Diagram of Comsci G12 Midterms | Quizlet
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Hardware
All of the physical parts of a computer, network, etc.
Components
Internal hardware of a computer
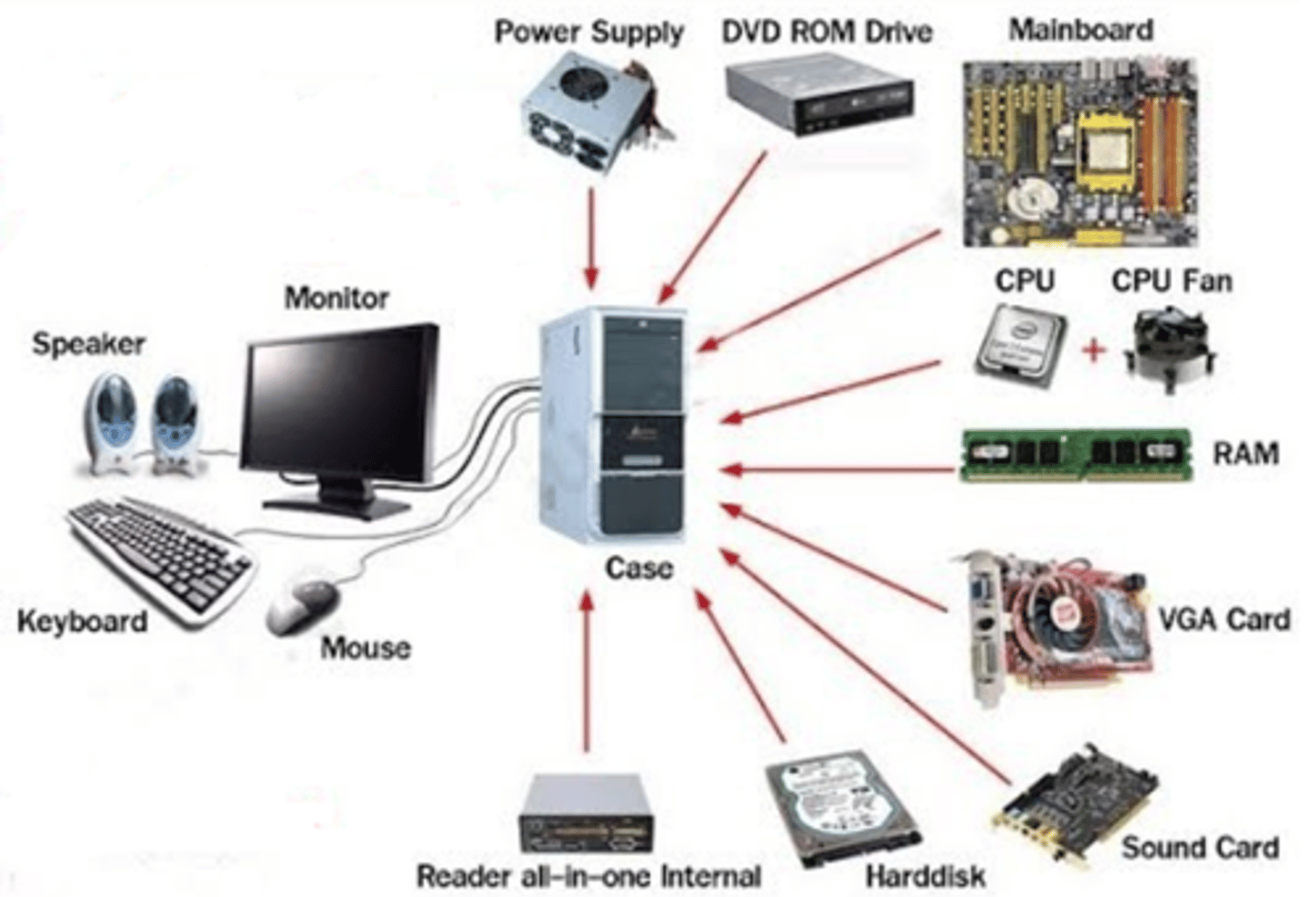
Peripherals
External hardware used for input/output (I/O devices)
Software
A general term that describes computer programs or sets of instructions that are used on computer/network systems
Operating System (OS)
System software that manages hardware and software resources to provide common services for a device
Desktop Programs
Software that is installed and runs from the OS of a device
Web Applications
Software that runs on a web server and must be accessed via a web browser. Many also have apps as well
Mobile App
Software that is run on a mobile device
Network
A set of computer systems that are interconnected and share resources as well as data
WAN
Wide Area Network. Regional/Country level network; multiple LANs make up a WAN
LAN
Local Area Network. Office/Business/Home level network
Human Resources
All of the people within an organization that use the technology. Includes end-users (uses hardware/software) and technology managers (sets up hardware/software)
Client
Hardware/software that accesses a service made available by a server, and sends requests for data/service
Server
Program/host computer that fulfills requests (provides data) from clients (may reside in the same or other computers)
Router
Routes data at the network level (chooses where data goes)
Firewall
A barrier/filter between a trusted system and the outside world, designed for security
Switch
Connects devices to form a network (servers and/or clients)
