Session 6: Adaptations of Metabolism
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Give three examples of states which can lead to alterations in metabolism
1) Pregnancy
2) Various types of exercise
3) Feeding/fasting and starvation
Pregnancy is a ___ and ___ demanding state
Pregnancy is a nutrient and energy demanding state
During pregnancy - there is a progressive increase in the requirements for the developing ___ and ___
During pregnancy - there is a progressive increase in the requirements for the developing foetus and placenta
During pregnancy, most substances cross the placenta by ___ and ___ ___
Passive and facilitated diffusion
The transfer of a MINORITY of substances such as amino acid transport to the placenta are conducted by...
Active transport
What is the principal fuel for the developing foetus during pregnancy?
Glucose
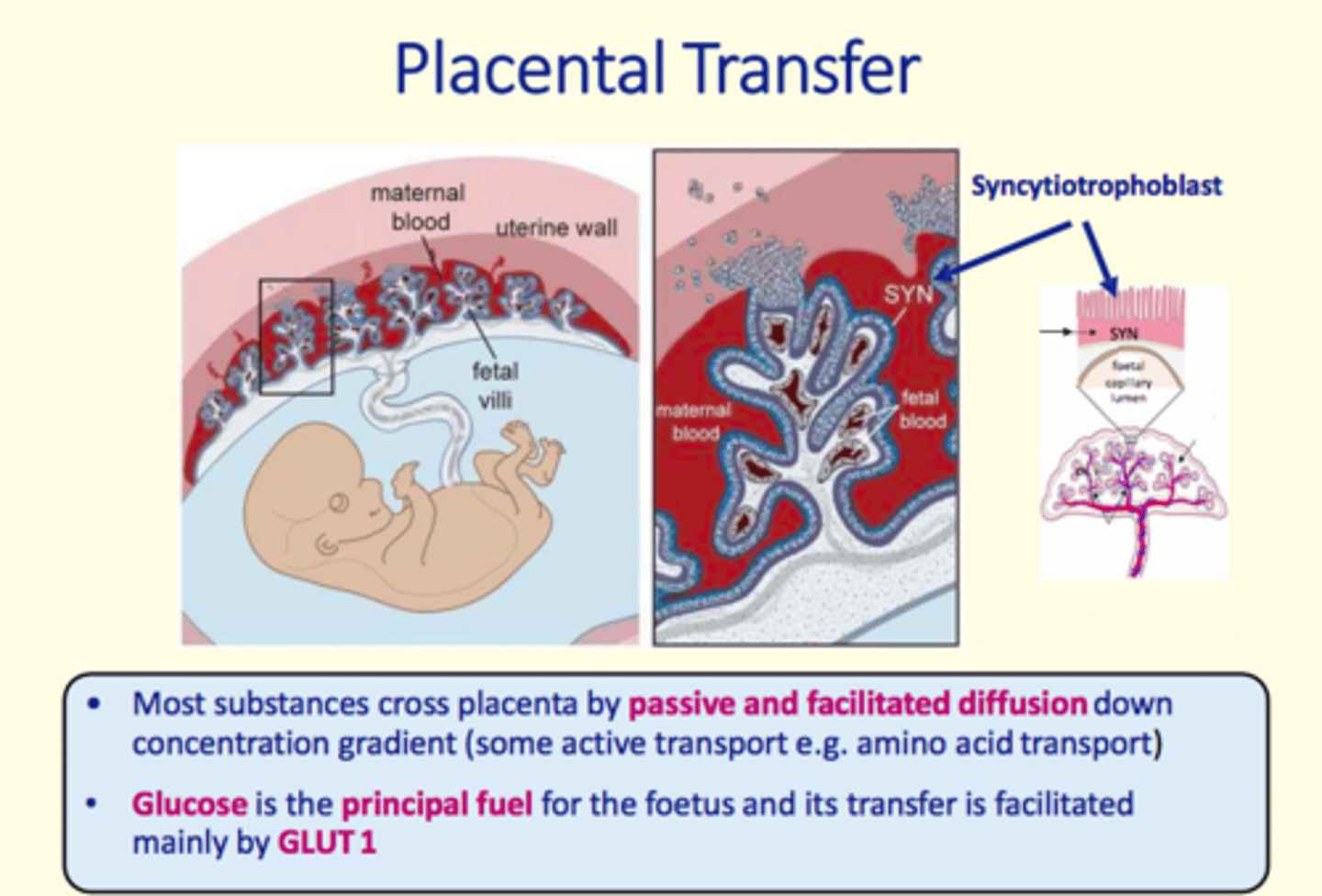
What is the primary glucose transporter which transfers glucose to the foetus via the placenta?
GLUT1 transporter
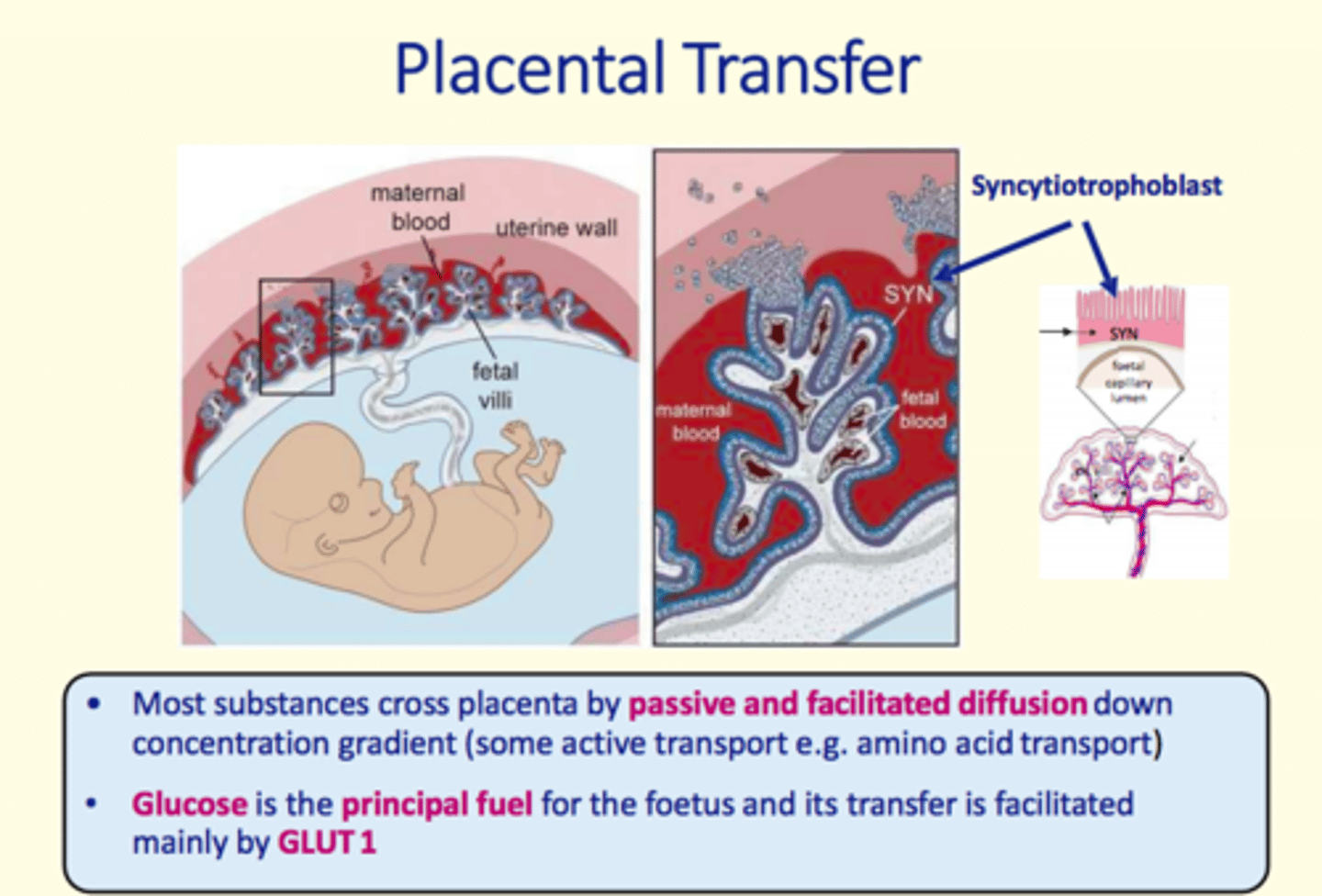
Specialised epithelial cells found in the outermost layer of the placenta which facilitates transfer of metabolites, drugs, waste, gases between foetal and maternal circulation
Syncytiotrophoblasts (SYN)
What are the two main phases of metabolic adaptation during pregnancy
1) The anabolic phase = prepatory increase in maternal store of nutrients
2) The catabolic phase = increase in the AVAILABILITY of nutrients in the blood
Briefly explain the changes which occur during first phase of metabolic changes during pregnancy (anabolic phase)
- First half of pregnancy
- Maternal fat stores increase
- Increased insulin levels and increase in insulin sensitivity = help achieve increase in maternal fat stores
- These changes meet the demand of the growing fetus in late pregnancy, birth & lactation
Briefly explain the changes which occur during the second phase of metabolic changes during pregnancy (catabolic phase)
- Second half of pregnancy
- Increase in maternal nutrients available in the blood (glucose, free fatty acids, ketones)
- Decreased insulin sensitivity or increased insulin resistance = help achieve increased availability of maternal nutrients such as glucose for benefit of fetal growth in late pregnancy (when most of the foetal growth occurs)
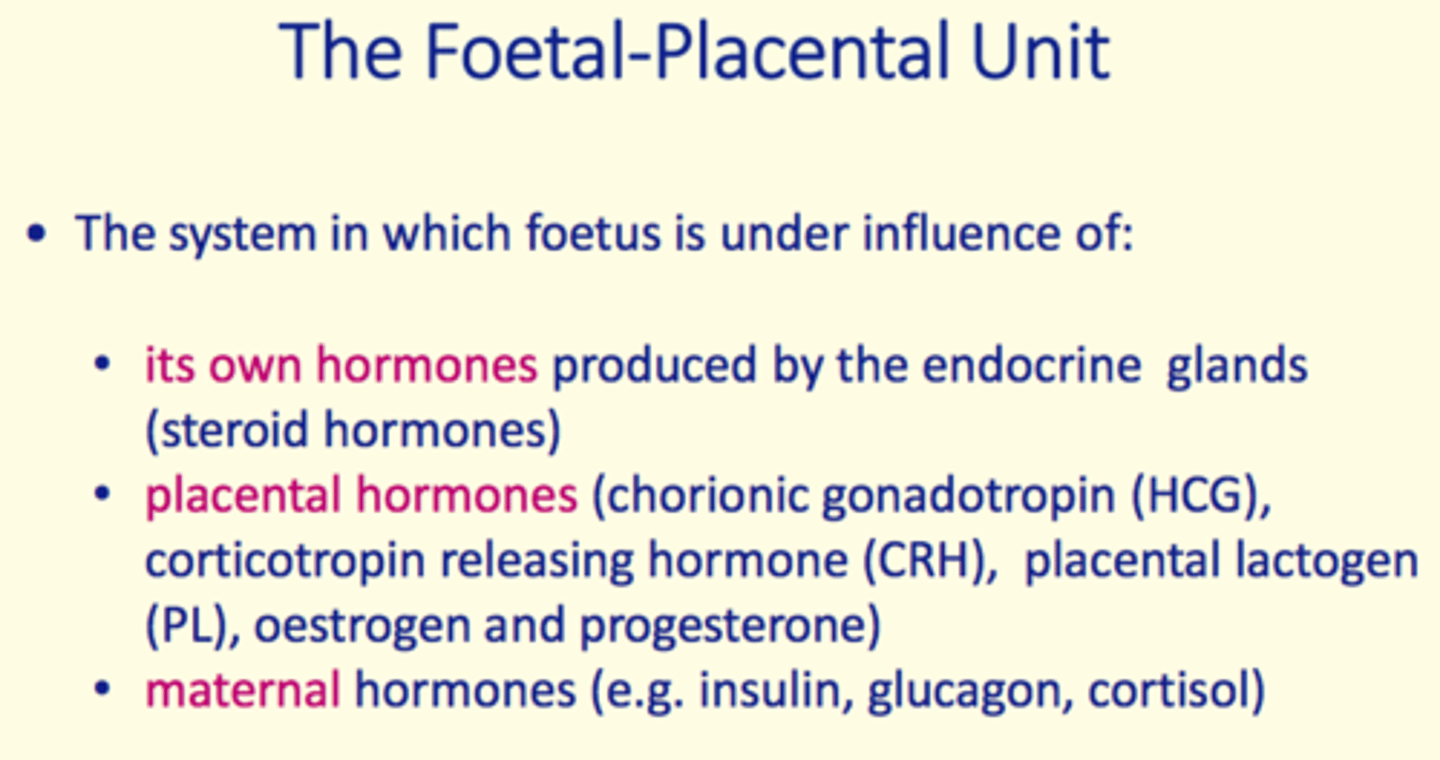
Foetal-placental unit
The system which the fetus is under the influence of
What does the foetal-placental unit consist of?
