step 3: 7. Intangible Assets and Inventories
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
an intangible asset is an _____, _______ asset with no physical substance
identifiable
non-monetary
what does identifiable mean
can be sold separately without selling the business
arises from a contract
examples of intangible assets
goodwill
development costs
patents
computer software
trademarks
goodwill is the ______ payment made and can be defined as the amount paid over and above the ___ value of the ______net assets and liabilities acquired
(like a premium you are willing to pay for the business)
excess
fair
identifiable
_____ generated goodwill is not recognised
internally
purchased goodwill, acquired by buying another entity is capitalised
t/f
t
research is the original and planned investigation undertaken with the prospect of gaining new scientific or technical knowledge and understanding
research is the original and planned investigation undertaken with the prospect of gaining new scientific or technical knowledge and understanding
development is the application of research findings or other knowledge to a plan or design for the production of new or substantially improved materials etc, before the start of production
development is the application of research findings or other knowledge to a plan or design for the production of new or substantially improved materials etc, before the start of production
examples of research activities
activities aimed at gaining new knowledge
searching for information
examples of development activities
design
with research and development you are applying the ____ concept
accruals
research is ____recognised as an intangible asset, but shown as an ____in SPL
no certainty of future economic benefits
not
expense
development ___ be recognised as an intangible asset when all PIRATE criteria are met
must
PIRATE
Probable future economic benefits
Intention to complete, and use/sell
Resources adequate to complete
Ability to use/sell
Technical feasibility of completing asset
Expenditure can be measured reliably
PIRATE
Probable future _____benefits
______ to complete, and use/sell
Resources adequate to complete
Ability to use/sell
______feasibility of completing asset
Expenditure can be measured _____
economic
Intention
Technical
reliably
amortisation
depreciation for intangible assets
indefinite life on intangible assets :
no foreseeable limit for when asset can be used
intangible asset is not amortised
useful life re-assessed every year
impairment review conducted annually
intangible asset with an indefinite life is not ________
amortised
finite life on intangible assets
amortise over the usefull life
residual value of intangible assets is normally ___
0
impairment - an asset is impaired if it’s carrying amount is greater than its recoverable amount

impairment loss is the amount by which the carrying amount of an asset _____its recoverable amount
exceeds
impairment indicators: external sources
significant fall in the assets market value
increases in interest rates (bad economy)
impairment indicators: internal sources
damage in asset
fall in cash flows
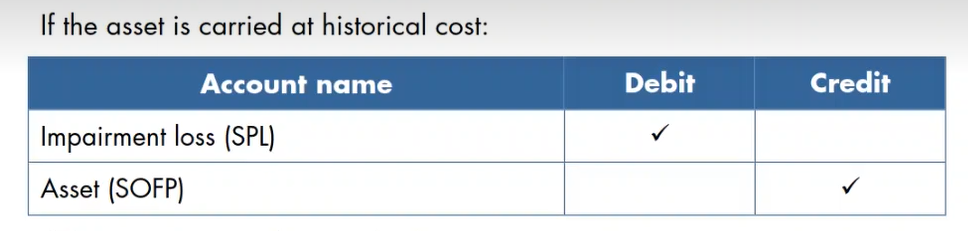
accounting for impairment cost, when the asset is carried at historical cost
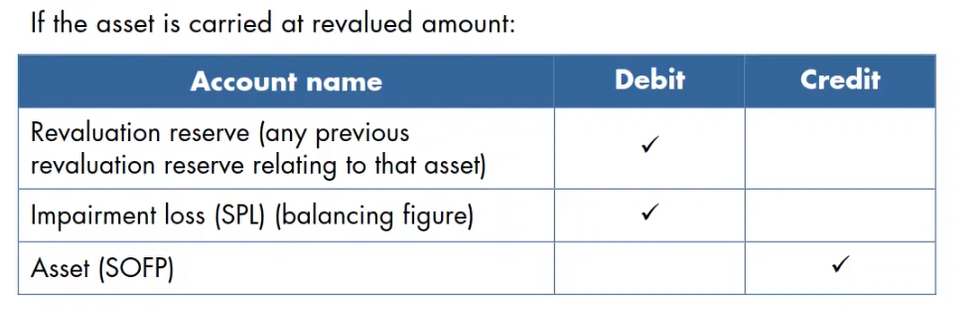
accounting for impairment cost, when the asset is carried at revalued amount
NRV =
selling price - selling costs - costs to complete
cost =
purchase prince + directly attrituble costs
LIFO (Last In, First Out) is ______ by IAS
prohibited
LIFO (Last In, First Out)
assumed most recent purchases are used first
therefore, the items in inventory are the earliest purchases
FIFO (First In, First Out)
items used in the order they are recieved
therefore items in inventory are the most recent purchases
AVCO (Weighted Average)
total cost of items in inventory / total number of items
according to IAS 16 PPE, if a tangible non-current asset is valued using the revaluation model it is carried in the SOFP at:
historical cost less accumulated depreciation
fair value
fair value less any subsequent accumulated depreciation
market value
fair value less any subsequent accumulated depreciation
which of these intangible assets cane be capitalised in the financial statements
goodwill arising on the purchase of another business
its workforce
a licence purchased during the teas
a brand the company has developed over a period of several years
1 and 3
an impairment review has been carried out in respect of an item with:
carrying amount = 100,000
value is use = 80,000
fair value less costs of disposal = 90,000
replacement cost = 95,000
what is the amount of impairment loss that should be recognised
10,000
difference between the carrying amount and recoverable amount
in this case fair value less costs of disposal (recoverable amount is the higher of the fair value less costs of disposal)
Sycamore plc carried out an impairment review on a freehold property. The property had previously been revalued to £850,000 when its carrying amount was £800,000. At the date of the review the carrying amount of the property was £840,000. Its value in use was £775,000 and its fair value less costs of disposal was £760,000.
how much of the impairment loss should be recognised in the statement of profit or loss?
The impairment loss is £65,000 (840,000 – 775,000, based on value in use).
Recoverable amount is the higher of fair value less costs of disposal and value in use.
Since there is a revaluation surplus of £50,000 (850,000 – 800,000) in respect of the property, £50,000 of the impairment loss can be set against the revaluation surplus (recognised in other comprehensive income).
The balance of £15,000 is recognised in profit or loss.
A piece of land acquired for £100,000 and subsequently revalued to £120,000 has been impaired and its value has fallen to £85,000.
show the journal entry

internally generated brands should never be capitalised
t/f
t
intangible assets can be revalued
t/f
t
although rare, there is the choice between cost model and revaluation model
impairment loss should be disclosed
t/f
t
impairment losses are recognised in the profit or loss if the asset had not previously been ____
otherwise, they are treated as downward revaluations
revalued
FRC
independent regulator of accounting and auditing in the UK
corporate governance
the systems by which companies are directed and controlled
audit committee
a collection of non-executive directors charged with overseeing various controls in place over the audited financial statements
non-executive director
a board member whose responsibility it is to evaluate the effectiveness of the financial reporting process
audit committee is responsible for:
monitor integrity of the audited financial statements
whether the financial statements communicate the company’s position, performance
review risk management and internal controls
address the agency problem
3 things to prove negligence
duty of care existed
duty of care breached
caused loss to the claimant