Bio II Unit 1 Test
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
evolution
1. process by which species have changed and diversified since life arose
2. descent with modification; the idea that living species are descendants of ancestral species that were different from the present day ones; also defined more narrowly as the change in the genetic composition of a population from generation to generations.
scientists
_________ use a process of inquiry that includes making observations, forming logical hypotheses, and testing them.
3
Most light microscopes have _ objective lenses.
cell
1. smallest most basic unit of life.
2. life's fundamental unit of structure and function; the smallest unit of organization that can perform all activities required for life.
energy
1. capacity to do work.
2. the capacity to cause change, especially when working
homeostasis
1. maintenance of internal conditions within certain boundaries.
2. the steady state physiological condition of the body.
metabolism
1. all chemical reactions occuring in the cell
2. the totality of an organism's chemical reactions, consisting of catabolic and anabolic pathways, which managed the material and energy resources of the organism.
organ
made up of tissues and a specialized center of body function composed of several different types of tissues.
organ system
1. organs working together in performing vital body functions
tissue
made up of similar cells in function, structure, or both
biosphere
1. zone of air, land, and water at the surface of the Earth where living organisms are found.
2. The entire portion of Earth inhabited by life; the sum of all the planet's ecosystem
community
1. populations interact among themselves.
2. all the organisms that inhabit a particular area; and assemblage of populations of different species living close enough together for potential interaction.
population
1. a group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area and interbreed, producing fertile offspring.
2. all members of a species in a particular area
ecosystem
1. community and the physical environment
2. all the organisms in a given area as well as abiotic factors with which they interact; one or more communities and the physical environment around them.
adaptation
inherited characteristic of an organism that enhances its survival and reproduction in a specific environment
atom
the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element
autotroph
an organism that obtains organic food molecules without eating other organisms or substances derived from other organisms. These organisms use energy from sun or from oxidation of inorganic substances to make organic molecules from inorganic ones.
biodiversity
1. the variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem
control
1. an element that remains unchanged or unaffected by other variables.
conclusion
1. a statement based on experimental measurements and observations. It includes a summary of the results, whether or not the hypothesis was supported, the significance of the study, and future research
cytoplasm
1. the contents of the cell bounded by the plasma membrane; in eukaryotes, the portion exclusive of the nucleus.
deductive reasoning
1. a type of logic in which specific results are predicted from a general premise.
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
1. a nucleic acid molecule, usually a double-stranded helix, in which each polynucleotide strand consists of nucleotide monomers with a deoxyribose sugar and the nitrogenous base adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. Capable of being replicated and determining the inherited structure of a cell's proteins.
domain
1. a taxonomic category above the kingdom level. The three ________ are Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya.
2. a discrete structural and functional region of a protein.
element
1. any substance that cannot be broken down to any other substance by chemical reactions.
eukaryotic
1. a type of cell with a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles. (protists, plants, fungi, and animals)
experiment
1. a scientific test. often carried out under controlled conditions that involve manipulating one factor in a system in order to see the effects of changing that factor.
gene
1. a discrete unit of hereditary information consisting of a specific nucleotide sequence in DNA (or RNA, in some viruses).
heterotroph
1. an organism that obtains organic food molecules by eating other organisms or substances derived from them.
hypothesis
1. a testable explanation for a set of observations based on the available data and guided by inductive reasoning. narrower in scope than a theory.
inductive reasoning
1. a type of logic in which generalizations are based on a large number of specific observations.
molecule
1. two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
multicellular
1. having or consisting of many cells
mutation
1. a change in the nucleotide sequence of an organism's DNA or in the DNA or RNA of a virus.
natural selection
1. a process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.
nucleus
1. an atom's central core, containing protons and neutrons.
2. the organelle of a eukaryotic cell that contains the genetic material in the form of chromosomes, made up of chromatin.
