ANAT 1551 Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Chemical Control
Slower, more general, older, and requires some sort of transport.
Examples: Circulatory (endocrine system) and Lymphatic vessels.
Nervous Control
Faster, more specific, newer, requires nerves.
Sensory Function
The nervous systems ability to sense changes in the internal and external environments through sensory receptors.
Integrative Function
Analyze the sensory information, and makes decisions regarding appropriate behaviors.
What neurons serve the sensory function?
Sensory or Afferent neurons.
What neurons serve the integrative function?
Association or Interneurons.
Motor Function
Respond to stimuli by initiating action.
What neurons serve the motor function?
Motor or Efferent neurons.
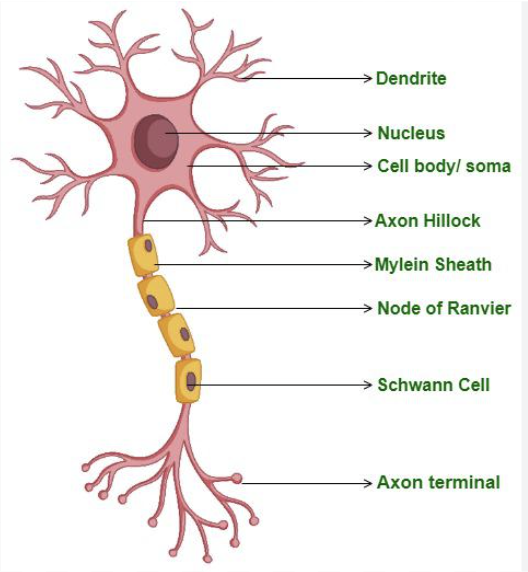
Cell Body
Contains nucleus, lysosomes, mitochondria, a Golgi complex, chromatophilic substances, and neurofibrils.
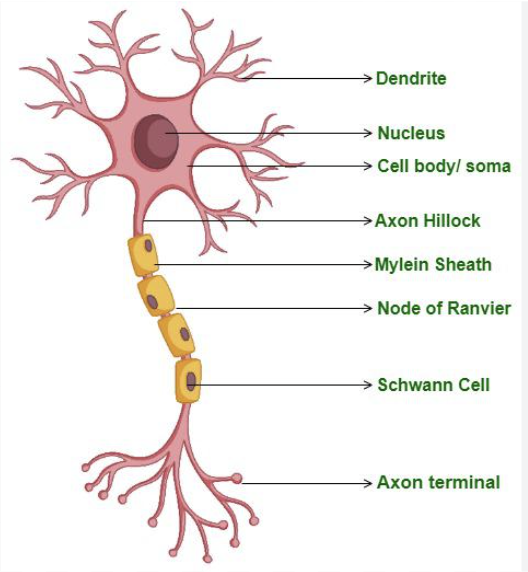
What is another name for the cell body?
Perikaryon
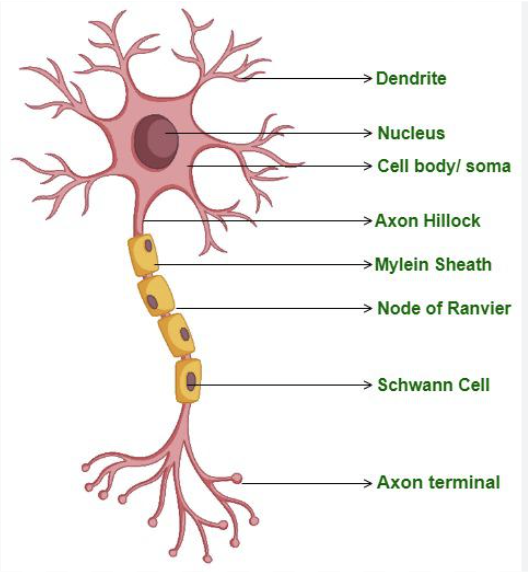
What is the function of a dendrite?
Conduct(carries out) impulses from receptors or other neurons to the cell body.
