FAA Pre-Solo Witten Exam
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms

What personal documents and endorsements are you required to have before you fly solo?
Medical Examination and endorsement to fly solo from your flight instructor and logbook

What are your student pilot limitations regarding carriage of passengers or cargo and flying for compensation of hire?
As a student pilot you may not fly with passengers if there is not an instructor present. You may not fly for compensation of cargo for hire at all

Explain student pilot limitations concerning visibility and flight above clouds
As a student pilot, you are only able to fly VFR, and you should stay at least 2,000 ft away horizontally from a cloud and 1,000 feet above. You must always have visual reference to the ground.

Who has the final authority and responsibility for the operation of the aircraft when you are flying solo?
The PIC, (Pilot in command)

What preflight action concerning the airport and aircraft performance is specified in the regulations for a local flight?
You must announce to the control Tower that you are flying solo so that they can guide you while keeping you along with other aircraft safe

During engine run up, you cause rocks, debris, and propellor blast to be directed toward another aircraft or person. Could this be considered careless or reckless operation of an aircraft.
This is careless/reckless action because this puts other aircraft in danger. No more than 1200 RPM’s during taxi

Hours after consumption of any % by weight or more alcohol in your blood
24 hours

What are the general requirements to the use of safety belts and shoulder harness?
it is the responsibility of the pilot in command to make sure everyone in the cabin has on their seatbelts and or shoulder harness

What is the minimum fuel reserve for day VFR flight, and on what cruise speed is the fuel reserve based
Enough fuel to fly to an intended destination along with an extra 30 minutes during daytime and 45 minutes of extra fuel during nighttime.

A transponder with mode C is required at all times in all airspace at and above __ MSL. Excluding that airspace at and below __ feet AGL.
A transponder with mode C is required at all times in all airspace at and above 10,000 feet MSL, excluding that airspace at and below 2,500 feet AGL.

What aircraft certificates and documents must be on board when you are flying solo?
(Student)- Student pilot certificate, Medical certificate, Logbook, Valid photo ID. (Airplane) Air Worthiness certificate, Registration, Radio station license (if an international flight), Operating limitations, Weight and Balance

No person may operate an aircraft so close to another as to create a(n)
collision

Who has the right of way when 2 aircraft are on final approach to land at the same time?
The lower plane has the right of way, however the planes shall not take advantage of this
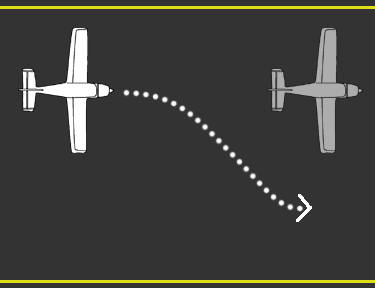
What action do you need to take if you are overtaking another aircraft and which aircraft has the right of way
Alter your course to pass well clear of the aircraft, the one being passed has the right of way

What should you do if you are flying a head on collision course with another aircraft
Both planes turn to the right

Except when necessary for takeoffs and landings, what are the minimum safe altitudes when flying over congested areas?
When flying over congested areas, you must be at least 1,000 ft above the highest obstacle while within 2,000 ft horizontally of any obstacle

If an altimeter setting is not available at an airport, what setting should you use before departing on a local flight?
If the altimeter is not available, you manually set it to the airports field elevation
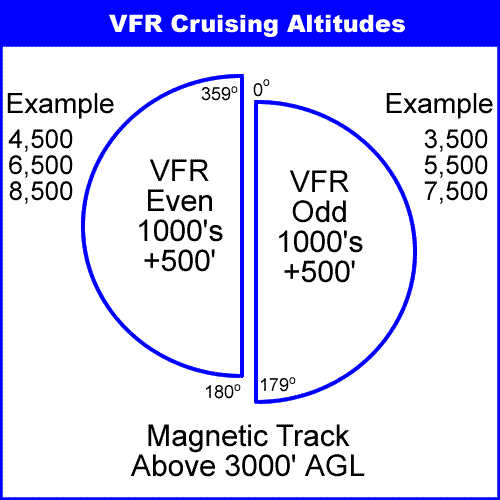
What altitudes should you use when operating under VFR in level cruising flight at more than 3,000 ft AGL
When flying VFR in level cruising flight more than 3,000 ft AGL, use odd thousand-foot altitudes plus 500 ft For headings 0–179°. For example, 1,000 + 500 ft (3,500, 5,500) for headings from 180°–359° fly an even 1,000 + 500 ft (4,500, 6,500)

