Chemical Bonding
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
types of bonds
ionic, covalent and metallic bonding
ionic bond (definition)
bond formed when one or more electrons are transfered from one atom to another
ionic bond (description)
a chemical bond resulting from the attraction between oppositely charged ions.
ionic bond (types of elements)
metals with nonmetals
ionic bond (nature of)
electrostatic attraction
ionic compounds (properties)
1. crystalline solids
2. high melting and boiling point
3. electrolytes
4. soluble in water (usually)
how are ionic compounds electrically neutral?
the positive and negative charges balance out (cancel out)
coulombic attraction
the attraction between oppositely charged particles
metals in ionic bonds
few valence electrons - tend to lose them - for positive ions
cation
a positively charged ion
nonmetals in ionic bonds
many valence electrons - gain a few - form negative ions
anion
a negatively charged ion
group 1A (charge formed)
1+
group 2A (charge formed)
2+
group 7A (charge formed)
1-
group 6A (charged formed)
2-
formula unit
smallest unit of an ionic compound
electrolyte
substance that forms ion when it is dissolved in water, capable of conducting an electrical current
isoelectronic
having the same electron configuration as another species
metallic bond (definition)
a bond formed by the attraction between positively charged metal ions and the electrons around them
metallic bond (model)
mobile electrons are delocalized and form a "sea of electrons" around metal atoms
alloy (definition)
a mixture of two or more elements, one of which is a metal
alloy (examples)
Sterling silver, Bronze, Brass and Steel
sterling silver
silver alloyed with copper
bronze
copper alloyed with tin
brass
copper alloyed with zinc
steel
iron alloyed with small amounts of carbon
