Week 3 – Mathematics as a Language
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bachelor of Science in Medical Technology (1st Year): MATHEMATICS IN MODERN WORLD
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
a system of conventional spoken, manual (signed), or written symbols by means of which human beings, as members of a social group and participants in its culture, express themselves.
Language
Language itself is: (3)
Precise
Concise
Powerful
It can make very fine distinctions among set of symbols.
Precise
It can briefly express long sentences
Concise
It gives upon expressing complex thoughts
Powerful
“and” is equivalent to
Plus (+)
“is” may have
different meaning
ones used for counting
“Cardinal numbers”
ones used for telling positions
“Ordinal numbers”
used only as a name to identify something
“Nominal numbers”
Addition Key Words (+)
Increased by
More than
Combined, together
Total of
Sum, plus
Added to
Comparatives (Greater than, etc)
Subtraction Key Words (-)
Decreased by
Minus, less
difference between/of
less than, fewer than
left, left over, after
save (Old fashioned term)
Comparatives (Smaller than, etc)
Multiplication Key Words (.) (x) ()
Of
Times, multiplied by
Product of
Increased/decreased by a factor of (this last type can involve addition or subtraction and multiplication)
Twice, triple, etc.
Each (They got three each, etc.)
Division Key Words (a/b) (a:b) (÷)
Per, a
Out of
Ratio of, quotient of
Percent (Divide by 100)
Equal pieces, split average
Equals Key Words (=)
Is, are, was, were, will be
gives, yields
sold for, cost
For the set of natural numbers
N
Ex: N= {x/x = 1,2,3, 4...}
For the set of integers
Z or I
Ex: Z or I = {x/x = 1, -1,1,2, -2,3, -3,}
For the set of all positive integers
Z⁺ or I⁺
For the set of all rational numbers
Q
Ex: Q = {x/x ∈ I or x = a/b, where b≠0}
For the set of all positive rational numbers
Q⁺
For the set of irrational numbers
P
Ex: P = {x/x ∉ Q}
For the set of all real numbers
R
R = {x/x ∈ Q or P}
Students can connect one number with one object then count them with understanding.
One-to-one Correspondence
Tells how many things are in a set.
When counting a set of objects, the last word in the counting sequence names the quantity for that set.
Cardinality

A set S having all its elements as sets is called _____
For example:
S = { {1, 2}, {2, 4}, {3, 5, 7} }
Set of sets
Two finite sets A and B are equivalent if their cardinal number is same, i.e., n(A) = n(B).
Equivalent sets
Two sets A and B are said to be equal if every element of A is a member of B, and every element of B is a member of A.
Equal sets
Any set of ordered pairs
Relation
A type of relation where there is exactly one output for every input.
For every x there is exactly one y.
Function
serves as a set of rules that govern the structure and presentation of mathematical proofs.
It allows us to determine the validity of arguments in and out of mathematics.
A proposition is a statement that is, by itself,
either true or false. They can be expressed in
symbols P, Q, R, or p, q, r.
Logic
means single idea statement
Simple
conveys two or more ideas
Compound
is a statement that is either true or false, but not both.
Proposition
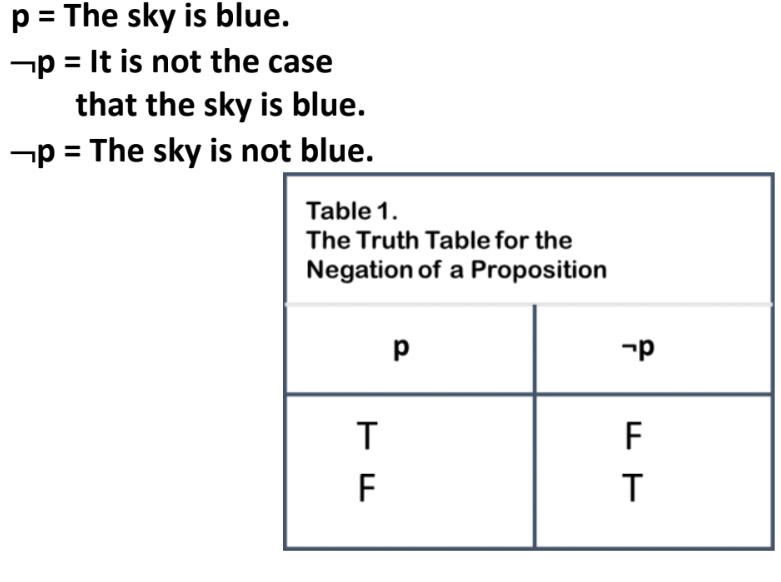
Let p be a proposition. The statement “It is not the case that p” is also a proposition, called the _______, or ¬p (read “not p”)
Negation of p
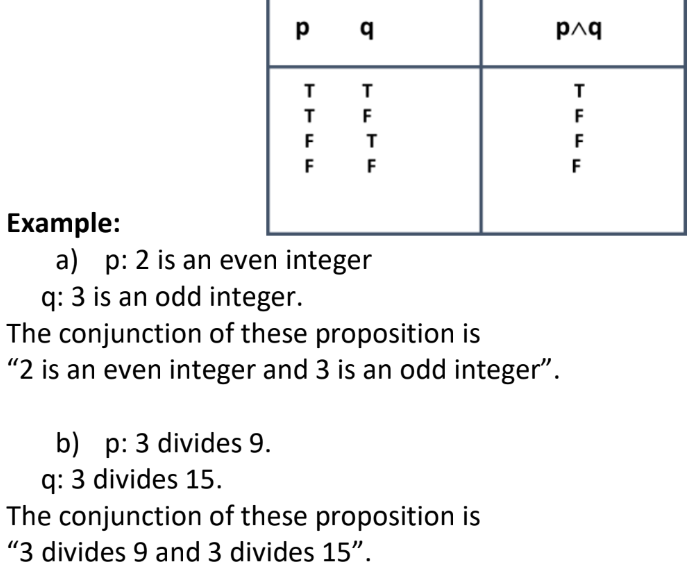
Let p and q be propositions. The proposition “p and q,” denoted by pq is true when both p and q are true and is false otherwise.
Conjunction of p and q
Let p and q be propositions. The proposition “p or q,” denoted by pq, is the proposition that is false when p and q are both false and true otherwise.
Disjunction of p and q

Let p and q be propositions. The implication p→q is the proposition that is false when p is true and q is false, and true otherwise. In this implication p is called the hypothesis (or antecedent or premise) and q is called the conclusion (or consequence).
Implication p→q