3. a cluster of neutrons.
nutrient
1. a substance that provides nourishment essential for growth and the maintenance of life.
observation
1. the action or process of observing something or someone carefully or in order to gain information.
organelle
1. any of several membrane enclosed structures with specialized functions, suspended in the cytosol of eukaryotic cells.
organic molecule
1. molecules that are made of carbon and hydrogen, and can include other elements.
organism
1. an individual living things, consisting of one or more cells.
photosynthesis
1. the conversion of light energy to chemical energy that is stored in sugars or other organic compounds; occurs in plants, algae, and certain prokaryotes.
plasma membrane
1. the membrane at the boundary of every cell that acts as a selective barrier, regulating the cell's chemical composition.
prokaryotic
1. a type of cell lacking a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles. (bacteria and archaea).
scientific method
1. a method of procedure that has characterized natural science since the 17th century, consisting in systematic observation, measurement, and experiment, and the formulation, testing, and modification of hypotheses.
scientific theory
1. an explanation of an aspect of the natural world and universe that can be repeatedly tested and corroborated in accordance with the scientific method, using accepted protocols of observation, measurement, and evaluation of results.
species
1. a population or group of populations whose members have the potential to interbreed in nature and produce viable fertile offspring but do not produce viable, fertile offspring with members of other such groups.
subatomic particle
1. a particle which is smaller than an atom in size, the three in an atom are protons, neutrons, and electrons.
unicellular
1. (of protozoans, certain algae, spores, etc.) consisting of a single cell.
variable
1. a factor that varies in an experiment
1. Homeostasis
2. Organization
3. Metabolism
4. Growth
5. Adaptation
6. Response to stimuli
7. Reproduction
the seven characteristics of life
envionment
Living things find energy and or nutrients by interacting with the ______________.
movement
Ability to respond often results in __________
behavior and conscious activity
Homeostasis may be ________ and may not require _____________.
split in two
bacteria simply _________
embryo
union of egg and sperm produces _______
genes
embryo grows according to ________ inherited from parents.
adaptations
Living things have ___________
adaptation
modifications that make organisms suited to their way of life.
taxonomy
discipline of naming and classifying organisms according to certain rules
1.Domain
2.Kingdom
3.Phylum
4.Class
5.Order
6.Family
7.Genus
8.Species
Order of Taxonomy (most inclusive to least inclusive)
genus and species
In a binomial name for an organism, the first word is _______ and the second one is _____.
Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya
What are the three domains?
Archaea
Prokaryote (unicellular and lacks membrane bound nucleus)
May be representative of first cells on Earth
Bacteria
Prokaryote (unicellular and lacks membrane bound nucleus)
Eukarya
Eukaryote
Unicellular or multicellular
Membrane bound nucleus
DIVIDED INTO FOUR KINGDOMS
Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia
the four kingdoms
Protista
unicellular and multicellular
autotrophic and heterotrophic
eukaryotic
Fungi
unicellular and multicellular
heterotrophs
unable to move
Plantae
multicellular
autotrophic
unable to move
Animalia
multicellular
heterotrophic
able to move
Science
The word __________ is derived from Latin and means "to know"
inquiry
the search for information and explanations of natural phenomena
observations
repeating specific _________ can lead to important generalizations in INDUCTIVE REASONING
hypotheses
in deductive reasoning, initial observation may give rise to multiple _____________.
testable
A hypothesis must be _______
supernatural religious
__________ and _________ explanations are outside the bounds of science
scientific process
Very few experiments of scientific inquiries adhere to the _________
scientific process
-inductive reasoning
-deductive reasoning
revolving nosepiece
What is number 2 in the diagram of the compound light microscope?
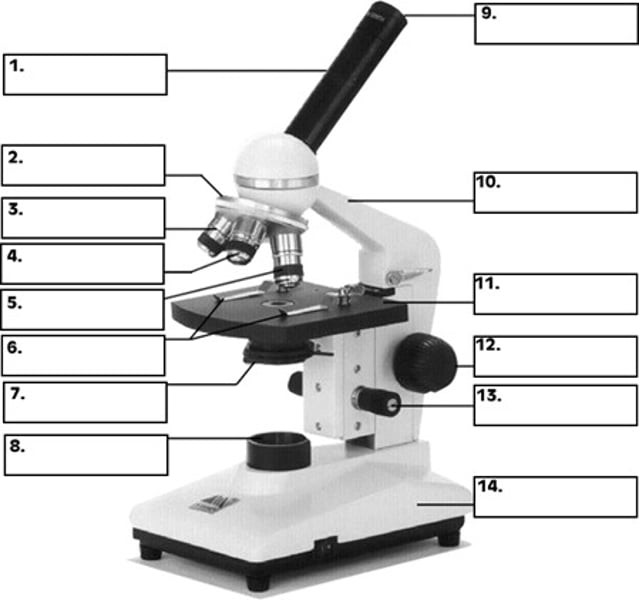
low power objective
What is number 3 in the diagram of the compound light microscope?