covalent bond (definition)
a chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule
covalent bond (types of elements)
two or more nonmetals
covalent bond (aka)
molecular bond (aka)
molecular compounds (properties)
1. can be solid, liquids or gases
2. lower melting and boiling points
3. not electrolytes
molecule
smallest unit of a covalent compound, two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
single bond
a covalent bond in which two atoms share one pair of electrons
double bond
a covalent bond in which two atoms share two pairs of electrons
triple bond
a covalent bond in which two atoms share three pairs of electrons
coordinate covalent bond
a covalent bond in which one atom contributes both bonding electrons
polar covalent bond
a covalent bond in which electrons are not shared equally
electronegativity
The ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound
diatomic molecule (definition)
a molecule that consists of two atoms of the same element when in the free state
diatomic molecule (elements)
N₂,O₂,F₂,Cl₂, Br₂, I₂, H₂
octet rule
atoms react by gaining or losing electrons so as to acquire the stable electron structure of a noble gas, usually eight valence electrons
molecular orbitals
an orbital resulting from an overlapping of atomic orbitals when two atoms combine
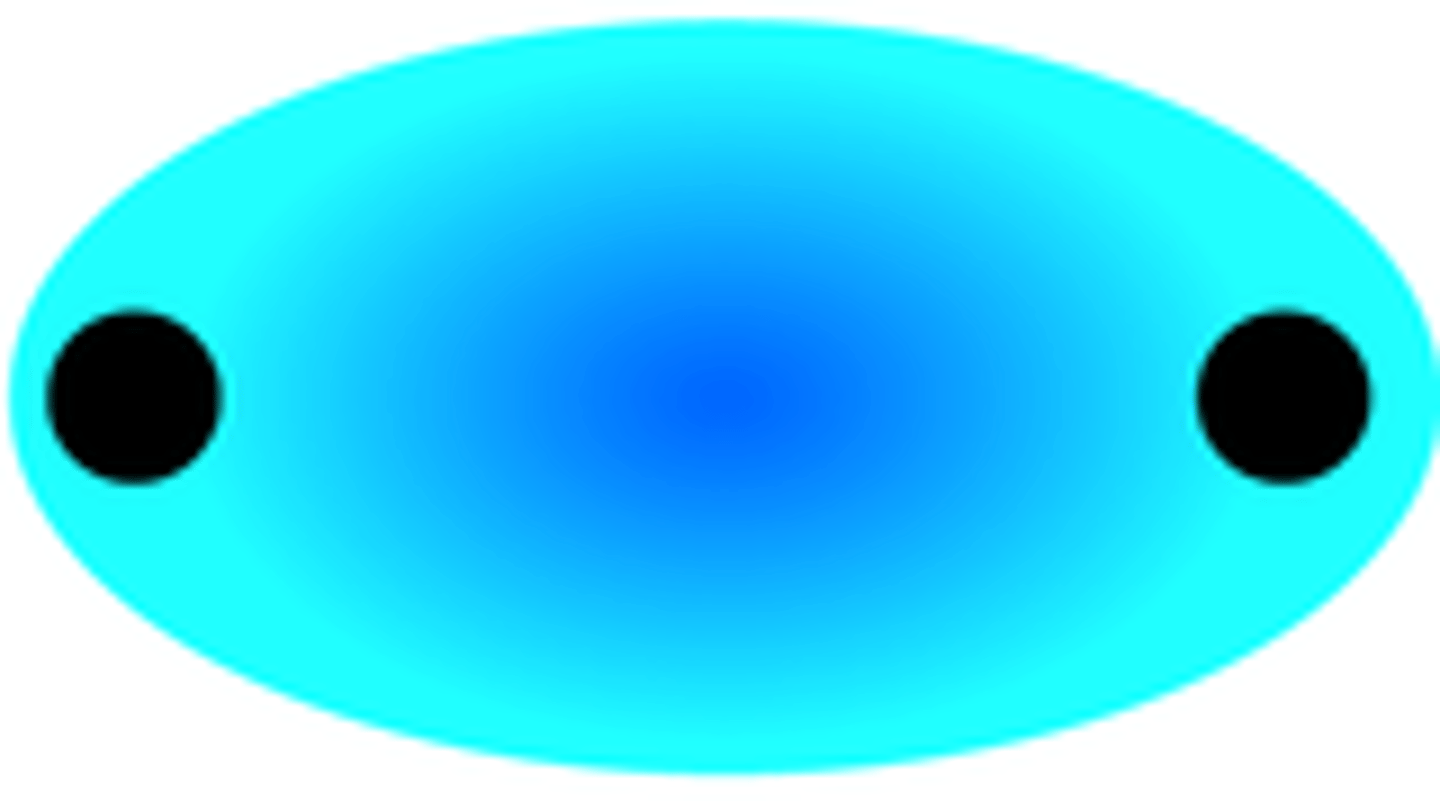
sigma bond (definition)
covalent bonds formed by orbitals overlapping end-to-end, with the electron density concentrated between the nuclei of the bonding atoms
sigma bond (description)
overlap of two S orbitals, 2 P orbitals (end-to end), or a S and P orbital
-represents the sharing of one pair of electrons (single bond)
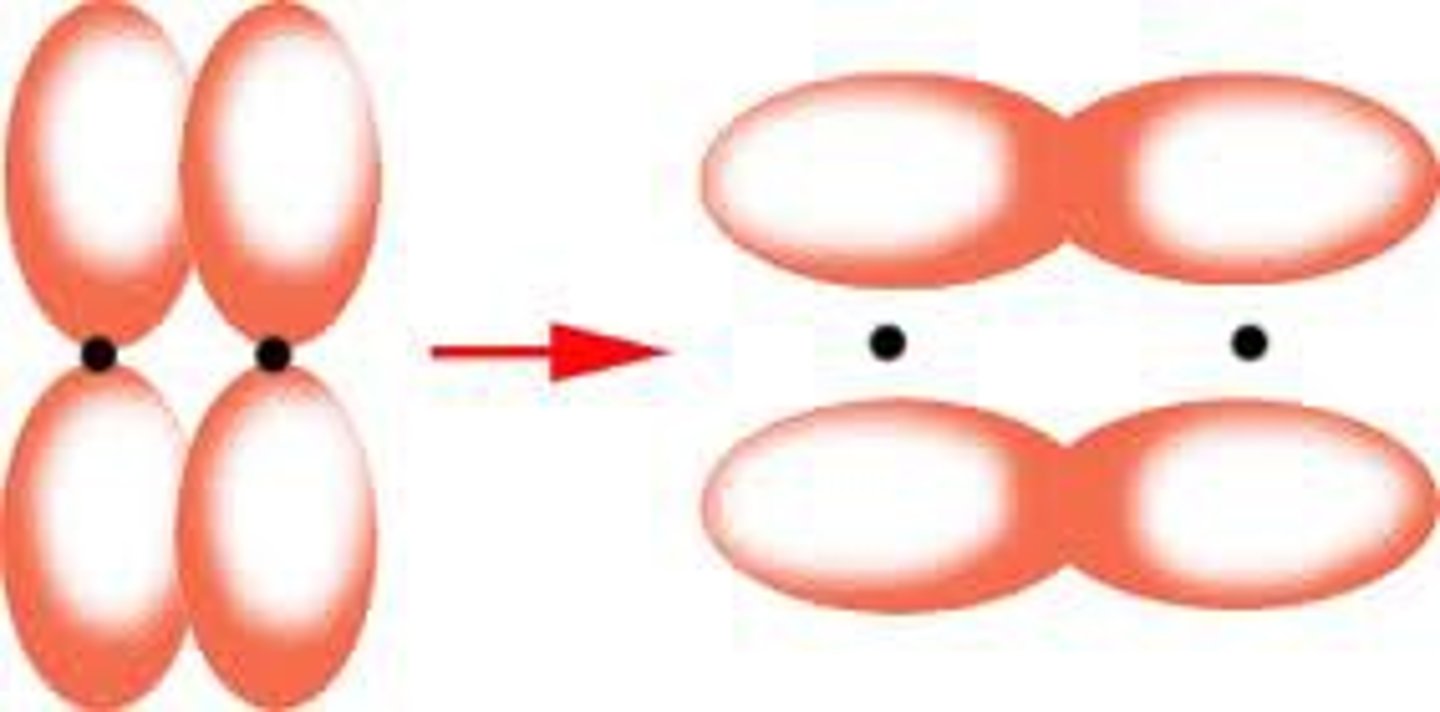
pi bond (definition)
a bond that is formed when parallel orbitals overlap to share electrons
pi bond (description)
