hematology 1 exam
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What % is albumin in plasma proteins
55%
Where is albumin synthesized
Liver
What is the function of albumin
Transport of hydrophobic substances in blood
Maintaining normal body osmolality
Buffer
What % of globulins is in plasma protein
38%
What different types of globulins are there
Alpha, beta, gamma
Are the functions of globulins similar to albumin
Yes
Where are alpha and beta globulins synthesized
Liver
What are gamma globulins synthesized by
B Lymphocytes
What are the functions of gamma globulins
Function is as antibodies involved in immunity
What % of fibrinogen is in plasma protein
7%
Where is fibrinogen synthesized
Liver
Functions of fibrinogen
Blood clotting
Walling off infectious processes
What does RBCs contain
Hemoglobin (hb)
What % of oxygen does heme transport
99%
What % of carbon dioxide does globin transport
23%
What is the structure of hemoglobin and what are they composed of
1 globin molecule composed of 4 polypeptide chains ( 2alpha 2 beta)
4 hemes composed of protoporphyrin ring with an iron atom in the center
What color are oxygen bound hemes
Bright red
What color are hemes that are not bound to oxygen
Dull red or blue
Is heme a pigment molecule
Yes
what regulates the amount of iron that is absorbed
Amount of iron storage- if there is lots in storage not much iron will be absorbed
Rate of RBC production- if rbcs are being manufactured quickly then more iron is absorbed
What does transferrin do
Carries iron to the bone marrow for RBC production
What is ceruloplasmin
Copper containing alpha globulin
What does ceruloplasmin do
Transfers iron onto transferrin in blood from the intestinal absorptive cells and macrophages
What % of iron is found in hemoglobin
60%
Where is the other 40% of iron stored
in storage or in myoglobin
What are 2 storage forms found in macrophages of the liver, spleen, and bone marrow
Ferritin (main) and hemosiderin
Is ferritin readily available for RBC production
Yes
Is hemosiderin accessible for RBC production
less accessible
Process for extravascular hemolysis
1- heme breakdown to bilirubin macrophages
2- unconjugated bilirubin transported in blood to liver
3- urobilinogen transported to kidney
4- urobilinogen oxidized by intestinal bacteria
What happens in intravascular hemolysis
it becomes bound to a plasma protein called haptoglobin and is carried to the kidney where it is excreted in the urine (hemoglobinuria)
What does regenerative anemia suggest