When practicing steep turns, stalls, and manuevering during slow flight the entry altitude
should be no less than 1,500 ft AGL

When is a go around appropriate?
When you are past the first ⅓ of the runway, an unstable approach, bounce landing, if ATC commanded so, or if there is an obstruction on the runway.

What general Steps should you follow after an engine failure in flight?
You check/correct your airspeed, find/picth for the best and most efficient glide speed, and refer to your checklist

List the minimum equipment and instruments that must be working properly in your aircraft for day VFR flight
Airspeed indicator, Tachometer, Oil pressure, Manifold pressure, Altimeter, Temperature, Oil temperature, Fuel gauges, Landing gear position indicator, Anti collision lights, Magnetic compass, Emergency locater transponder (ELT), Seat belts

List the minimum equipment and instruments that must be working properly in your aircraft for nighttime flight
Fuses (or circuit breakers), Landing light, Anti-collision lights, Position lights, Source of power (Battery or alternator)

V-speeds? Vso, Vs1, Vx, Vy, Vfe, Va, Vno, Vne, Vs, Vg, Vle
[Vso]: Power off stalling speed, with wing flaps and landing gear in the landing position (dirty) [Vs1]: Stalling speed in the clean configuration. [Vx]: best angle of climb over a given distance. [Vy]: Best rate of climb over a given period of time. [Vfe]: Full flaps, or maximum flaps extension speed. [Va]: (not color coded) design maneuvering speed. The speed in which you can move a flight control one time in smooth air to its full deflection without consequences. [Vno]: Maximum structural cruising speed (should only be done in smooth air). [Vne]: Never exceed speed. [Vs]: Stalling speed in the clean configuration. [Vg] Best glide speed. [Vle]: Maximum landing gear extension speed. (maximum speed with landing gear out)

Best glide speed for your aircraft (cessna 152)
65 knots

Maximum allowable flap setting for takeoff in your aircraft (cessna 152)
No more than 10°

The total fuel capacity for your aircraft, and normal consumption rate
26 gallons of total fuel, with 24.5 gallons of usable fuel. normal consumption rate is 6.5 gallons per hour

What are the grades of fuel that can be safely used in your aircraft (Cessna-152), and what are the colors of the recommended fuels?
AVGAS 100 (Green), and AVGAS 100LL (Blue)

What happens when these 2 grades of fuel are mixed?
if both AVGAS 100 and AVGAS 100LL were mixed it would turn clear

The Maximum oil capacity of your aircraft (Cessna-152) to begin a flight is?
4-6 quarts

The maximum crosswind component specified by your instructor for solo takeoffs and landings in the training aircraft is?
15 knots

When do you use carburetor heat?
Carburetor heat should be used when on downwind and or outside the green arc

what are the indications of carburetor icing?
Decreased performance of the aircraft (engine roughness, drop in RPM’s)

What are the traffic patterns for each runway at your airport? (KHWD) What is the MSL altitude for the traffic pattern?
Runway 28L: 650 ft MSL, Runway 28R: 850 ft MSL

How do you enter the traffic pattern at KHWD? what is any radio communications are required?
Get the ATIS at Cal State east bay, State the ATIS information and your location, and enter the traffic pattern on a right base.

