216 Nutrition , Anthropometric and Assessment technique terms
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
weight loss planned
intentional weight loss
weight loss unplanned
involuntary weight loss of greater than 5% of body weight in 1 month or involuntary weight loss of greater than 10% in 6 months; weight loss of more than 20% indicates severe protein-calorie malnutrition
overnutrition
Too much food energy or excess nutrients to the degree of causing disease or increasing risk of disease; a form of malnutrition
malnutrition
deficiencies, excesses or imbalances in a person's intake of energy and/or nutrients
At risk for undernutrition
alcoholics, behavioral/mental health issues, children, chronic/acutely ill, decreased cognitive function, elderly, illiterate, disabled, low income, traumatic brain injured, substance abusers
nutritional health history
focuses on the clinical, physical and psychosocial factors that may affect a patient's nutritional intake; includes
food preparation, weight, dietary preferences, dietary supplements/vitamins, appetite, food intolerances/allergies, water intake
24 hour diet recall
All foods, beverages and accurate amounts (as possible) consumed within the last 24 hours
Body Mass Index (BMI)
a screening tool that identifies the amount of body fat based on height and weight; first tool to indicate nutritional status
inspection
visual examination of the external surface of the body
inspection, palpation, percussion, auscultation
Order of assessment EXCEPT for the abdomen:
Palpation
an examination technique in which the examiner's hands are used to feel the texture, size, consistency, and location of certain body parts
percussion
tapping on a surface to determine the difference in the density of the underlying structure
Auscultation
listening to sounds within the body (usually with a stethoscope)
light palpation
detects surface characteristics and accustoms the person to being touched; finger pads 1 cm
deep palpation
assesses an organ or mass deeper in a body cavity; using finger pads of dominant hand gently press down 5 cm
tympany
The percussion note one should hear over the abdomen
Dullness on percussion
sign of fluid or solid mass under area being percussed
Resonance (percussion sound)
a low-pitched, hollow sound, usually heard over normal lung tissue
Hyperresonance Percussion Sound
lower-pitched, booming sound found when too much air is present such as in emphysema or pneumothorax
flatness
extremely dull sound produced by very dense tissue such as muscle or bone
bell of stethoscope
cup-shaped endpiece used for soft, low-pitched heart sounds; bruits, murmurs
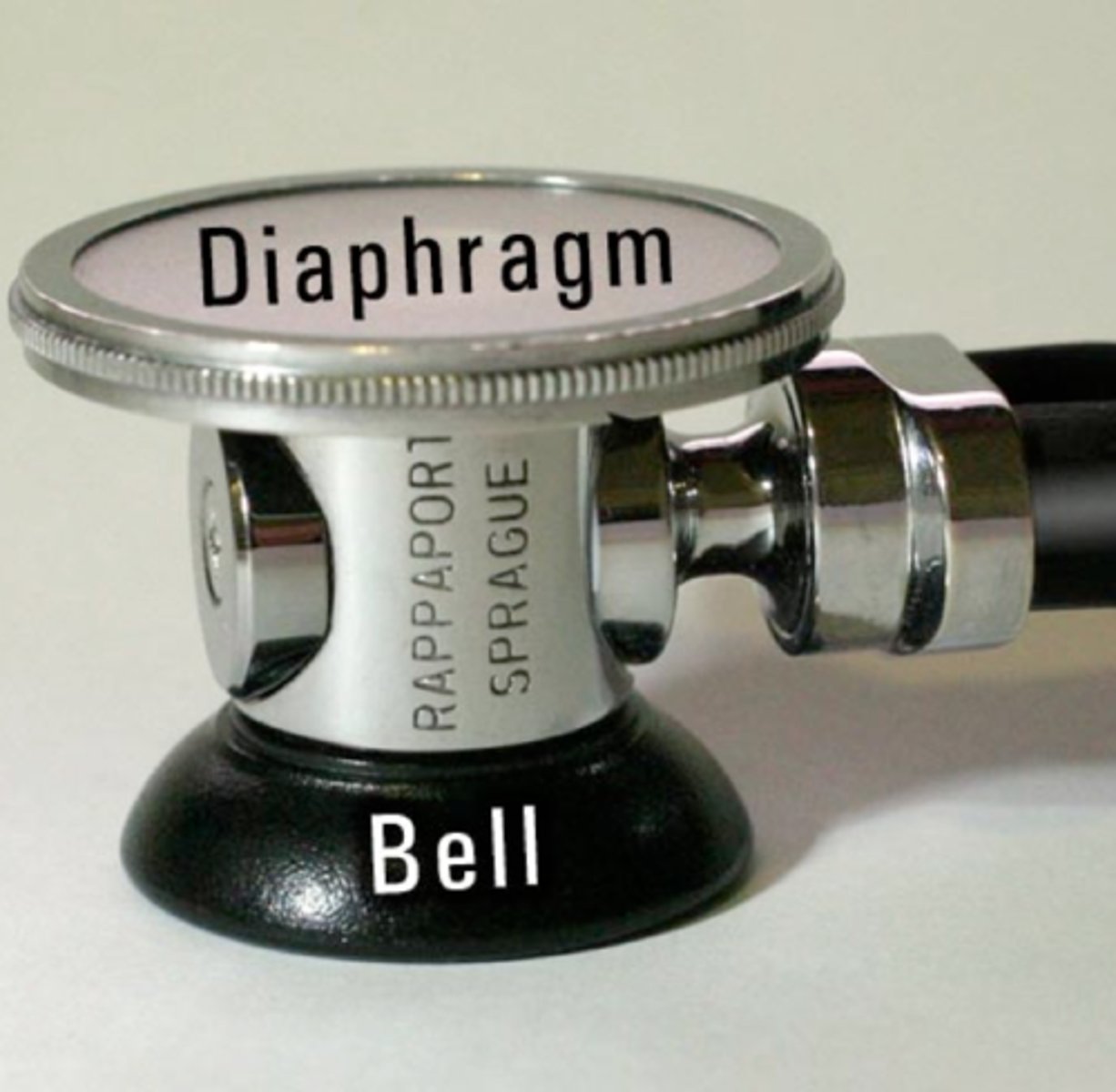
Diaphragm of stethoscope
flat endpiece of the stethoscope used for hearing relatively high-pitched sounds
