Electricity and Magnetism: Key Concepts and Laws
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
Electric Circuit
Closed path for electric current flow.
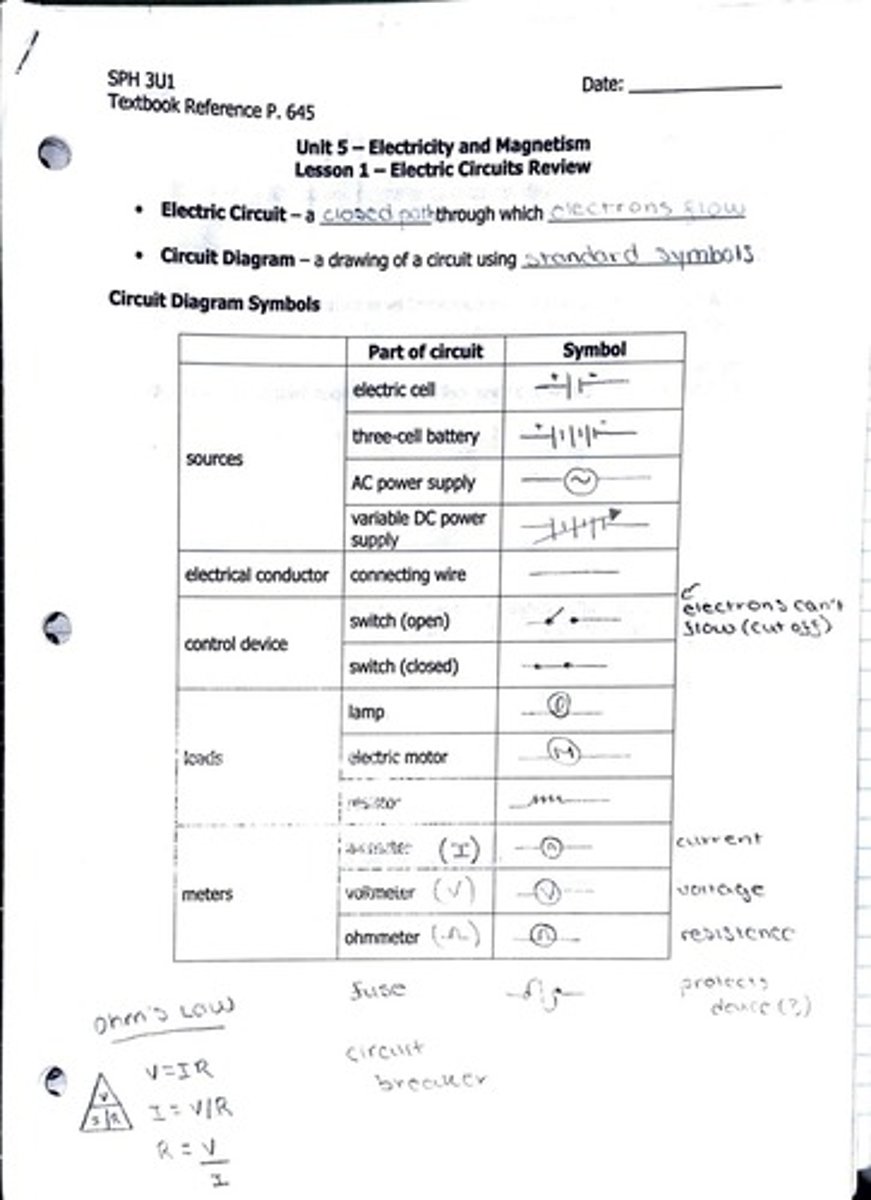
Circuit Diagram
Visual representation of an electric circuit.
Electric Cell
Device that converts chemical energy to electrical energy.
Three-Cell Battery
Battery consisting of three electric cells.
AC Power Supply
Source providing alternating current electricity.
Variable DC Power Supply
Source providing adjustable direct current electricity.
Electrical Conductor
Material that allows electric current to pass.
Connecting Wire
Wire used to connect components in a circuit.
Open Switch
Switch that interrupts current flow in a circuit.
Closed Switch
Switch that allows current to flow in a circuit.
Lamp
Device that produces light when electric current passes.
Electric Motor
Device converting electrical energy to mechanical energy.
Voltmeter
Instrument measuring electric potential difference in volts.
Ohmmeter
Device measuring electrical resistance in ohms.
Electric Potential Energy
Energy stored due to electric charge positions.
Electric Potential Difference
Voltage difference between two points in a circuit.
Electric Potential (V)
Amount of electric potential energy per unit charge.
Charge (Q)
Quantity of electricity measured in coulombs.
Electric Current
Flow of electric charge through a circuit.
Direct Current (DC)
Electric current flowing in one direction only.
Load
Component that consumes electric power in a circuit.
Source
Device providing electric energy to a circuit.
I
Electric current measured in amperes (A).
Q
Amount of charge measured in coulombs (C).
~t
Time interval measured in seconds (s).
Ampere
One coulomb per second passing a point.
Coulomb
Unit of electric charge; 6.2 x 10^18 electrons.
Ammeter
Device used to measure electric current.
Nerve cells
Cells that transmit signals using electric current.
Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL)
Total voltage in a circuit equals voltage drops.
Series circuit
Single path for current; shares voltage across loads.
Parallel circuit
Multiple paths for current; voltage remains constant.
Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)
Total current entering a junction equals leaving it.
Junction
Point in a circuit where currents converge.
Voltage
Electric potential energy per unit charge.
Equivalent resistance
Total resistance in a circuit configuration.
Resistance
Opposition to current flow, measured in ohms (Ω).
Ohm's Law
Voltage equals current times resistance (V=IR).
Current through a wire
Amount of charge passing a point over time.
Electric potential
Energy per charge in an electric field.
Resistor
Component that resists current flow.
Circuit
Closed loop allowing electric current to flow.
Kirchhoff's Laws
Rules for current and voltage in circuits.
Magnetic Field
Region around a magnet affecting magnetic objects.
Magnetic Field Lines
Visual representation of magnetic fields' direction.
North Pole
Magnet end that points towards Earth's north.
South Pole
Magnet end that points towards Earth's south.
Attraction
Force drawing opposite magnetic poles together.
Repulsion
Force pushing like magnetic poles apart.
Circuit Analysis
Problem-solving for electric circuits using laws.

