Hinduism
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Hindus
Followers of Hinduism

Hinduism
Oldest documented religion
India
Hinduism's geographic place of origin
Aum/Om
a syllable chanted in meditation

Swastika
Once an ancient Hindu symbol used to ward off evil spirits, the Nazis adopted it as their official symbol.

Brahmins
Hindu priests

Brahman
Main Hindu God who created the universe and everything in it.

Caste System
A Hindu social class system that controlled every aspect of daily life
Vedas
Sacred Hindu text

Sanskrit
key Hindu language

dharma
one's duty in life
karma
the effects that good or bad actions have on a person's soul
moksha
Release from the cycle of reincarnation
atman
one's individual soul
yoga
"union"; focusing the physical & spiritual self on union with one's creator

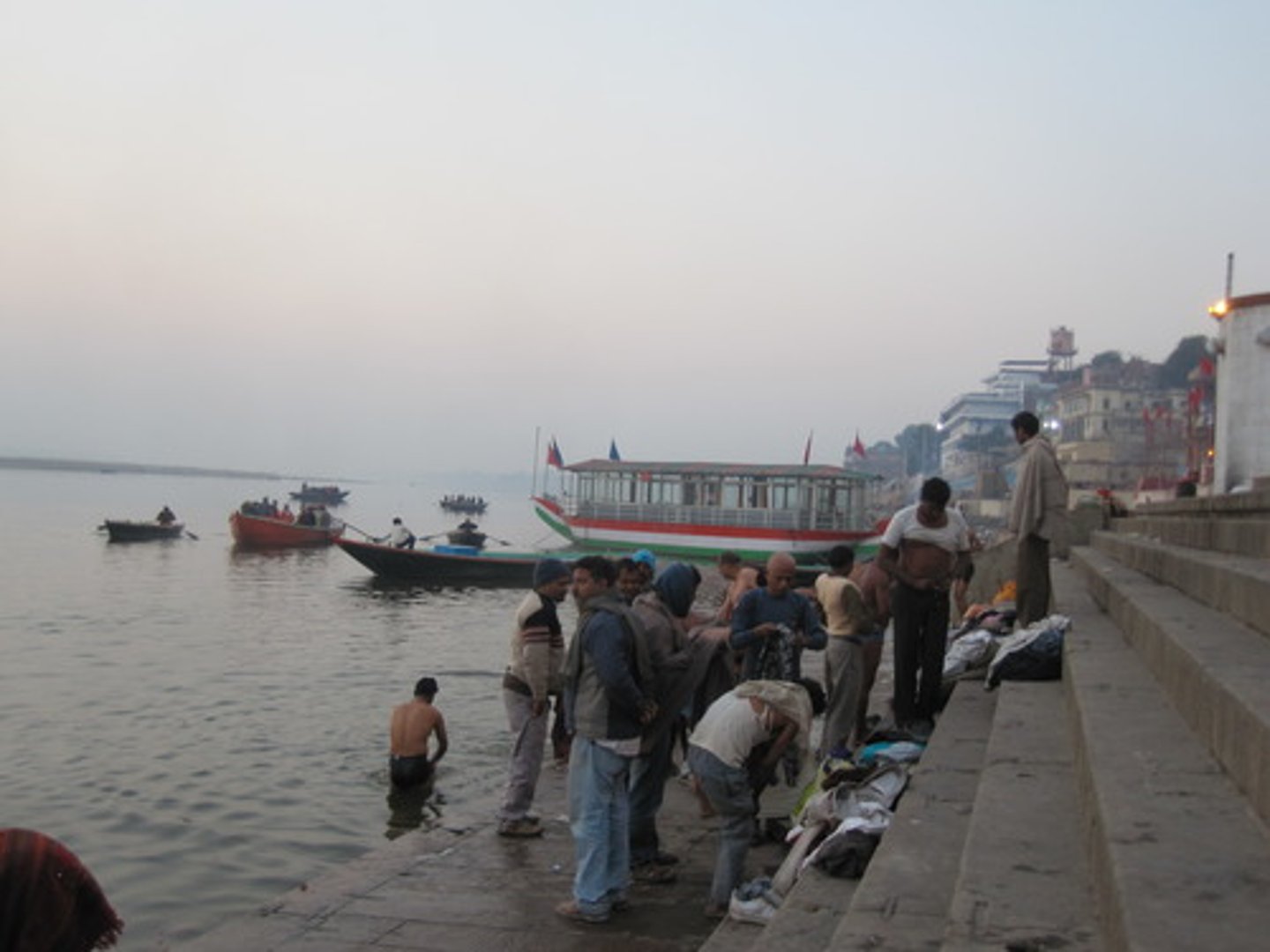
Ganges River
holiest Hindu site

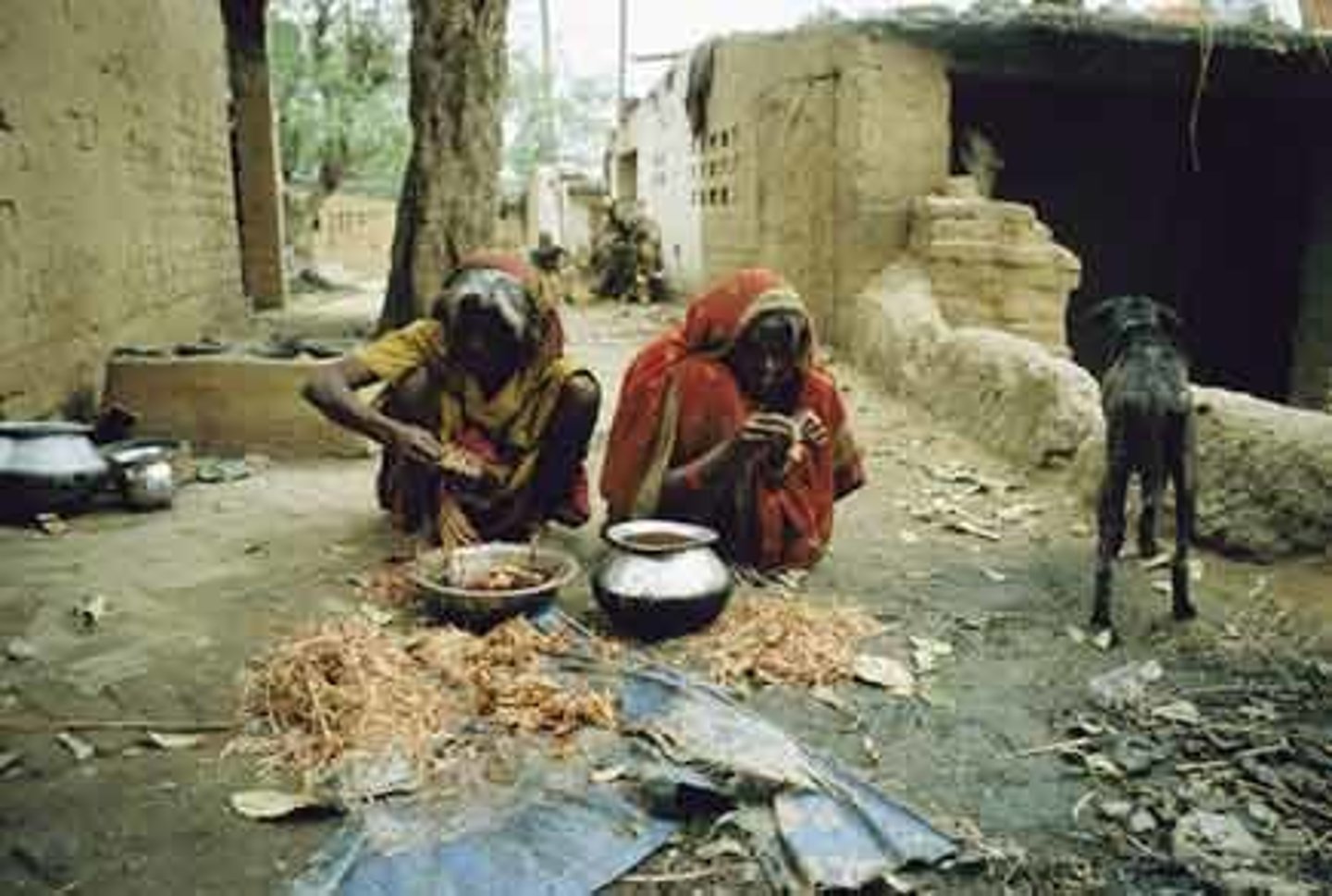
Untouchables
Hindus outside of the Caste System in the lowest social class

