HK 302 exam 1 pathology
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
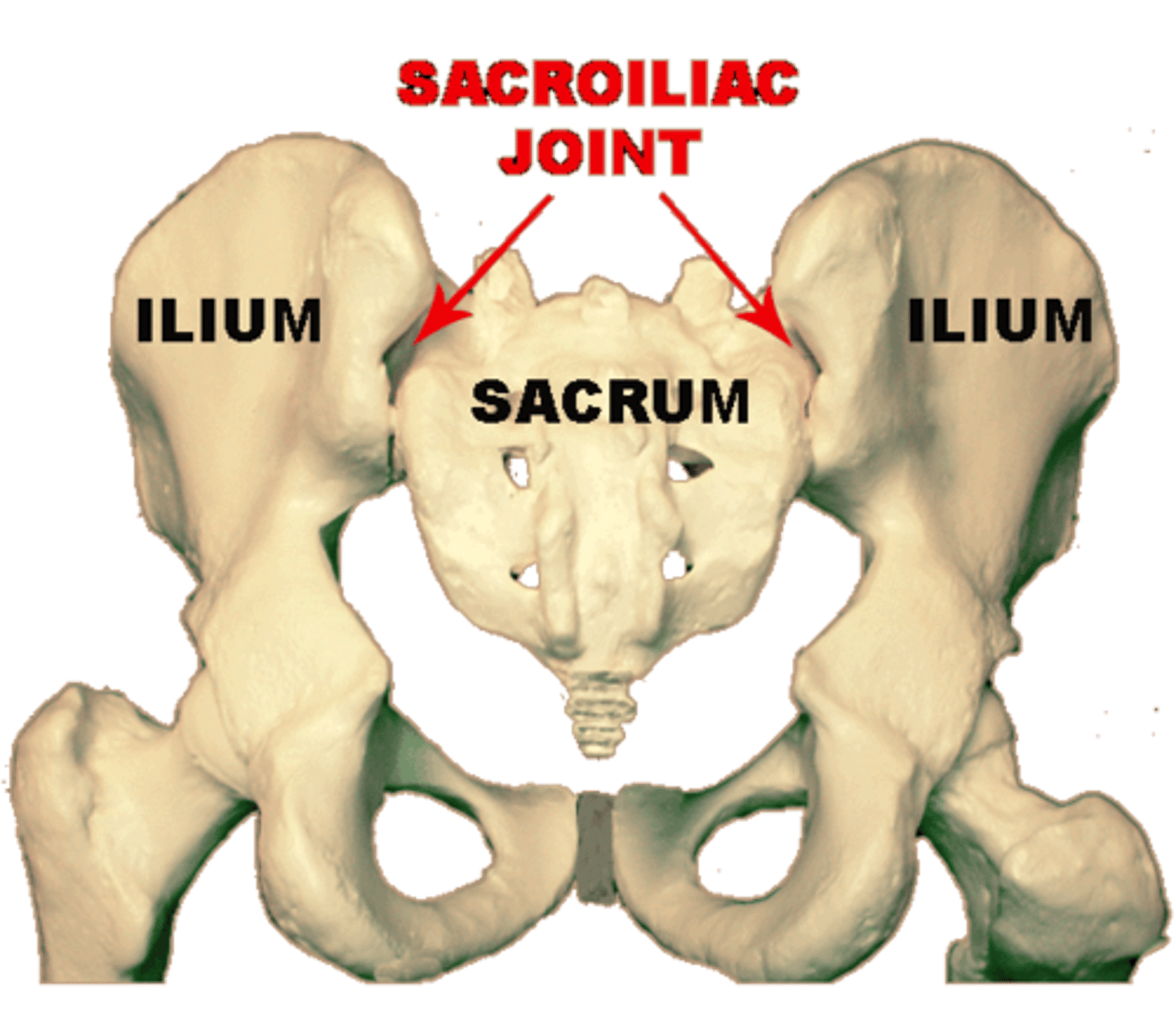
SI joint pain/ dysfunction signs and symptoms
- difficulty with sit to stand after prolonged sitting
- tenderness/tight in musculature and sacrotuberous ligament
SI joint pain management
ice, NSAIDs (anti-inflammatory drugs)
- rehabilitation for flexibility of near muscles and spinal stabilization.