A bond formed when parallel p orbitals overlap creating two regions of electron density, one above and one below the internuclear axis.
VSEPR stands for?
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
VSEPR Theory
the repulsion between electron pairs causes molecular shapes to adjust so that the valence electron pairs stay as far apart as possible
list these in order of increasing polarity
HF, HI, HBr, HCl
HI, HBr, HCl, HF
factors contributing to molecular polarity
1. bond polarity
2. molecular shape
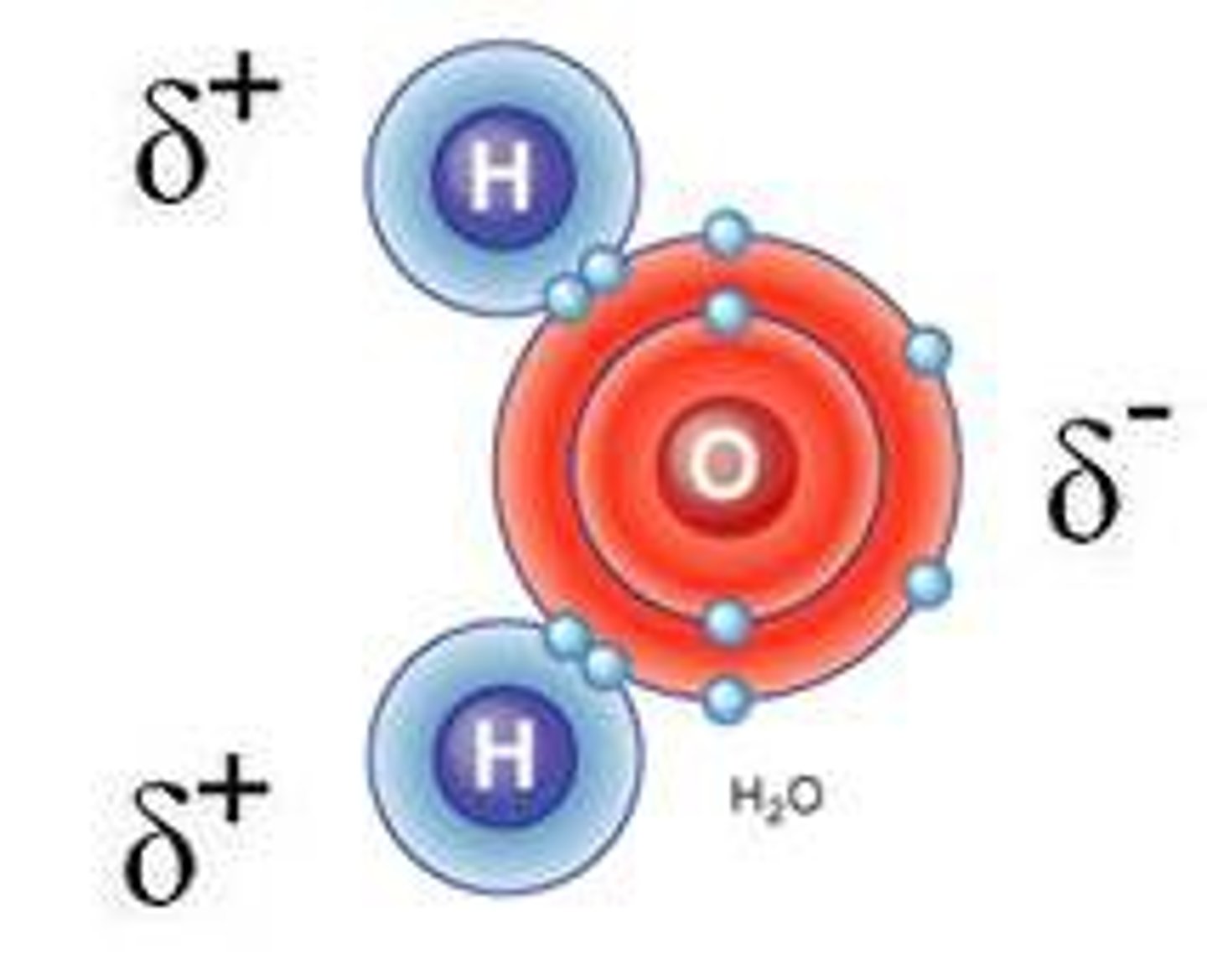
shape of water molecule
coordinate covalent bond (diagram)
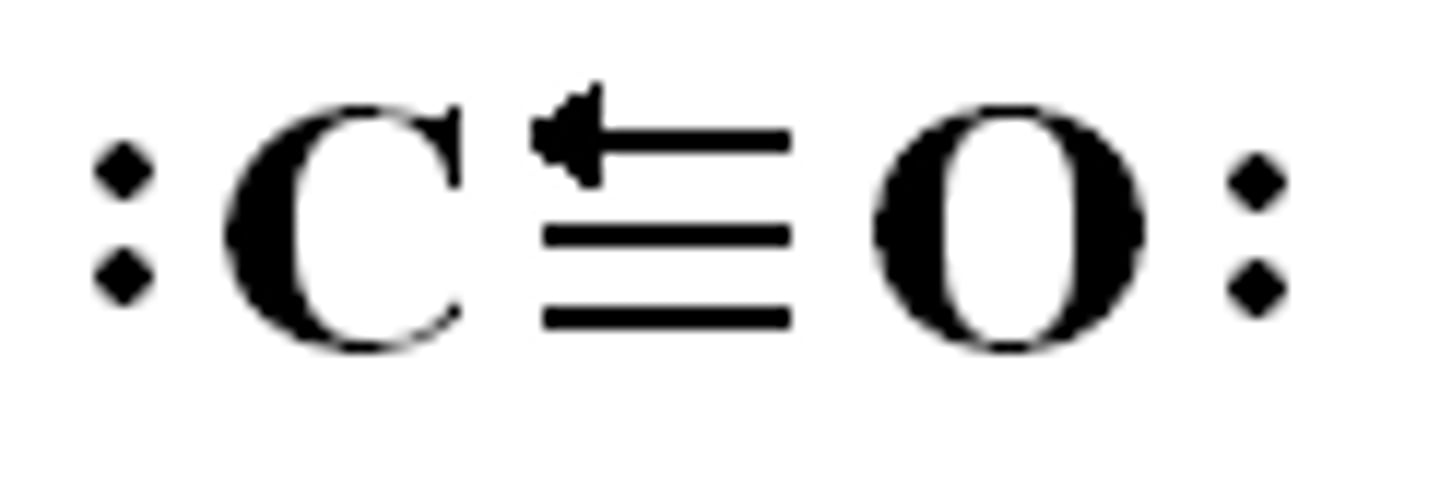
single bond (example)
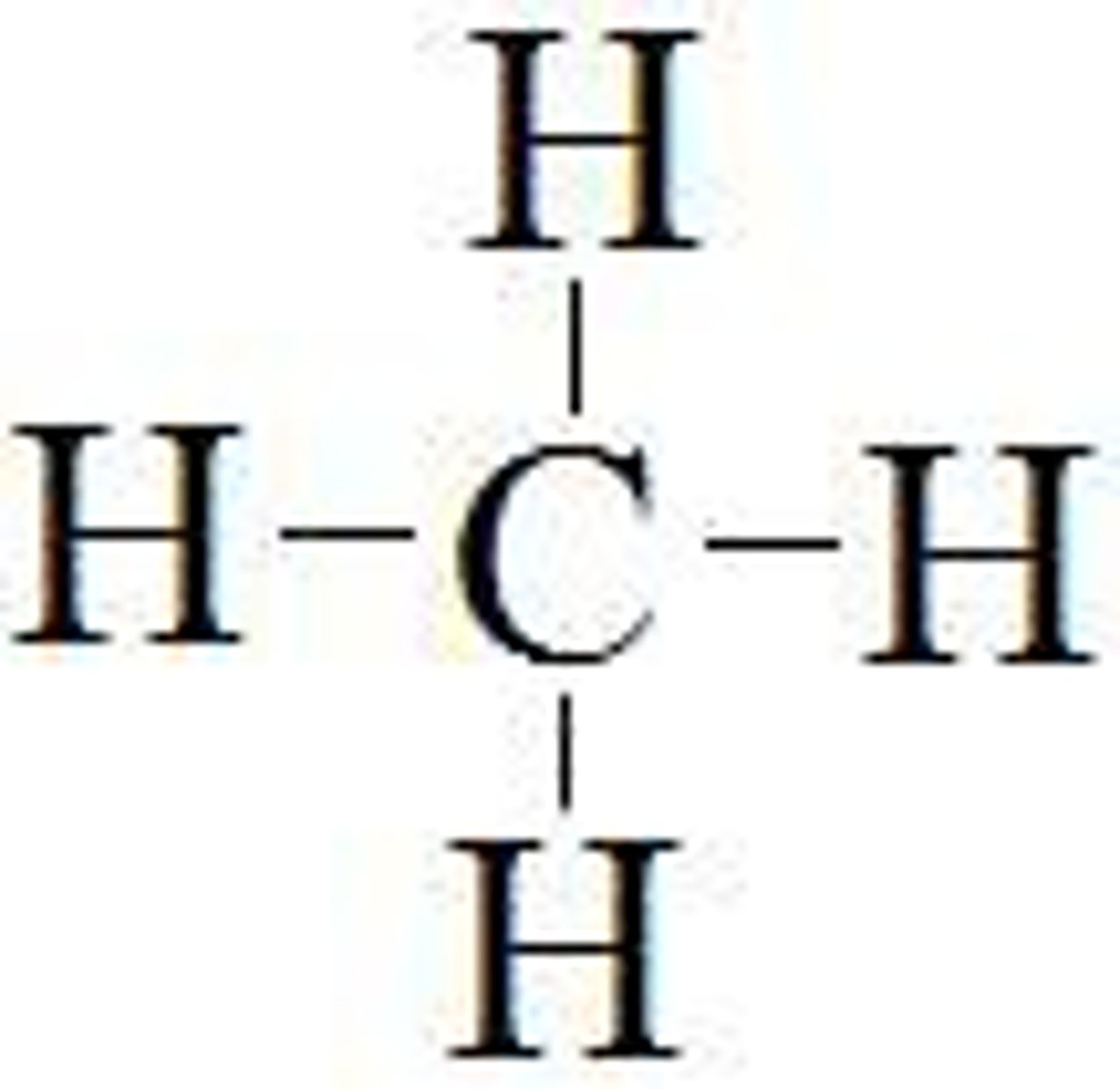
double bond (example)
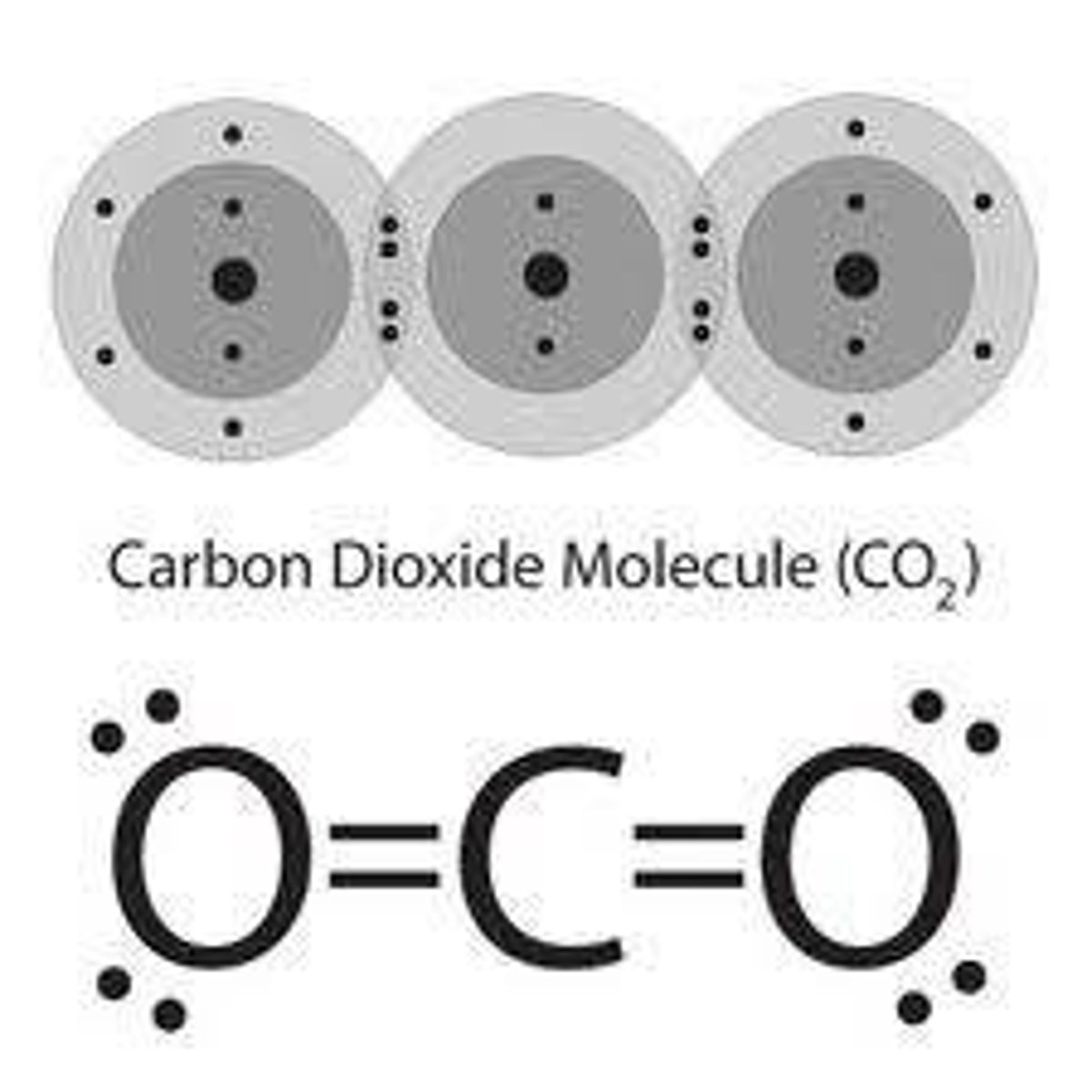
triple bond (example)
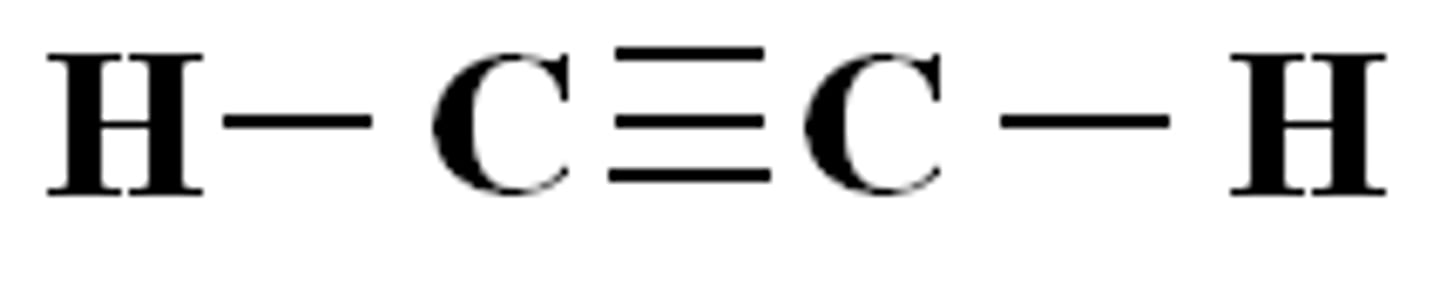
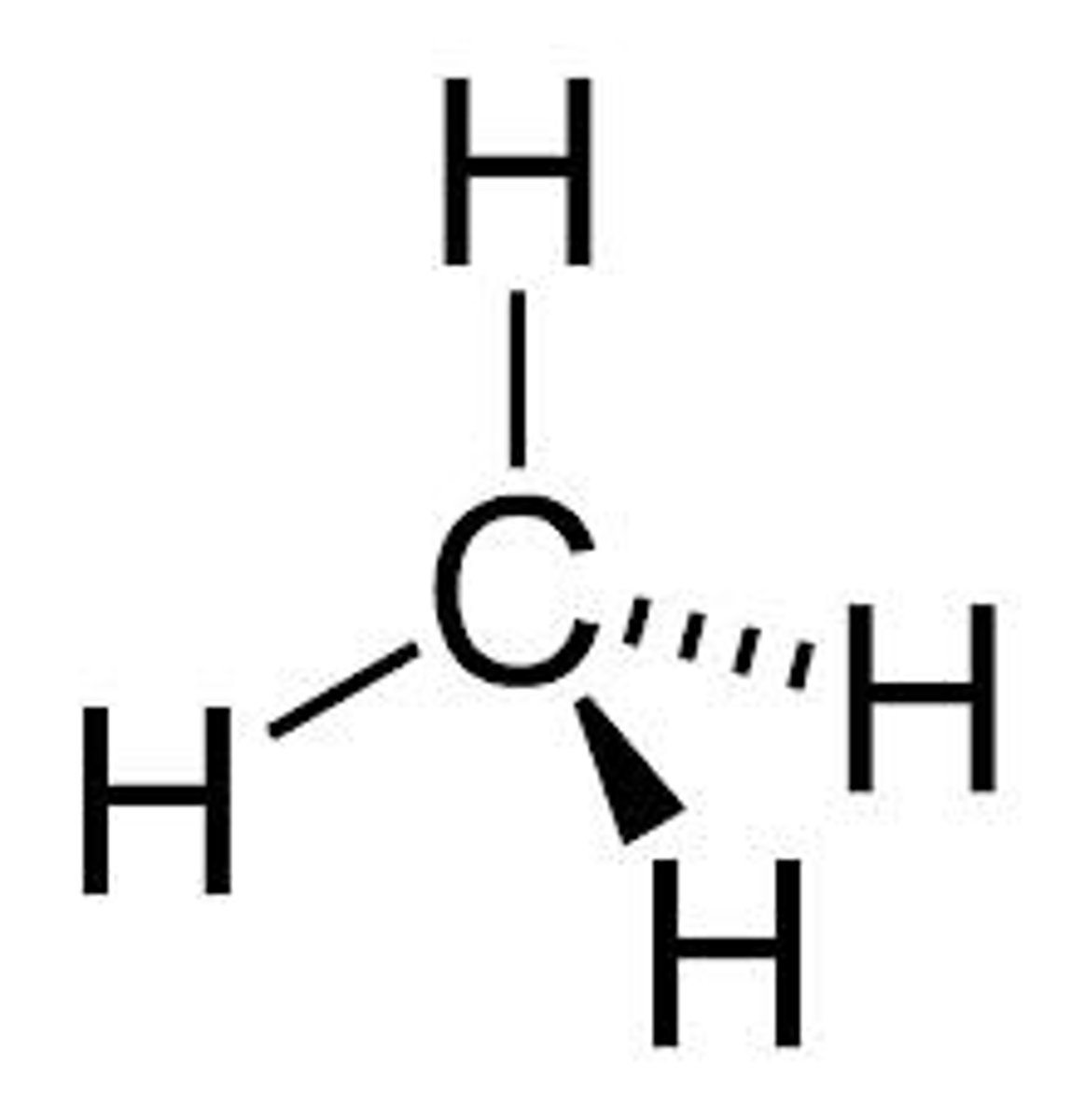
sp³ hybrid bond
...hybrid bond type?