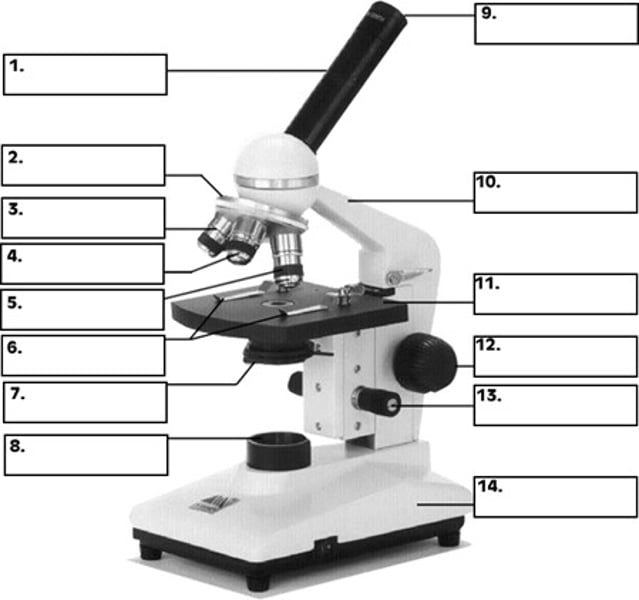
high power objective
What is number 4 in the diagram of the compound light microscope?
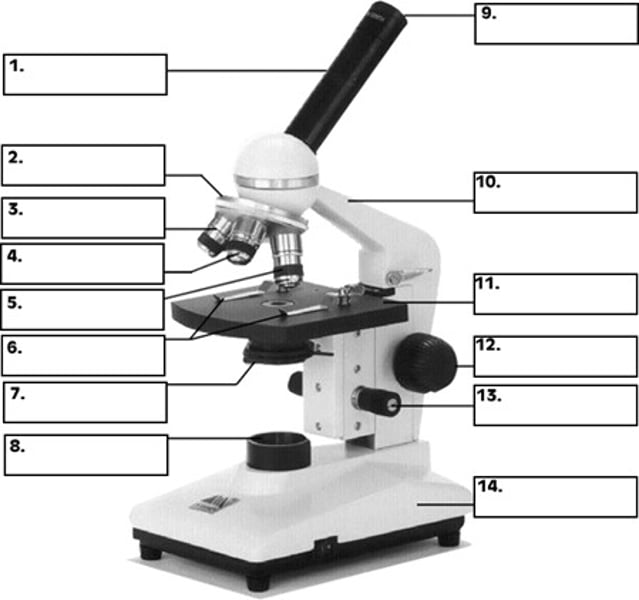
oil immersion objective
What is number 5 in the diagram of the compound light microscope?
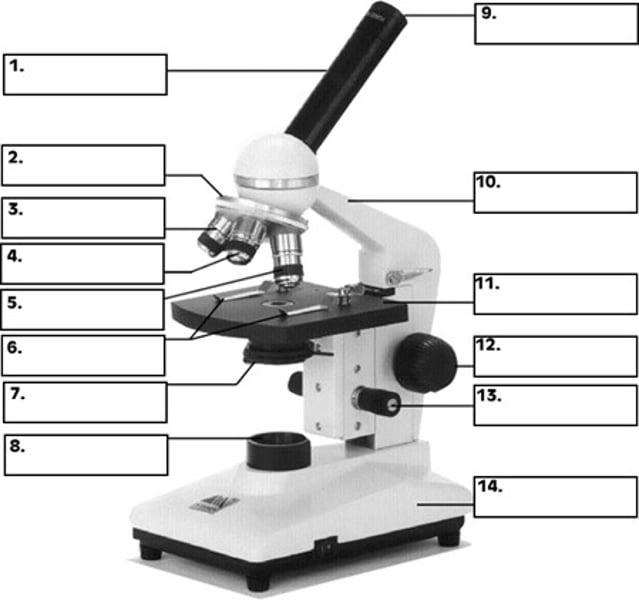
stage clips
What is number 6 n the diagram of the compound light microscope?