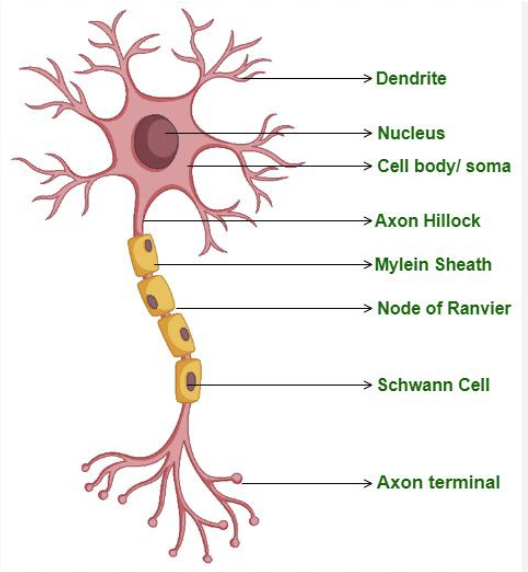
What is the function of an Axon?
Conducts(carries out) nerve impulses from the neuron to the dendrites, or cell body of another neuron, or an effector organ of the body(muscle or gland).
What is the gap between two neurons or the gap between the neuron and an effector cell called?
Synapse
What is a nerve?
Bundles of hundreds or thousands of axons that serve a specific region of the body.
Ganglia
A collection of nerve cells OUTSIDE the CNS.
Axonal Transport
Faster than axonal flow, may occur in retrograde, uses proteins like “motors” to transport materials.
Axon flow
Slower than axonal transport, pushes cytoplasm from hillock to axon terminal.
Neuroglia (or glia)
Specialized tissue cells that support neurons, attach neurons to blood vessels, produce the myelin sheath around axons, and carry out phagocytosis.
What are the types of Neuroglia?
“All Our Mammals Eats Sour Snacks” Astrocytes, Oligodendrocytes, Microglia, Ependymal cells, Schwann cells and Satellite cells.
What cells produce myelin sheath?
Schwann Cells
What is the function of myelin sheath?
Electrically insulates the axon and INCREASES the SPEED of nerve impulse conduction.
What are the Nodes of Ranvier and where are they found?
Gaps in the myelin sheath that run along the axon.
What cell forms the myelin sheath for the CNS axons?
Oligodendrocytes
What is the neurolemma and what is it’s function?
Outer nucleated layer of the Schwann cell which encloses the myelin sheath and forms a regeneration tube.
How does the neurolemma aid in regeneration?
Forming a regeneration tube that guides and stimulates regrowth of the axon.
Which cell lacks a neurolemma and what does that mean for the cell?
Oligodendrocytes, they do not regenerate.
White Matter
A collection of nerve cell bodies of the central nervous system WITH myelin sheath.
Gray Matter
A collection of nerve cell bodies and dendrites of the central nervous system WITHOUT myelin sheath.
Neucleus
A mass of nerve cell bodies and dendrites inside the CNS.
Neurons have the property of..
Electrical excitability/irritability.
Current
The flow of charged particles.
Membrane potential
An electrical voltage across the membrane.
When does graded and action potential occur?
Ion channels in the membrane open allowing ions to move across the membrane and change the membrane potential.
Leakage(nongated) channels
Channels that are always open.
Example: Cardiac tissue.
Gated channels
Open and close in response to some sort of stimuli.
Voltage-gated channels
Respond to a DIRECT change in the membrane potential.
Example: Action potential.
Ligand-gated channels
Respond to a specific CHEMICAL stimulus.
Example: Acetylcholine.
Mechanically gated ion channels
Respond to a MECHANIAL vibration or pressure.
Example: Hearing.
The membrane of a NONCONDUCTING neuron is ___ outside and ___ inside.
Outside: Positive
Inside: Inside
What is the typical value for the resting membrane potential?
-70mV
What causes the resting membrane potential?
Unequal distribution of ions across the plasma membrane (Na+ outside and K+ on the inside).
Who discovered the Galvanometer?
