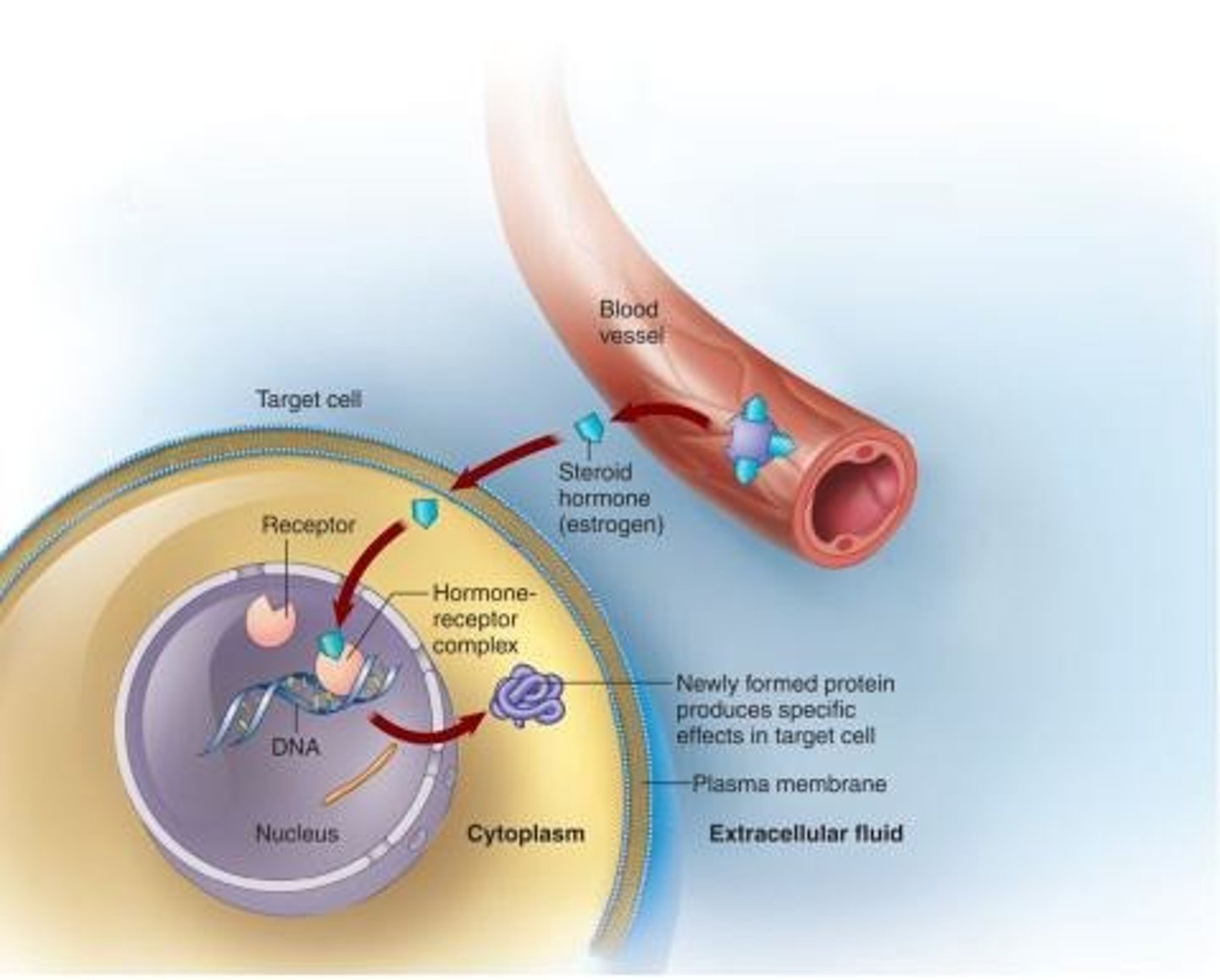
Steroid hormones
Bind to nuclear receptors, affecting DNA activity.