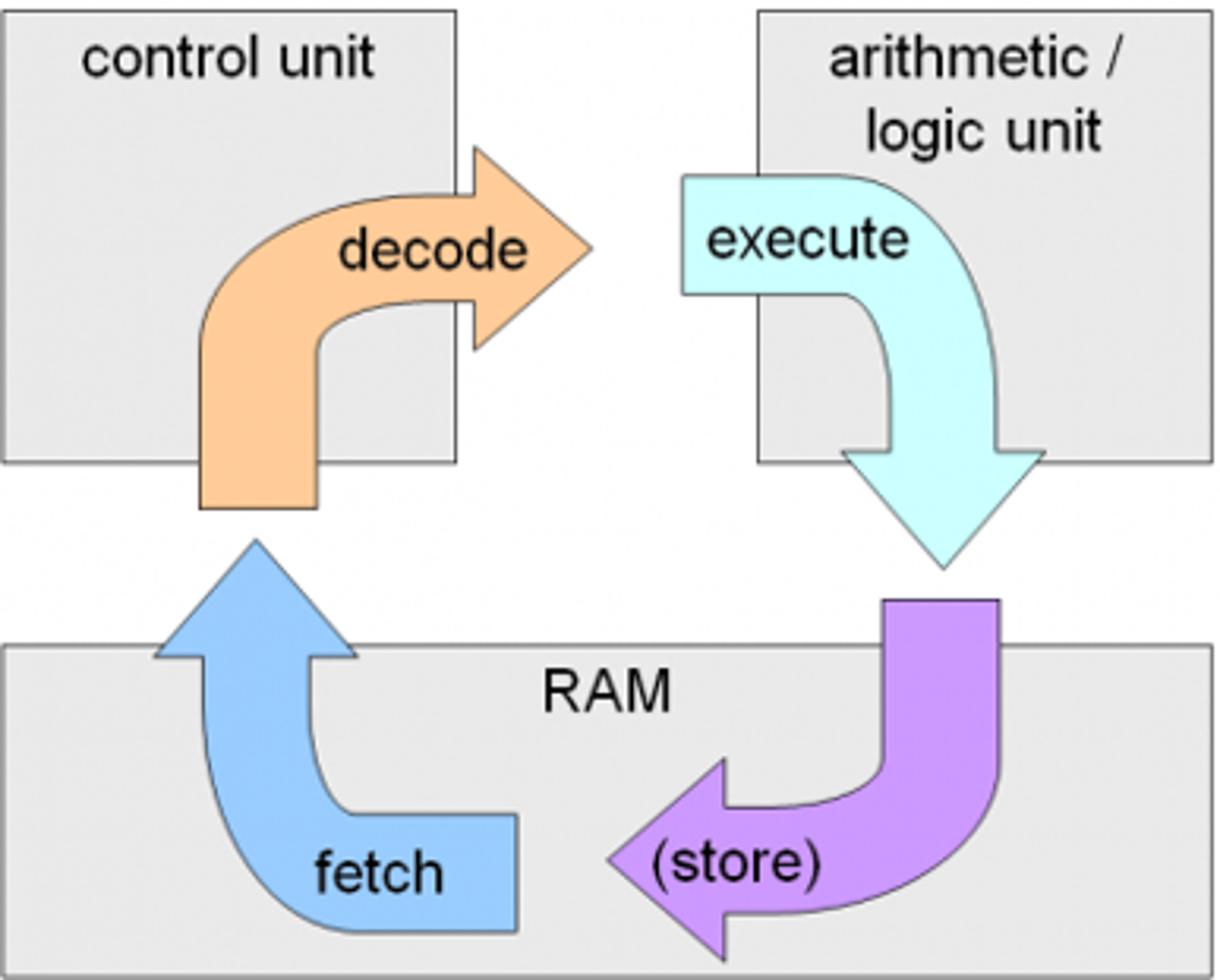
CPU
Central Processing Unit. The key component of a computer system, which contains the circuitry necessary to fetch, decode and execute program instructions from and to main or random access memory (RAM)
Busses
Electrical connections that connect the CPU to other components in order to transport data. Normally built into the motherboard
TERM
Address Bus
DEFINITION
Links RAM to CPU via MAR
TERM
Data Bus
DEFINITION
Links RAM to CPU via MDR
TERM
Control Bus
DEFINITION
links RAM to CPU via CU
TERM
RAM
DEFINITION
Random Access Memory. Stores and processes the data and instructions the computer has loaded since starting up and everything the user has opened/loaded. Counts as volatile and primary memory
How data is transferred between CPU and storage
Program data is fetched from storage and placed in the RAM. Each instruction is then executed by the CPU one at a time
TERM
MAR
DEFINITION
Memory Address Register. Fetches the next RAM address of the instruction the CPU wants, through the address bus
TERM
MDR
DEFINITION
Memory Data Register. Fetches data from the specific RAM address given by the MAR, through the data bus
TERM
CU
DEFINITION
Control Unit. Stores fetched addresses, and controls the flow of data in the CPU. Decodes data from MDR into an instruction, which is then held in the IR (Instruction Register) and passed to the ALU
TERM
ALU
DEFINITION
Arithmetic Logic Unit. Executes all arithmetic (+/-) and logic (and/or) instructions that come from the CU. May be referred to as cores, which all process simultaneously
TERM
Cache
DEFINITION
