endocrine system
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
what do glands in the endocrine system work to maintain?
homeostasis
what does the endocrine system use to release hormones and activity?
chemical communication
what are the three parts in the theory of communication?
the sender, the message, and the reciever
hormones are _____ released by _____ that control the function/_____ of cells generally ___ from the source of production
chemicals, glands, activity, far
autocrine
cells produce hormones that effect themselves
paracrine
cells produce hormones that effect other nearby cells
what are the five things hormones can do ?
-alter cell membrane permeability
-stimulate protein/enzyme synthesis
-activate/deactivate enzymes
-induce exocytosis
-stimulate mitosis
what are the three chemical classes of hormone?
amino acid based
steroid based (sterol)
eicosanoid (lipid-based)
what is the most important functional difference between the 3 categories of hormone?
solubility
amino-acid hormone solubility
soluble in water, insoluble in fat
what benefits come from AA based hormones being able to move through water easily?
can easily move through bodily fluids and blood
target cells have ____ for each hormone
receptors
does every cell have all hormone receptors?
no
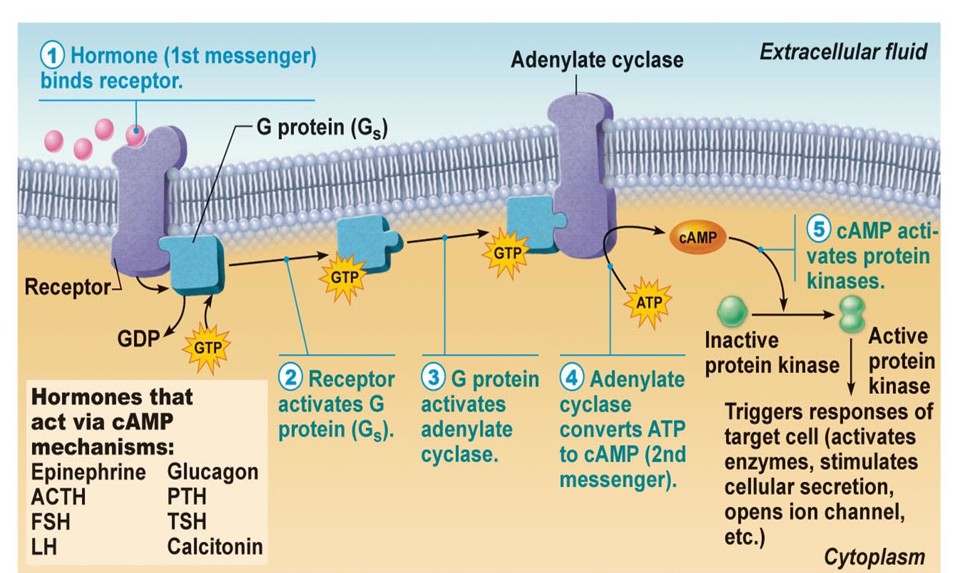
what is this process?
amino acid hormones in the cell membrane
step 1 of amino acids hormones in the cell membrane
the hormone binds to the receptor
step 2 of amino acids ihormones n the cell membrane
the receptor activates g proteins
step 3 of amino acid in the cell
g protein activates adenylate cyclase
step 4 of amino acids hormones in the cell
adenylate cyclase converts ATP to cAMP
step 5 of amino acids hormones in the cell
cAMP activates protein kinases
how do fat soluble hormones act in the cell membrane?
they can go right through the membrane
where do fat-soluble hormones bind to receptors?
in the cytoplasm
where do amino acid hormones bind to receptors?
the cell membrane
receptor-hormone complex with fat-soluble hormones can bond to ___ to initiate _____
DNA, gene expression
what are the three controllers of release/retention of hormones
humoral stimulus
neural stimulus
hormonal stimuli
what is humoral stimulus?
blood levels of certain ions/nutrients
what is neural stimulus?
nerve fibers stimulate hormone release
what are hormonal stimuli?
hormones telling glands to release hormones
____ regulates most hormonal release in the body
hypothalamus
the hypothalamus has a direct link to what gland?
the pituitary
what two hormones does the hypothalamus produce?