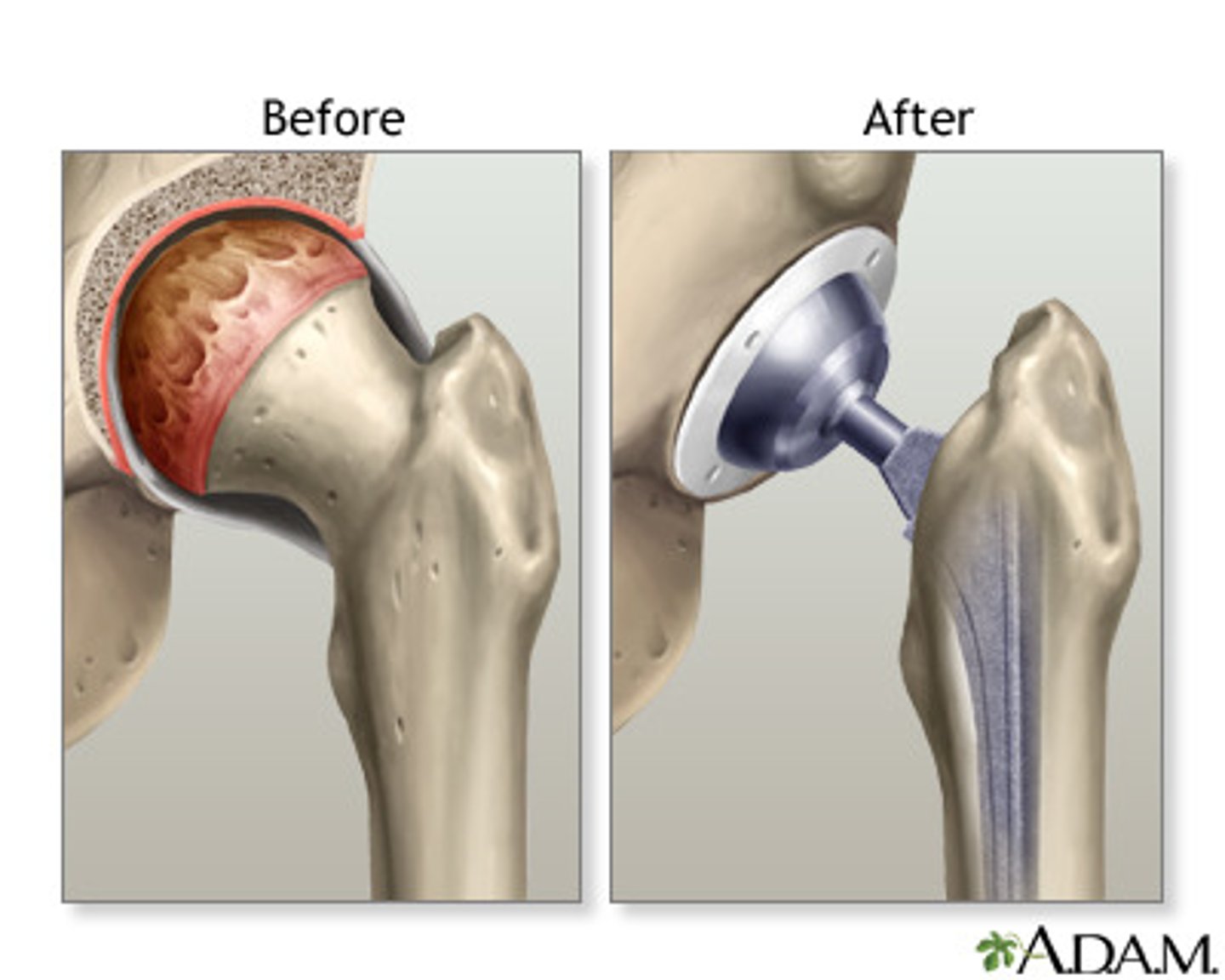
total hip replacement
- cant flex past 90 degrees
- should avoid internal rotation
sports hernia
hip adductor or rectus obdominus avulsion (torn) from pubic rami
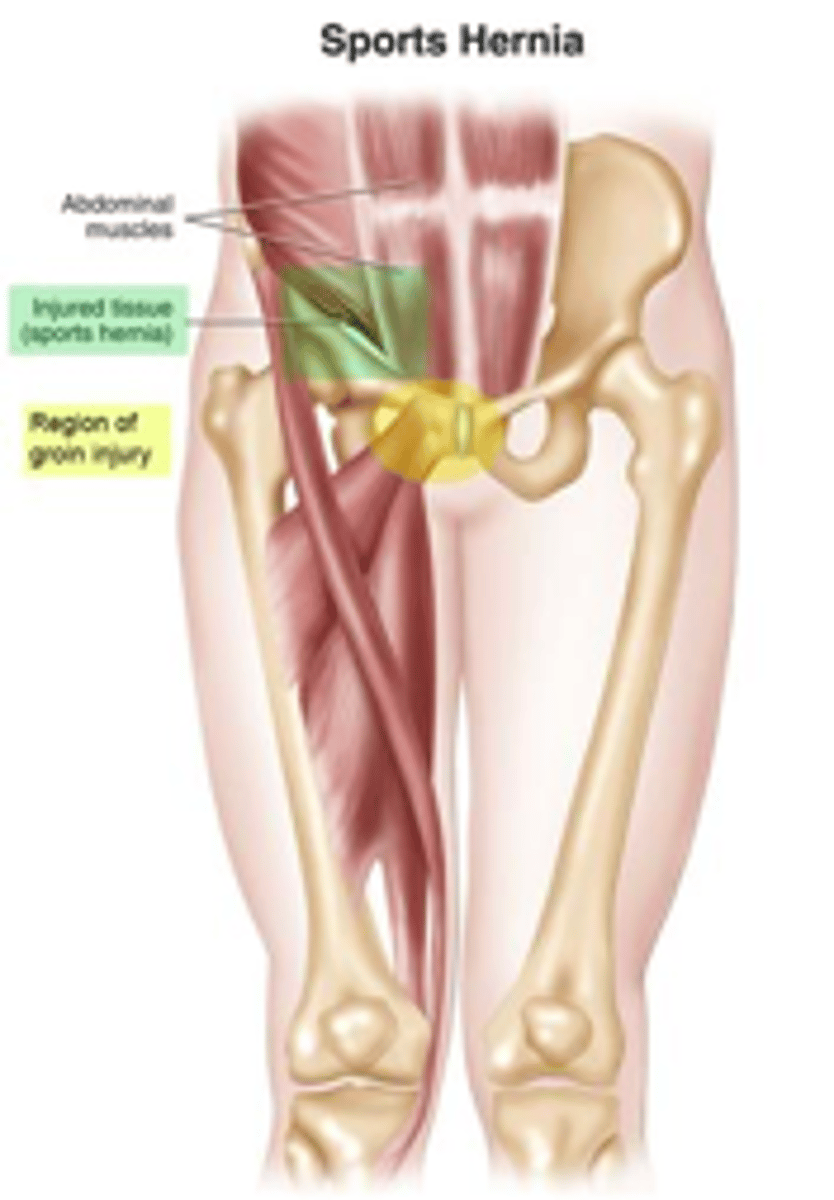
another name for sports hernia
athletic pubalgia (pubic bone)
trendelenburg gait
weakness in gluteus medius
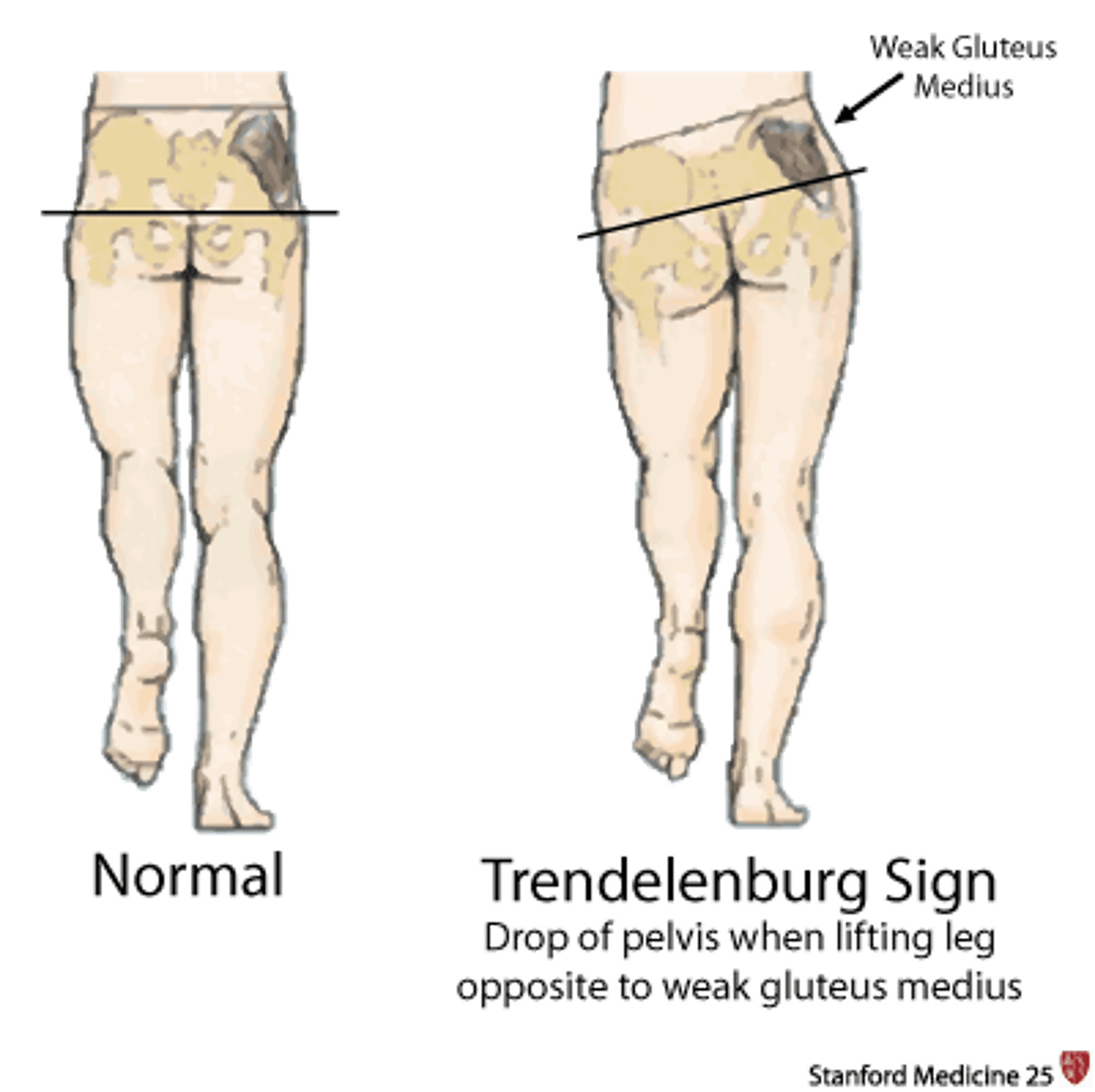
trendenburg gait leads to
- uncompensated pattern with opposite hip drop
- compensated pattern with same side trunk lean
piriformis genetic differences
superficial to sciatic nerve
- can cause pain if tight
- 20% of people's sciatic nerve goes through piriformis muscle