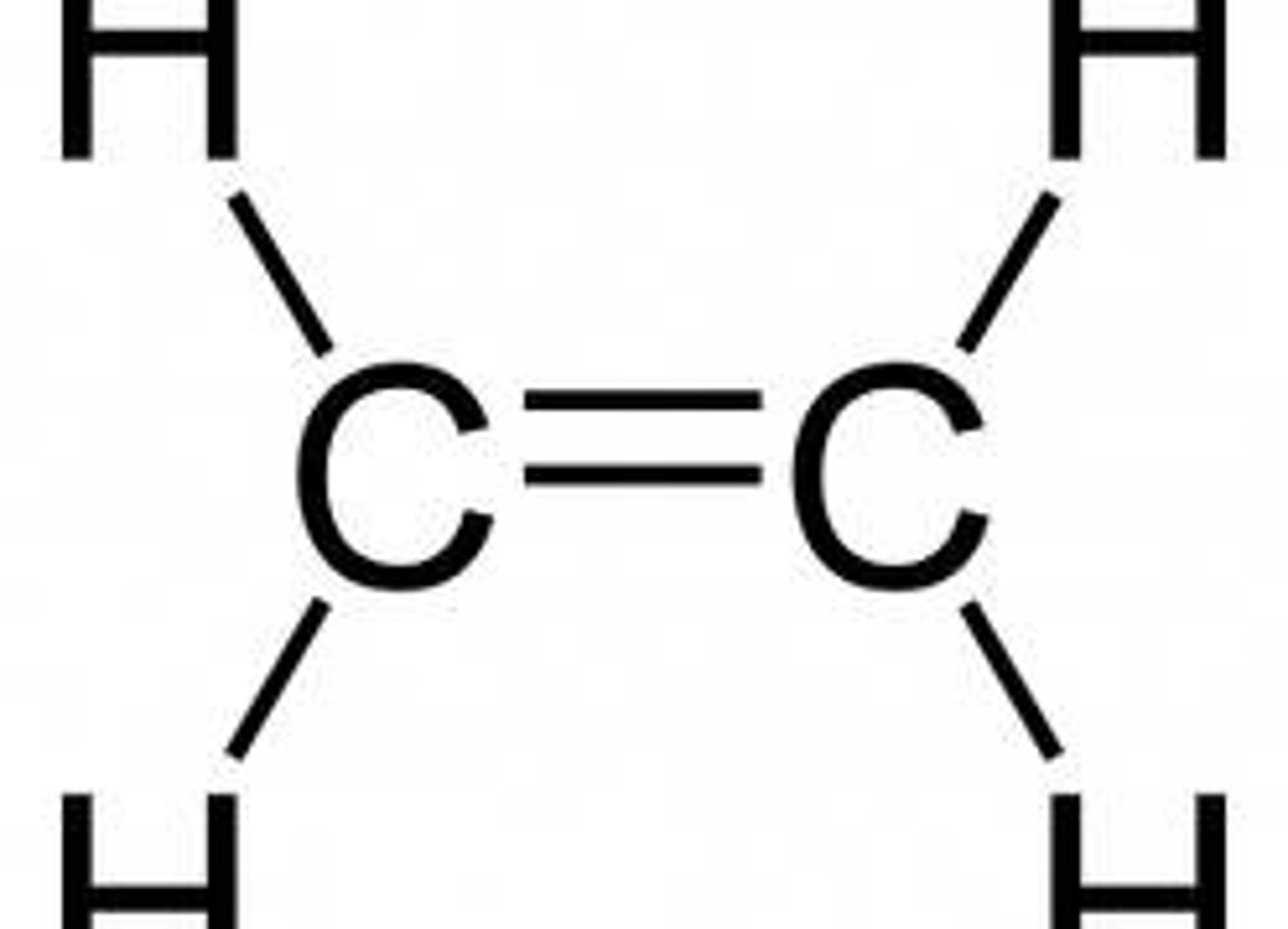
sp² hybrid bond
...hybrid bond type?
sp hybrid bond
...hybrid bond type?
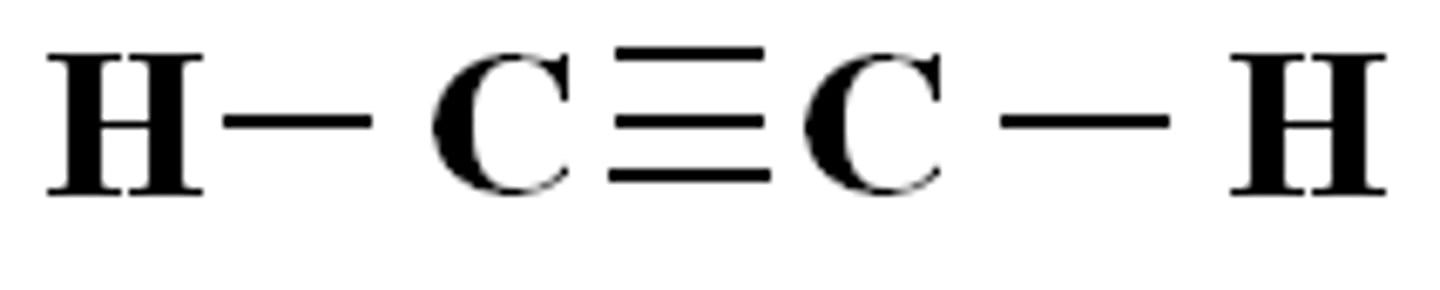
sigma bond (diagram)
...
pi bond (diagram)
...
bond dissociation energy
energy required to break a covalent bond - the higher the BDE the stronger the bond