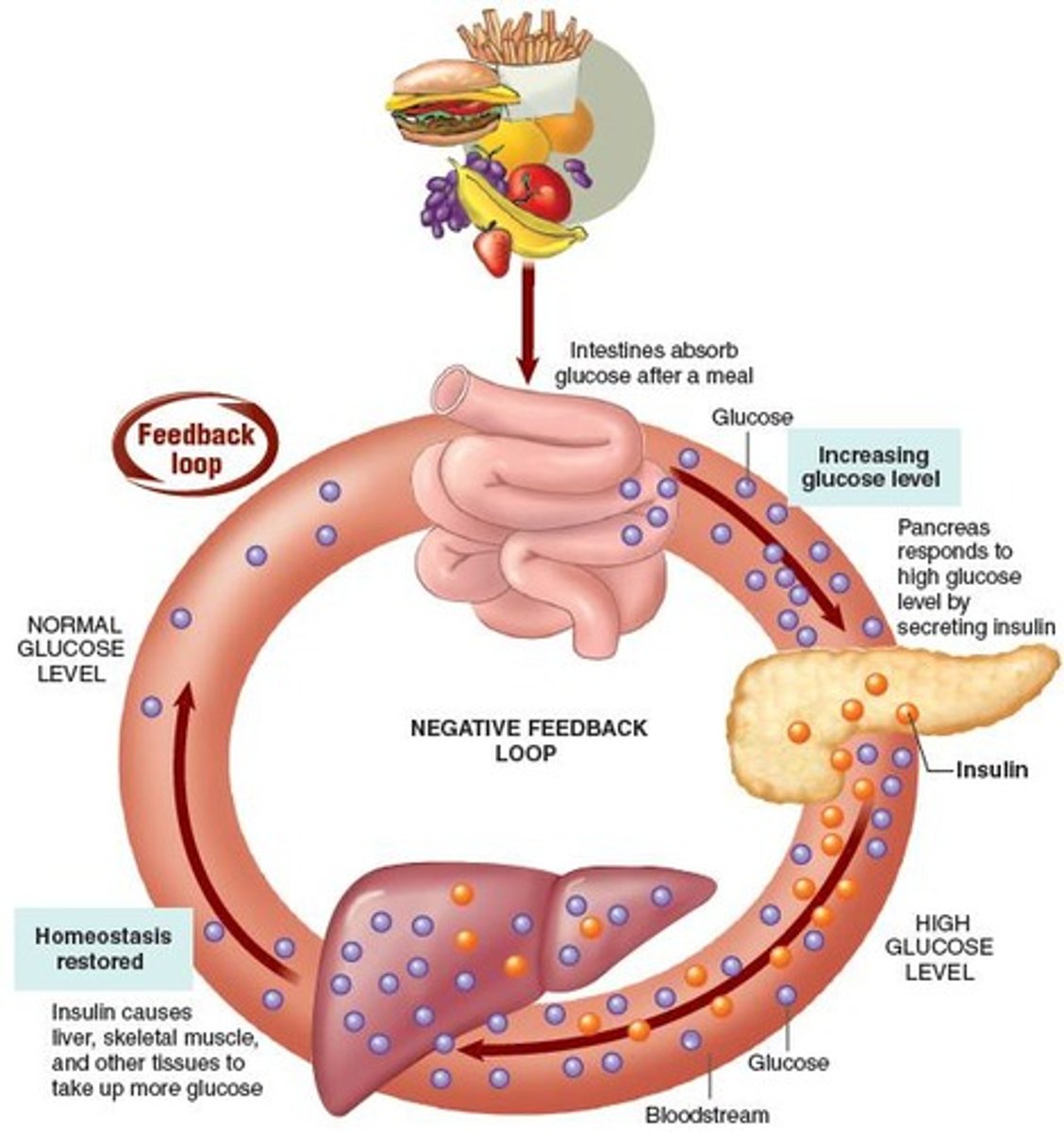
Negative feedback
Mechanism reversing physiological changes in the body.
Positive feedback
Mechanism amplifying physiological changes, less common.
Hypersecretion
Excessive secretion of hormones by glands.
Hyposecretion
Insufficient secretion of hormones by glands.
Polyendocrine disorders
Multiple hormones experiencing hyper or hyposecretion.
Target cell insensitivity
Reduced response to hormones, mimicking hyposecretion.
Prostaglandins (PGs)
Local hormones acting on nearby cells.
Prostaglandin A (PGA)
Class of prostaglandins influencing various body functions.
Prostaglandin E (PGE)
Class of prostaglandins affecting respiration and blood pressure.
Prostaglandin F (PGF)
Class of prostaglandins involved in reproduction.
Anterior pituitary gland
Gland secreting several key hormones.