Johann Schweigger
Who is Du Bois Reymond?
Discovered action potential. The first person to notice that during action potential the membrane potential of the nerve changed from -70mV to +30mV. He used a galvanometer to find that difference.
Who is Julius Bernstein?
First showed change in electronegativity with a galvanometer in 1902.
What happens during action potential?
Voltage gated Na+ and K+ channels open up in sequence.
Julius Bernstein first showed this change in electronegativity with a GALVANOMETER.
What is the role of Na+/K+ pumps when a neuron is at REST?
The pumps push out 3 positive charges (Na+) out and pushing in only 2 positive charges (K+). This maintains the concentration gradients for these ions.
K+ role in resting membrane potential (RMP)
K+ diffusion is the most important factor in setting RMP.
K+ diffuses OUT of the cell due to it’s concentration gradient
K+ delusion out is limited by the electrical gradient (the pull of the -RMP on the + ion)
If K+ was the only ion that leaked, RMP would be where the K+ concentration and electrical gradients were in equilibrium (-90mV)
Na+ role in resting membrane potential (RMP)
Na+ also influences the RMP because there are a few Na+ leak channels.
Na+ diffuses in due to it’s concentration gradient and the electrical gradient.
This small leakage means the RMP is below -70mV.
Absolute refractory period
Another impulse cannot be made AT ALL.
Relevtive refractory period
An action potential can be triggered only by a SUPRAthreshold stimulus(one stronger than the previous stimulus).
LOCAL anesthetics
Prevent opening of voltage gated Na+ channels so nerve impulses cannot pass in a specific region.
GENERAL anesthetics
A medically induced state of unconsciousness that prevents a patient from feeling pain during major surgery or procedures.
All-or-Non Law
If a stimulus is strong enough to generate an action potential (threshold), the impulse travels at a constant and maximum strength or existing conditions. A stronger stimulus will not cause a large impulse.
Where is Saltatory Conduction only be found?
Myelinated matter.
What is Saltatory Conduction?
Impulse: moving wave of electronegativity that depolarizes as it moves down serving as a stimulus for the next section.
Jumps from one node of Ranvier to another.
Electrical synapses
Ionic current spreads directly from one cell to another through gap junctions.
Electrical synapse allows for faster communication can synchronize the activity of a group of neurons or muscle fibers.
May set up a two way transmission of impulses. e.g cardiac tissue.
Who is Otto Loewi?
First person to discover chemical solutions (vagusstoff) which turned out to be acetylcholine.
Temporal
How long you have to stimulate to get a response.
Spatial
Where you have to stimulate to get a response or how many axons it takes.
EPSP
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potentials
a depolarization caused by the opening of ion channel by the ENTRY of Na+
membrane becomes less negative
IPSP
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential
hyper polarization caused by opening of ion channels by EXIT of K+ or the ENTRY of Cl-
membrane becomes more negative
Acetylcholinesterase
Breaks down acetycholine
Drugs screw up:
Passage of neurotransmitters
tie up neurotransmitter so it can’t function
tie up receptor sites
Production of neurotransmitters
screws up formation of neurotransmitter
block release of neurotransmitter
Conduction of impulse
changes the charge on the membrane
Monoamine Oxidase (MAO)
Breaks down monoamines inhibitors used to treat depression.
Monoamines
A class neurotransmitters and neuromodulators that include dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin.
Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT)
Breaks down catecholamines
Catecholamines
Hormones and neurotransmitters, primarily dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine.
Seizures
Uncontrollable excessive activity in part or all of CNS.
Triggered by
Flashing lights
Alchohol
Drugs
CO2
Grand Mal Seizures
More severe, involves a sudden loss of consciousness, body stiffening, and rhythmic jerking.
Petit Mal
Less severe, sudden lapses in consciousness, a person may appear to be staring blankly, blinking, or twitching.
Famous people who have seizures
John the Baptist, Julius Caesar, Alexander the Great, and Neil Young.
Multiple scrolosis
Disease that causes progressive myelin sheath surrounding the neurons of the CNS.