1) Foetal hormones
2) Placental hormones
3) Maternal hormones
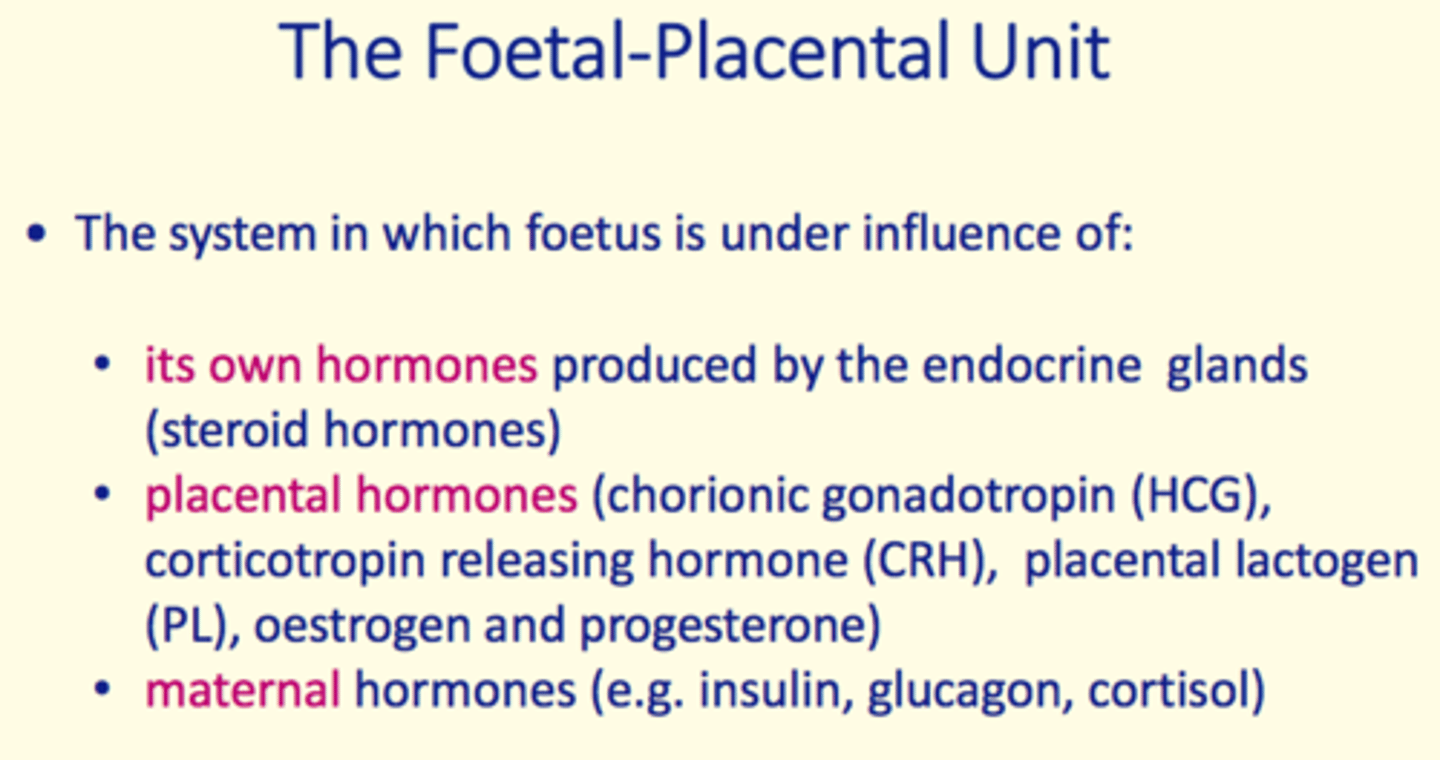
Foetal hormones
produced by endocrine gland (steroid hormones)
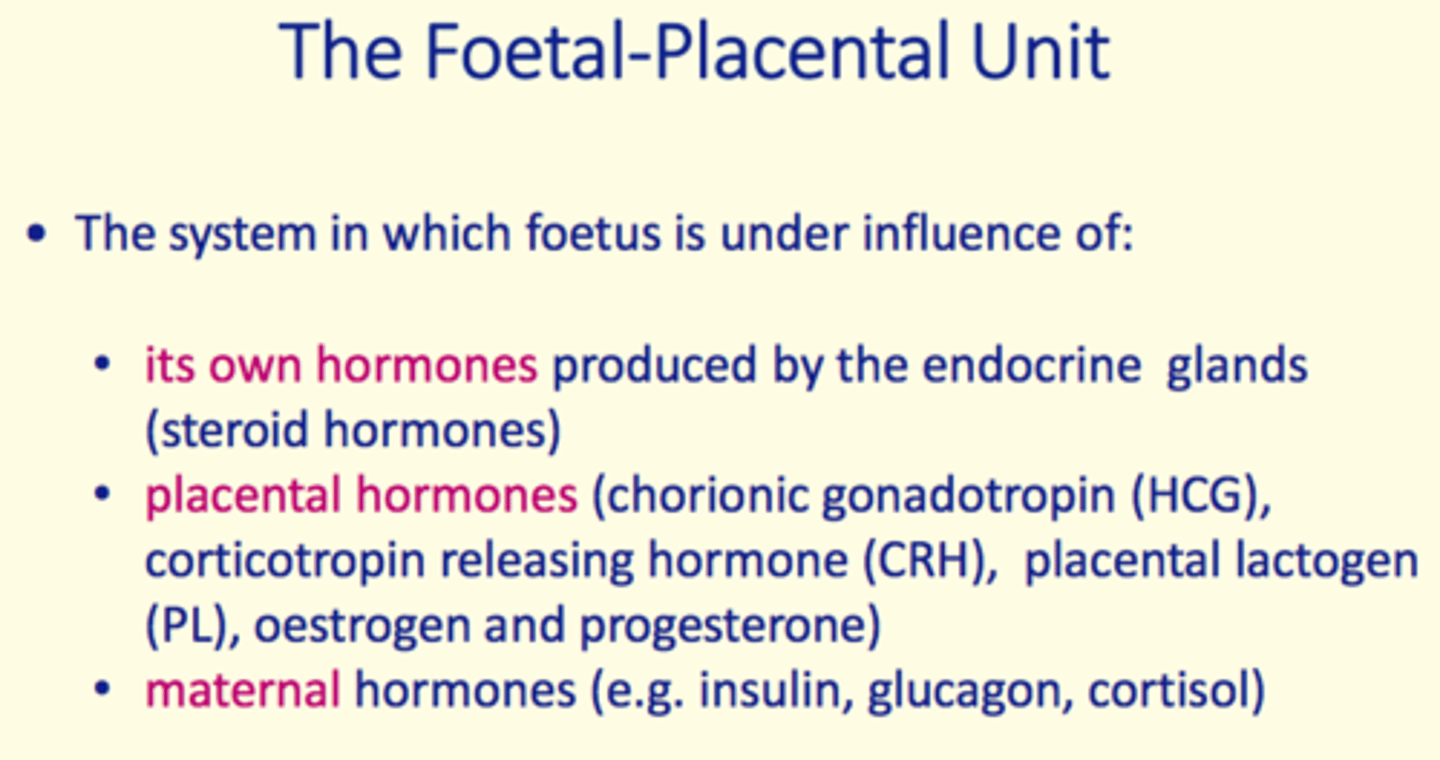
Placental hormones
1) Chorionic gonadotropin (HCG)
2) Corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH)
3) Placental lactogen (PL)
4) Oestrogen
5) Progesterone
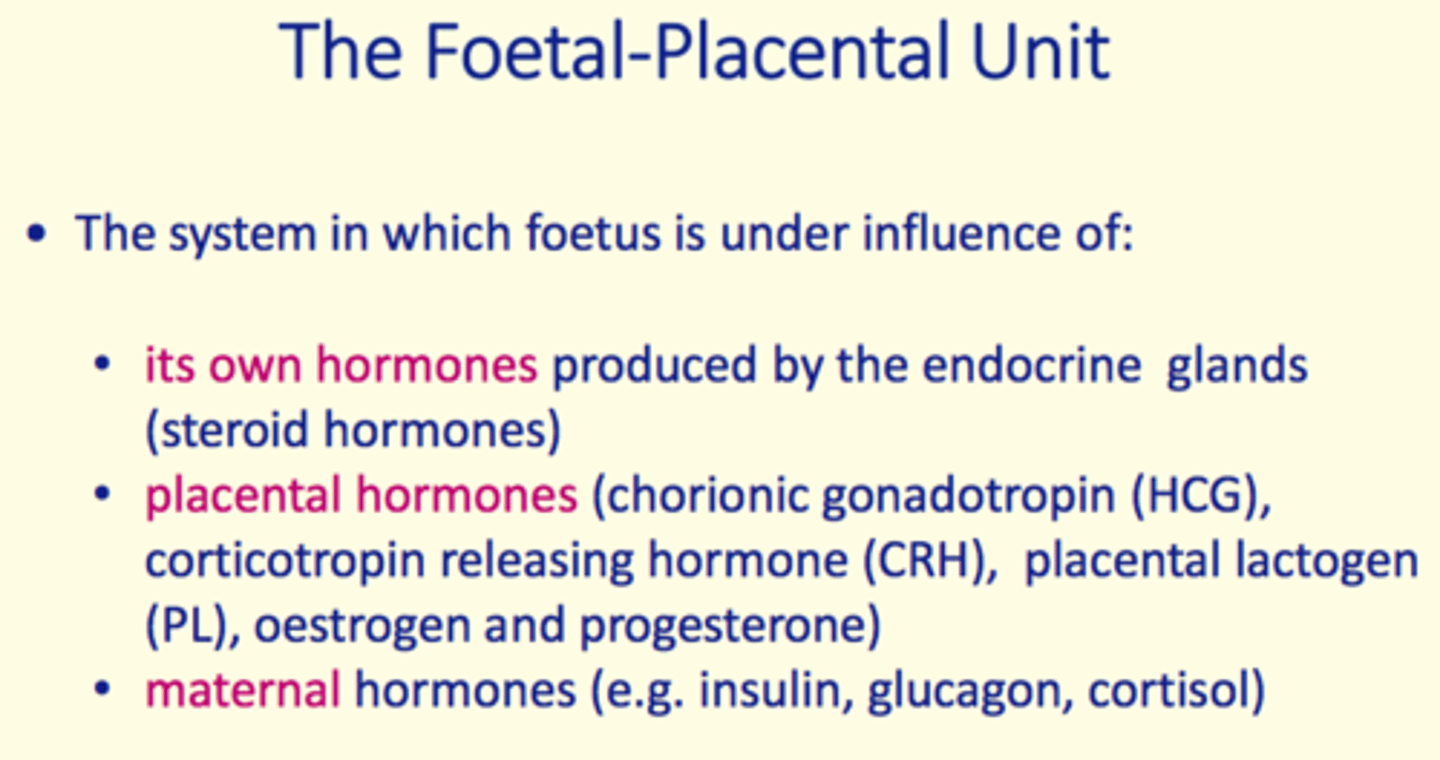
Maternal hormones
Insulin
Glucagon
Cortisol
What are the anti-insulin hormones in pregnancy?
The hormones which exert an 'anti-insulin' effect
Which placental hormones have an 'anti-insulin' effect?
1) Corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH)
2) Placental lactogen (PL)
3) Oestrogen
4) Progesterone
What effect does the 'anti-insulin' effect exerted by placental hormones have on maternal metabolism?
1) Reduced maternal glucose uptake in adipose and muscle tissue
2) Allow more glucose to be available for the fetus
What can sometimes occur as an impact of the 'anti-insulin' effect during pregnancy?
Transient hyperglycaemia due to the enhanced insulin resistance (due to production of anti-insulin hormones during pregnancy)
During late pregnancy = blood glucose is ~10% ___ as the insulin levels are ~1.65x ___ in fasting state and ~3x ___ in postprandial state
During late pregnancy = blood glucose is ~10% lower as the insulin levels are ~1.65x higher in fasting state and ~3x higher in postprandial state
Episodes of ___ can occur between meals and at ___ due to continuous usage of glucose by the fetus
Episodes of hypoglycaemia can occur between meals and at night due to continuous usage of glucose by the fetus
Generally, mothers experience an increased ___ during pregnancy as a symptom
appetite
Which hormones increase the sensitivity of maternal pancreatic B-cells to blood glucose?
Oestrogen and progesterone increase the sensitivity of maternal pancreatic B-cells to blood glucose
This leads to:
- B-cell hyperplasia
- B-cell hypertrophy
Collectively, the changes to maternal B-cells during pregnancy (increased sensitivity to blood glucose) leads to an increased production of ___ hormone
insulin
If maternal B-cells do not respond normally during pregnancy - blood glucose levels can become VERY ___
elevated
What condition can occur as a result of abnormal response of maternal B-cells during pregnancy?
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes
Form of diabetes mellitus occuring during pregnancy in which maternal pancreatic B-cells do not produce sufficient insulin to meet requirements of the fetus during late pregnancy
Fasting plasma glucose during gestational diabetes
>5.6 mmol/L
List three known and underlying causes of gestational diabetes
1) B-cell dysfunction associated with obesity and chronic insulin resistance (similar to T2D) = most common
2) Autoantibodies produced (similar to T1D)
3) Genetic susceptibility (similar to maturity-onset diabetes)
Most common CAUSE of gestational diabetes
B-cell dysfunction associated with obesity and chronic insulin resistance (similar to T2D)
Most rare CAUSE of gestational diabetes
Genetic susceptibility (similar to maturity-onset diabetes) = occurs in 1-5% cases
How many pregnancies does gestational diabetes affect?
3-10% pregnancies
What complications can gestational diabetes increase the risk of occurring?
1) Miscarriage
2) Congenital malformation (risk 4x higher)
3) Foetal macrosomia (large baby) - increased risk of foetal shoulder dystocia
4) Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy = gestational hypertension & pre-eclampsia
What potential complications can occur as a result of gestational diabetes to the FETUS
1) Miscarriage
2) Congenital malformation of fetus (4x higher)
3) Foetal macromasia - shoulder dystocia of foetus
What potential complications can occur as a result of gestational diabetes to the MOTHER
1) Increased risk of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy including = gestational hypertension and pre-eclampsia
Indications of pre-eclampsia in mother
High BP
Proteinuria
What is a good predictor of risk of developing gestational diabetes BEFORE pregnancy?
Measuring insulin resistance in woman BEFORE pregnancy
A woman who is at high-risk of developing gestational diabetes will have ___ insulin resistance before pregnancy
higher
A woman who is at low-risk of developing gestational diabetes will have ___ insulin resistance before pregnancy
lower
Majority of women who have gestational diabetes go on to develop type ___ diabetes later in life
Type 2 diabetes
Risk factors for gestational diabetes in mother
1) Maternal age >25
2) BMI >25 kg/m^2
3) Race/ethnicity = more common in black/hispanic/asian
4) Personal/family history = diabetes, macrosomia
Management of gestational diabetes
1) Dietary modification in obese women = reduce calories
2) Insulin injections = persistent hyperglycaemia
3) Regular ultrasounds to monitor fetus
What is considered 'hyperglycaemic' levels of glucose in a pregnant women (bloods)?
