Medieval Europe: Late Antiquity, Byzantine, Early Medieval, Romanesque, Gothic
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
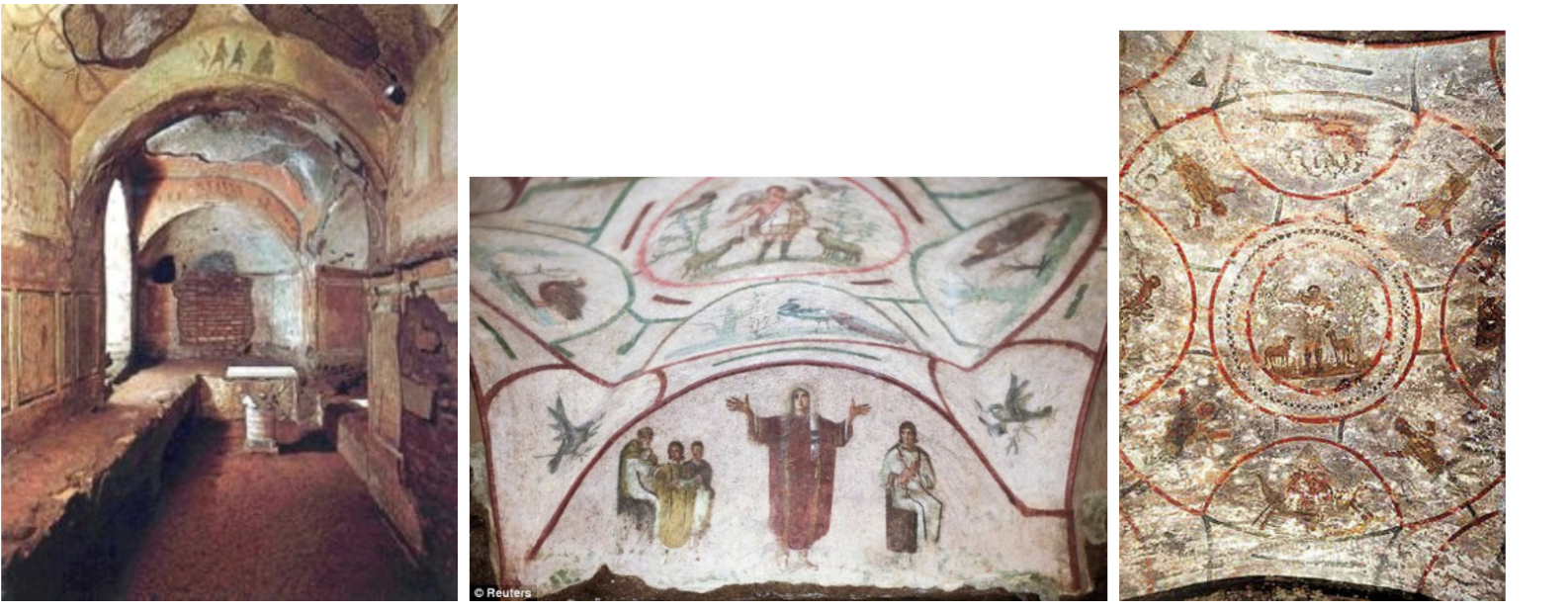

What is this?
Catacomb of Priscilla. Rome, Italy. Late Antique Europe. c. 200–400 C.E. Excavated tufa and fresco
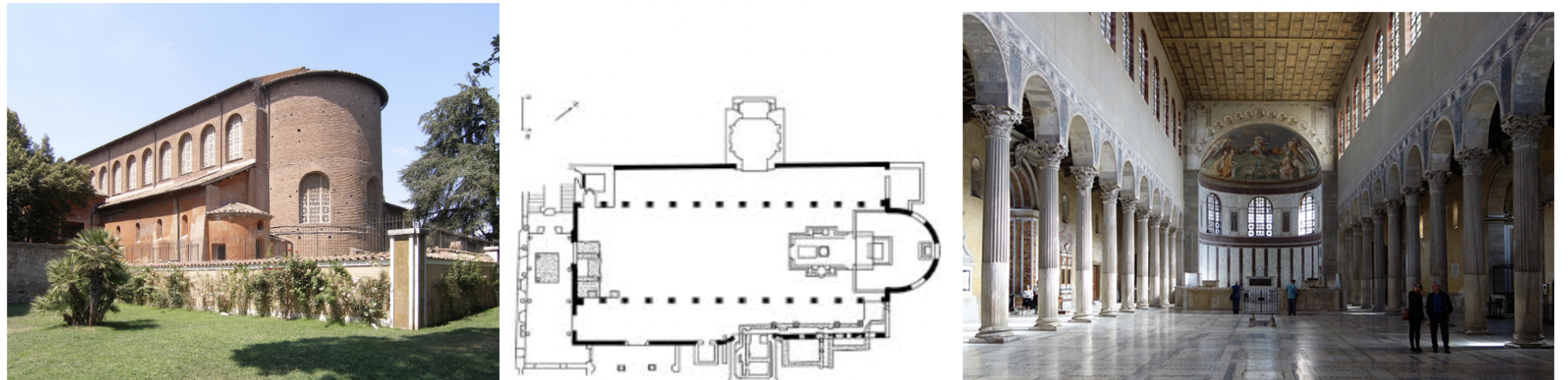
What is this?
Santa Sabina. Rome, Italy. Late Antique Europe. c. 422–432 C.E. Brick and stone, wooden roof.