Suggests an extra marrow cause such as hemorrhage or hemolysis
How does the bone marrow respond to regenerative anemia. And what is it characterized as
Increasing RBC production. Characterized by an increased reticulocyte count (immature RBCs)
Causes of Non regenerative anemia
Anemia of chronic disease
Marrow tumor
Nutritional deficiency
What happens to the bone marrow in nonregenerative anemia
The bone marrow fails to increase RBC production adequately.
Low or absent reticulocytes response
What does normocytic cell look like
Same size or slightly smaller than the nucleus of small lymphocyte
What is rouleaux
4 or more RBC stacked like coins
When is rouleaux seen
Inflammations
Multiple myeloma which produce increased plasma proteins
Equine sample
What is agglutination
RBC cluster that looks like grapes
What are causes of agglutination
AIHA
Intra AIHA
What is hypochromic associated with
Low MCH/ MCHC
When do you see hypochmromic
Iron deficiency anemia
Why is there less color on hypochromic cells
Decreased hemoglobin concentration
What shape is macrocytic RBC
Round
Where do you see macrocytic RBC
Horses have slight macrocytosis (anisocytosis)
Are macrocytic larger than the nucleus of small lymph
Yes
What does RDW stand for
Red cell distribution width
What does anisocytosis mean
Term used to describe variation in size of RBCS
Mix of large or small cells
What does MCV mean
Mean cell volume
What does MCV represent
Average size of all RBC in patient sample
What is poikilocytosis
The shape of cells
Can analyzers determine RBC morphology
No
What do echinocytes look like
Short points with central pallor
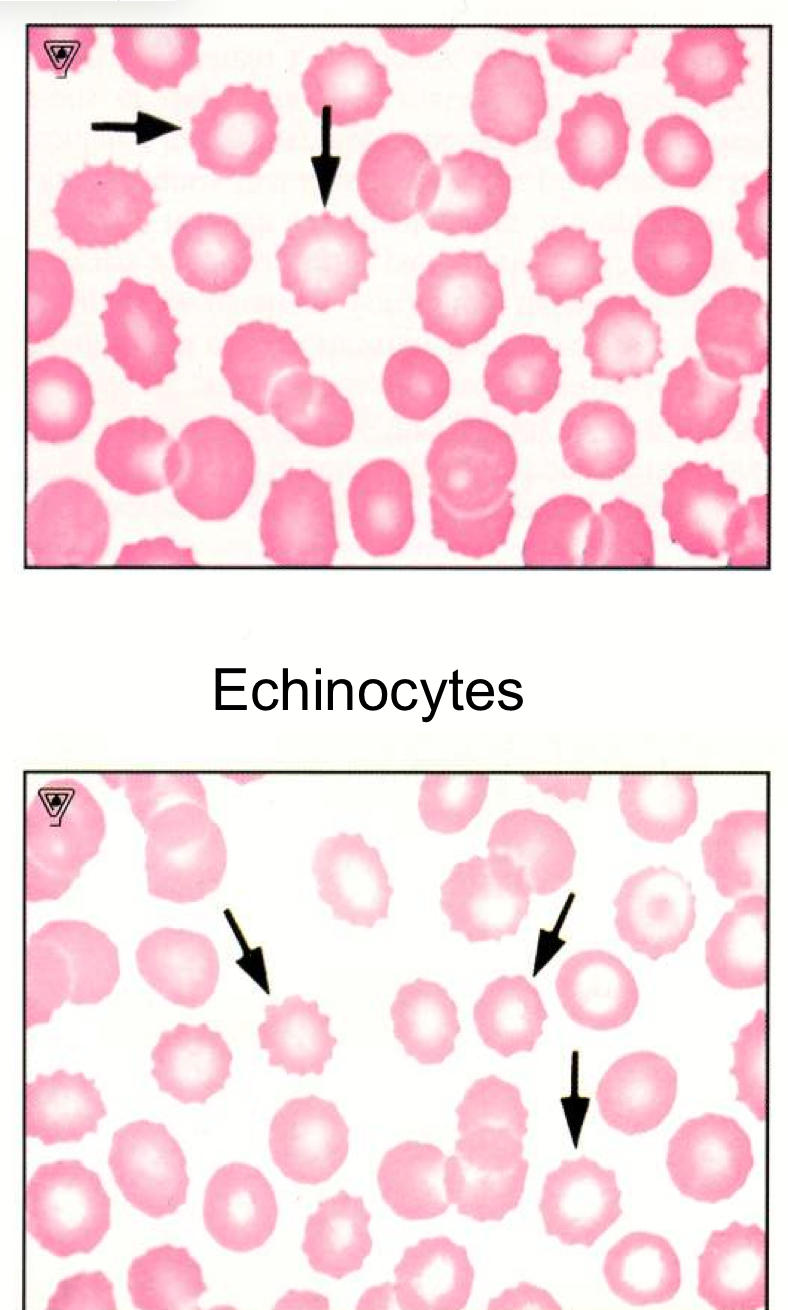
Do crenated cells lack central pallor
Ya
When do you see echinocytes
Severe renal disease
Feline liver disease
Burns
What do crenated cells look like
Echinocytes
What do acanthocytes look like
No central pallor
Long sea urchin like spike
What disorders cause acanthocytes
Hemangiosarcoma
Liver disease
DIC
Vasculitis
Iron deficiency anemia
What are target cells associated with
Iron deficiency anemia
Splenectomy
Obstructive liver disease
What are schistocytes
Cell fragments from RBC destruction
What are dacryocytes
Tear drop cells
When do you see tear drop cells
In iron deficiency
Do spherocytes have central pallor
No
What are spherocytes caused by
Immune hemolysis
What are ghost cells
Hemoglobin leached from RBC from intravascular hemolysis
What species are how’ll jolly bodies seen in normally
Cats and horses
What are Howell jolly bodies a sign of
RBC regenerative anemia