Crisis Intervention Exam 3
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 7, 8, and 16
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
stress
a state of mental or emotional strain or tension resulting from adverse or very demanding circumstances
trauma
a deeply disturbing emotional shock following a stressful event
psychic trauma
the result of experiencing an acute overwhelming threat in which disequilibrium occurs
most people are
extremely resilient and will quickly return to a state of mental and physical homeostasis
acute stress disorder
when symptoms continue for a period of 2 days to 1 month and have an onset within 1 month of the traumatic event
if acute stress disorder symptoms develop, they will typically diminish in
1-3 months
hysterical neurosis
Freud called the condition that young Victorian women who had experienced childhood sexual abuse experienced
traumatized combat veterans (especially veterans of Vietnam) were said to have _ or _ when they showed effects of trauma without physical injuries
“shell shock” or “combat fatigue”
PTSD was introduced in the
3rd edition of the APA’s DSM (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual)
PTSD
a psychological disorder that’s triggered by a terrifying event
symptoms of PTSD may include
flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety. as well as uncontrollable thoughts about the event
criteria for diagnosis. the person was exposed to…
death, threatened death, actual or threatened serious injury, or actual or threatened sexual violence
4 major symptom clusters for PTSD
re-experiencing the event, heightened arousal, avoidance, and negative thoughts, mood, or feelings
symptoms of PTSD must be present for at least
1 month
PTSD preschool subtype
used to diagnose PTSD in children younger than 6 years old
PTSD is now developmentally sensituve, meaning that
diagnostic thresholds have been lowered for children and adolescents
PTSD dissociative subtype
diagnosed when PTSD is seen with prominent dissociative symptoms. these dissociative symptoms can be either experiences of feeling detached from one’s own mind or body, or experiences in which the world seems unreal, dreamlike, or distorted
_ to _% of children will experience at least 1 traumatic event by the age of 18
30-50%
_ to _% of boys will develop PTSD
3-16%
_ to _% of girls will develop PTSD
1-6%
nearly _ of children will develop PTSD if they see a parent killed or sexually assaulted
100%
nearly _ of children will develop PTSD if they are sexually assaulted
90%
nearly _ of children will develop PTSD if they witness a school shooting
77%
nearly _ of children will develop PTSD if they witness violence in their neighborhood
35%
diagnostic criteria for children
must experience disorganized or agitated behavior
may demonstrate regressive behaviors (i.e. bed wetting or thumb sucking)
may relive trauma through repetitive play
generalized nightmares (i.e. monsters)
may believe that they can see into the future
somatic complaints of headaches or stomachaches
type I trauma
sudden and distinct traumatic experience
type II trauma
long-term and persistent trauma. seems to change the personality of the sufferer
type II trauma 3 major symptoms
somatization (physical ailments)
dissociation (divisions of personality)
affect dysregulation (changes in impulse control, attention, perception, and significant relationships)
the Vietnam archetype
hyper-vigilance
lack of goals
individual/individualizer
bonding, debriefing, and guilt
civilian adjustment
substance abuse
attitude
antiwar sentiment
beginning treatment for PTSD
initiating intervention: victims may refuse early intervention because it’s too difficult to talk about the trauma and/or they believe that people of good character should be able to cope with traumatic events
importance of acceptance: disclosure is difficult because the events of the trauma may seem horrifying and socially unacceptable
grounding
a process by which the therapist refocuses the client’s attention to the current environment
cognitive processing therapy (CPT)
therapy designed to help individuals with PTSD by utilizing elements of CBT
3 phases of CPT
education regarding PTSD, thoughts, and emotions
formal processing of trauma
reinforce the skills
EMDR
form of psychotherapy developed by Francine Shapiro that emphasizes the role of distressing memories of PTSD. bilateral stimulation to mimic REM sleep to process memories. controversial
risks of PTSD treatment
no magical cures
intensity of treatment may impact occupations or relationships
may get worse before it gets better
re-experiencing the event is very painful
difficult to give up thoughts of revenge related to the trauma
pain associated with accepting the world as it is
difficult to accept one’s own limitations
multiphasic/multimodal treatment
combining different therapeutic approaches to address various aspects of a condition
eclectic therapy
a flexible approach to therapy that draws on multiple theoretical orientations and techniques to tailor treatment to each individual's unique needs
instrumental acts of lethality
occur for a financial or concrete gain
expressive acts of lethality
attempt to reduce psychological pain
suicide
the act or an instance of taking one’s own life voluntarily and intentionally
women have a _ attempt rate of suicide
higher (3x men)
men have a _ completion rate
higher (3x women)
men tend to use more _ methods of suicide
violent (shooting, stabbing, or hanging)
women methods of suicide
drug overdose, cutting
suicide is related to _ and _
social support and marital status
one study found that half the subjects who had committed suicide were found to have
no close friends
_ have a higher suicide rate than married or cohabiting individuals
divorced people
long-term stressors can include:
serious illness (especially those which cause great pain or severe disability)
abusive environments from which there is little or no hope of escape
occupational stress (psychologists, psychiatrists, nurses, dentists, lawyers, unskilled laborers, etc.)
