Biology midterm one grade 12 integumentary system
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
The skin is made up of four types of tissues:
1- Epithelial tissue: cover the body surface .
2-Connective tissue :supports and protects.
3-Muscle tissue :enables movement.
4-Nerve tissue :is the body’s communication network
The skin has two main
layers :
Epidermis
2-dermis
The outer layer of the skin is the epidermis which consists of
a thin layer of epithelial cells:
The outer layer of epidermal cells contain
Keratin
Keratin is
Keratin : is a protein that waterproofs and protects the
cells and tissues below.
The inner layer of epidermal cells continually divide by
mitosis to replace the cells that are shed ,and produces a
pigment called
Melanin
Melanin…
Melaninprotects deeper cells from damaging effects of
ultraviolet rays of sunlight, the amount of melanin produced
determines skin color.
The dermis is made up of ….. tissue which
prevents the skin from tearing and enables the skin to
its normal state after it is stretched.
connective
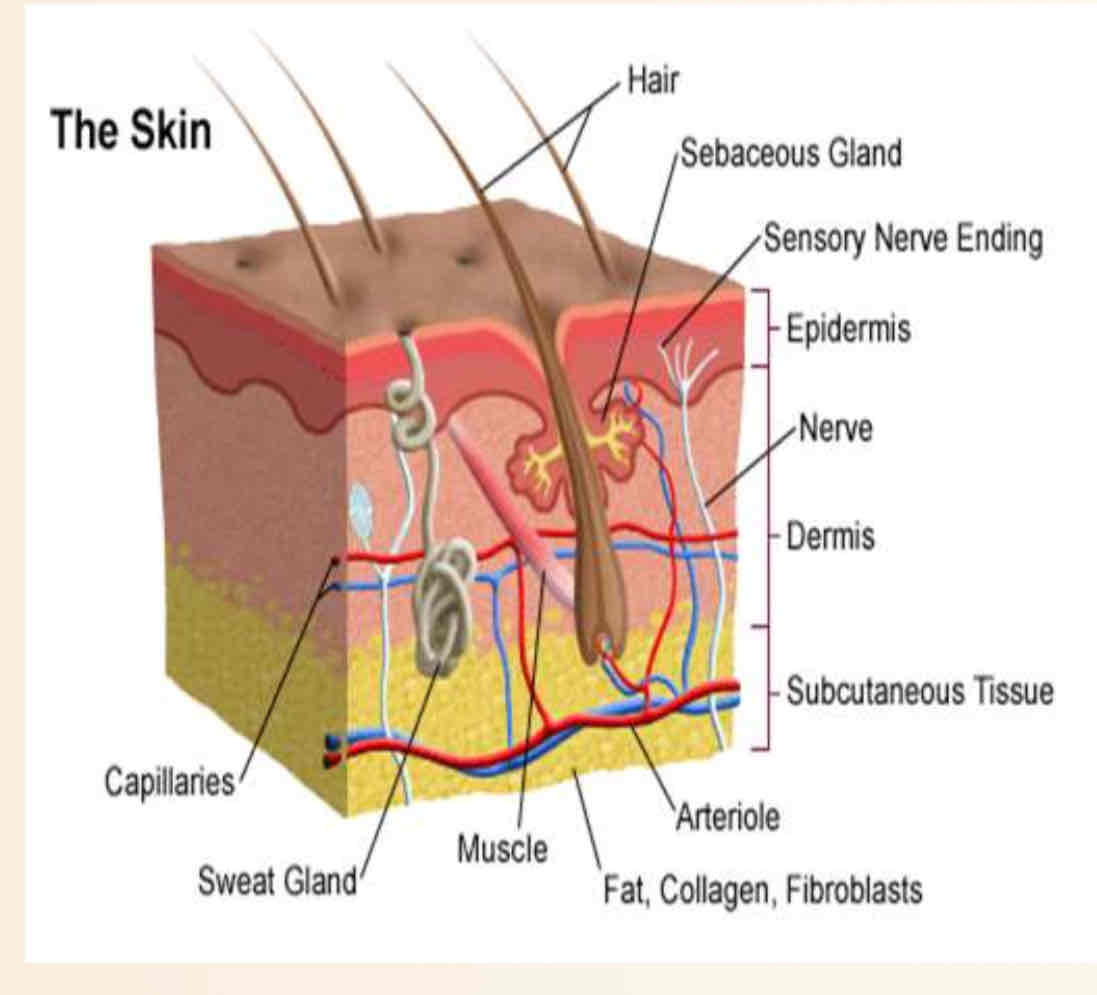
The dermis contains:
1- Nerve cells
2- Muscle fibers
3- Sweat glands
4- Oil glands sebaceous gland
5-Hair follicles
Note
Hair follicles :holes in the dermis from which Hair cells grow out of .
Cells at the base of a hair follicle divide and push cells away from the
follicle. This causes hair to grow
Just note
Around the hair follicles are sebaceous glands:
These oil-producing glands lubricate skin and hair.
When glands produce too much oil, the follicles can
become inflamed and blocked. This can result in a
whitehead, a blackhead, or acne—an inflammation of
the sebaceous glands
Note
Skin regulates body temperature so when you’re cold… when yours hot
When you are cold, your muscles contract causing goose bumps. In animals, these
contractions cause hair to stand up and trap air to warm the animal. With little hair to
keep us warm, humans depend on fat in the subcutaneous layer for warmth
When you are hot, your body sweats. The evaporation of sweat cools your body.