Small, high-speed memory both inside and close to the CPU, used to hold frequently used data. Allows CPU to access RAM (slower) less frequently. Counts as volatile and primary memory
Volatile Memory
Memory that loses its contents when the power is turned off
Non-volatile Memory
Memory that retains its contents when the power is turned off
Primary Storage
Volatile memory with high read/write speed, such as RAM, ROM, and Cache
Secondary Storage
Non-volatile memory with slower read/write speed, such as HDDs and SSDs
Tertiary Storage
Internet/Cloud storage
Offline Storage
Non-volatile memory that is fully offline, such as CD-RW, DVD-RW, Blue-ray, USB, and Tape Drives
ROM
Read Only Memory. Non-volatile, permanent memory that is read only and can not be changed
BIOS
Basic Input/Output System. A small ROM program that allows the computer to know how to find the operating system to 'boot' the computer after power is restored
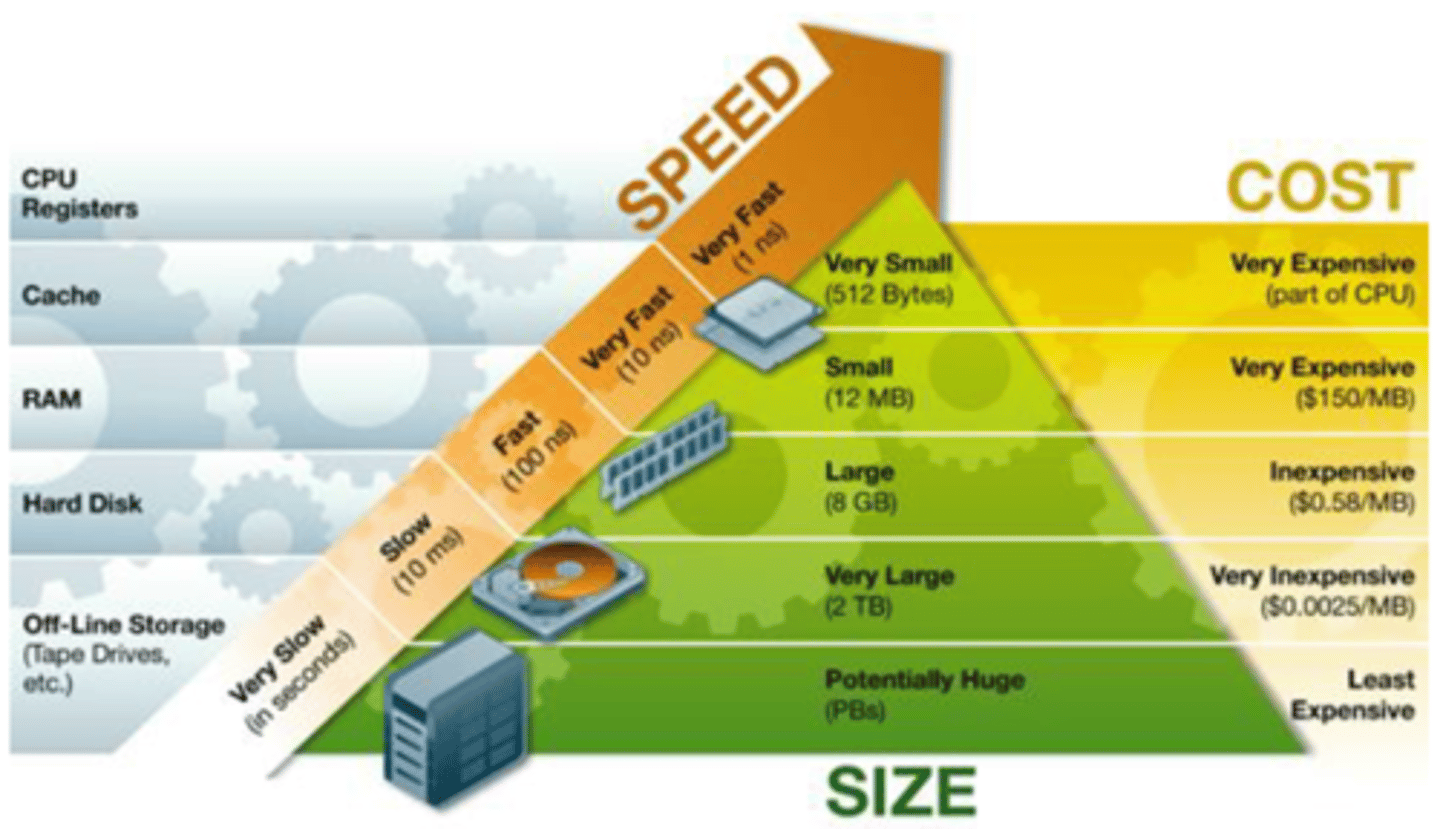
Speed/Cost/Size of Memory
As memory read/write speed increases, the cost also increases, but the size decreases
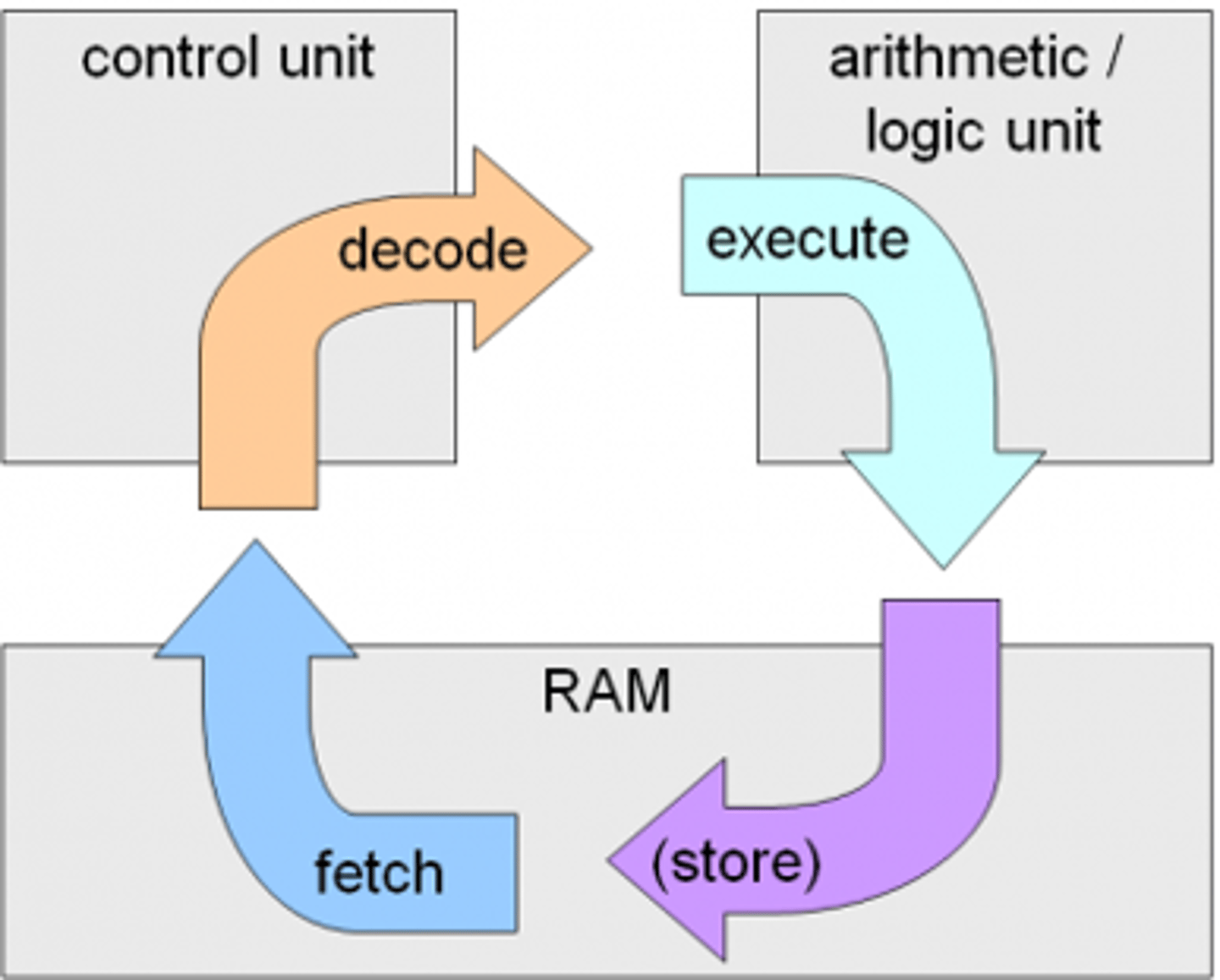
Machine Cycle
Also called the fetch-execute cycle. Fetch=>Decode=>Execute=>Store
Program Counter (PC)
The register that keeps track of instructions: it contains the address of the next instruction to be executed
Persistent Storage
Non-volatile storage to store long-term data, similar to secondary storage
Fundamental Operations of a Computer
Add, Compare, Retrieve, and Store
Add
Takes a value and adds it to the ALU (which already has a current value stored)
Compare
Compares to results or values
Retrieve
Retrieves data/instructions from the RAM
Store