7.5-8 mmol/L post-prandial glucose
>5.5-6 mmol/L fasting glucose
Some benefits of exercise
1) Improved body composition = increased muscle, decreased adipose
2) Improved glucose tolerance = increase muscle glycogenesis
3) Increased insulin sensitivity in tissues
4) Decrease in blood triglyceride levels (decreased VLDL + LDL; increased HDL)
5) Decreased BP
6) Psychological benefits
The switch from a state of rest to exercise causes RAPID changes in which systems?
1) MSK
2) CVS
3) Respiratory system
4) Temperature regulation system
During exercise, the metabolic response needs to ensure four things. What are they?
1) Increased energy demand of skeletal/cardiac muscle are met
2) Minimal disturbance to metabolic homeostasis
3) Glucose supply to brain is maintained
4) End products of metabolism removed ASAP
What three factors does the metabolic response to exercise depend on?
1) Type of exercise (type of muscle used)
2) Intensity, duration
3) Physical/nutritional state of individual

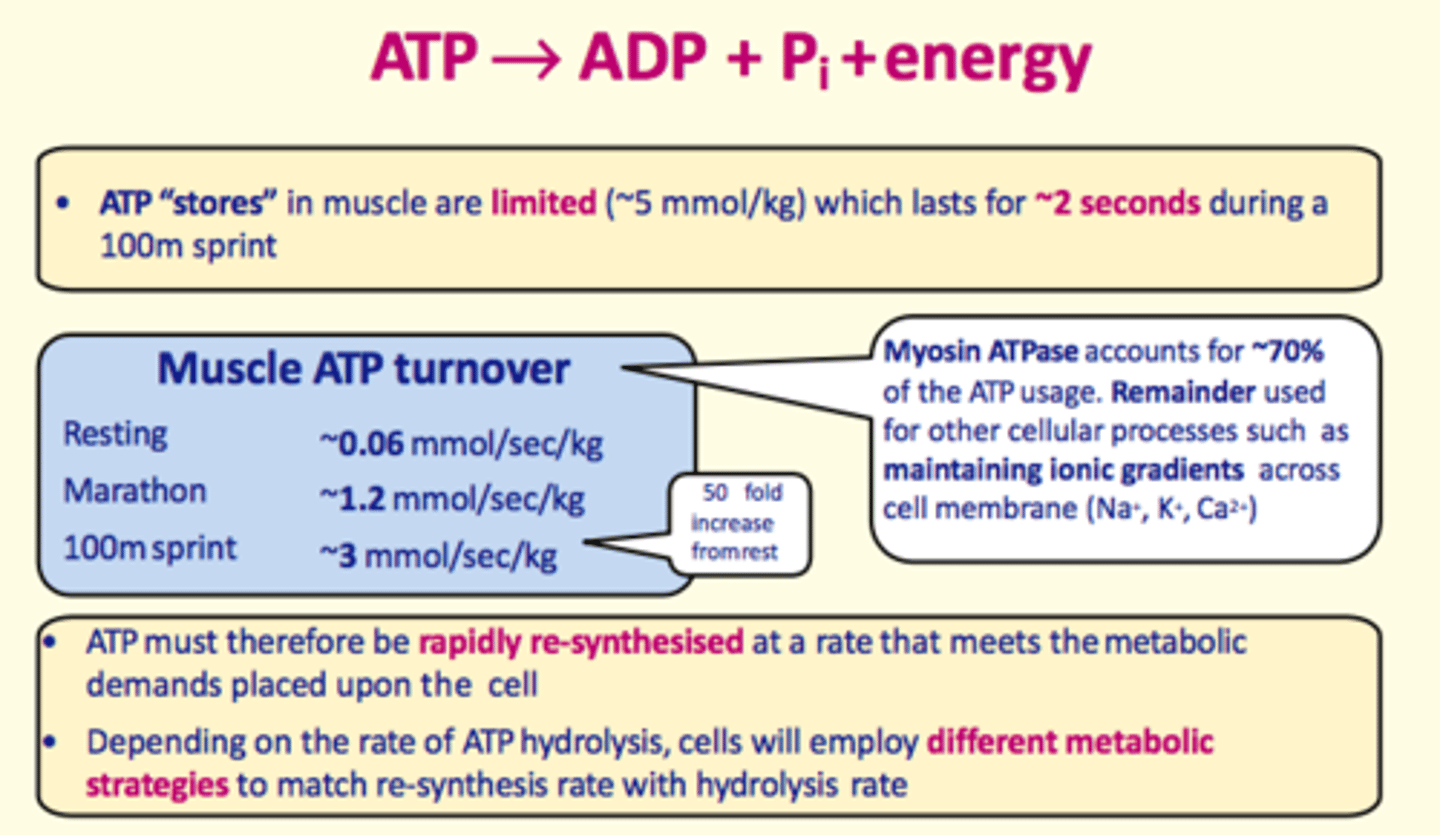
ATP stores in muscles are ___ (~5mmol/L) which lasts for ~___ during a 100m sprint
ATP stores in muscles are limited (~5mmol/L) which lasts for ~2 seconds during a 100m sprint
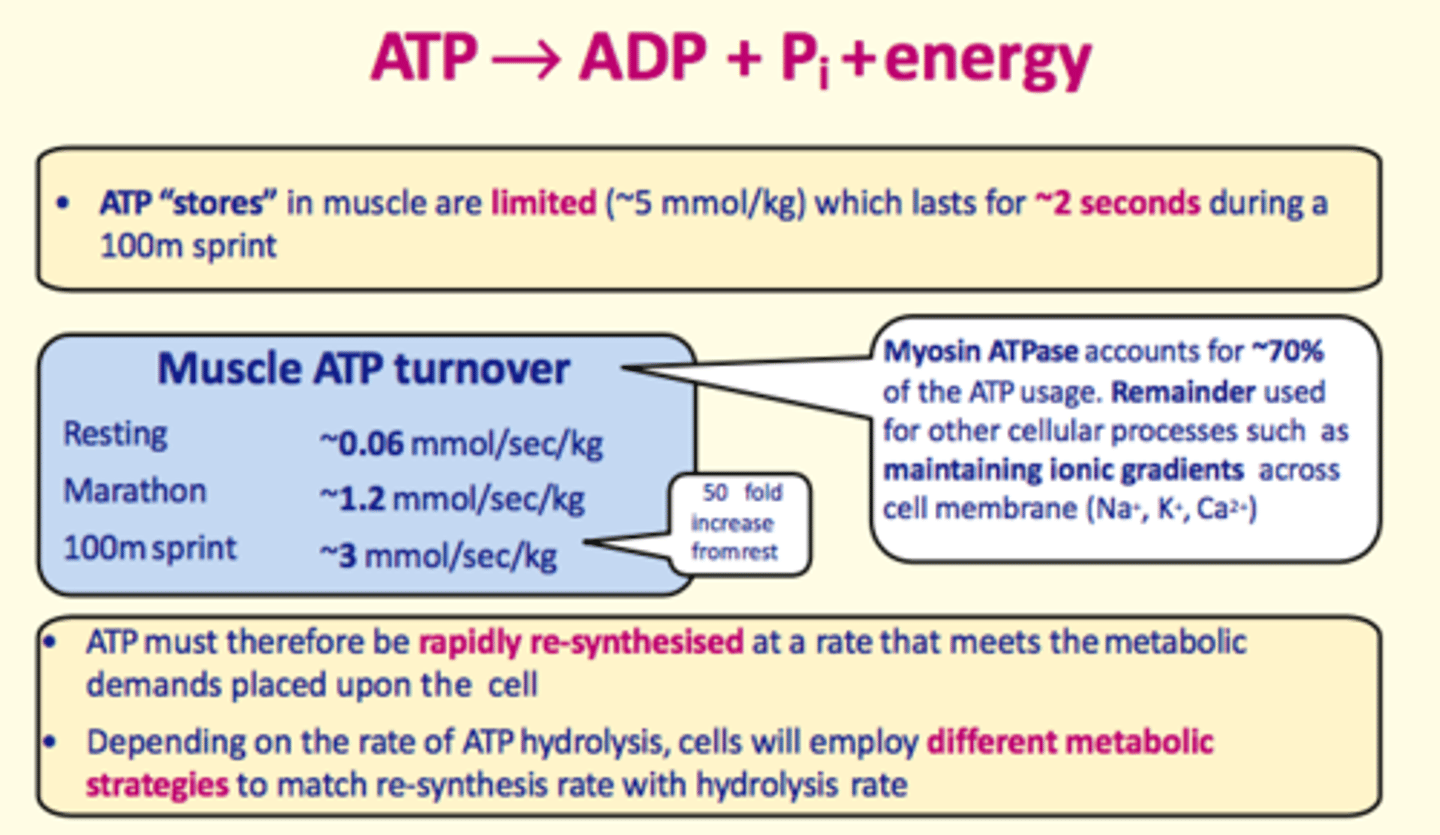
ATP must be rapidly regenerated during exercise at a rate that meets the increased metabolic demands of tissues that require it.
Cells will take on different metabolic strategies so that the regeneration rate of ATP matches the rate of...
hydrolysis of ATP
Sources of ATP during exercise
1) Muscle creatine phosphate stores
2) Glycolysis (inefficient; 2ATP per cycle)
3) Oxidative phosphorylation (efficient; but requires oxygen)
4) Break down of muscle glycogen (glycogenolysis)
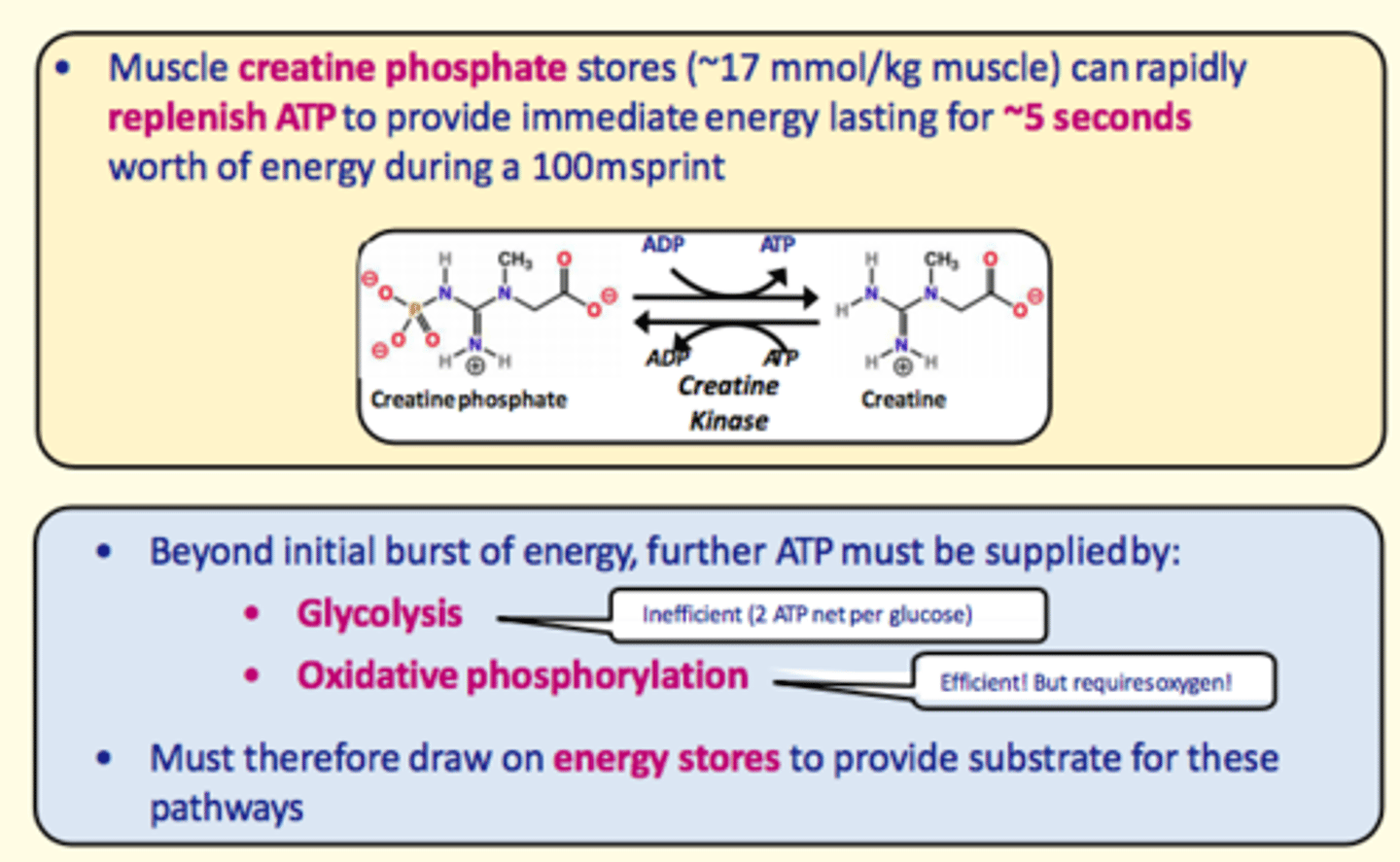
Muscle creatine phosphate stores
~17 mmol/kg muscle
rapidly replenishes ATP providing immediate energy
lasts only ~5 seconds
Glycogenolysis can sustain what type of exercise and for what duration?