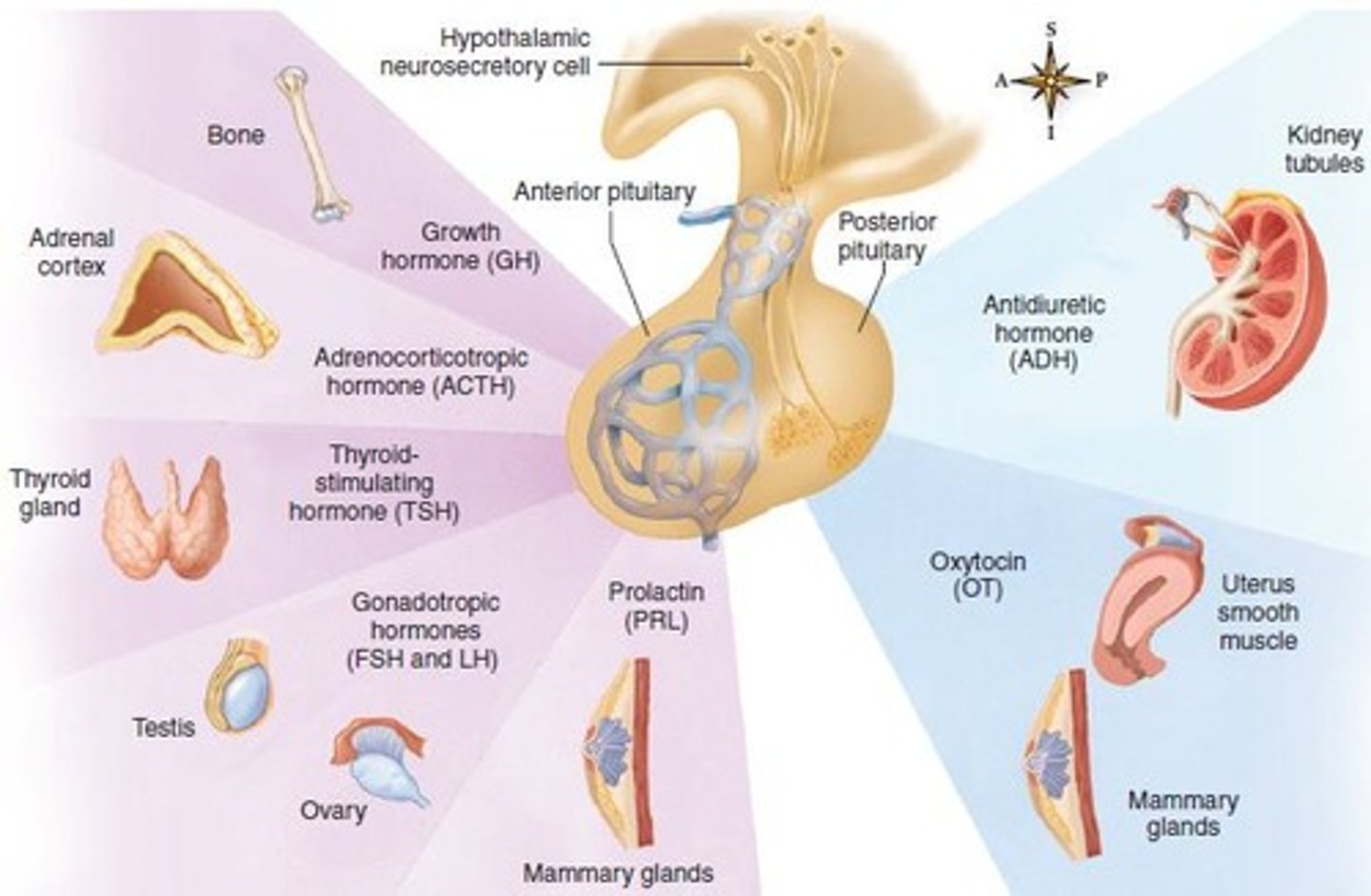
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Stimulates thyroid gland growth and hormone secretion.
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Stimulates adrenal cortex growth and glucocorticoid secretion.
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Initiates ovarian follicle growth and maturation.
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Triggers ovulation and stimulates ovarian hormone production.
Growth hormone (GH)
Stimulates growth and cell reproduction.
Prolactin
Stimulates milk production in mammary glands.
LH
Stimulates estrogen secretion and follicle growth.
FSH
Works with LH to promote follicle maturation.
GH
Stimulates growth and accelerates protein anabolism.
Hyperglycemia
Elevated blood glucose levels due to GH effects.