resonance
alternate bonding for the same molecule
linear molecules
two or three atoms - bond angle 180° - ex: HCl, CO₂, CO
bent molecules
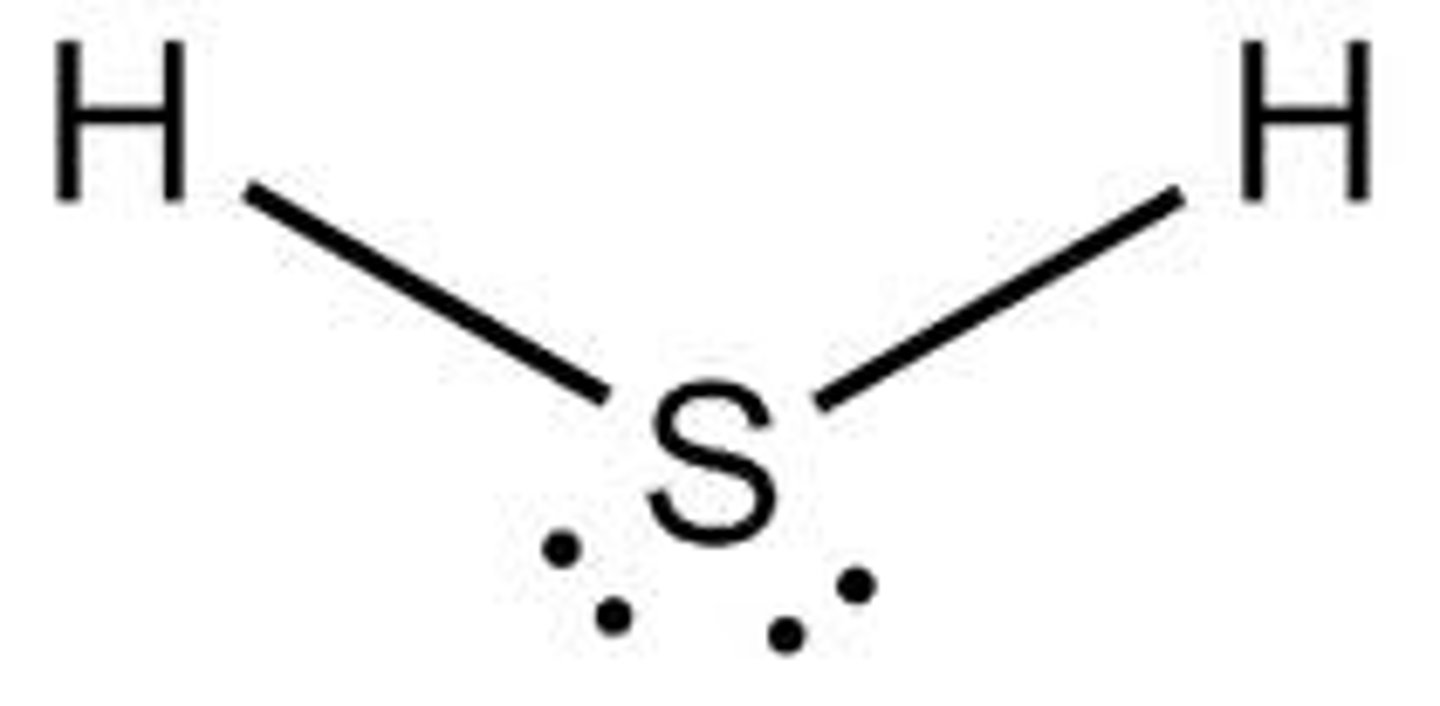
three atoms - bond angle 109° - ex: H₂O, H₂S
