1.3.2 databases
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
database
organised collection of data
allows for
adding
modifying
deleting
searching
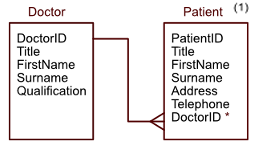
relational databases
link between tables that tells us how they are related to each other
flat file database
a database that consists of a single table
simple, quick to set up
the flat file will most likely be based around a single entity and its attribute
can become inefficient with lots of repetitive data
slow to query
take up lots of space
primary key
a primary key is a unique identifier for each record in the table
the unique identifier is the “ID” as this is always different for each row in the table
the primary key is shown by underlining it
foreign key
attribute which links two tables together
the foreign key will exist in one table as the primary key and act as the foreign key in another
secondary key
an additional attribute used for indexing records
allows a database to be searched quickly
the patient is unlikely to remember their patientID but will know their surname
therefore, a secondary index (secondary key) is set up on the surname attribute
this makes it possible to order and search by surname which makes it easier to find specific patients in the database
entity relationship modelling
One-to-one
each entity can only be linked to one other entity
One-to-many:
table can be associated with many other tables
Many-to-many:
entity can be associated with many other entities and the same applies the other way round

normalisation
the process of coming up with the best possible layout for a relational database
first normal form - normalisation
all field names should be unique (top of table going down)
values in fields should be from the same domain (same type)
values in fields should be atomic (1 value in each cell)
no two records can be identical
each table needs a primary key
second normal form - normalisation
data in 1NF
any partial dependencies have been removed (we only need one field to identify any record)
third normal form - normalisation
data is in 2NF
any transitive dependencies have been removed
remove non key dependencies (value of field is determined by he value of another field that isn’t the primary key)
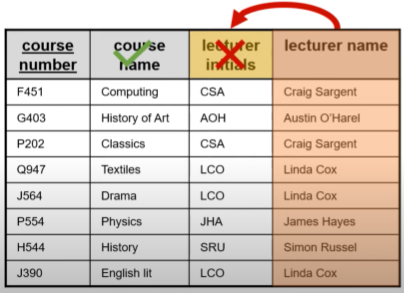
indexing
provides the position of each record according to its primary key
this is used to look up and access data quickly
the primary key is automatically indexed; however, the primary key is almost never queried since it is not normally remembered
this is why secondary keys are used
secondary keys are indexed to make the table easier and faster to search through on those particular attributes
capturing data
data needs to be input into the database and there are multiple methods of doing this
if pedestrians are participating in a survey, their responses will need to be manually entered into the database
Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR) - scan checks
Optical Mark Recognition (OMR) - multiple choice questions
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) - reads text by interpreting the shape of letters
selecting data
selecting the correct data is an important part of data pre-processing - SQL
this could involve only selecting data that fits a certain criteria to reduce the volume of input
for example, a camera catching speeding cars will only select cars going above a certain speed
abstraction
managing data
collected data can alternatively be managed using SQL to sort, restructure and select certain sections
exchanging data
the process of transferring the collected data
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange)
this doesn’t require human interaction and enables data transfer from one computer to another
XML, JSON - human readable open formats for structing data
CSV - comma separated values - each record stored on a separate line
what is SQL
Structured Query Language
declarative language used to manipulate databases
enables the creating, removing and updating of databases
SELECT, FROM, WHERE, ORDER BY - SQL
SELECT statement is used to collect fields from a given table and can be paired with the FROM statement to specify which table(s) the information will come from
WHERE statement can be used in conjunction to specify the search criteria
SELECT MovieTitle, DatePublished
FROM Movie
WHERE DatePublished BETWEEN #01/01/2000# AND #31/12/2005#
ORDER BY DatePublished;
ORDER BY - SQL
values are automatically placed in ascending order and adding ‘Desc’ to the end of statement will cause values to be displayed in descending order
ORDER BY DatePublished Desc
JOIN - SQL
JOIN provides a method of combining rows from multiple tables based on a common field between them
SELECT Movie.MovieTitle, Director.DirectorName, Movie.MovieCompany
FROM Movie
JOIN Director
ON Movie.DirectorName = Director.DirectorName
CREATE - SQL
allows you to make new databases
CREATE TABLE TableName
( Attribute1 INTEGER NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY, Attribute2 VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL, … )
Data Types - SQL
CHAR(n): this is a string of fixed length n
VARCHAR(n): this is a string of variable length with upper limit n
BOOLEAN: TRUE or FALSE
INTEGER/INT: integer
FLOAT: number with a floating decimal point
DATE: the date in the format Day/Month/Year
TIME: the time in the format Hour/Minute/Second
CURRENCY: sets the number as a monetary amount
ALTER - SQL
used to add, delete or modify the columns in a table
adding a column
ALTER TABLE TableName
ADD AttributeX and their dataTypes
deleting a column
ALTER TABLE TableName
DROP COLUMN AttributeX
modifying a column
ALTER TABLE TableName
MODIFY COLUMN AttributeX NewDataType
INSERT INTO - SQL
used to insert a new record into a database table
INSERT INTO (column1, column2)
VALUES (value1, value2)
UPDATE - SQL
used to update a record in a database table
UPDATE TableName
SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2
WHERE columnX = value
DELETE - SQL
used to delete a record from a database table
DELETE FROM TableName
WHERE columnX = value
referential integrity
the process of ensuring consistency in a database
this ensures that information is not removed if it is required elsewhere in a linked database
if two database tables are linked, one of these tables cannot be deleted as the other table requires its contents
transaction processing
a transaction is defined as a single operation executed on data
however a collection of operations can also sometimes be considered a transaction
ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability)
ensures data integrity
Atomicity - transaction must be processed in its entirety or not at all
Consistency - any change in the database must retain the overall state of the database
Isolation - transactions shouldn’t be interrupted by other transactions
durability - once a change has been made to a database it must not be lost
record locking
the process of preventing simultaneous access to records in a database
it is used in order to prevent inconsistencies or a loss of updates
while one person is editing a record, this ‘locks’ the record so prevents others from accessing the same record
lock removed after transaction is completed
redundancy
the process of having one or more copies of the data in physically different locations
this means that if there is any damage to one copy the others will remain unaffected and can be recovered