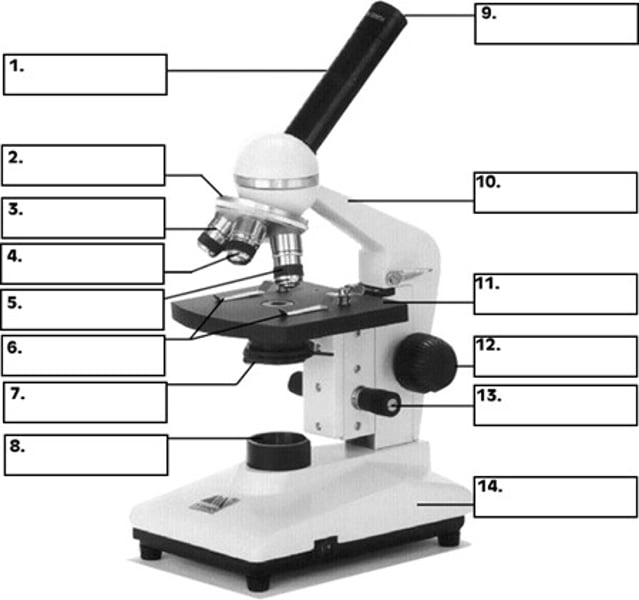
diaphragm
What is number 7 in the diagram of the compound light microscope?
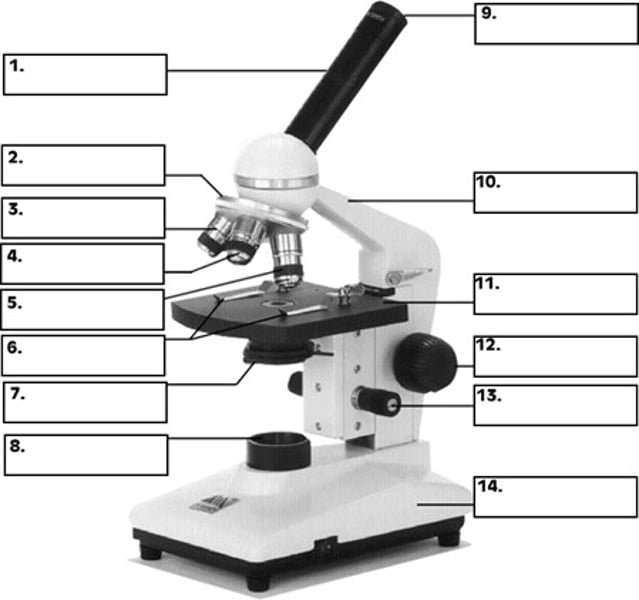
light source
What is number 8 in the diagram of the compound light microscope?
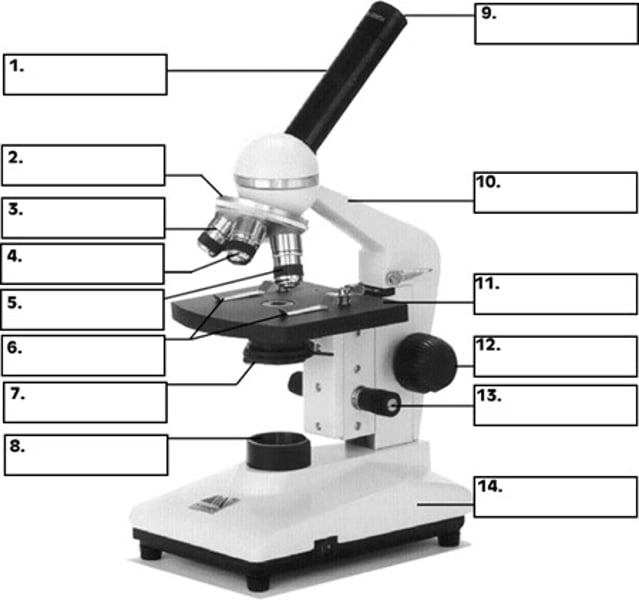
eyepiece
What is number 9 in the diagram of the compound light microscope?