Gigantism
Excess GH in childhood causing abnormal growth.
Acromegaly
Excess GH in adulthood causing enlarged features.
Pituitary Dwarfism
GH hyposecretion in childhood leading to stunted growth.
Prolactin (PRL)
Stimulates breast development and milk secretion.
ADH
Increases water reabsorption in kidneys.
Diabetes Insipidus
Condition from ADH hyposecretion causing excessive urination.
Oxytocin (OT)
Stimulates uterine contractions and milk ejection.
Thyroxine (T4)
Thyroid hormone that increases metabolic rate.
Triiodothyronine (T3)
Active thyroid hormone enhancing metabolism.
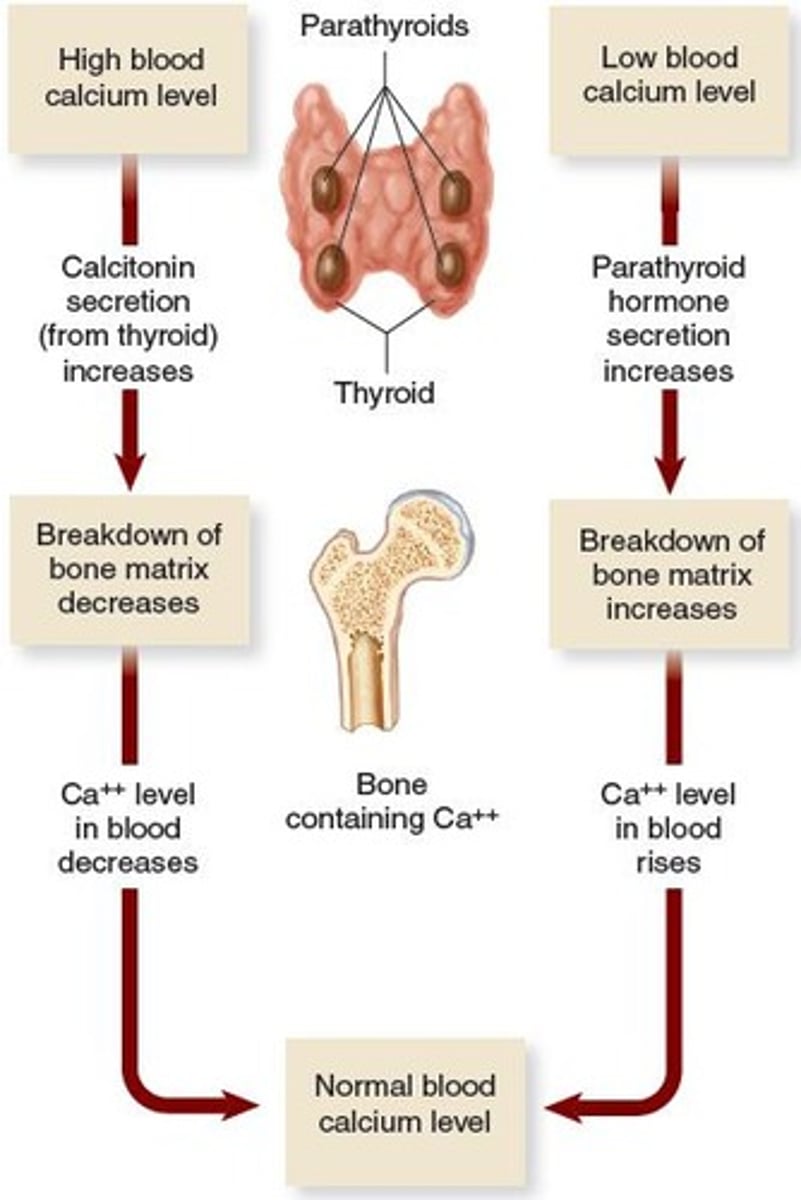
Calcitonin (CT)
Lowers blood calcium by inhibiting bone breakdown.
Hyperthyroidism
Excess thyroid hormones increasing metabolic rate.
Graves Disease
Inherited hyperthyroidism with symptoms like exophthalmos.
Hypothyroidism
Insufficient thyroid hormones leading to decreased metabolism.
Goiter
Painless thyroid enlargement from iodine deficiency.
Cretinism
Severe hypothyroidism in early development causing retardation.
Myxedema
Hypothyroidism in adults characterized by edema.
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
Increases blood calcium by promoting bone breakdown.
Homeostasis
Regulation of body functions like temperature and appetite.