What is this?
Rebecca and Eliezer at the Well and Jacob Wrestling the Angel, from the Vienna Genesis. Early Byzantine Europe. Early sixth century C.E. Illuminated manuscript (tempera, gold, and silver on purple vellum).
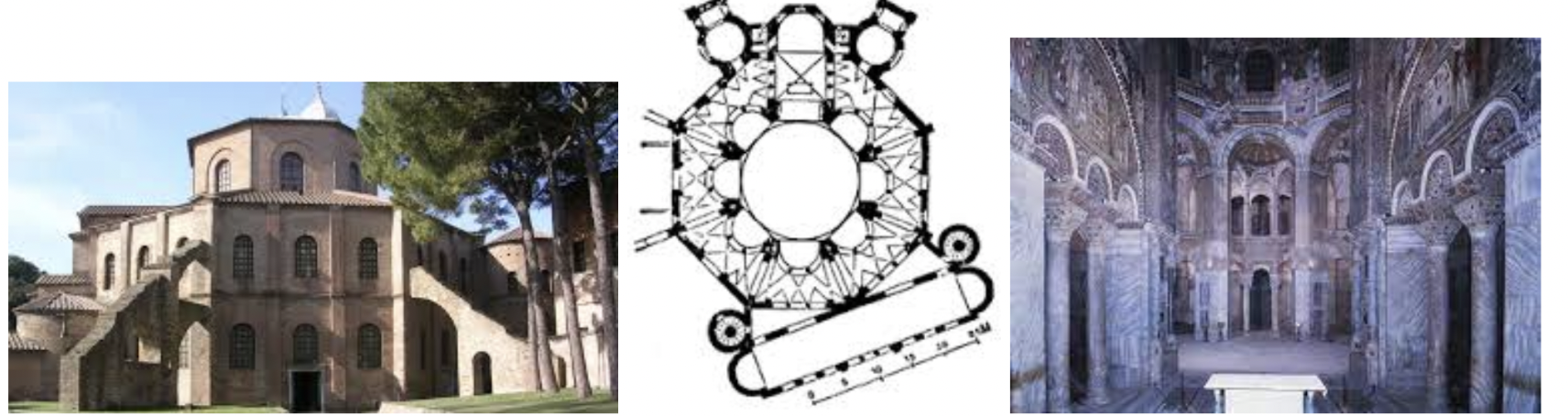
What is this?
San Vitale. Ravenna, Italy. Early Byzantine Europe. c. 526–547 C.E. Brick, marble, and stone veneer; mosaic.

What is this?
Hagia Sophia. Constantinople (Istanbul). Anthemius of Tralles and Isidorus of Miletus. 532–537 C.E. Brick and ceramic elements with stone and mosaic veneer
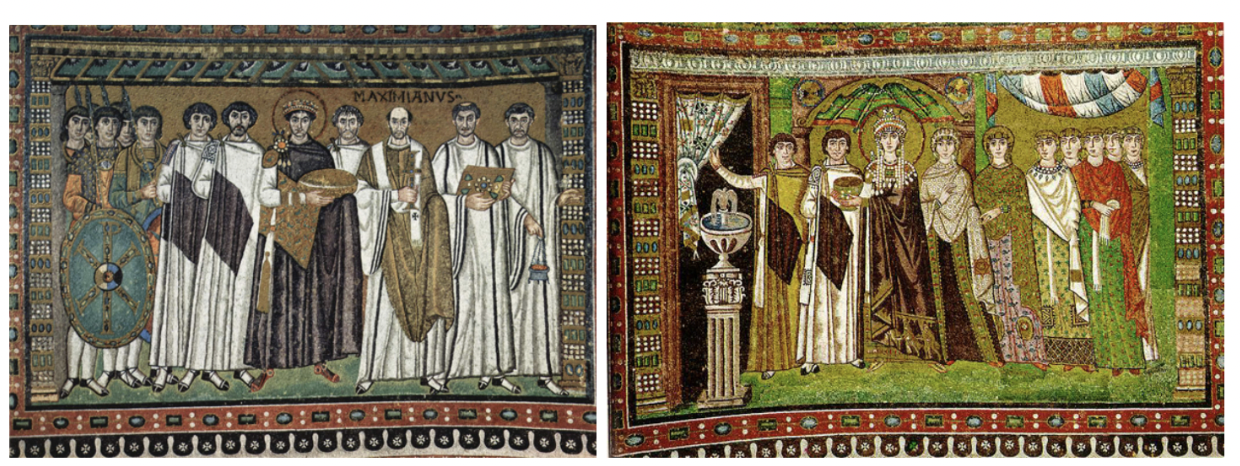

What is this?
Justinian and Theodora mosaics. Ravenna, Italy. Early Byzantine Europe. c. 526–547 C.E. Brick, marble, and stone veneer; mosaic.