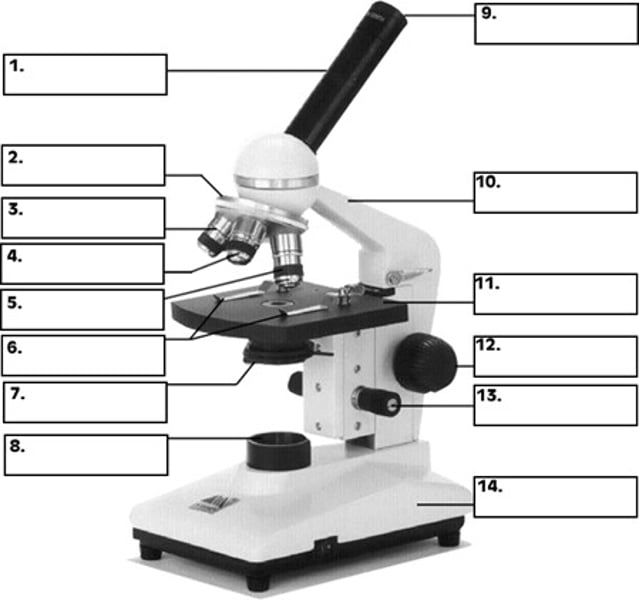
arm
What is number 10 in the diagram of the compound light microscope?
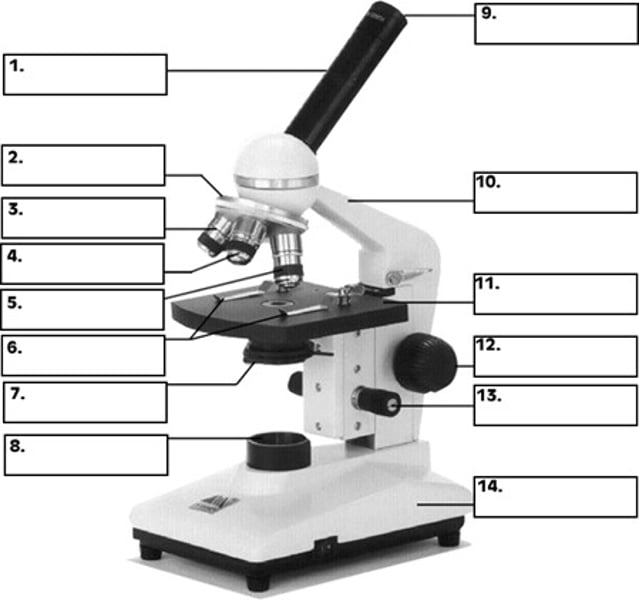
stage
What is number 11 in the diagram of the compound light microscope?
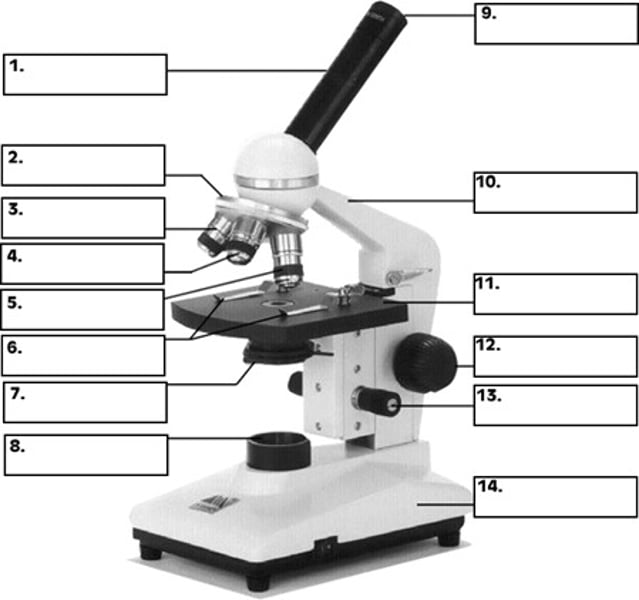
coarse adjustment
What is number 12 in the diagram of the compound light microscope?