Glucocorticoids
Chiefly cortisol; regulates glucose metabolism.
Mineralocorticoids
Primarily aldosterone; manages sodium and potassium levels.
Sex Hormones
Androgens secreted by adrenal cortex in both sexes.
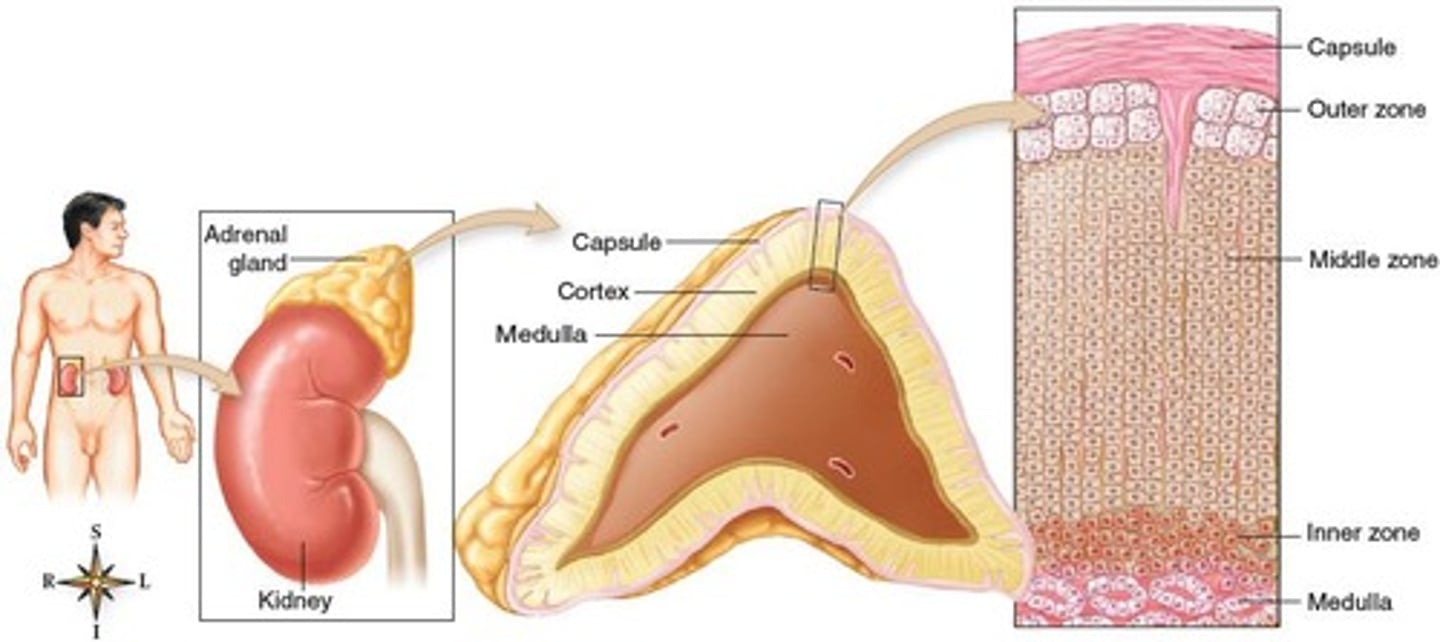
Adrenal Cortex
Outer layer secretes mineralocorticoids, middle glucocorticoids.
Cortisol
Maintains blood glucose; increases gluconeogenesis.
Hyperglycemia
Elevated blood glucose levels; can result from cortisol.
Blood Pressure Regulation
Glucocorticoids help maintain normal blood pressure.
Immune Response
Glucocorticoids decrease immune and allergic responses.
Epinephrine
Adrenaline; intensifies sympathetic nervous system effects.
Norepinephrine
Enhances stress response; increases heart rate and blood pressure.
Cushing Syndrome
Caused by glucocorticoid hypersecretion; symptoms include moon face.
Addison Disease
Hyposecretion of cortical hormones; leads to muscle weakness.
Glucagon
Secreted by alpha cells; increases blood glucose levels.
Insulin
Secreted by beta cells; decreases blood glucose levels.
Type 1 Diabetes
Autoimmune destruction of pancreas; insulin hyposecretion.