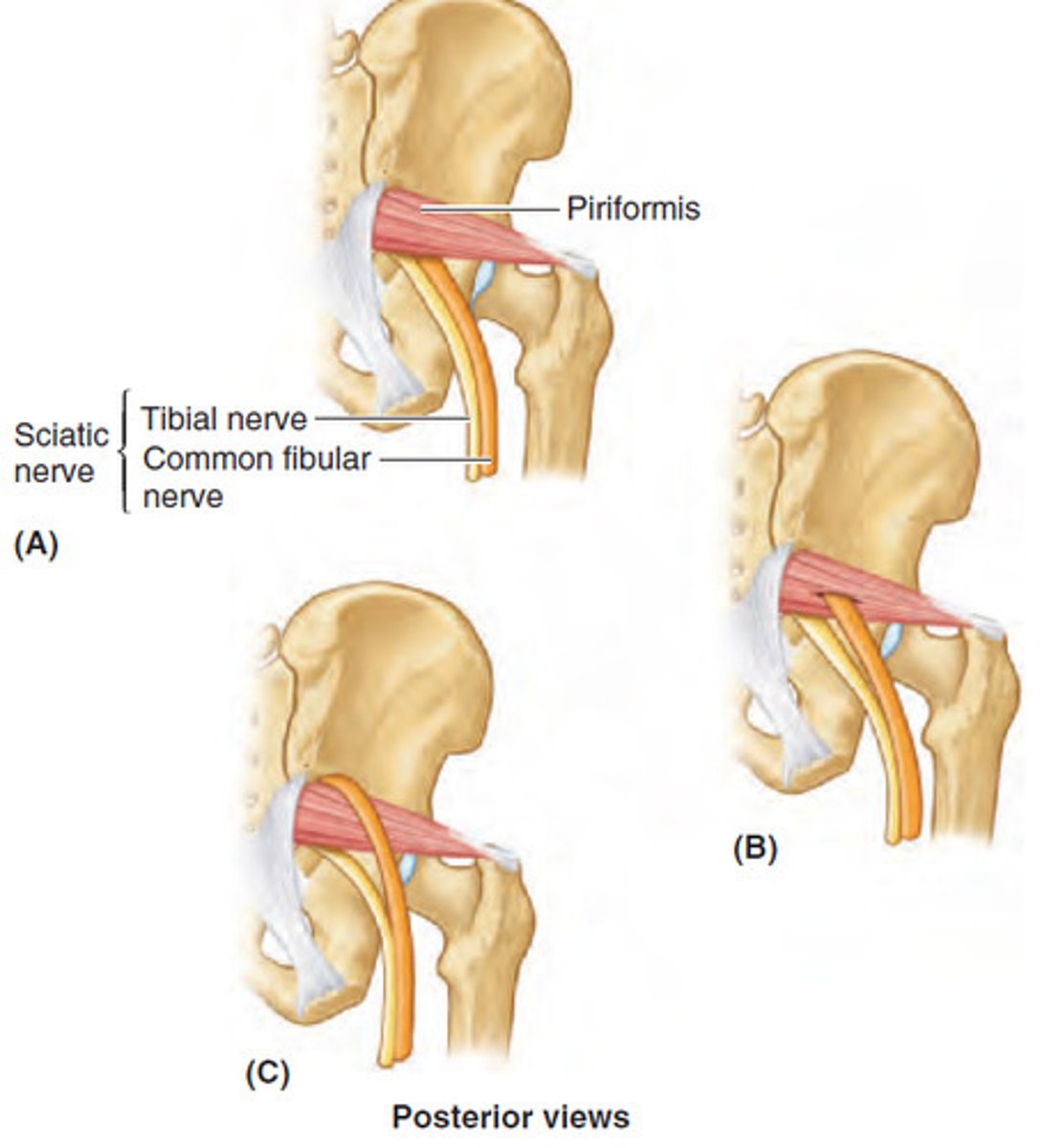
piriformis syndrome
- numbness and tingling down leg
- more common in females than males
- radiating pain distally
syndrome
a group of symptoms that reflect a disease
piriformis syndrome treatment
- rehabilitation
- medication
- surgery in extreme situation
- easier to prevent than to treat
role of lateral hip rotators at knee and foot
control of internal and external rotation at the hip will impact the amount of varus and valgus stress at the knee
weak lateral rotators commonly allow
internal rotation
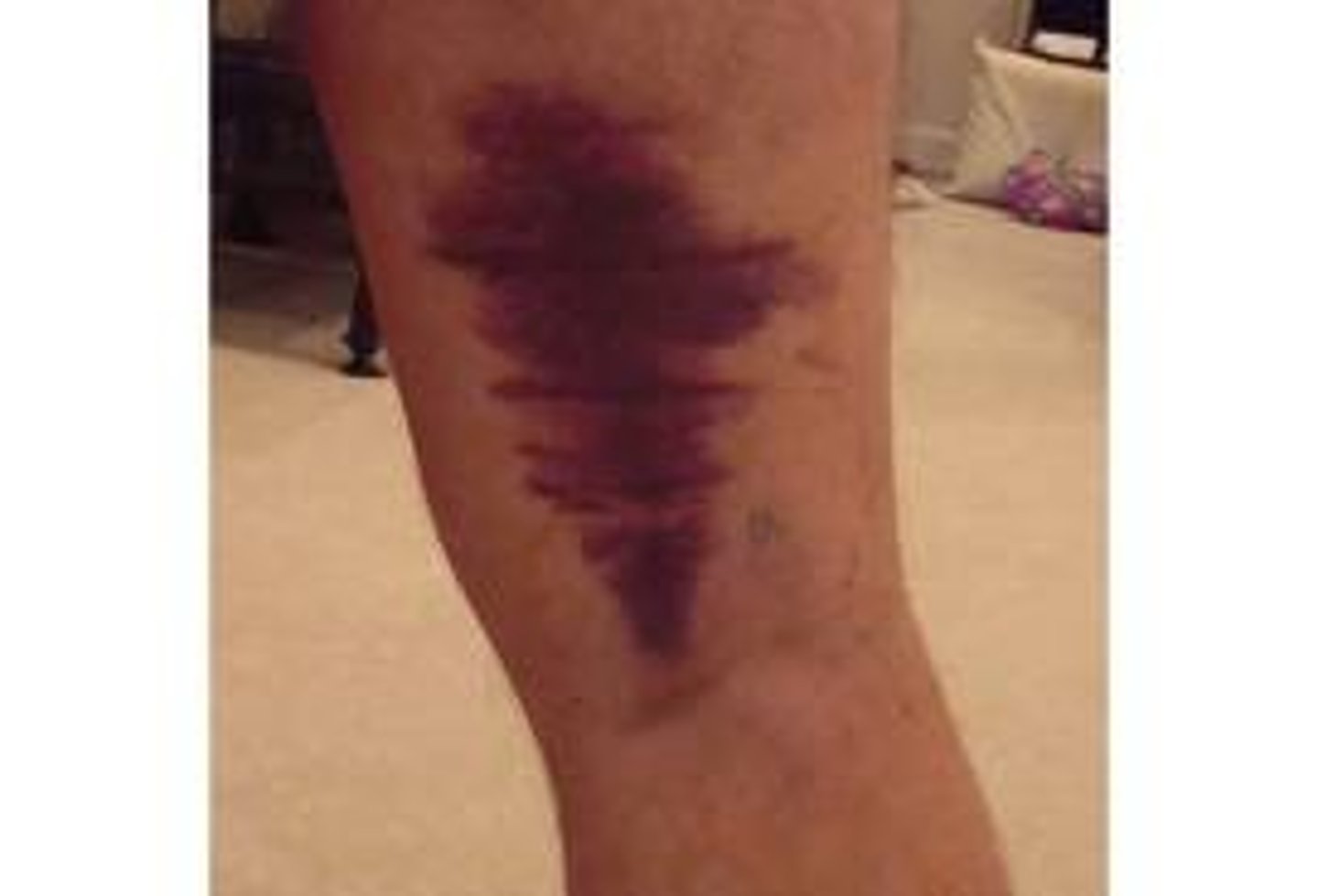
hamstring strain
- strain or tear to the tendons or large muscles at the back of the thigh
- ecchymosis - bleeding under skin
IT band friction syndrome
IT band crosses over lateral femoral epicondyle reatedly when the knee flexes
IT band friction syndrome pain
1-2 cm above knee and most painful at 20-30 degrees flexed where it passes over the epicondyle
IT band friction syndrome is caused by
training errors while running, lacking flexibility, abnormal foot mechanics
MCL injury
valgus knee force
- foot on ground and collapse inward
- knee rolled on
MCL injury recovery
non-surgical if injured in isolation
- miss 1-2 weeks or up to three months
MCL injury recovery time
depends on location of injury
- ends could have avulsion
middle heals faster
ACL injury
- overall rare injury - 1-2% of athletes per year
- loud pop immediate effusion
- 80% can't continue
effusion
swelling in joint
ACL injury repair
usually surgery required to reconstruct knee
- 6-12 months
ACL injury mechanism
plant twist POP
patella dislocation
- usually laterally because of femur anatomy
- young patients
patella dislocation symptoms
painful, immediate swelling
- recurrent problems
patella dislocation repair
surgical correction or activity modification
dislocation
articulating surfaces are not touching
subluxation
partly touching but not correct placement
reduce
put something back into place
medial meniscectomy
meniscus removal
- can be done with camera?