What radio calls are recommended in the traffic pattern at an uncontrolled airport? What radio calls are required at KHWD?
Radio calls regarding position (10 miles out), and positions on pattern entry

What is CTAF
CTAF: common traffic advisory frequency. It allows pilots to communicate at non-towered airports

How can you determine if a runway is closed?
Previously stated on the ATIS, Visual markings on the runway itself, (Such as X’s) or physical barriers on the runway.
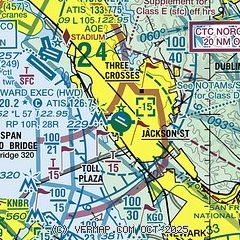
What are the typical dimensions of class D airpsace?
A cylindrical shape from the surface to around 2,500 ft AGL, a ceiling with a radius around 4-5 nautical Miles.

What are the requirements that must be met prior to entering class D airspace?
2-way radio communications must be established with ATC, You must call the tower and receive a response before entering, Once your callsign is read then you may enter.

Visibility requirement for Class D airspace?
3 miles of visibility, along with cloud clearance of 500 ft below, 1,000 ft above, and 2,000 ft horizontally. These apply to VFR flight below 10,000 ft MSL

Standard direction of turns in the traffic pattern
Upwind, Crosswind, Downwind, Base, and Final

What is the maximum speed permitted for an aircraft below 10,000 ft MSL?
250 KIAS

What is The maximum speed allowed in Class B airspace?
Maximum speed in class B airspace is 250 knots, and 200 knots in the Class B corridor

If you receive ATC instructions that you feel may compromise safety or will cause you to violate an FAR what should you do?
Politely refuse or say that you are unable to do so and briefly provide a reason.
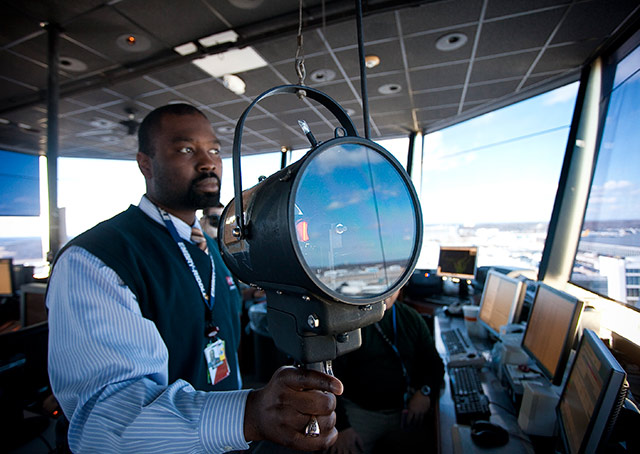

What is the meaning for each of the following ATC light signals? Steady Green, Flashing green, Steady Red, Flashing Red, Flashing white, Alternating Red and green.
[Steady green]: Clear for takeoff/clear to land. [Flashing green]: Clear to taxi/return for landing. [Flashing red]: Taxi clear of landing area/Airport is unsafe. [Steady Red]: Stop/Give way to other aircraft. [Flashing white]: Return to the starting point on airport, [Alternating Red and Green]: General warning/Exercise extreme caution.

In addition to equipment requirements and a student pilot certificate, what other requirements if any, must be met before a student pilot is authorized to fly solo within Class B airspace?
They must receive flight and ground training by an instructor in that respective air space. They must get their logbook endorsed by their instructor.

What are the general transponder equipment and use requirements when operating within or near Class B airspace?
Mode C transponder, and ADS-B out capability.