Evaporation transfers heat energy from your body to your surroundings
Skin has an important role in vitamin D production
Skin responds to exposure to the Sun's
ultraviolet rays by producing vitamin D.
Vitamin D helps the body absorb
calcium and is essential for proper bone
formation
Skin protects our bodies, and helps us sense our surroundings
Unbroken skin keeps microorganisms out of the body.
• Skin helps maintain body temperature by preventing the loss of too much
water.
• Melanin protects from ultraviolet rays.
• Nerves in the skin relay messages about changes in the environment to the
brain. The nerves make a person aware of pain, pressure, and changes in
temperaturE
Skin serves several important functions:
1-It regulates body temperature.
2-produces vitamin D
3- protects our bodies, and helps us sense our surroundings
Damage to the Skin
Skin usually repairs itself. If it did not, the body could be
invaded by microbes through breaks in the skin.
- For minor scrapes, epidermal cells divide and replace
the injured cells.
- Deeper injuries that harm blood vessels result in bleeding.
Blood clots form a scab to close the wound. Cells beneath
the scab
divide and fill the wound, while blood cells help fight infections
How does the
ultraviolet radiation of
the sun affect the skin?
Can cause skin cancer or skin burn
Degrees of skin burn
First-degree burns :only
involve epidermal cells.
2. Second-degree burns: damage
both dermis and epidermis,
causing blisters and scars.
3. Third-degree burns: damage
muscle
tissue and nerve cells in both
layers, and skin function is lost
Skin cancer due to uv rays
Ultraviolet radiation
can damage DNA in skin cells, causing those cells to
divide uncontrollably.
This gland releases an oil
known as sebum.
Sebaceous gland
The skin has three layers
1- Epidermis
2-dermis
3-hypodermia
Skin
Skin
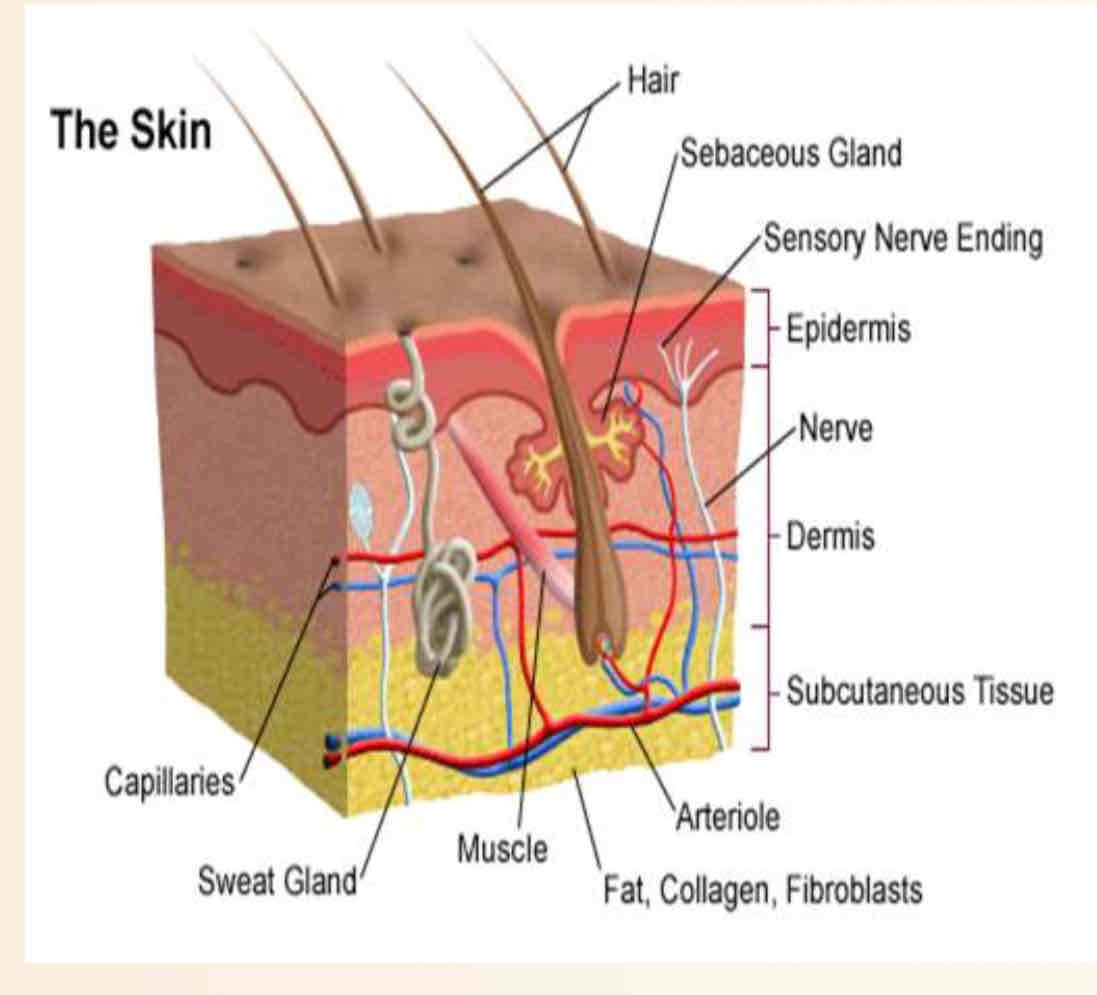
What layer of skin produces melanin?
Inner layer of epidermis