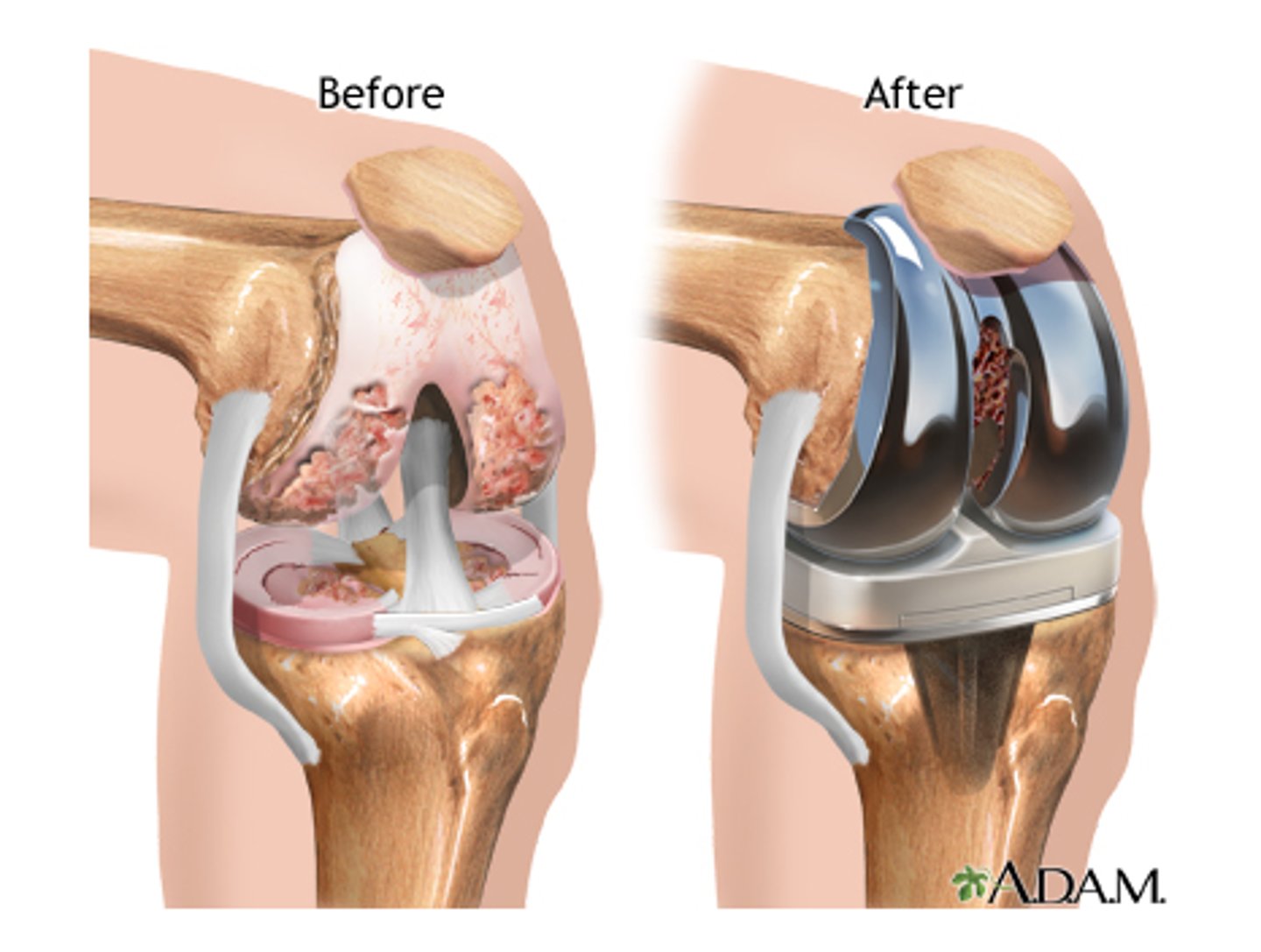
total knee replacement
no cruciate ligaments left - make space for prostheses
tibia/fibula fracture
- rare
- usually rod and pins
fracture
skin intact
comound facture
skin pierced
maisonneuve fracture
- rare
- high ankle sprain that tears syndesmosis
- fractures proximal fibula - sometimes missed in eval
maisonneuve type of fracture
spiral fracture of proximal fibula and torn syndesmosis
- fracture of medial malleolus
- talus rotates and tears tibia and fibula apart
ankle sprain avulsion fracture
(tear bone)
- peroneus brevis forced beyond resisting ankle inversion
- lateral 5th metatarsal tender
peroneals protect ankle
contract so ankle doesn't sprain
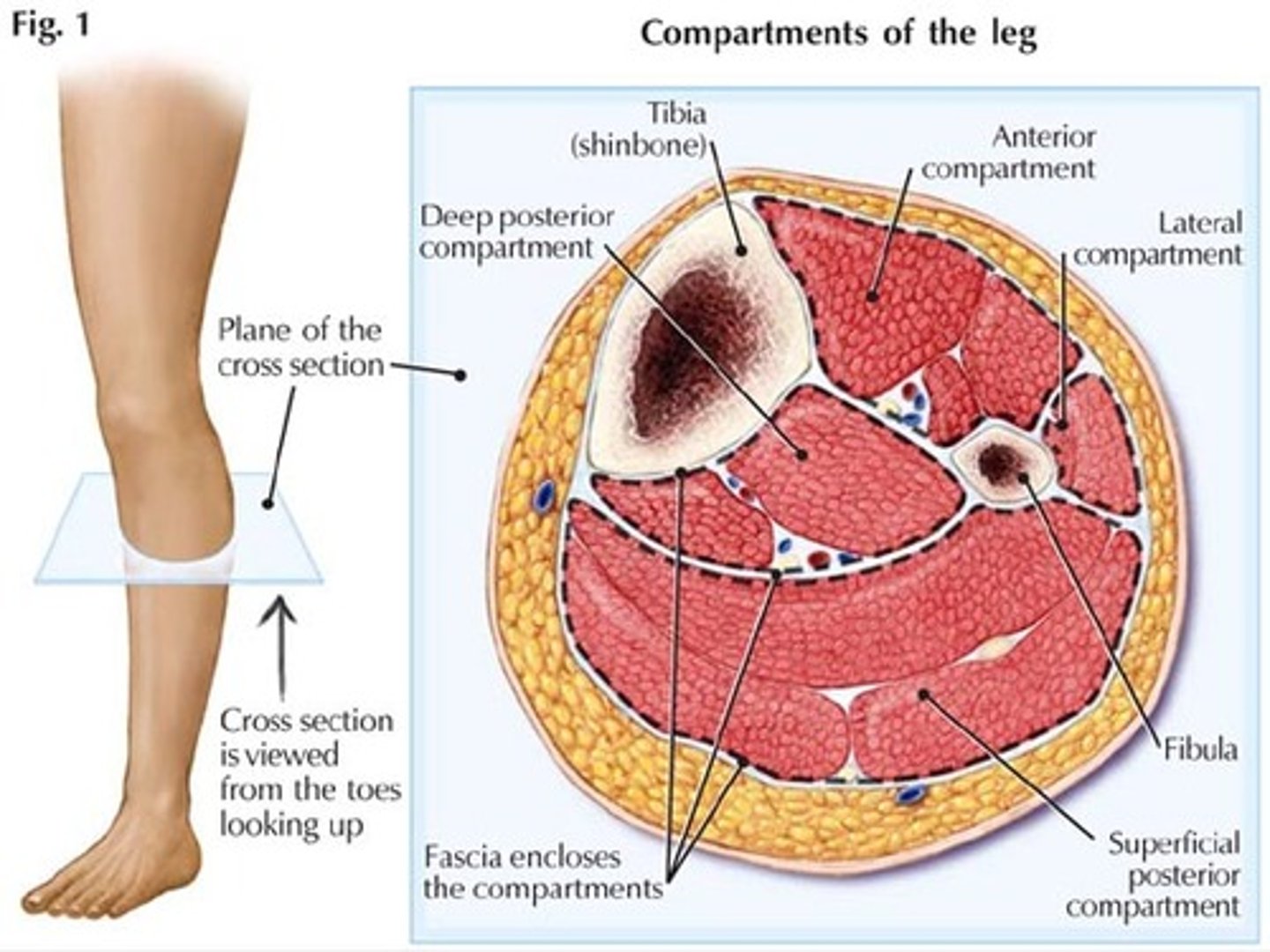