Breakdown of muscle glycogen (glycogenolysis) can sustain high intensity exercise under anaerobic conditions for up to ~2 minutes
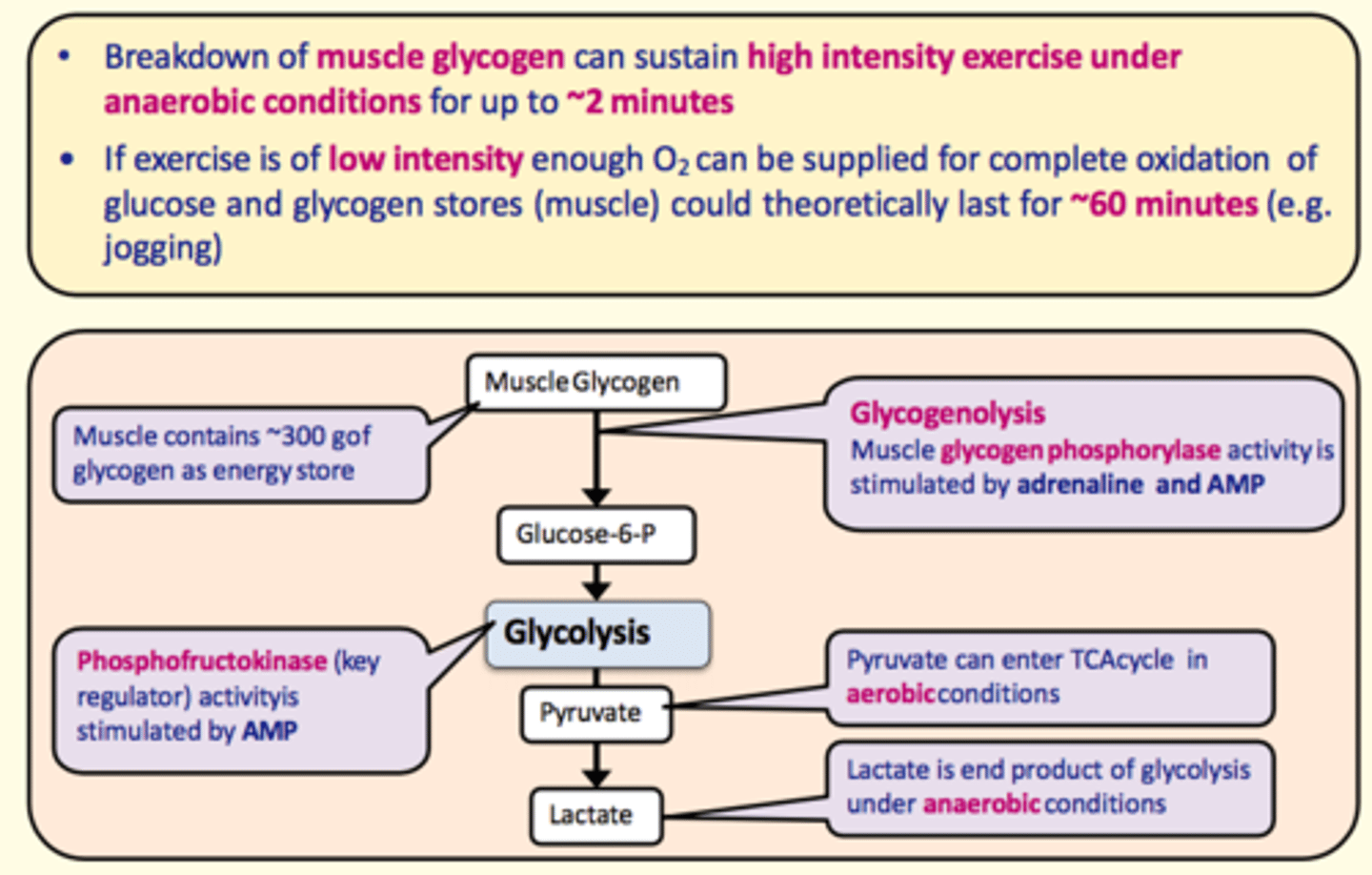
In case of low-intensity exercise, what duration of this low-intensity exercise could glycogenolysis provide energy for?
If exercise is of low intensity - enough O2 can be provided for complete oxidation of glycogen and glucose stores in muscle to provide energy for ~60 minutes (e.g., jogging)
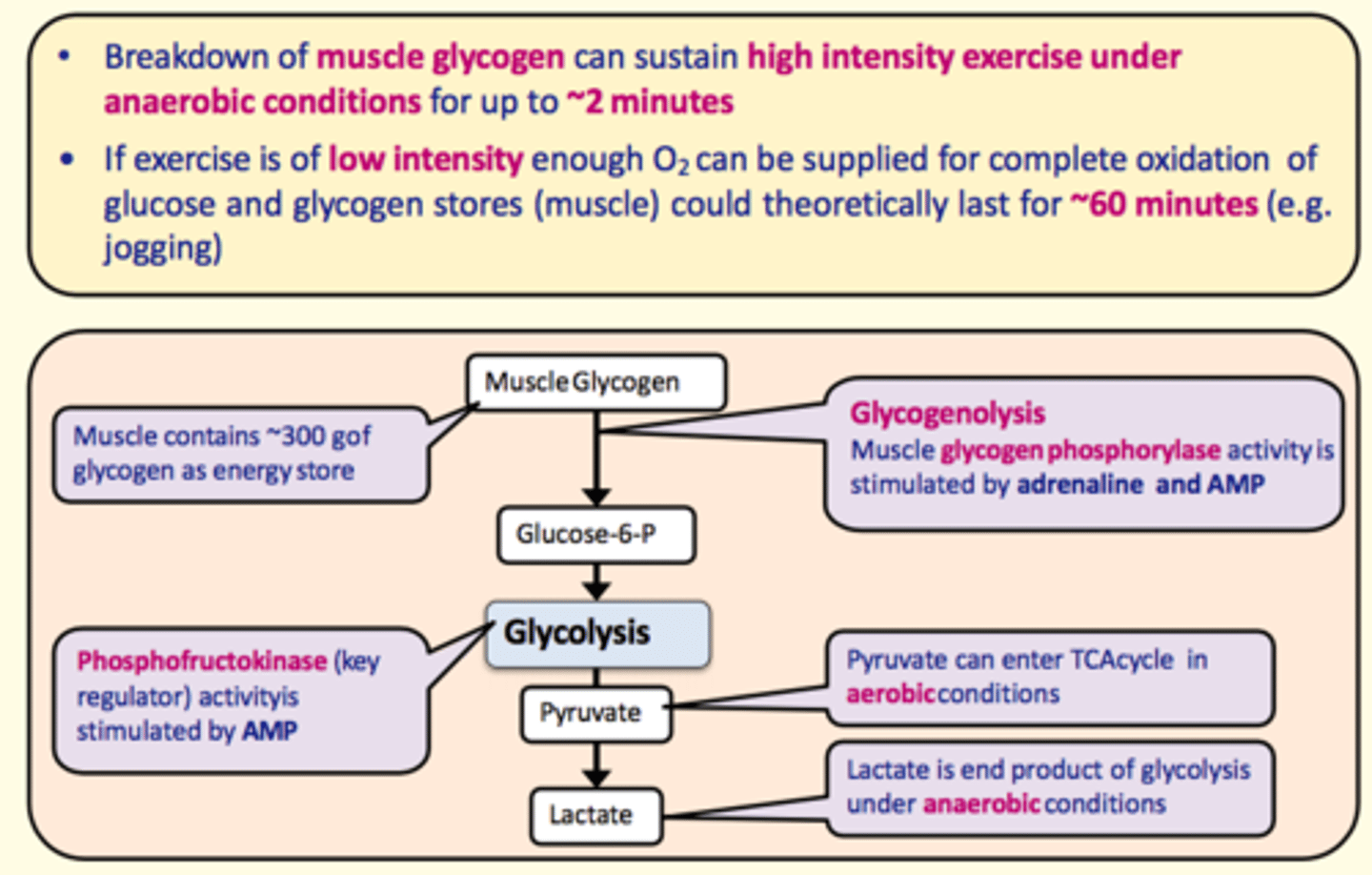
Muscle glycogen is broken down into ___ during glycogenolysis. This takes place in the liver
Glucose-6-phosphate
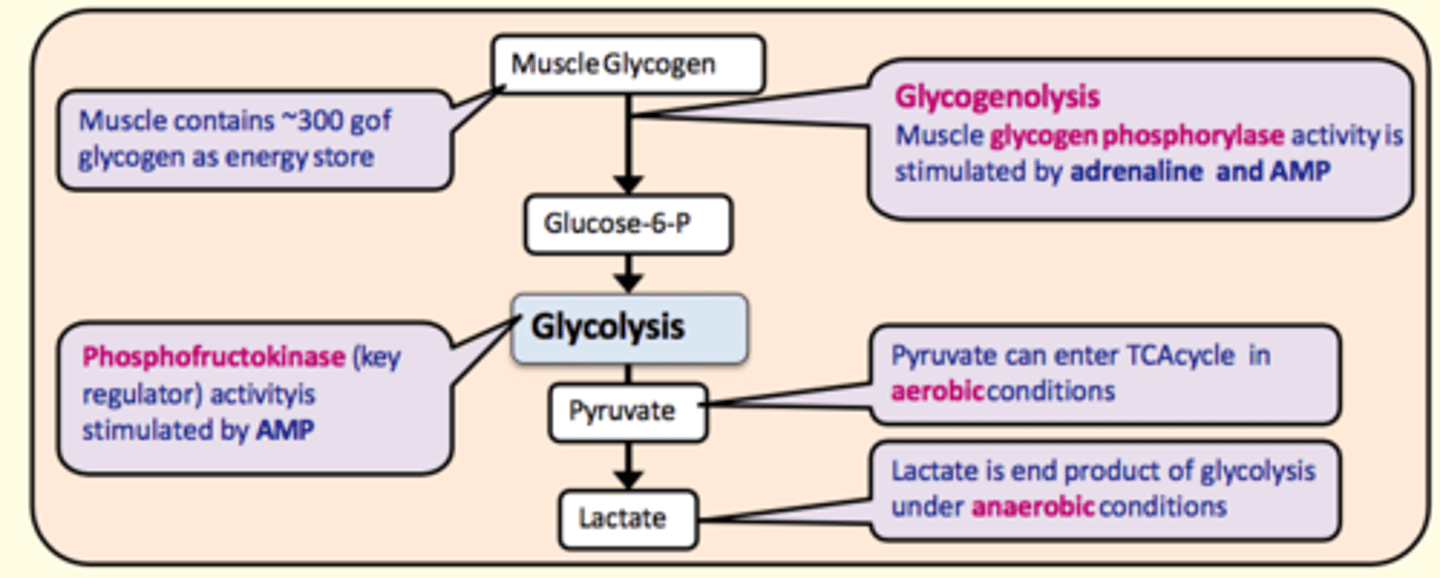
What enzyme catalyses the conversion of glycogen to glucose-6-phosphate during glycogenolysis?