What is this?
Virgin (Theotokos) and Child between Saints Theodore and George. Early Byzantine Europe. Sixth or early seventh century C.E. Encaustic on wood.

What is this?
Merovingian looped fibulae. Early medieval Europe. Mid-sixth century C.E. Silver gilt worked in fligree, with inlays of garnets and other stones.

What is this?
Lindisfarne Gospels : St. Matthew, cross-carpet page; St. Luke portrait page; St. Luke incipit page. Early medieval (Hiberno Saxon) Europe. c. 700 C.E. Illuminated manuscript (ink, pigments, and gold on vellum).

What is this?
Church of Sainte-Foy. Conques, France. Romanesque Europe. Church: c. 1050– 1130 C.E.; Reliquary of Saint Foy: ninth century C.E., with later additions. Stone (architecture); stone and paint (tympanum); gold, silver, gemstones, and enamel over wood.

What is this?
Tympanum. Conques, France. Romanesque Europe. Church: c. 1050– 1130 C.E.; Reliquary of Saint Foy: ninth century C.E., with later additions. Stone (architecture); stone and paint (tympanum); gold, silver, gemstones, and enamel over wood.

What is this?
Reliquary of Saint Foy. Conques, France. Romanesque Europe. Church: c. 1050– 1130 C.E.; Reliquary of Saint Foy: ninth century C.E., with later additions. Stone (architecture); stone and paint (tympanum); gold, silver, gemstones, and enamel over wood.

What is this?
Bayeux Tapestry . Romanesque Europe (English or Norman). c. 1066–1080 C.E. Embroidery on linen.

What is this?
Chartres Cathedral. Chartres, France. Gothic Europe. Original construction c. 1145–1155 C.E.; reconstructed c. 1194–1220 C.E. Limestone, stained glass.
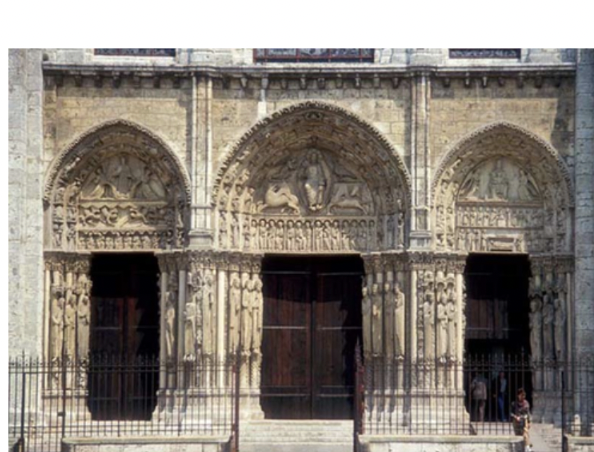

What is this?
Great Portal of the West Facade Chartres, France. Gothic Europe. Original construction c. 1145–1155 C.E.; reconstructed c. 1194–1220 C.E. Limestone, stained glass.

What is this?
Notre Dame de la Belle Verriere window. Chartres, France. Gothic Europe. Original construction c. 1145–1155 C.E.; reconstructed c. 1194–1220 C.E. Limestone, stained glass.

What is this?
Dedication Page with Blanche of Castile and King Louis IX of France, Scenes from the Apocalypse from Bibles moralisées . Gothic Europe. c. 1225–1245 C.E. Illuminated manuscript (ink, tempera, and gold leaf on vellum).

What is this?
Golden Haggadah (The Plagues of Egypt, Scenes of Liberation, and Preparation for Passover). Late medieval Spain. c. 1320 C.E. Illuminated manuscript (pigments and gold leaf on vellum).

What is this?
Arena (Scrovegni) Chapel, including Lamentation. Padua, Italy. Unknown architect; Giotto di Bondone (artist). Chapel: c. 1303 C.E.; Fresco: c. 1305. Brick (architecture) and fresco.

What is this?
Lamentation. Padua, Italy. Unknown architect; Giotto di Bondone (artist). Chapel: c. 1303 C.E.; Fresco: c. 1305. Brick (architecture) and fresco.

What is this?
. Röttgen Pietà . Late medieval Europe. c. 1300–1325 C.E. Painted wood.