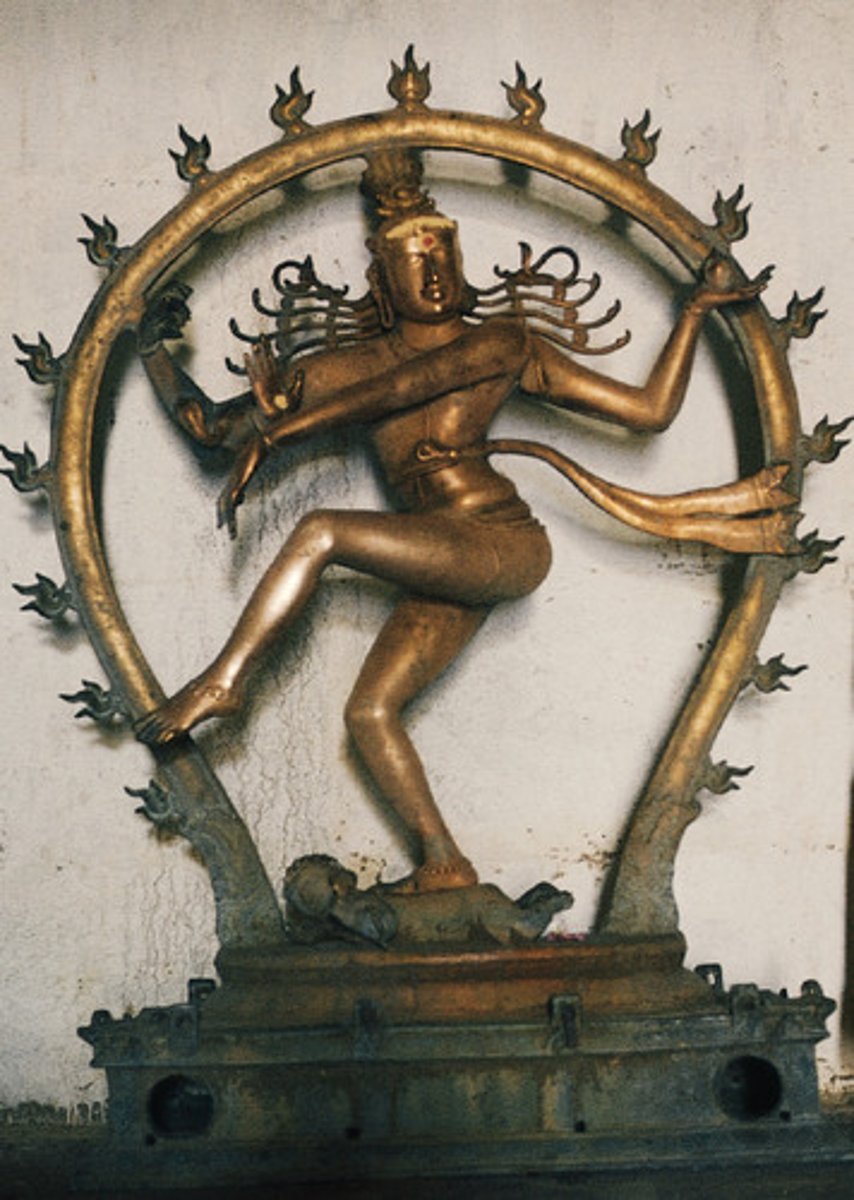
Shiva
Hindu "destroyer" deity

Brahma
Hindu "creator" deity

Vishnu
Hindu "protector" deity

Kashatriyas
Warriors, soldiers under Brahmin in the caste system
Vaishyas
Hindu caste of artisans and merchants.
Shudras
The landless peasants and serfs of the caste system.
Diwali
Hindu festival of lights
Atman
Ultimate reality
atman
soul reincarnated
Ganesha
elephant headed god, new begginings
How are Atman and Brahman related?
Atman is considered to be a part of Brahman; realizing that Atman is Brahman is the key to spiritual liberation (moksha).
Function of Hinduism’s many deities
They help devotees focus their worship, understand spiritual concepts, and connect personally with the divine.
Examples:
Brahma – the creator
Vishnu – the preserver
Shiva – the destroyer and transformer
Lakshmi – goddess of wealth and prosperity
Saraswati – goddess of knowledge and arts
How ganesha got his head
Shiva cut off Ganesha’s head. To console Parvati, Shiva replaced it with the head of a nearby elephant, bringing Ganesha back to life.
What does Ganesha’s story mean?
teaches about acceptance, transformation, and the importance of wisdom. It shows that even unexpected changes can lead to something powerful and good.
3 paths of liberation
Karma Yoga
Bhakti Yoga
Jnana Yoga
Karma yoga
Karma Yoga – Path of selfless action and duty
Service
Bhakti Yoga
Bhakti Yoga – Path of devotion and love toward a personal deity
Love
Jnana Yoga
Jnana Yoga – Path of knowledge and wisdom through meditation and study
Meditation
Which Hindu text is most associated with Bhakti Yoga?
Bhagavad Gita
It emphasizes devotion to Lord Krishna as a path to liberation, alongside karma (action) and jnana (knowledge) yogas.
How did Ghandi influence Hinduism?
He emphasized living a simple, ethical life rooted in spiritual values, inspiring both religious and political movements. Made it more accessible and relevant in modern times, promoting peace and social justice.
What are two principles that connect the divine to this world in Hinduism?
Back:
Dharma – the moral law and duty that sustains the universe and guides human behavior
Karma – the law of cause and effect, where actions have spiritual consequences shaping future lives
How might reincarnation explain who we are and what we know?
Reincarnation teaches that the soul (Atman) is eternal and passes through many lives, carrying lessons and experiences from each one.
What is the correlation between the stages of life in Hinduism and Western culture?
Both traditions recognize phases of growth, responsibility, withdrawal, and reflection, though Hinduism integrates spiritual focus more explicitly in later stages.
Hinduism’s Four Ashramas:
Brahmacharya (Student) – Focus on learning and discipline
Grihastha (Householder) – Family life and career
Vanaprastha (Hermit/Retirement) – Gradual withdrawal from worldly duties
Sannyasa (Renunciate) – Spiritual pursuit and detachment
Western Culture Stages:
Childhood/Education – Learning and growth
Adulthood/Work & Family – Career and raising a family
Retirement – Slowing down, reflection
Late life – Legacy, often spiritual reflection
how are people separated in the west that is similar to the caste system?
social divisions exist based on class, wealth, education, and occupation.