Glycogen phosphorylase
Stimulated by:
- Adrenaline
- AMP
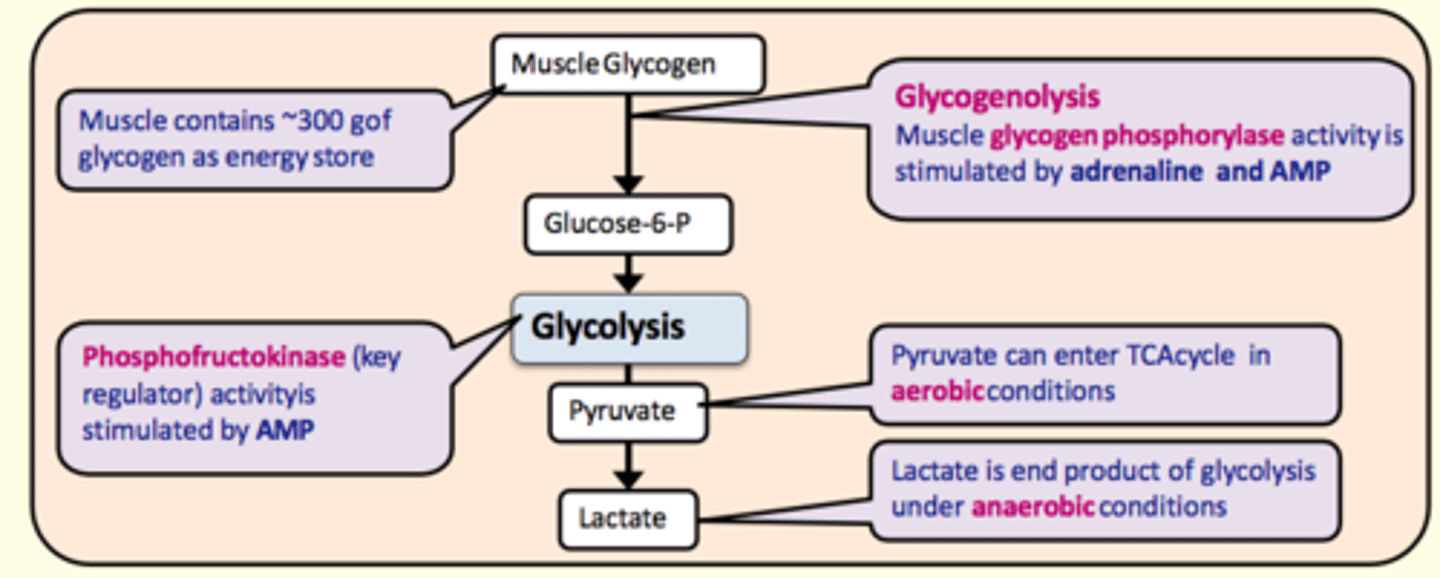
Key regulating enzyme in glycolysis
Phosphofructokinase
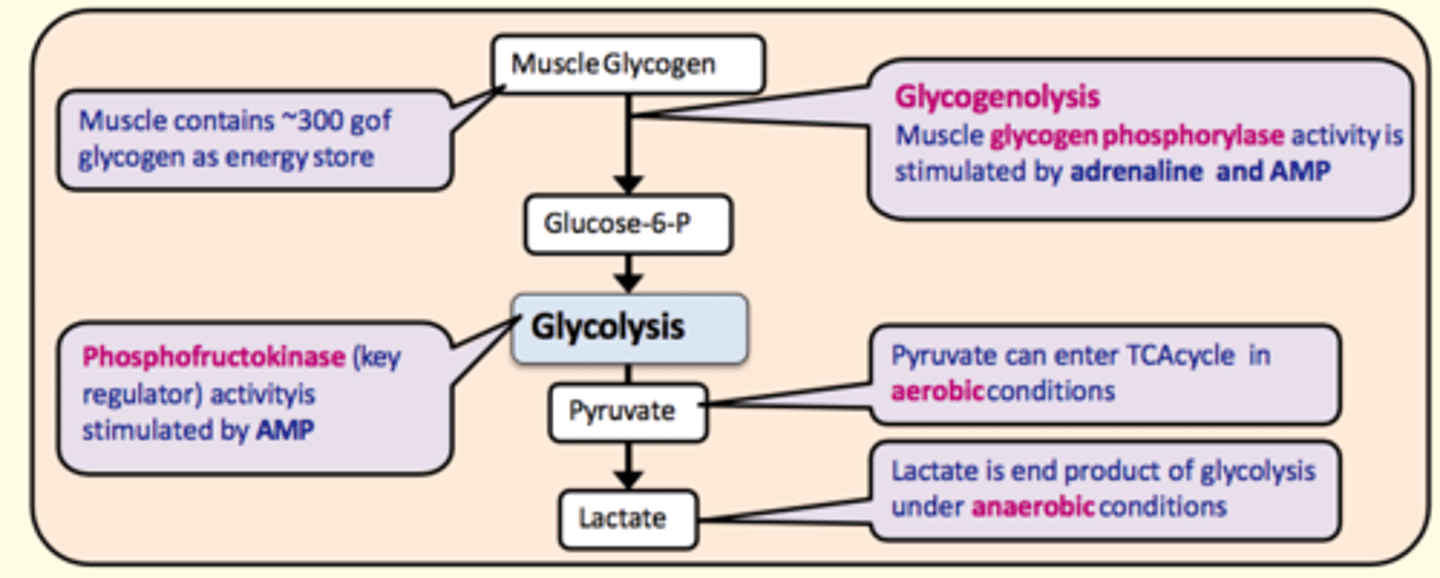
Pyruvate can enter the TCA cycle in ___ conditions
aerobic
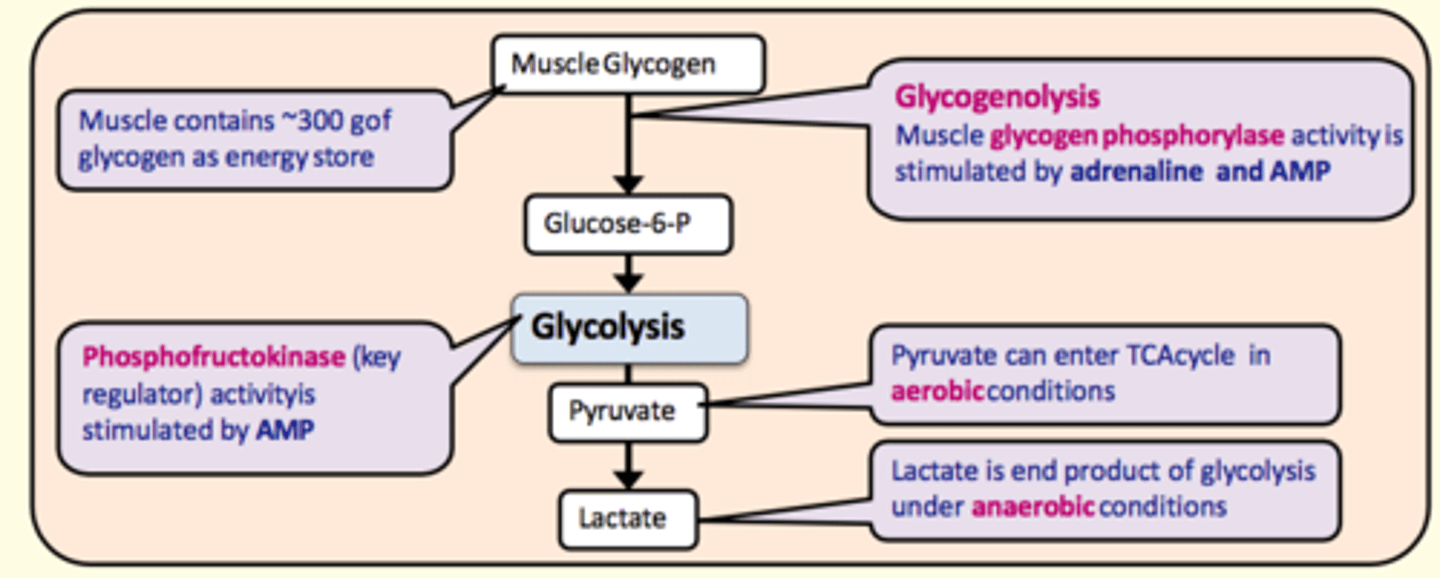
Lactate is the end-product of glycolysis under ___ conditions
anaerobic
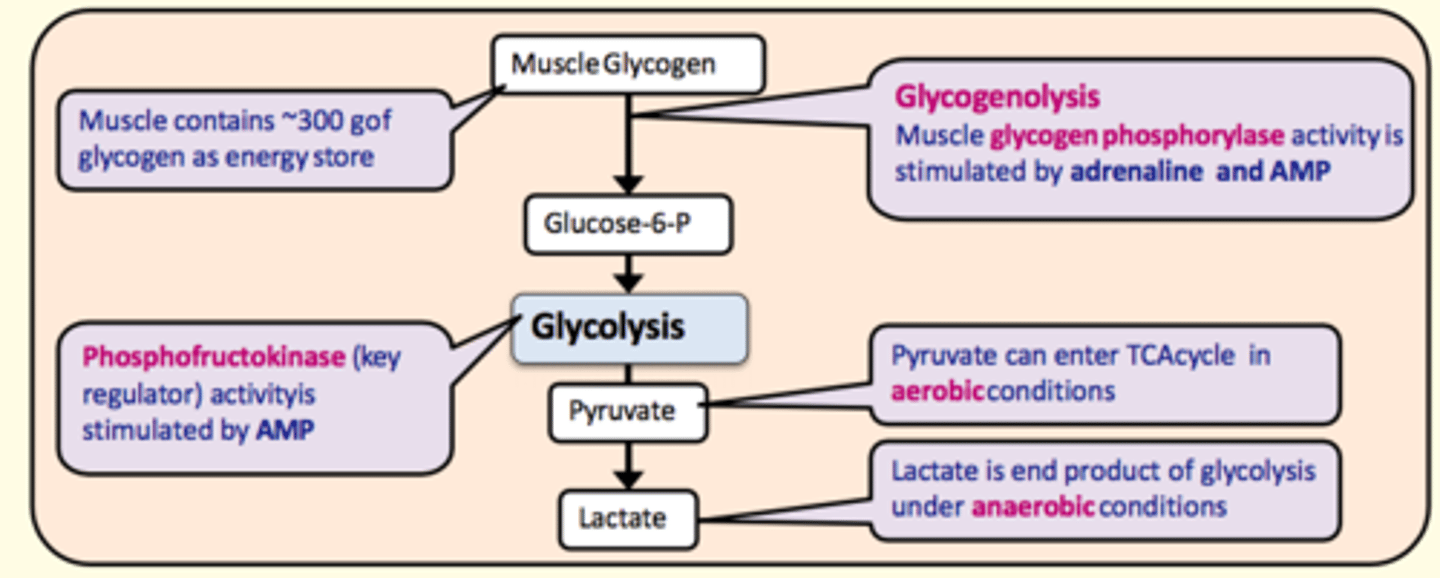
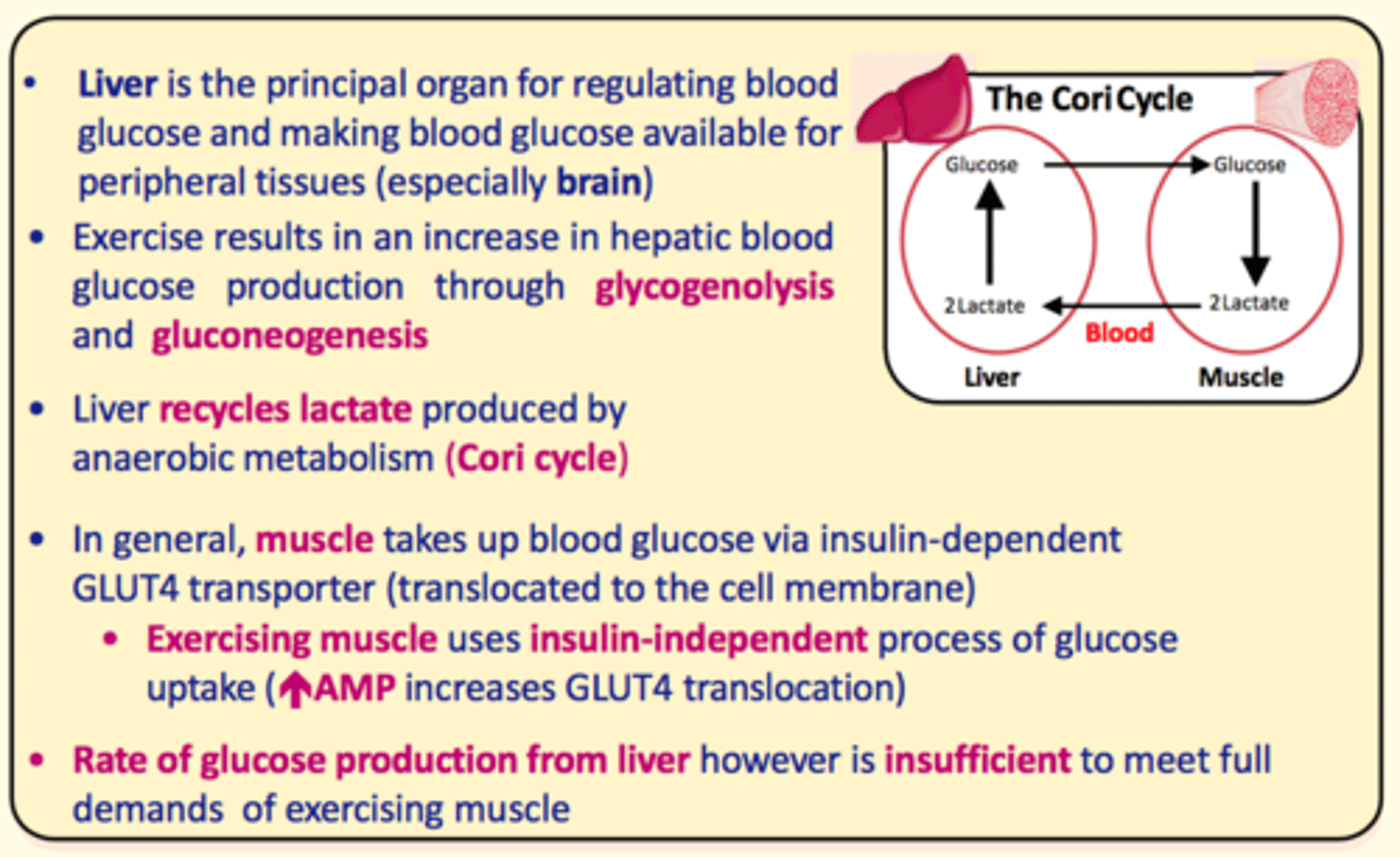
What organ is responsible for regulating blood glucose levels in the body and making glucose available for peripheral tissues (especially the brain)?