many suicide attempts are preceded by
changes in mood
the most common mood change that precedes suicide is a rise in
sadness. increased anxiety, tension, frustration, anger, or shame are also common
suicide attempts may ALSO be preceded by
shifts in patterns of thinking. individuals may see suicide as the only effective solution to their difficulties and often develop a sense of hopelessness
hopelessness
a pessimistic belief that their present circumstances, problems, or mood will not change
Eastern culture may see suicide as a means of
relieving dishonor, shame, or humiliation from oneself or one’s family
Western culture commonly sees suicide as
a sin
Schneidman’s cubic model (1987)
when all 3 elements of the cubic model (psychache, pertubation, and press) occur, the individual experiences a critical mass that will allow suicide to occur
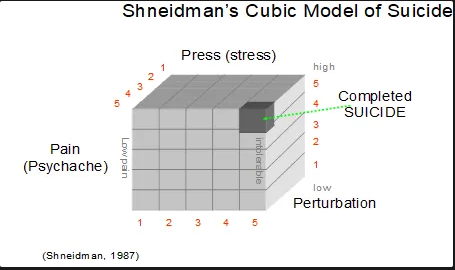
psychache
the hurt, anguish, soreness, and aching pain of the psyche or mind
pertubation
how disturbed one is and the degree of pain
press
stress due to negative factors piling up
Durkheim’s social integration theory (1897)
societal integration and social regulation are major determinants of suicidal behavior
societal integration
the degree to which people are bound together
social regulation
the degree to which the individual’s desires and emotions are regulated by social norms
4 types of suicide
egoistic suicide: related to one’s lack of integration or identification with a group
anomic suicide: related to perceived breakdown of the norms of a society (i.e., the financial ruin of the Great Depression)
altruistic: related to perceived social solidarity (i.e., suicide bombers)
fatalistic: occurs when a person sees no way out of an intolerable or oppressive situation (i.e., being confined to a concentration camp)
Schneidman’s 6 most common characteristics that are present when an individual attempts suicide
situational, motivational, affective, cognitive, relational, and serial
_% of murderers committed suicide after completing a homicide
30%
homicide followed by suicide is most likely to occur in these situations
elderly couples, domestic violence, infanticide by overwrought parents, and mental illness
nearly all suicidal/homicidal people offer
some kind of clues (verbal, behavioral, situational, or syndromic)
MMPI-2 (Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory-2)
Robust Personality Inventory that detects the presence of common mental disorders as well as suicidal intent
Beck Depression Inventory
brief scale designed to detect the presence of depression
SAD PERSONS scale
brief scale designed to detect the presence of lethality
CAMS Suicide Status Form
clinical interview template that focuses on ascertaining lethality
intervention goal, change at least one of the 3 “I’s”
inescapable, intolerable, interminable (endless)
CBT techniques are commonly used for suicide intervention, such as
cognitive restructuring, emotional regulation, and changing destructive behaviors through psychoeducation
“no harm” contracts
involves having the client sign a contract to do no harm before the next session. controversial
psychological autopsy
an examination of detailed post-mortem mental histories following suicides or deaths where the cause of death was uncertain
analyzing suicide notes
not commonly left. 4 categories:
problems are not of their own making but they know what they’re doing
incurable physical or mental illness that has drained all strength
love scorned and the note is directed toward the significant other
“last will and testament” with instructions but little insight for motivation
helping professionals are _ for burnout
prime candidates
recipe for burnout
high levels of motivation, idealistic, and expectation that their work will give their life a sense of meaning
burnout
physical or mental collapse caused by overwork or stress
burnout consists of
lost energy to the point of exhaustion
lost enthusiasm to the point of absolute indifference
passion is replaced by cynicism
complete lack of confidence that your work is having any positive impact
stages of burnout
enthusiasm
stagnation
frustration
apathy (lack of caring)
typical MO of burnout is to
increase effort (actually increases the problem) rather than attempting to change the situation
countertransference
the attributing to the client, by the crisis worker, of traits and behaviors of past and present significant others or events in the crisis worker’s own life
vicarious traumatization
a transformation that occurs when an individual begins to change in a manner that mimics a client’s trauma-related symptoms
compassion fatigue (secondary traumatic stress disorder)
a phenomenon where the crisis worker has symptoms similar to PTSD, except that the exposure is to the person relating the event and not the event itself
people are able to prevent or recover from burnout when they have
meaningful relationships with friends, family, and coworkers
_ is essential to preventing burnout
self-care. this entails hobbies, friendships, time to oneself, eating well, and working manageable hours
private practitioner
a clinician creates a business where he/she offers mental health services
factors that increase the chance of burnout among clinicians in private practice
isolation - crisis workers in private practice experience more isolation due to not having coworkers that have downtime to discuss issues
business concerns - financial, client base, marketing services
maintaining a public presence - clinicians in private practice must constantly maintain a public practice to ensure new clients see them as a viable option
difficult work schedules - evenings, weekends, and few vacations
mass violence
an intentional violent criminal act that results in physical, emotional, or psychological injury to a sufficiently large number of people
a mass shooting occurs in the US every
12 1/2 days
5 types of violence typology (mass shootings)
criminal intent, customer/client, worker-on-worker/student-on-student, intimate partner, ideological violence
affective characteristics of mass shooting perpetrator
lack of empathy coupled with aggression
lack of remorse for wrongdoing
shallowness of emotions
cognitive characteristics of mass shooting perpetrator
projection of blame on others
extremely egocentric, narcissistic
intense sense of entitlement or injustice
behavioral characteristics of mass shooting perpetrator
slick, manipulative, pushy
does not read or respond well to social cues
3 phases for mass violence survivors
acute, intermediate, and long-term phases
unique challenges for mass shooting survivors
the attack may have occurred in an environment they will frequent often
media coverage can be a reminder of the attack
resilience
the ability to successfully adapt to stressors, maintaining psychological well-being in the face of adversity
ASD prevalence after a mass shooting event at rates ranging from _ to _%
7 to 33%
there is a _% chance of meeting the criteria for PTSD months after a mass shooting
30%