compartment syndrome
increased pressure within space of lower leg causing compression in that compartment of the neural and vascular structures
acute compartment syndrome
caused by trauma and a medical emergency
chronic compartment syndrome
exertional
lower leg compartments divided by syndesmosis and fascia
anterior, lateral, deep posterior, superficial posterior
anterior compartment
tibialis, extensor hallicus longus and extensor digitorum longus
lateral compartment
peroneus longus and brevis
deep posterior compartment
posterior tibialis, flexor digitorum longus and flecor hallical longus
- posterior tibial Artery
- tibial Nerve
way to remember deep posterior compartment
Tom, Dick, Harry, And Nick
superficial posterior compartment
gastrocnemius, soleus, and plantaris
compartment syndrome measured by
intercompartmental pressure
- resture pressure > 15 mm Hg
- 1 minute post exercise 30 mm Hg or more
- 5 minute post exercise 20 mm Hg or more
compartment syndrome treatment
surgical release
inversion ankle sprain
ankle is plantarflexed with sudden inversion
- damage lateral ankle ligaments
inversion ankle sprain treatment
usually non-operative
- could cause impingement of talus and tibia - surgery to fix
march fractures
common in 2nd and 3rd metatarsals
avulsion fracture common in which metatarsal
5th with ankle sprain
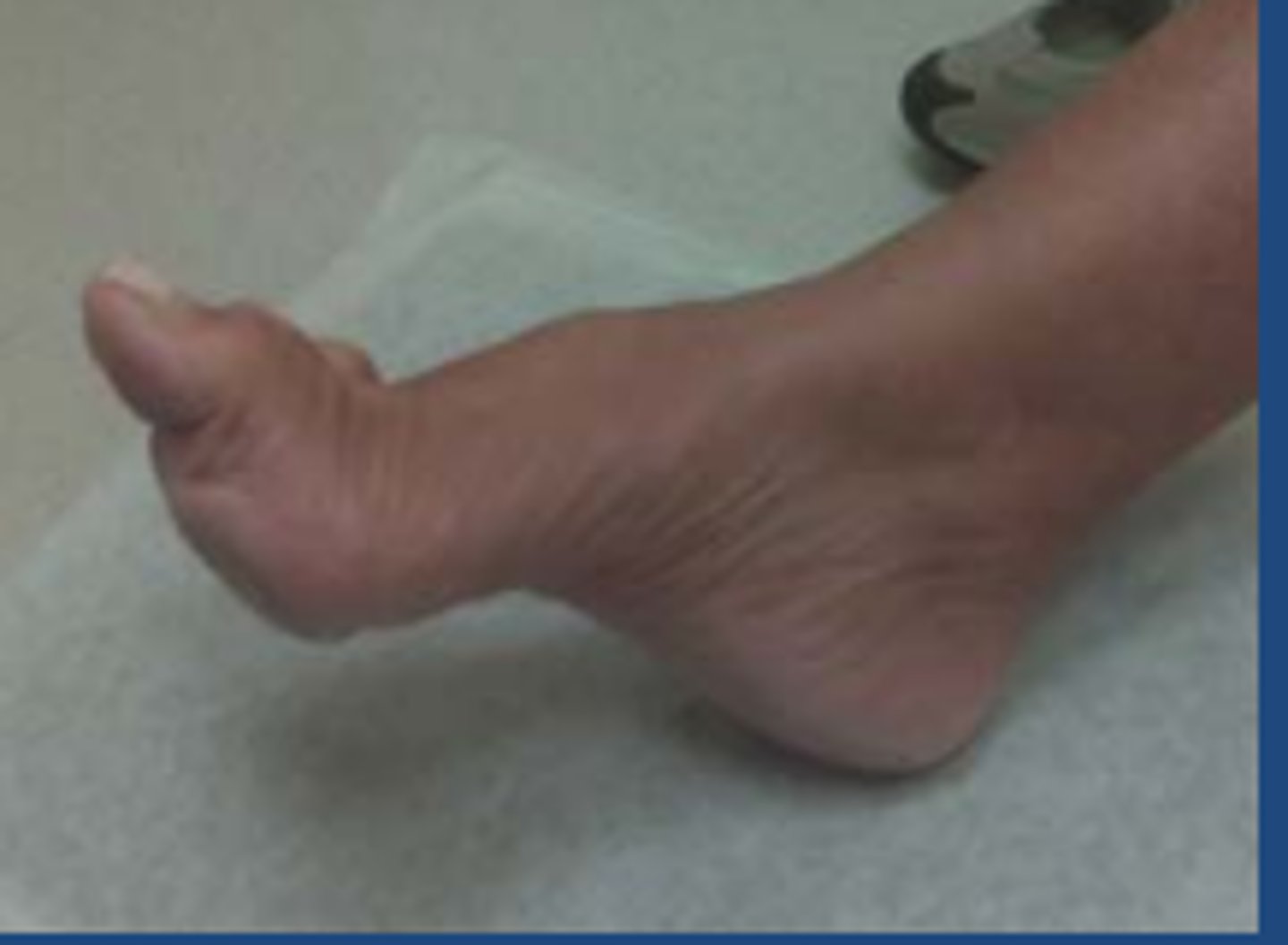
pes planus foot arch
flat foot
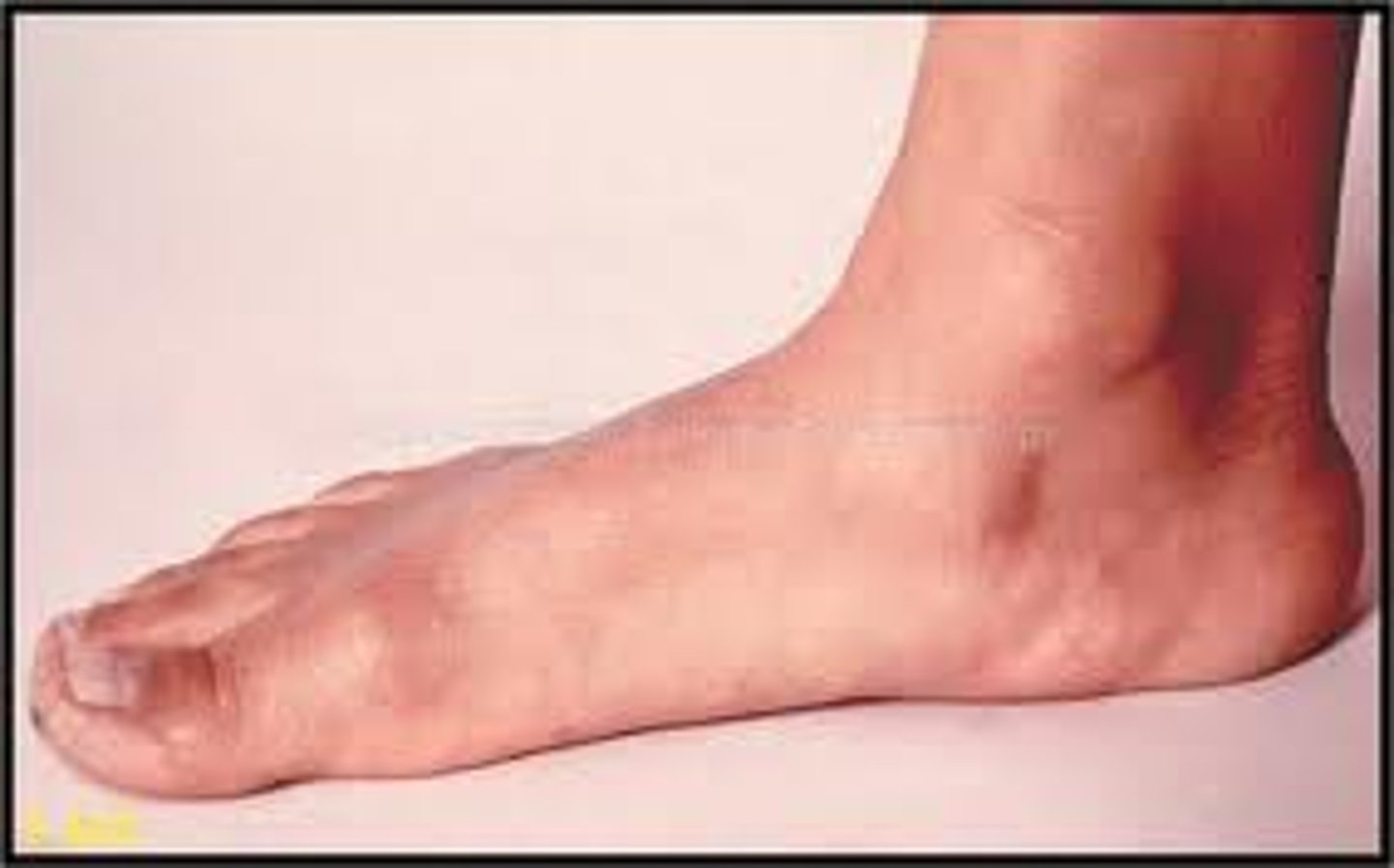
pes cavus foot arch
high arch