What is an ELT, and explain its use.
An ELT is an emergency locater transmitter that automatically transmits a distress signal upon the even of a crash to help other aircraft and rescue teams locate you. Upon set to “off”, it will not transmit, “Armed”meaning that it is ready to transmit, and “ON” meaning that it is currently transmitting a signal. The older ELT transmits on the frequency 121.5 and 243.0 Mhz, while newer ones transmit of 406 Mhz.
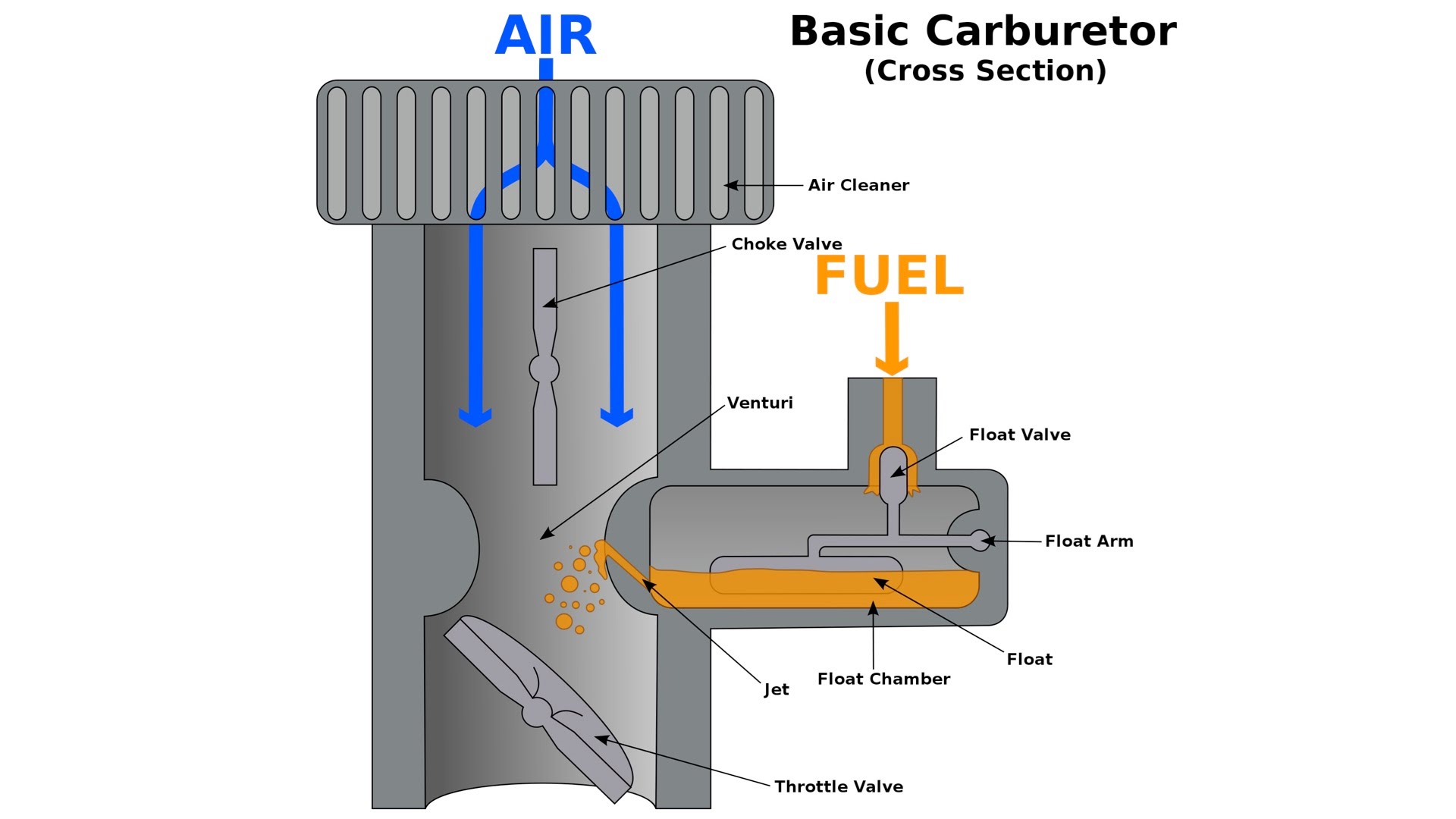
What is manifold pressure
the absolute pressure of the fuel-air mixture inside the intake manifold of an engine. With higher pressure meaning more air and thus more power. It's influenced by the throttle position, outside air pressure, and engine RPM.

What is the use of the alternator belt, and what happens when it malfunctions.
The alternator belt provides electricity to the airplanes electrical system, Upon malfunction it will cause a gradual loss of power in the electrical systems starting with less critical ones. When it malfunction a signal will come on indicating “LOW VOLTS” on the Ammeter.

What are hot spots
A spot on the taxiway where there is an increased risk of collision and danger