Takes a result and stores it in the RAM
Machine Code
A computer programming language consisting of binary or hexadecimal instructions which a computer can respond to directly
Assembly Code
A low-level symbolic code (often the fundamental instructions, e.g. ADD, STORE) converted by an assembler

Compound Operation
An operation which consists of multiple fundamental operations, often both reading and writing, executing simultaneously, e.g. +=, *=

Natural Language
Languages that happen in nature, e.g. animal/human language, english. Key characteristics: varying vocabulary, ambiguous, grammar/syntax may be inconsistent
Computer Language
Languages that computer speak, ranked from low to high level. Key characteristics: fixed vocabulary meaning only one thing (i.e. print, string), unambigous meanings (i.e. marcell='short'), grammar/syntax consistency (i.e. print(f'') stays as print(f''))
Readability/Speed/Language Level
As the computer language level increases, so does the readability, but execution speed decreases
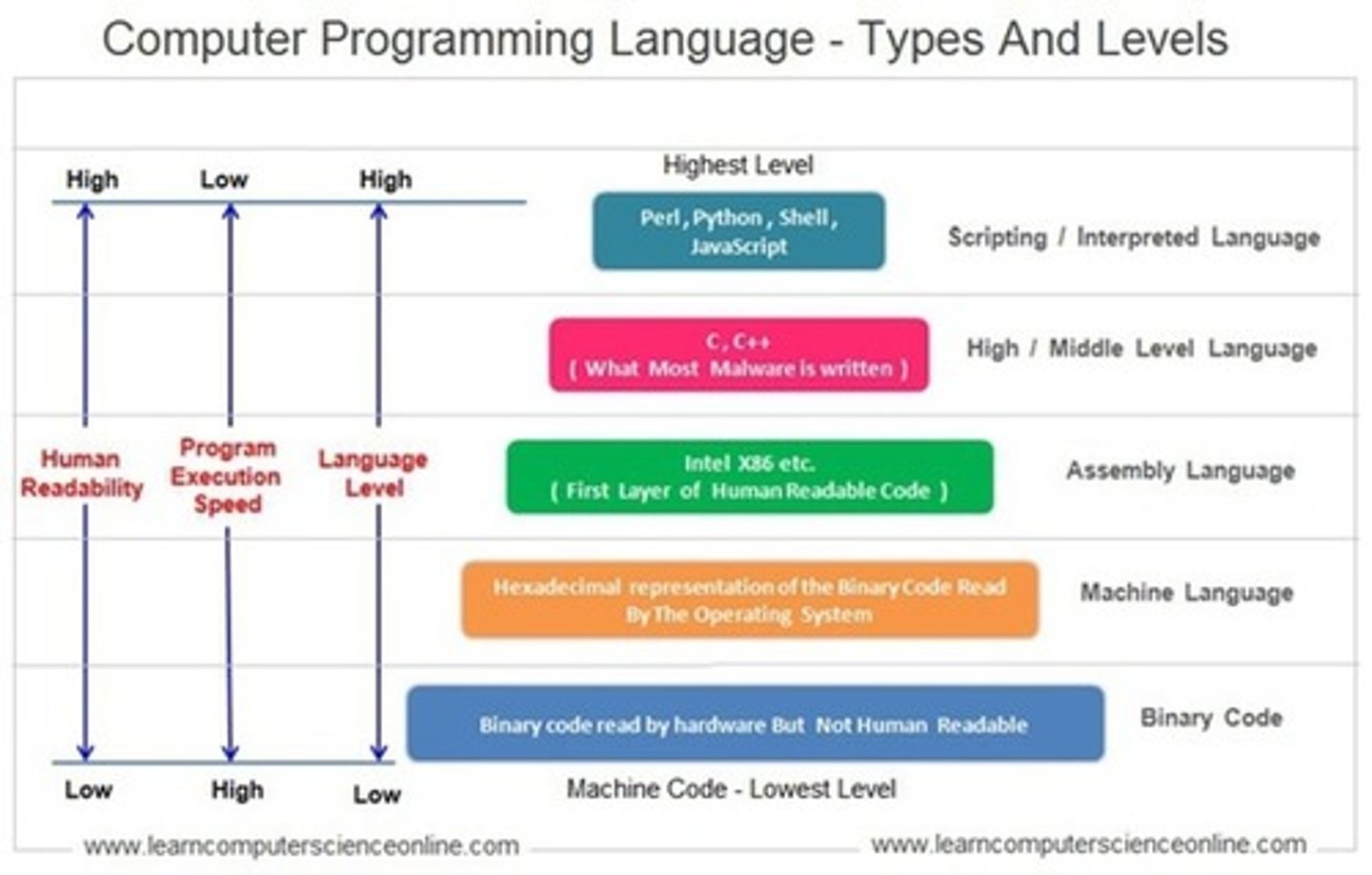
High Level Language
Computer language containing more natural language, but requires more interpretation from the computer (decreases execution speed)
Low Level Language
Computer language closer to binary code used by machines, which requires less interpretation (higher execution speed) but harder to read by humans
Interpreter/Translator
Converts high level language to machine language as program is running.
Key characteristics: translates one line at a time, needed every time program is run, returns list of errors, runs slowly as code needs to be translated every time.
Compiler