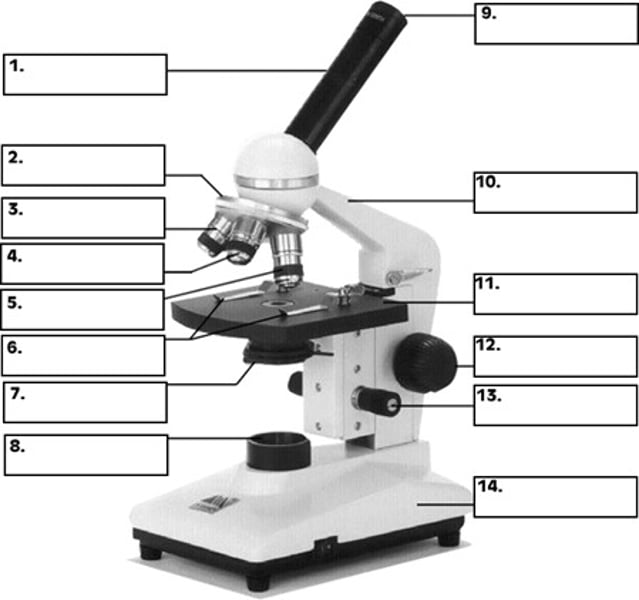
fine adjustment
What is number 13 in the diagram of the compound light microscope?
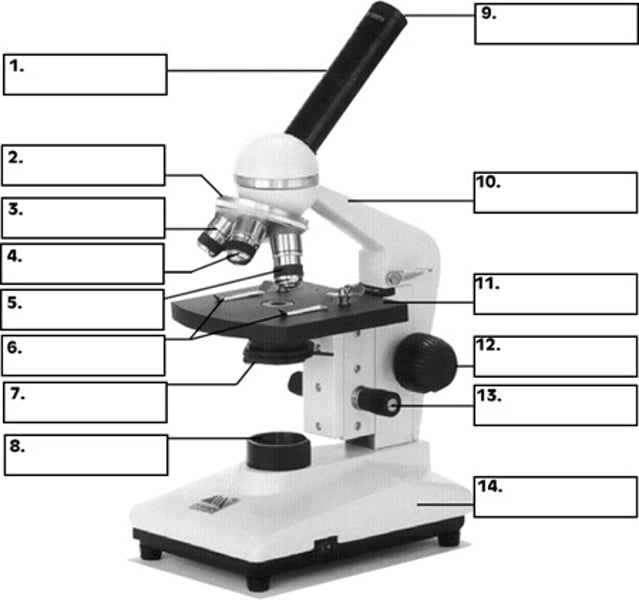
base
What is number 14 in the diagram of the compound light microscope?
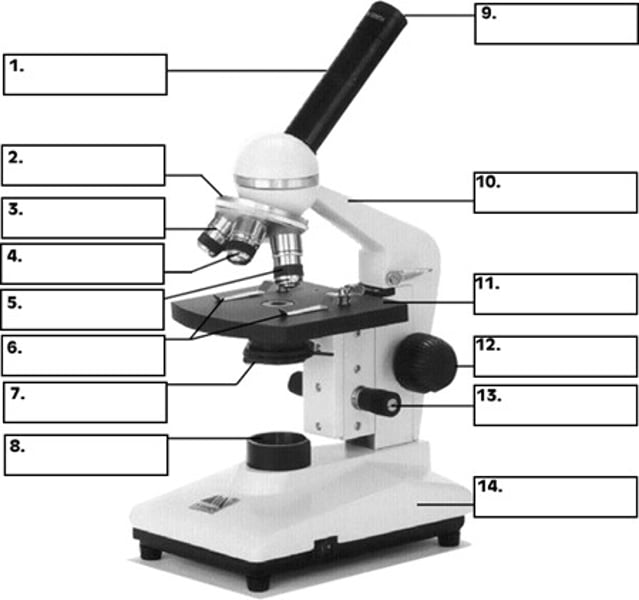
compound light microscope
the microscope that allows biologists to visualize objects from 1 millimeter to 0.1 micrometer. The light microscope is used to look at bacteria, eukaryotic cells, and thinly sliced sections of tissue. (fungal, animal, and plant tissue)
dissecting light microscope/stereoscope
the microscope used to look at whole organisms and or their structures. The effective range of magnification of this microscope is from 0.05 meters to 0.05 millimeters in size.
virus or biological molecule
Much can be seen from the compound light and dissecting light microscopes we use, what cannot be seen?
electron scanning microscope
microscope used to visualize extremely small objects (very large microscope)
total magnification
10x (eyepiece(s)) multiplied by the power of the objective lens
10x
Low power,______, always used to first focus on slide.
40x
High power,_____, used to see specimen in greater detail.
100x
Oil immersion lens,_____, always used with a drop of immersion oil on the slide.