ADH, oxytocin
where does the hypothalamus store its hormones?
the posterior pituitary
what do hormones travel through from the hypothalamus to the posterior pituitary?
the infundibulum
what does antidiuretic hormone do?
stop pee!
what kind of tissue is the posterior pituitary derived from?
nervous
what kind of tissue is the anterior pituitary derived from?
epithelial
what is the posterior pituitary perfused with?
one major artery and vein
what does the primary plexus in the anterior pituitary do?
pick up hormones from the hypothalamus
what does the secondary plexus do in the anterior pituitary
drop off hormones into the bloodstream
what hormone does the thyroid gland create?
thyroxin
what does the thyroid gland surround?
the trachea
why is the thyroid not an exocrine gland?
it secretes directly to the blood as opposed to ducts
what are the three different kinds of cells in the thyroid?
principal (follicle), colloid, parafollicular cells
what do principal cells of the thyroid create?
thyroglobulin
what do colloid cells of the thyroid do?
store thyroglobulin and iodine
what do parafollicular cells of the thyroid do?
produce calcitonin
the first step of thyroid synthesis
thyroglobulin made by follicular cells, go into follicle
the second step of thyroid synthesis
iodide is trapped from the blood
the third step of thyroid synthesis
iodide converted to iodine
the fourth step of thyroid synthesis
iodine attaches to tyrosine
the fifth step of thyroid synthesis
iodinated tyrosines are linked
the sixth step of thyroid synthesis
thyroglobulin is endocytosed
the seventh step of thyroid synthesis
thyroid hormone is processed by enzymes, diffuse from the cell into blood
what produces calcitonin?
parafollicular cells in the thyroid
release of calcitonin results in lowered blood ____
calcium
how does calcitonin work?
inhibits osteoclasts, enhances bone Ca absorption
what do the parathyroid glands create?
parathyroid hormone
what does the parathyroid hormone do?
control calcium levels
parathyroid hormone is the antagonist of
calcitonin
what are the two sections of the adrenal gland?
the adrenal medulla, the adrenal cortex
what are the three sections of the adrenal cortex?
zona glomerulosa, zone fasciculate, zona reticularis
what does the adrenal cortex generally create
corticosteroids
what does the zona glomerulosa create?
mineralocorticoids, e.g. aldosterone
what do mineralocorticoids do?
regulate ion concentration in blood
what does aldosterone do?
reduce excretion of Na from the body
where are glucocorticoids synthesized?
zona fasciculata
what does cortisol (glucocorticoid) do?
depress inflammation, increase blood sugar
where are gonadocorticoids created?
zona fascicularis/reticularis
most gonadocorticoids are weak _____
androgens
in a positive feedback loop, the product ____ its own production
enhances
in a negative feedback loop, the product _____ its own production
reduces or stops
where are chromaffin cells located?
the adrenal medulla
what do chromaffin cells in the adrenal medulla produce?
catecholamines - epinephrine and norepinephrine
where is the pineal gland located?
diencephalon
what does the pineal gland mainly produce
melatonin
what stimulates melatonin production?
limited light to eyes
what is the organ most directly related in regulating blood sugar?
pancreas
what two hormones are produced in the pancreas?
glucagon, insulin
what does glucagon do??
raise blood sugar
what does insulin do??
lower blood sugar
step one of how glucagon raises blood sugar
breakdown of glycogen into sugar
step 2 of glucagon raising blood sugar
gluconeogenesis
step 3 of glucagon raising blood sugar
release of glucose from liver into blood
step 1 of insulin lowering blood sugar
enhances cellular uptake of glucose
step 2 of insulin lowering blood sugar
inhibit gluconeogenesis
step 3 of insulin lowering blood sugar
inhibits breakdown of glycogen to glucose
diabetes mellitus is due to ____
low or non-functional insulin
since sugar cannot be absorbed into body cells in diabetes mellitus…..
blood sugar rises
stress makes body release more glucose
the waste products of gluconeogenesis cause what?
ketoacidosis (nail polish breath)
3 diabetes symptoms
polyuria
polydipsia
polyphagia
what do the ovaries produce?
estrogen and progesterone
what does estrogen do?
regulate monthly menstrual cycle
what does progesterone do?
support pregnancy and menstruation
what do the testes create?
testosterone
what defines an endocrine gland?
a gland that releases directly into the blood
what is hormone half-life?
the time it takes for 50% of the present hormone to dissapate
define catecholamines
hormones released in fight-or-flight to constrict blood vessels and increase blood flow