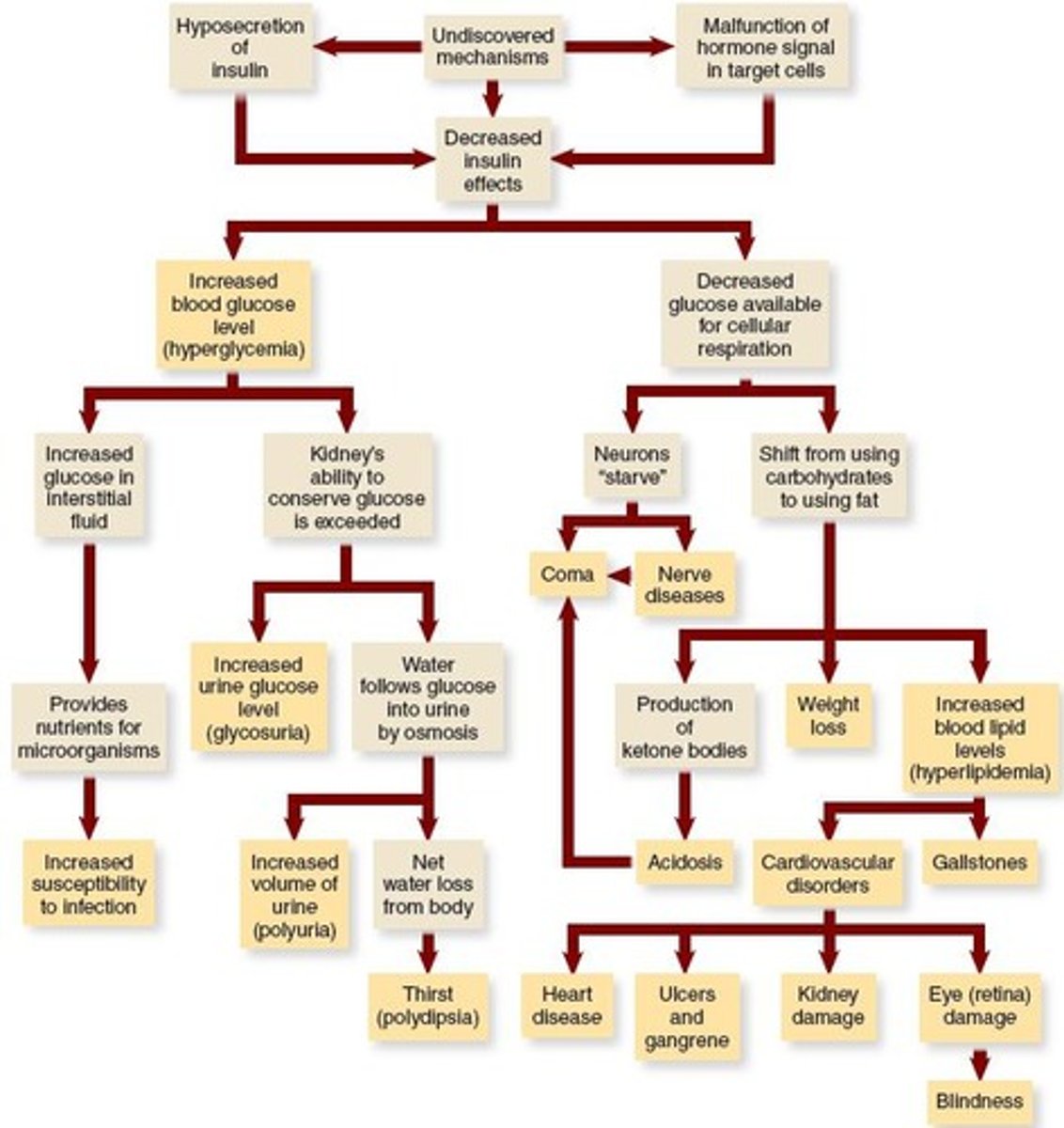
Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin resistance; common in overweight adults.
Polydipsia
Excessive thirst; symptom of uncontrolled diabetes.
Estrogen
Feminizing hormone; develops female body characteristics.
Testosterone
Masculinizing hormone; promotes male physical traits.
Thymosin
Hormone from thymus; matures T-lymphocytes.
Chorionic Gonadotropins
Indicates pregnancy; maintains corpus luteum.
Melatonin
Regulates sleep-wake cycle; secreted by pineal gland.
Ghrelin
Stimulates appetite; secreted by stomach lining.
Atrial Natriuretic Hormone (ANH)
Stimulates sodium loss; secreted by heart atrial wall.
Leptin
Regulates hunger; secreted by fat-storing cells.