Liver
Exercise results in an increase in hepatic blood glucose production in the liver via ___ and ___
glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis
The ___ recycles lactate produced by ___ metabolism in the ___ cycle
The liver recycles lactate produced by anaerobic metabolism in the cori cycle
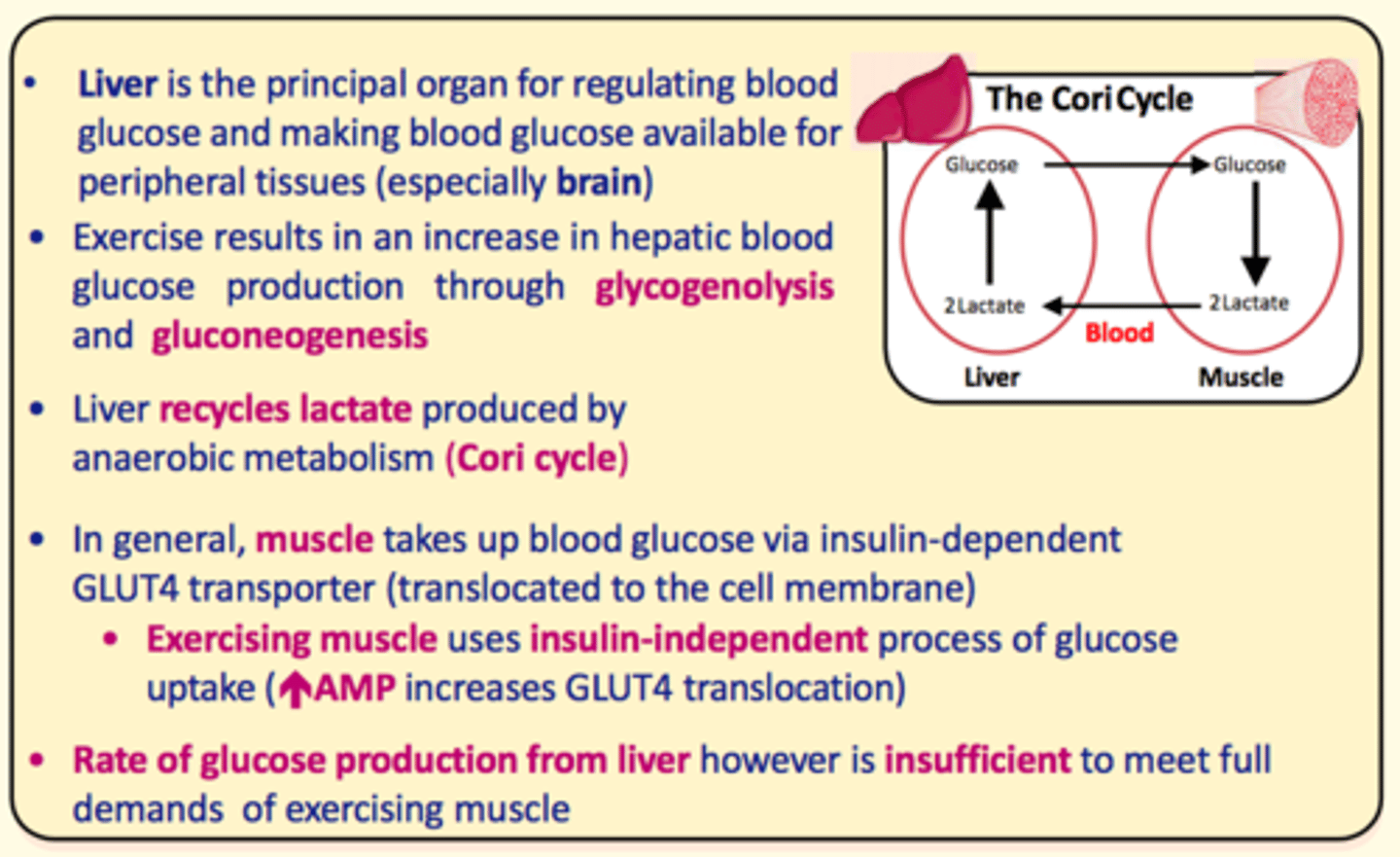
Muscle takes up blood glucose via insulin-dependent ___ transporter
GLUT4
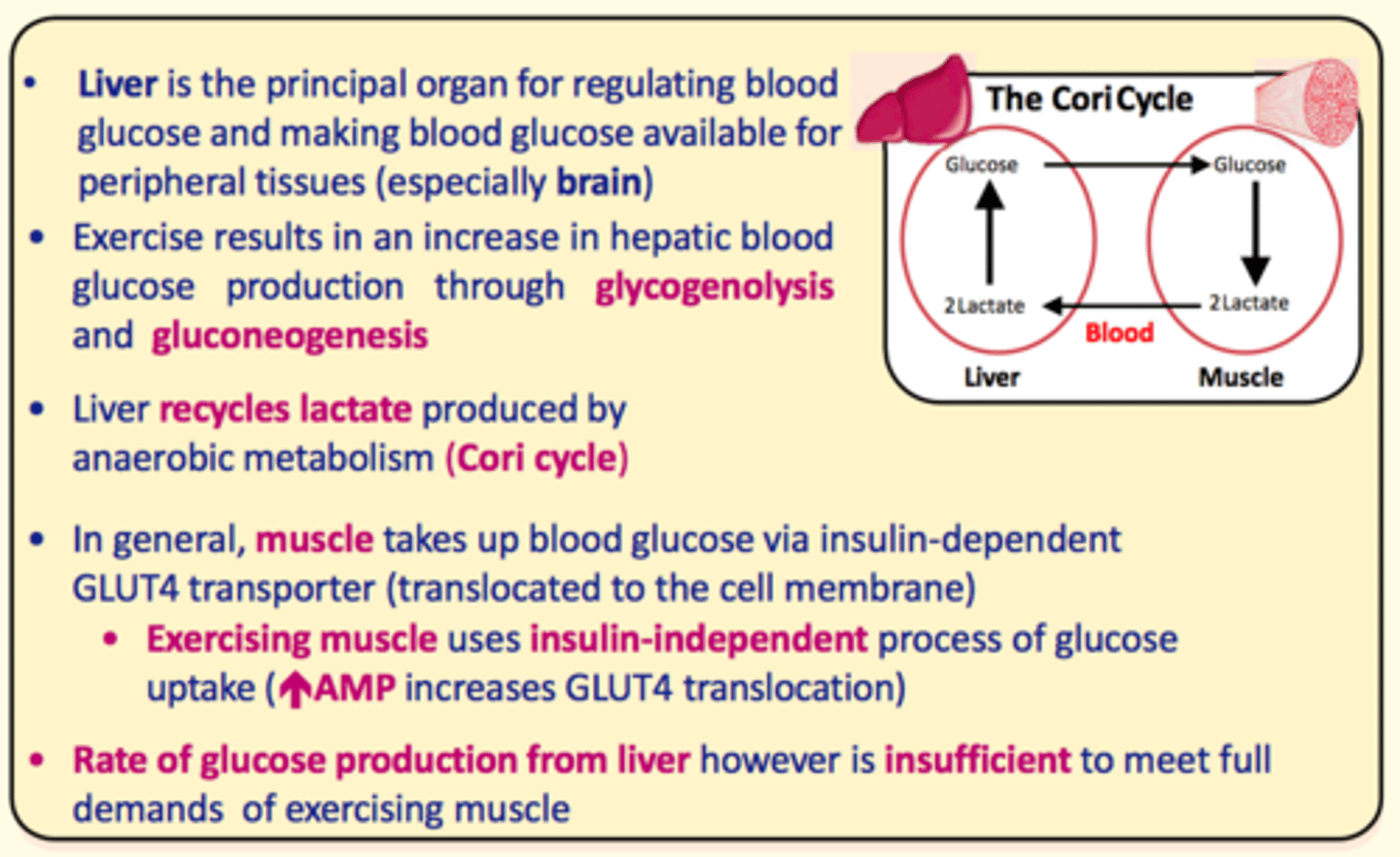
Exercising muscle uses insulin-___ process of glucose uptake
independent
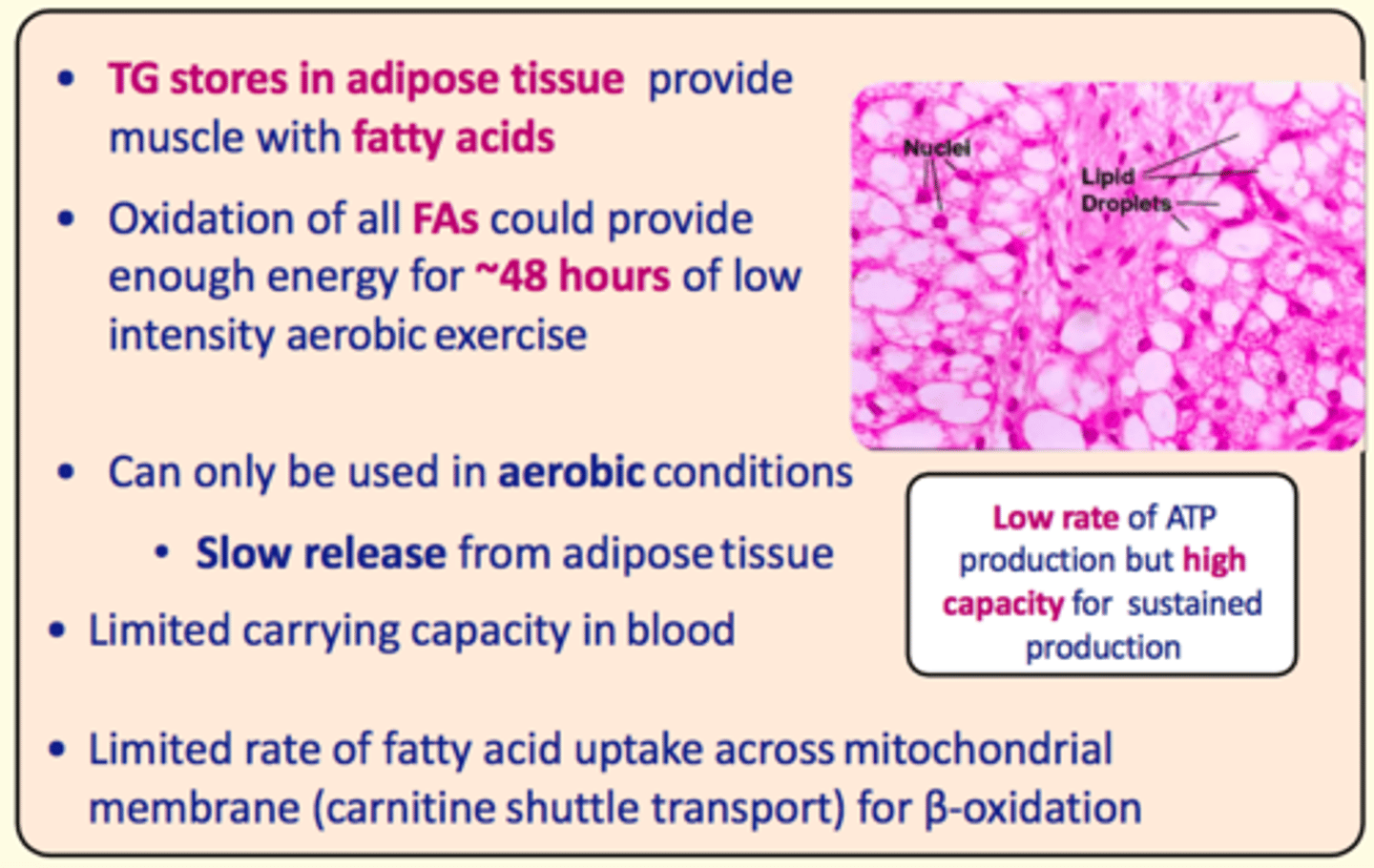
___ stores in adipose tissue provide the muscle with ___ acids
Triacylglycerol stores in adipose tissue provide the muscle with fatty acids
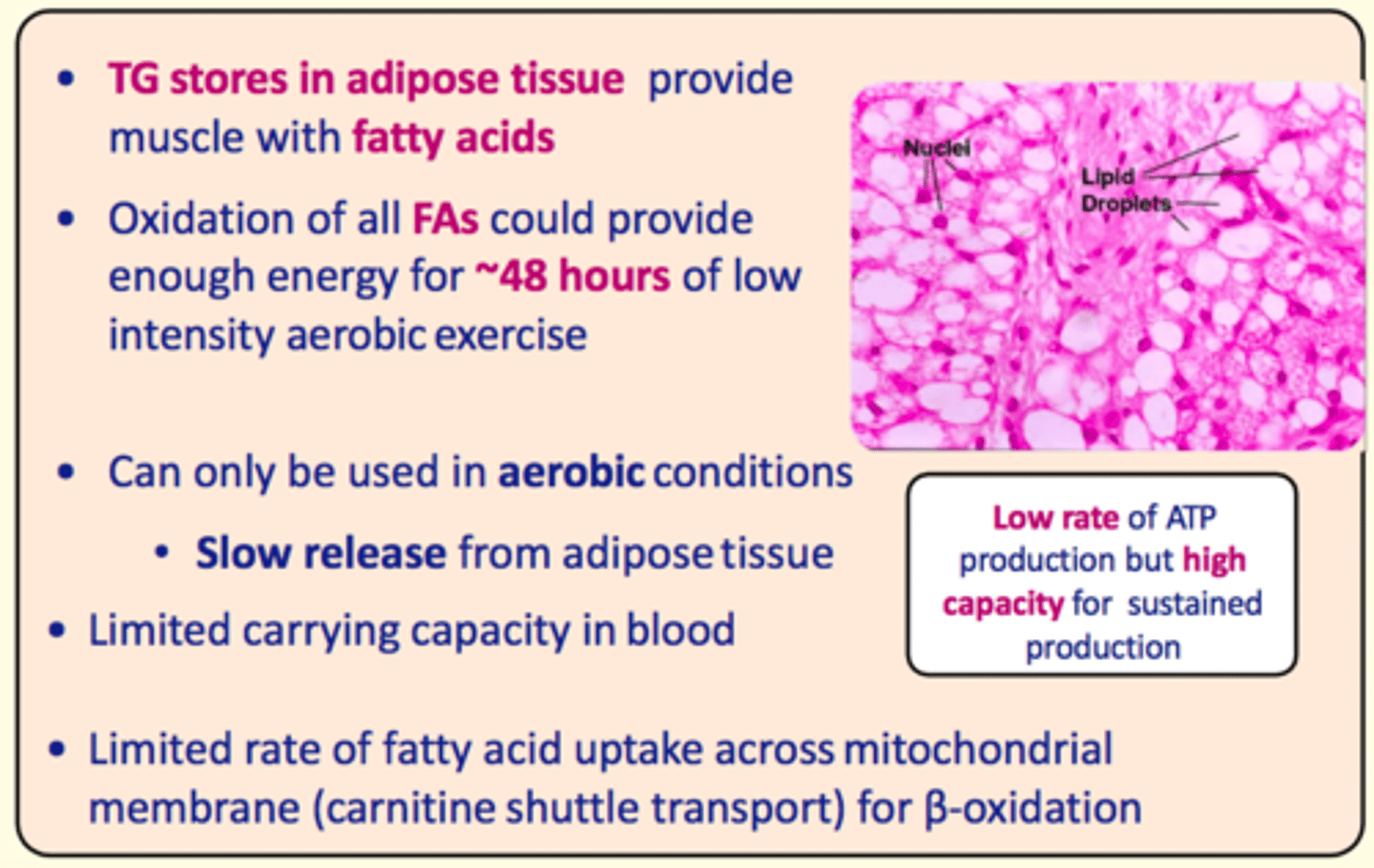
Oxidation of fatty acids could provide enough energy for up to...