Converts high level language to machine language as a single file/executable program.
Key characteristics: translates all code simultaneously, needed only once to create executable, only returns first error, compiling may take a long time but compiled file runs quickly.
Assembler
Converts assembly language to machine language.
Key characteristics: uses instruction set given by processor to convert, runs quickly as its simply direct translation
Virtual Machine (VM)
Software that emulates a simulated environment of another, and allows use of multiple systems on one computer
Variable
Storage location for data in a program. Can be changed during the program, and should not clash with reserved words (i.e. print, string). May hold many data types (i.e. integer, string)
Constant
A variable that can not change, fixed value (i.e. PI=3.14, GRAVITY=9.81)
Operators
Set of characters that represents an action.
4 types: boolean (true/false), arithmetic (basic math), assignment (=, +=, etc.), comparison (<, >, etc.)
Object
An instance of a class. It is a collection of data and methods, created from a "template" (class)
Conditional Statement
Describes relationship between two events based on certain conditions
Conditional Logic
Sets rules/conditions that cause processes to change based on inputs
Internet
- Interconnected set of networks and computers
- Permits transfer of data
- Permits delivery of services
- Data transfer governed by protocols (TCP/IP)
- Protocols and guidelines developed by W3C
World Wide Web (WWW)
- Set of hypertext-linked resources
- Resources identified by URIs (unique resource identifier)
- Transfers data between client and server via internet