Voltage Source
Provides electrical energy in a circuit.
Current (I)
Flow of electric charge measured in Amperes.
Resistance (R)
Opposition to current flow measured in Ohms.
Voltage (V)
Electric potential difference measured in Volts.
KVL (Kirchhoff's Voltage Law)
Total voltage around a closed loop equals zero.
KCL (Kirchhoff's Current Law)
Total current entering a junction equals total leaving.
Suspended Magnetic Objects
Align with Earth's magnetic field direction.
Gravitational Field
Region around mass affecting other masses.
Electric Field
Region around charged object affecting other charges.
Field Intensity
Strength of magnetic field, stronger near poles.
Circuit Steps
Process to solve for unknown circuit values.
Compass
Device aligning with magnetic field direction.
Attraction and Repulsion
Interaction between two magnets based on polarity.
Hans Christian Oersted
Scientist linking electricity and magnetism in 1819.
Conducting Wire
Wire through which electric current flows.
Oersted's Principle
Current creates circular magnetic fields around conductors.

Conventional Current
Flow of positive charge from positive to negative terminal.
Electron Flow
Movement of electrons from negative to positive terminal.
Right-Hand Rule
Method to determine magnetic field direction around conductor.
Left-Hand Rule
Used for determining electron flow direction.
X Symbol
Indicates magnetic field entering the page.
Dot Symbol
Indicates magnetic field exiting the page.
Solenoids
Coiled wire generating magnetic fields when current flows.

Andre-Marie Ampere
Scientist further investigating Oersted's discoveries.
Coiled Conductors
Looped wire enhancing magnetic field strength.
Magnetic Field Strength
Intensity of magnetic field produced by current.
Electromagnetism
Study of relationship between electricity and magnetism.
Magnetic Field Interaction
Effects of multiple magnetic fields on each other.
Current Direction
Path of electric charge flow in a circuit.
Magnetic Field Representation
Symbols used to depict magnetic field direction.
Motors and Generators
Devices utilizing electromagnetism for mechanical work.
Concentric Circles
Pattern of magnetic field lines around a conductor.
Coiled Conductor
Wire wound into a coil for magnetic effects.
Solenoid
Coiled wire generating a magnetic field when energized.
Electromagnet
Magnet created by electric current in a coil.
Strength of Electromagnet
Increased by adding more coils or using soft iron.
Right-Hand Rule for Solenoid
Thumb points current direction; fingers show field lines.
Applications of Solenoids
Used in subwoofers, electric bells, and lifting magnets.
Motor Principle
Electric current in a magnetic field experiences force.
Faraday's Experiment
Demonstrated current in conductor within magnetic field.
Magnitude of Force
Depends on current, magnetic field strength, and angle.
Right-Hand Rule for Motor Principle
Thumb for current, fingers for magnetic field direction.
Electromagnetic Induction
Production of electric current from changing magnetic fields.
Lenz's Law
Induced current opposes change in magnetic flux.
Oersted's Discovery
Electric current creates a magnetic field around it.
Field Lines
Visual representation of magnetic fields around magnets.
Soft Iron
Material used to enhance electromagnet strength.
Electric Bell
Device using electromagnet to ring a bell.
Subwoofer
Speaker using solenoid for low-frequency sound reproduction.
Current-Carrying Conductor
Wire through which electric current flows.