~48 hours of low-intensity aerobic exercise
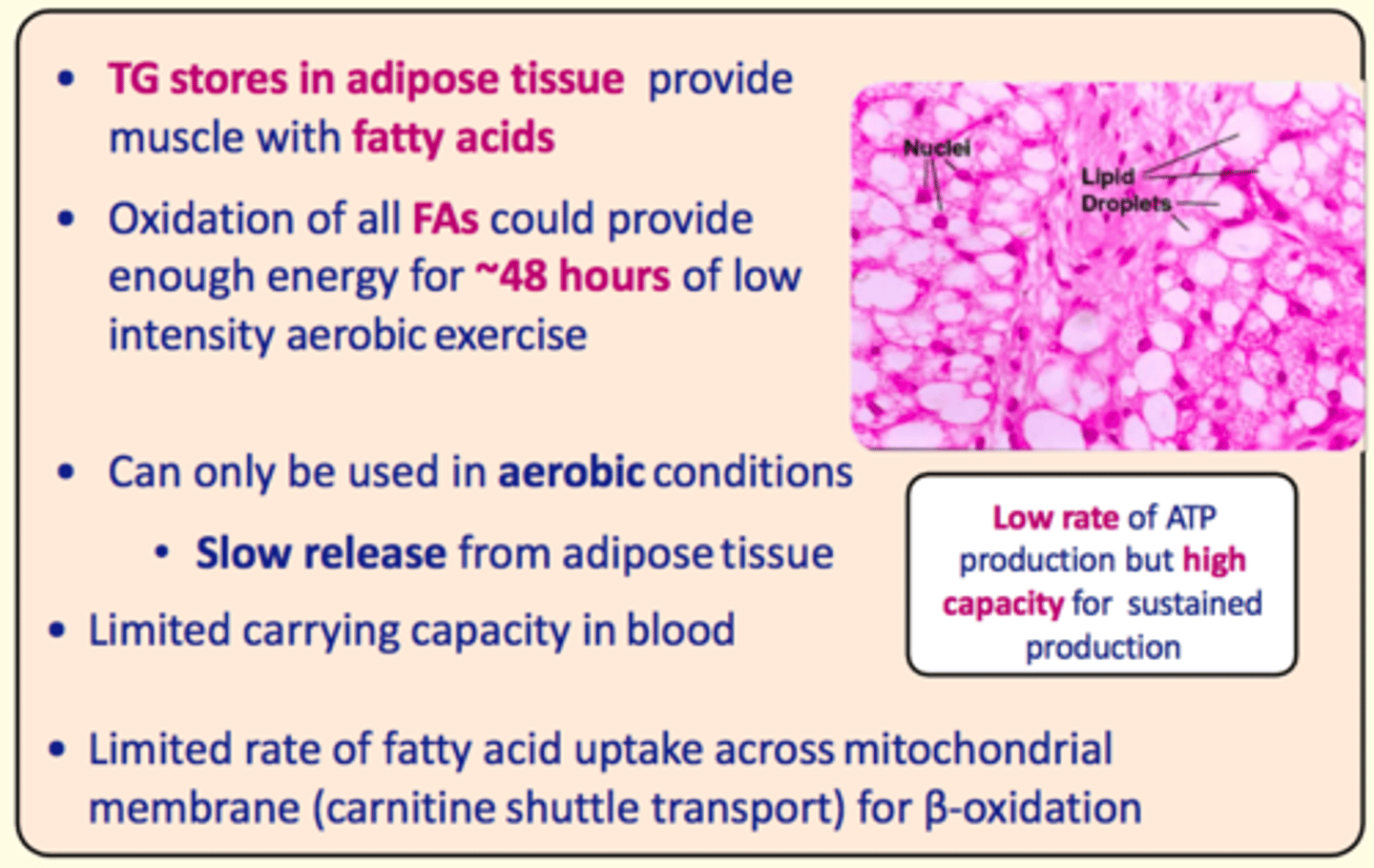
Pros of fatty acid metabolism in exercise
High capacity for sustained production
~48 hours of low-intensity aerobic exercise
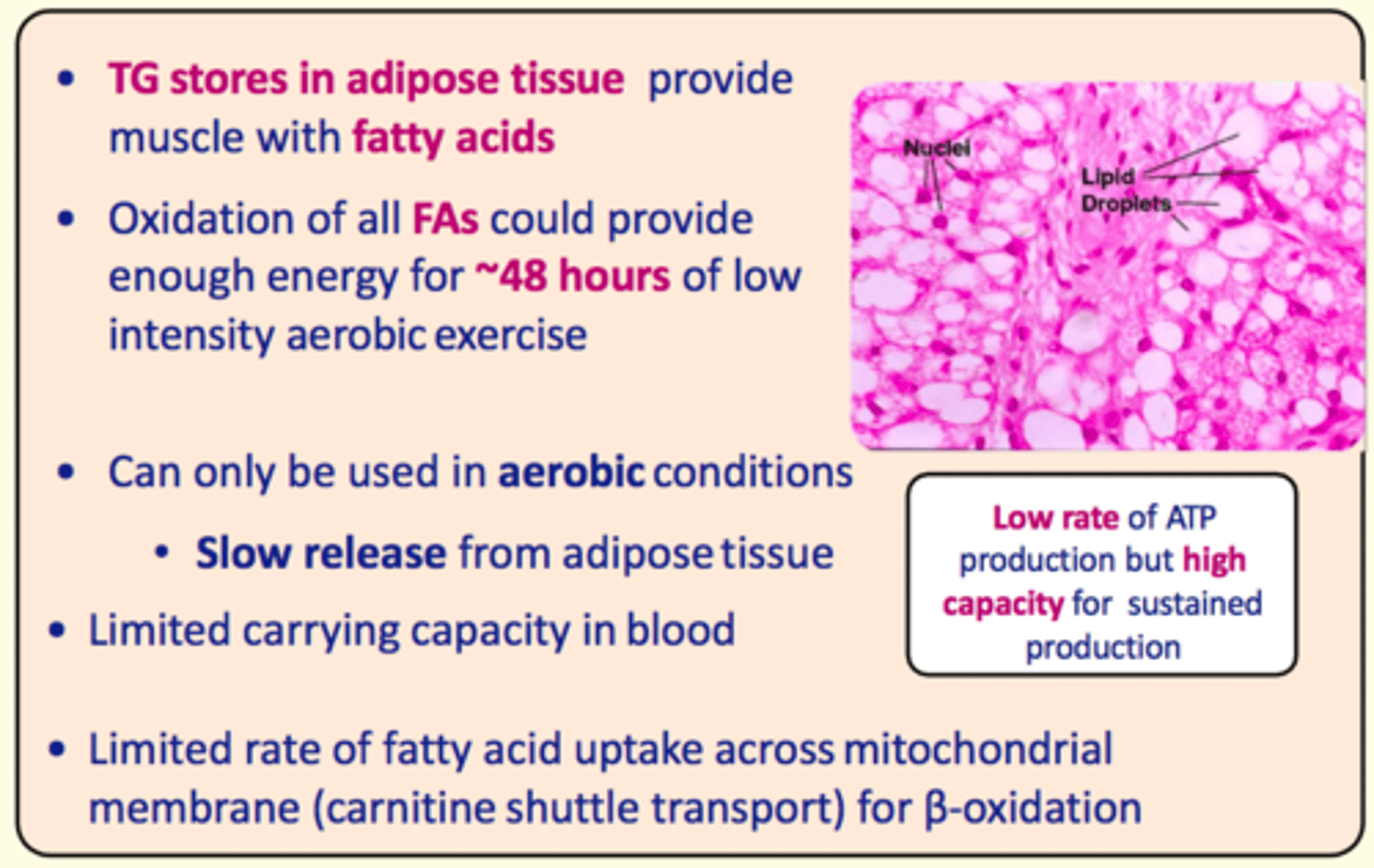
Cons of fatty acid metabolism in exercise
- Low rate of ATP production
- Can only be used in aerobic conditions
- Slow release from adipose tissue (not immediate)
- Limited carrying capacity in the blood
- Limited rate of FA uptake across mitochondrial membrane (carnitine shuttle transporter) for B-oxidation
100m sprint (short duration, high intensity)
Primarily anaerobic (cannot deliver sufficient oxygen to muscles in time)
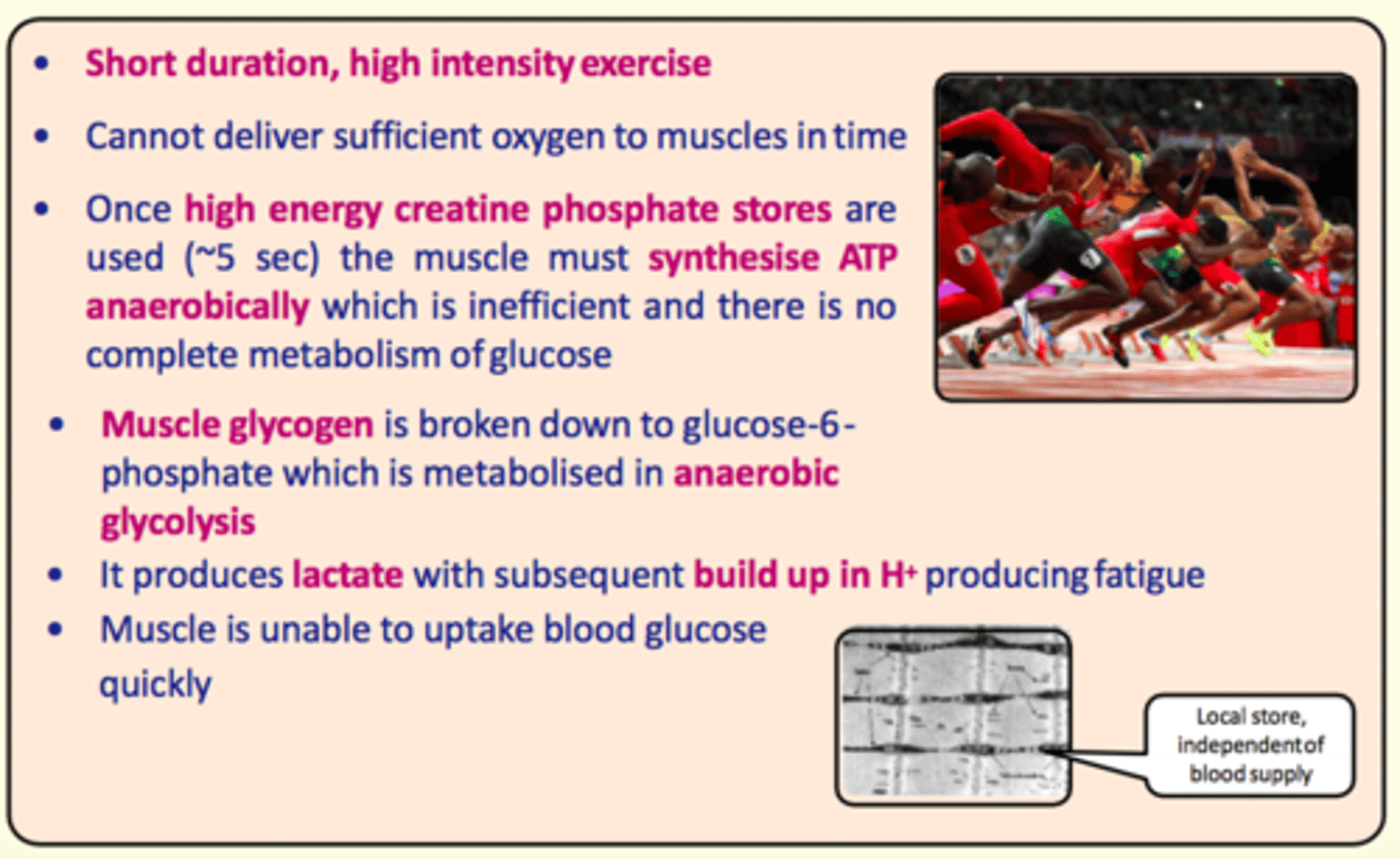
100m sprint energy sources
1) High-energy creatine phosphate stores (~5 seconds)
2) Muscle glycogenolysis to glucose-6-phosphate which is then metabolised in anaerobic glycolysis
3) Production of lactate from anaerobic glycolysis - build up of [H+] leading to muscle fatigue
![<p>1) High-energy creatine phosphate stores (~5 seconds)</p><p>2) Muscle glycogenolysis to glucose-6-phosphate which is then metabolised in anaerobic glycolysis</p><p>3) Production of lactate from anaerobic glycolysis - build up of [H+] leading to muscle fatigue</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8d8c7a9d-744a-47df-b2c8-3ff663f351a3.png)
1500m middle distance
Medium duration, medium intensity
~40% of metabolism is anaerobic
Remaining is aerobic via glucose and FA metabolism

Three phases of the 1500m middle distance exercise?
1) Initial start = muscle uses creatine phosphate & glycogen stores & glycolysis (anaerobic)
2) Long middle phase = ATP produced aerobically via glucose & FA oxidation
3) Final finishing sprint = anaerobic metabolism reliance again (muscle glycogen & glycolysis)

Marathon energy sources
95% aerobic metabolism using...
1) Glucose: muscle & liver glycogen
2) Fatty acid oxidation
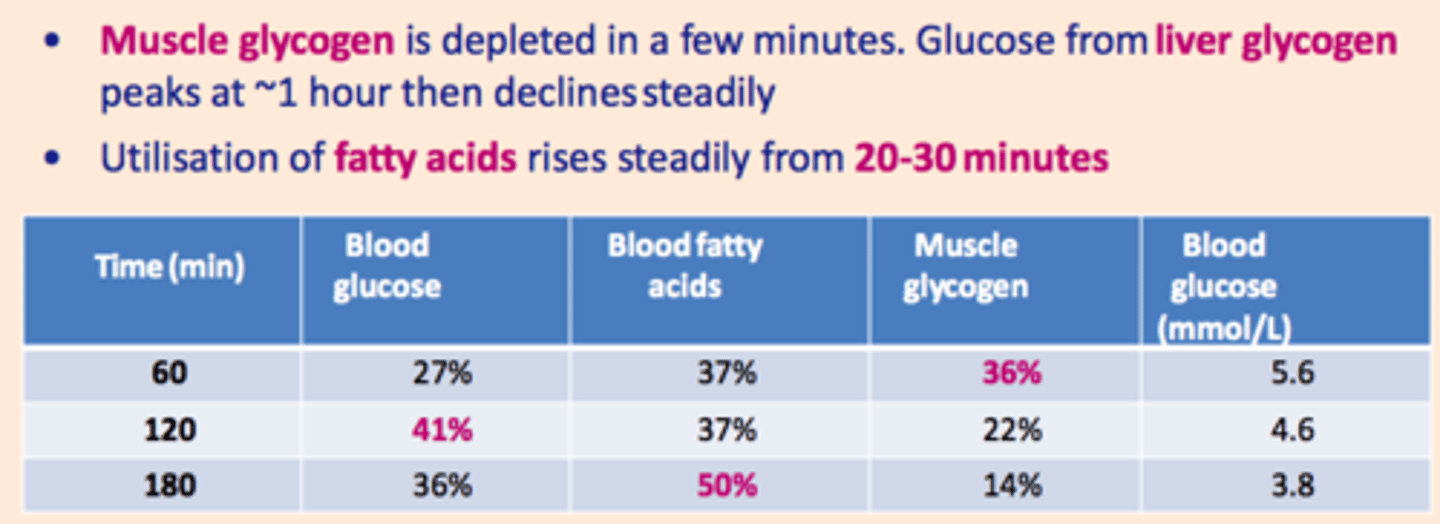
In the marathon... what is the order of energy source depletion?