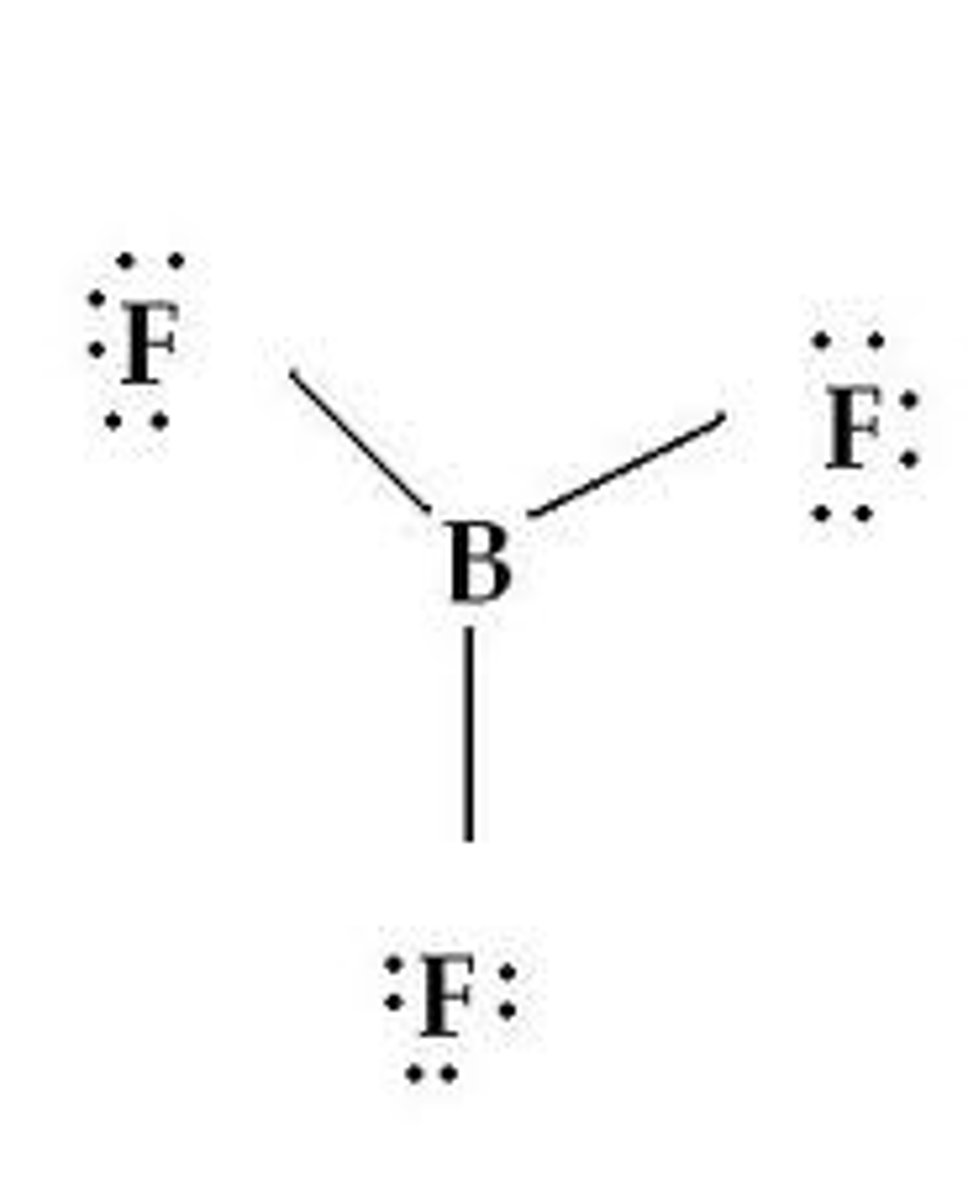
trigonal planar
four atoms - bond angle 120° - BF₃
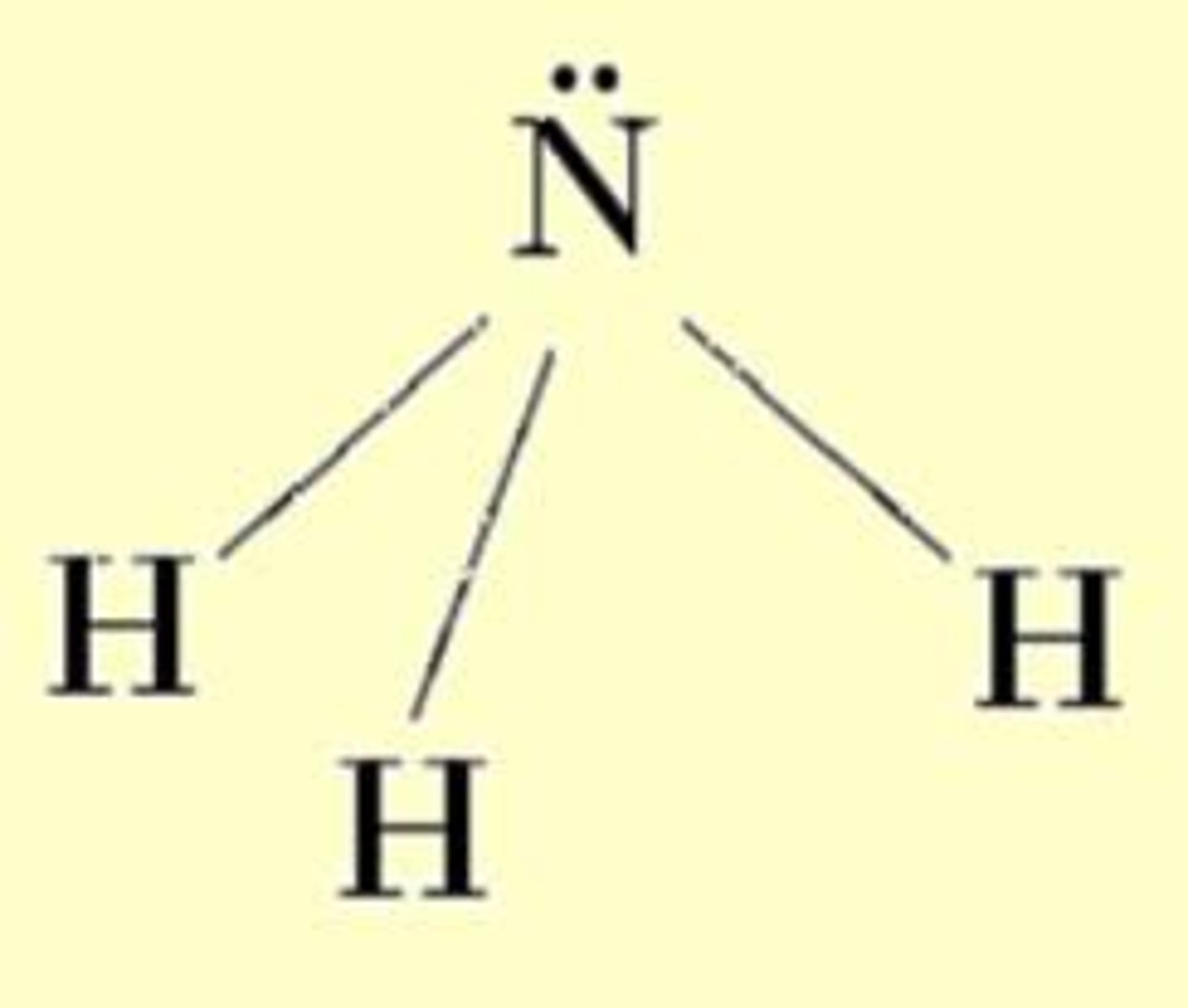
trigonal pyramidal
four atoms - bond angle 109° - ex: NH₃, NF₃
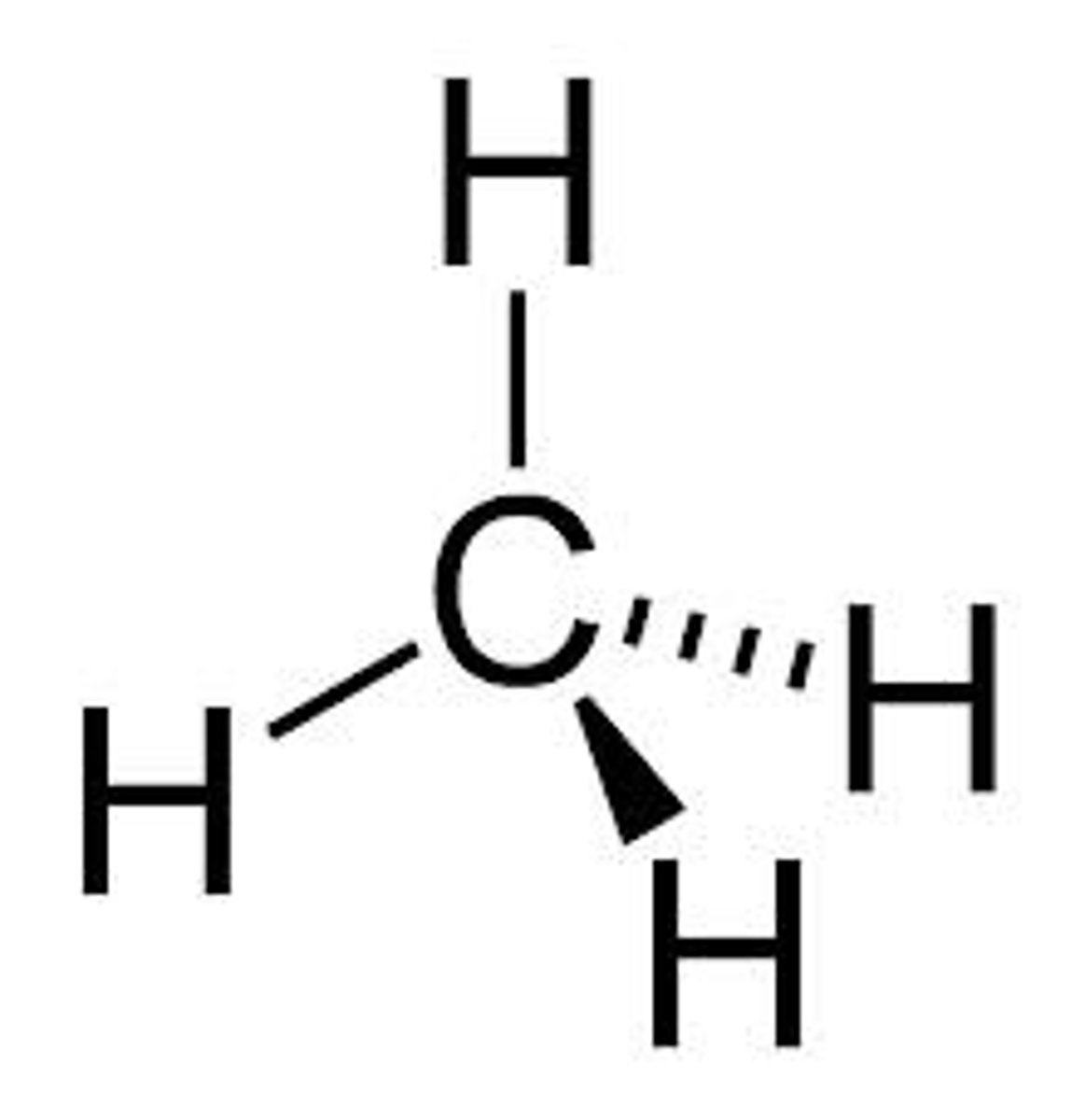
tetrahdral
five atoms - bond angle 109° - CH₄, CCl₄