- Resources can be read using a browser
Web 1.0
Consisted of read-only webpages made for information sharing; one-way content
Web 2.0
Consisted of read and write webpages in which people could interact, often used for social media; two-way content
Web 3.0
Consists of webpages that can read, write, and execute, designed for immersion; interconnected content
Hypertext
Text displayed with references (hyperlinks) to other text/files that the reader can immediately access, i.e. wikipedia.org links to Wikipedia's files
HTTP
Hypertext Transfer Protocol, governs transfer or exchange of hypertext. Protocol exists on the application layer
HTTPS
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. Encrypts data wiht SSL or TLS to create a more secure form of HTTP
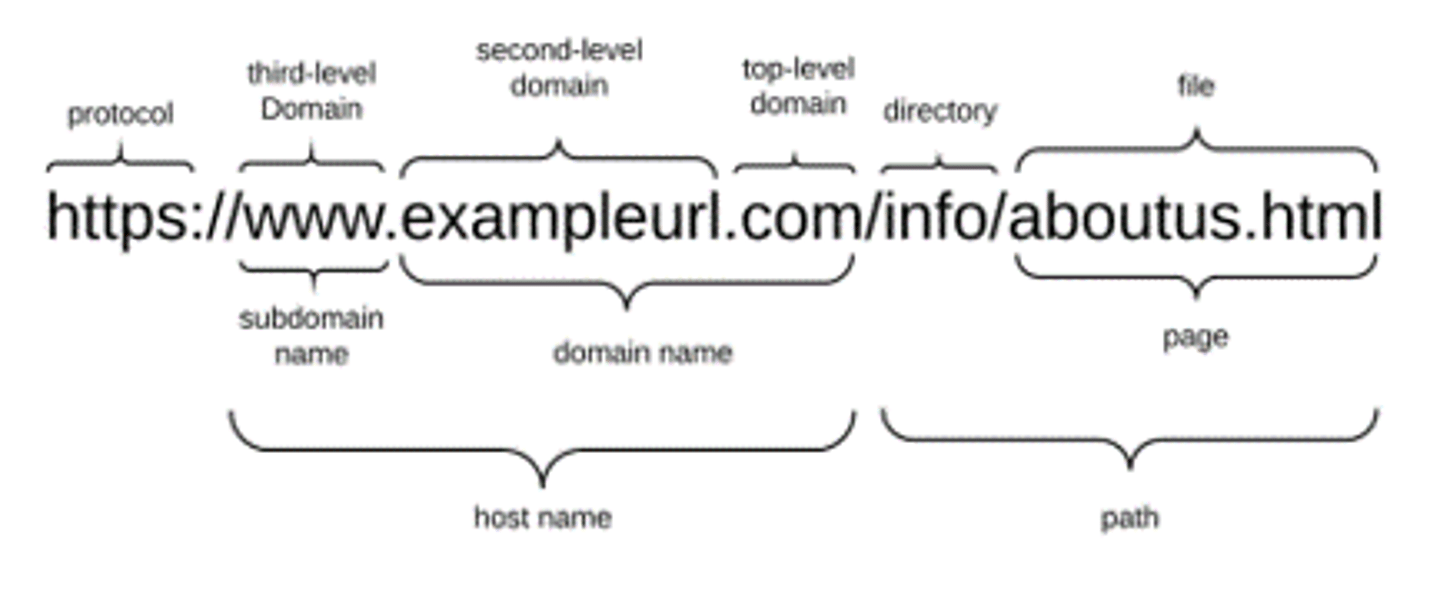
URL
Universal Resource Locator. Defines a pathway to a resource, i.e. web addresses. Consists of a protocol, domain name, directory, and file
Markup Language
Language that uses tags to annotate the information in a document for structuring, organization, and formatting
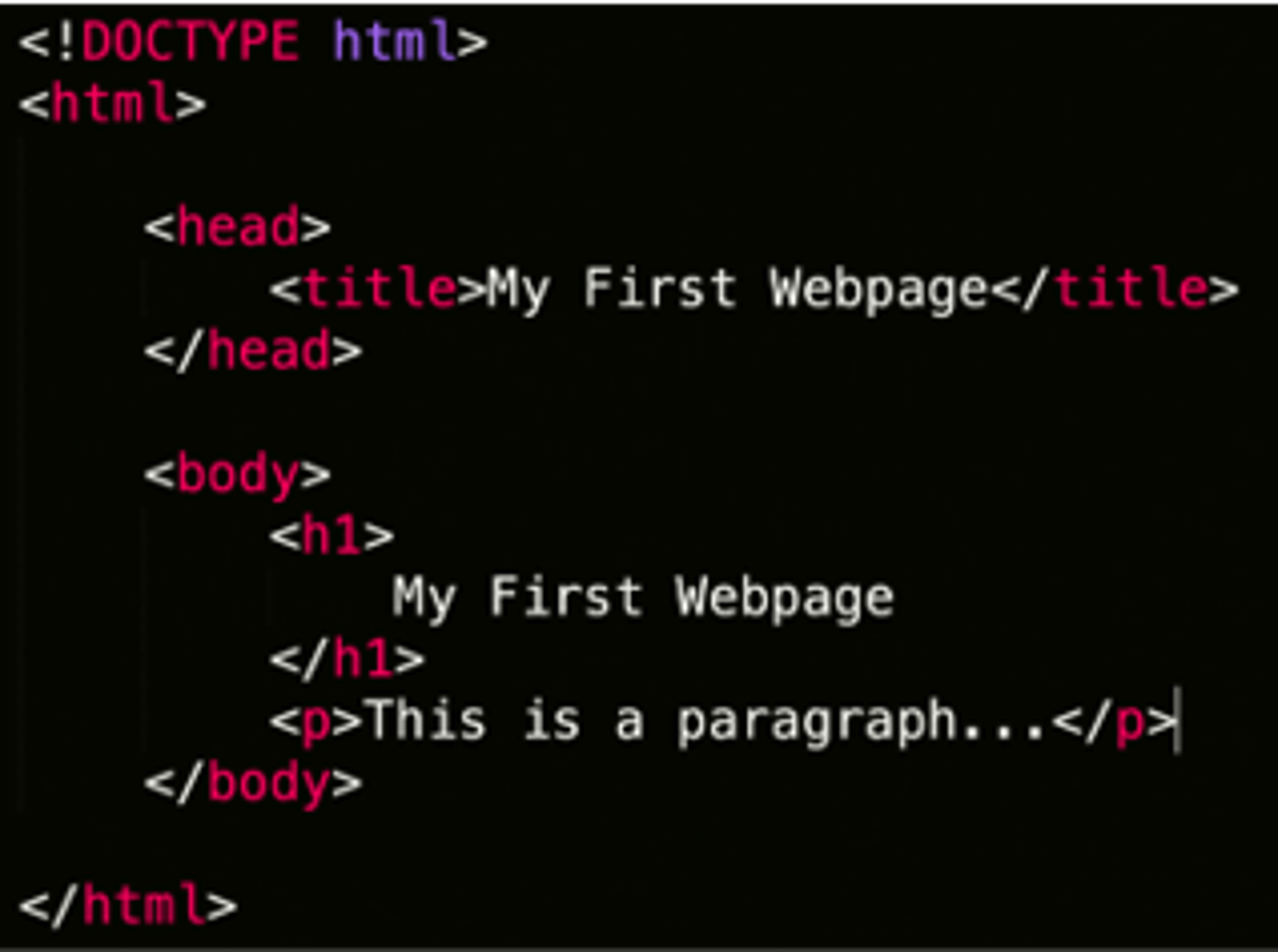
HTML
Hypertext Markup Language. Markup language for describing structure of a web page. May retrieve content with hyperlinks, and displays content sent over the internet
XML
Extensible Markup Language. A language for storing and transporting data. Extensible = easy addition of new information. Provides a common platform for sharing document information across applications.

XSLT
Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations. Transforms XML into an output document, and contains template rules/instructions
JavaScript (JS)