1) Muscle glycogen depleted in minutes
2) Blood glucose from liver glycogen peaks at 1 hour
3) Use of fatty acids steadily increases from 20-30 minutes
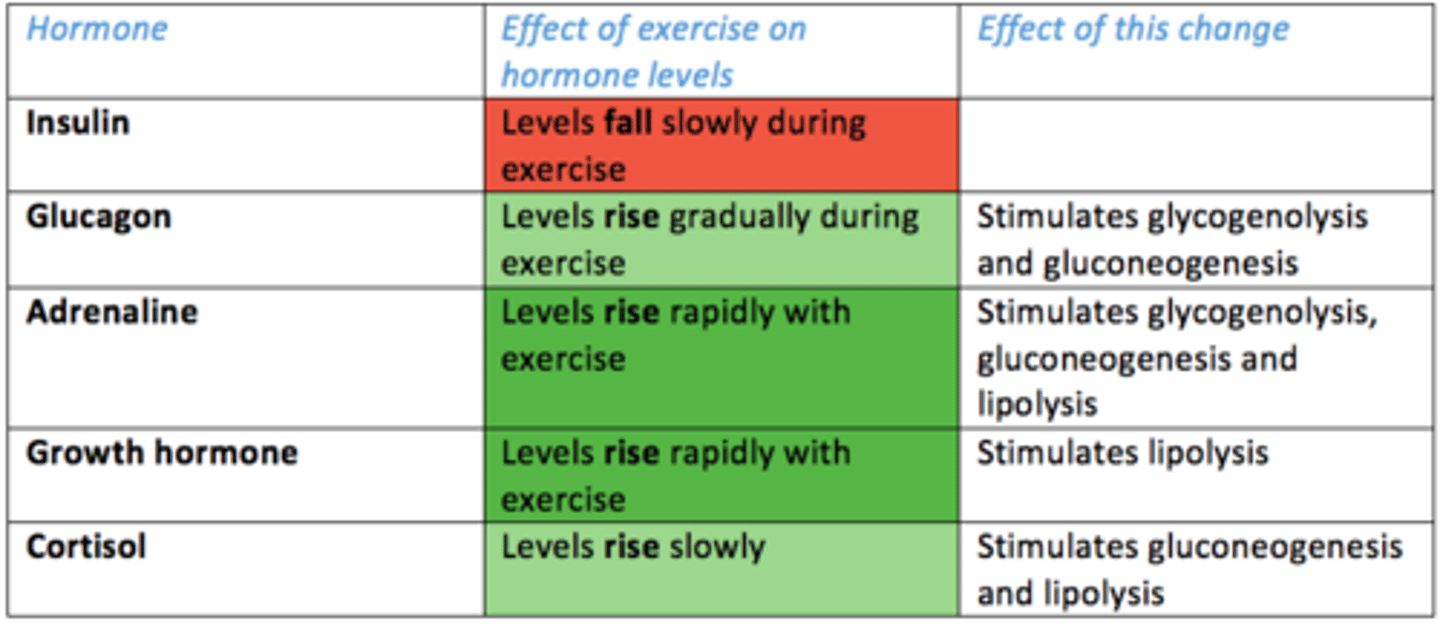
Hormones which control the metabolic response to exercise
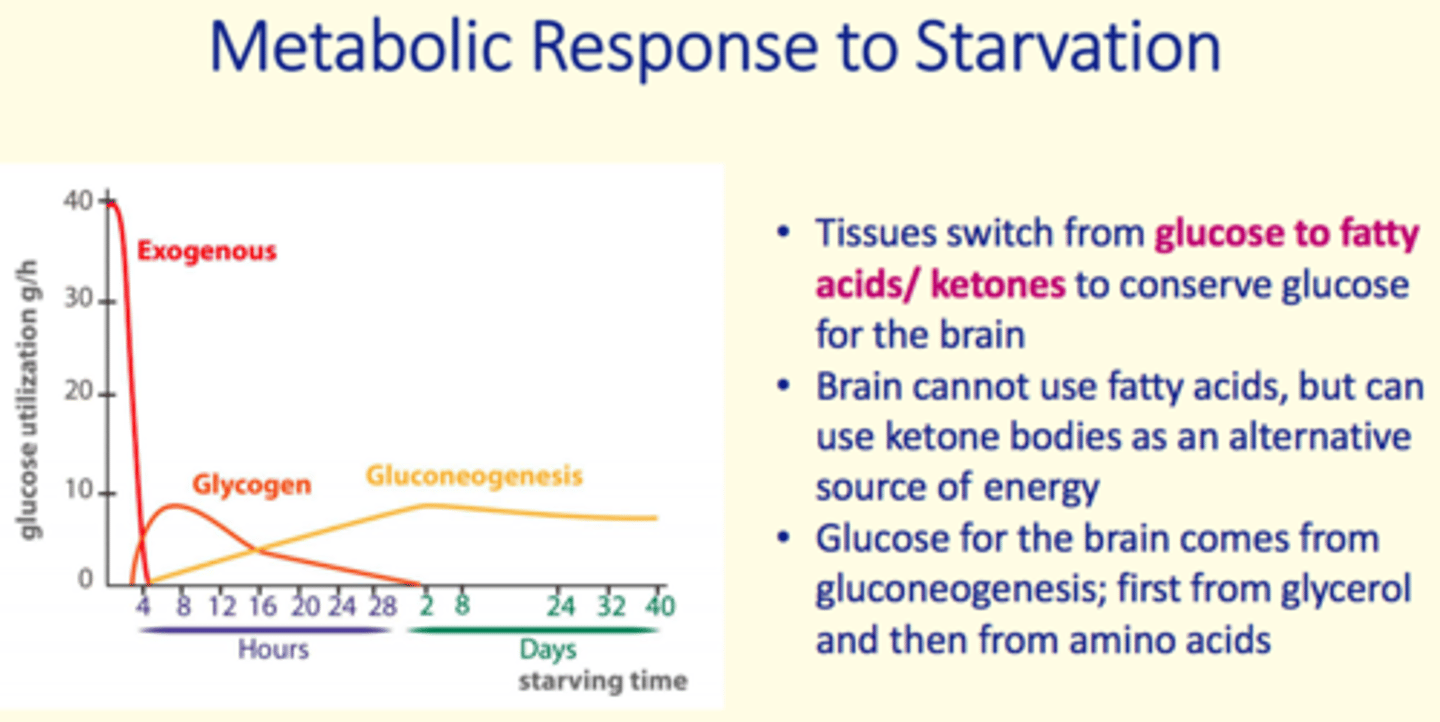
Why do tissues switch from glucose → fatty acid/ketone metabolism during starvation/fasting?
To conserve glucose for the brain
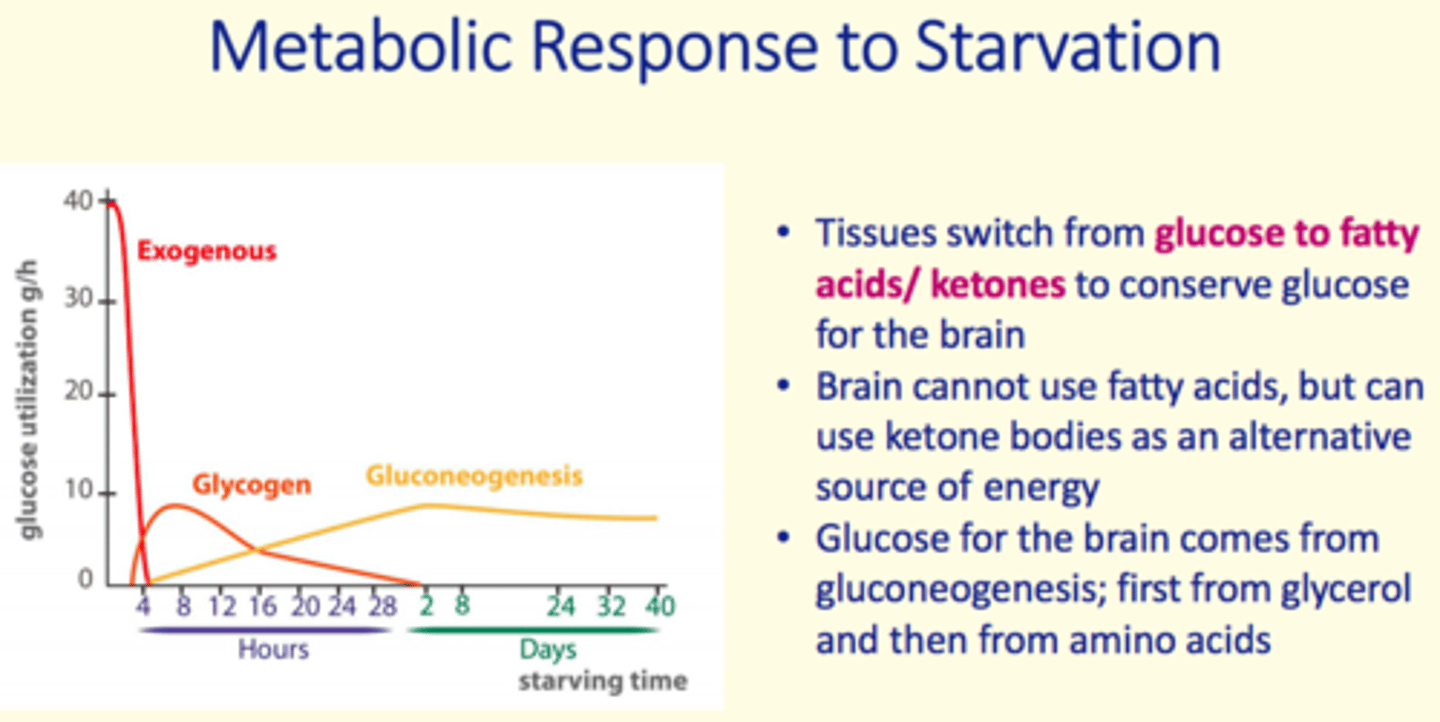
The brain ___ use fatty acids but __ use ketone bodies as an alternative source of energy
The brain cannot use fatty acids but can use ketone bodies as an alternative source of energy
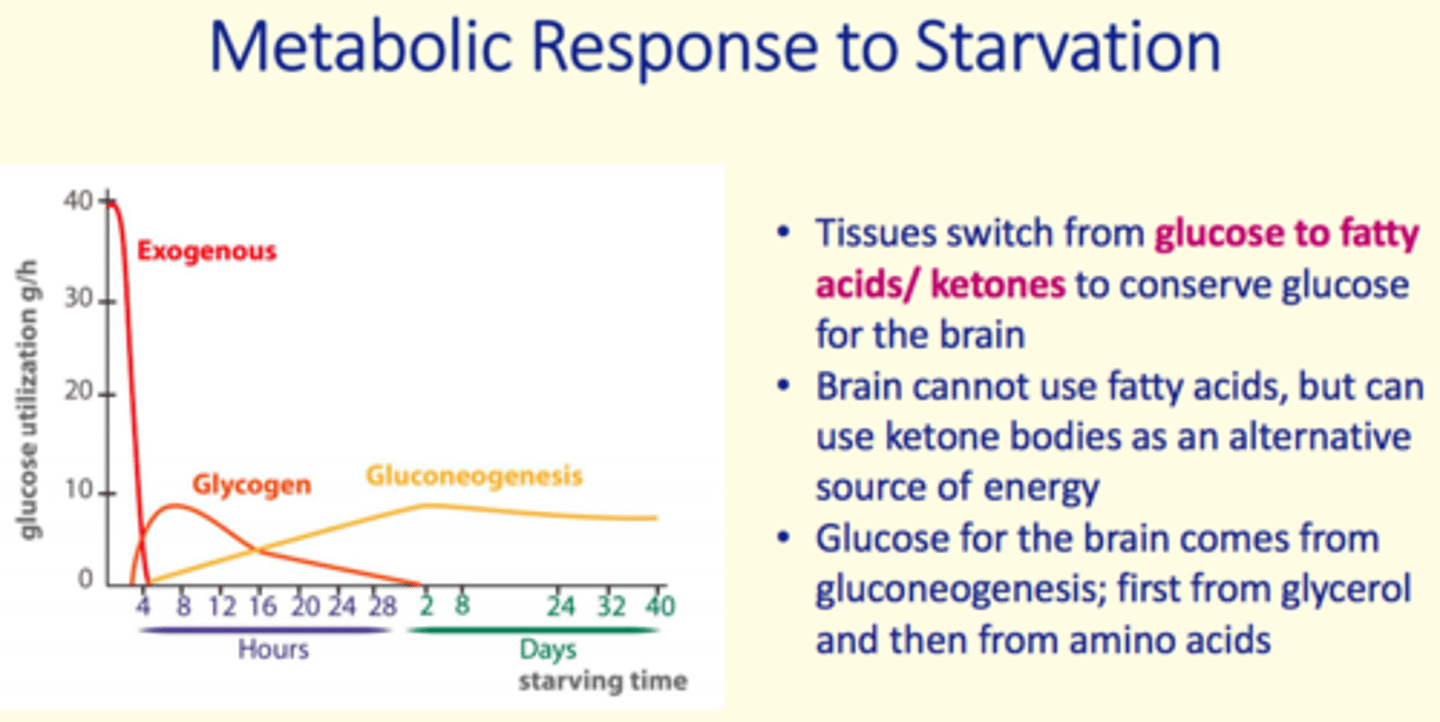
Glucose for the brain comes from...
Gluconeogenesis
1) From glycerol
2) From amino acids
Name a state in which insulin sensitive tissues do not respond well to insulin
Insulin resistance
Insulin sensitivity is decreased in early pregnancy
True or false?
False
What is a primary fuel for the foetus?
Glucose
What is the most likely metabolic pathway involved during short and intense exercise?
Glycogenolysis and glycolysis
Which ones of the following are the first fuels for exercising muscle during a sprint?
a) Muscle ATP and creatinine phosphate
b) creatinine phosphate and ketone bodies
c) Muscle ATP and creatine phosphate
d) Muscle ATP and fatty acids
c) Muscle ATP and creatine phosphate
During a sprint skeletal muscle works under anaerobic conditions and during a marathon run skeletal muscle works mainly under aerobic conditions
True or false?
True