Scripting language to add functionality to webpages. It is embedded into HTML along with CSS. Code is executed when page is download or an "event" (such as button press) is triggered, and allows dynamic web pages (changeable content without reload).
CSS
Cascading Style Sheets. Describes the visual presentation of a webpage, and is independent from HTML
DNS
Domain Name System. Part of the TCP/IP protocol, and translates text-based web addresses to numerical IP addresses, and vice versa.
TCP
Transmission Control Protocol. Receives packets of data from an application and divides it into segments, ready for IP. Establishes an initial connection.
IP
Internet Protocol. Delivers packets of data to the correct addresses. Defines the format of a packet, and includes routing information as a header in front of the TCP to tell where the packets should go.
TCP/IP
The set of protocols that governs the transfer of data over the Internet; TCP controls the retrieval, while IP controls the delivery.
FTP
File Transfer Protocol. Protocol for transferring files over a TCP based network.
Components of a Web Page
Header, Body, Footer, Navigation Bar, Banner, Hyperlinks, Sidebar
Meta tags
Information within the header that contains information about the webpage for search engines
Protocol
A set of rules to successfully carry out some process, i.e. TCP/IP for data transfer
Standards
Set of technical specifications that should be adhered to, to allow for functionality/safety/quality. Allows for interoperability (ability to exchange data) and accessibility (usable by as many people possible)
Search Engine
A program that searches for and identifies items in a database that correspond to keywords or characters specified by the user, used especially for finding particular sites on the World Wide Web
Web Crawler
A program used by search engines to maintain real-time information by looking at metatags
SEO
Search Engine Optimization. Helps website to be better "crawled", or searched, by search engines
News Page
A website that provides relevant articles, audio and video on current news
Business Page
A website that is used to officially represent a brand on the Internet, and which is often used as the landing page for advertising content
Personal Page
A website created by an individual, or small group like a band, to contain content of a personal nature rather than content pertaining to a company, organization or institution
Blogs
Web log. A regularly updated website typically run by an individual or small group, that is written in an informal or conversational style on a particular topic
Forum
An online discussion site where people can hold conversations in the form of posted messages
Ecommerce Pages
Online portals that facilitate online transactions of goods and services through means of the transfer of information and funds over the Internet
Wiki
A website that allows collaborative editing of its content and structure by its users
Social Media
Forms of electronic communication (such as websites for social networking and microblogging) through which users create online communities to share information, ideas, personal messages, and other content (such as videos)
Static Webpage
Fixed webpage that does not change unless re-designed on the serverside. Allows no interaction nor any input