First Aid USMLE STEP 1: Microbiology
1/570
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
571 Terms
Cell Wall Overall Picture - Compare Gram (+) to Gram (-)

Flagellum on bacteria is composed of what? What is the function?
Composition: Proteins
Function: motility
Pilus/Fimbria on bacteria is composed of what? What is the function?
Composition: Glycoprotein
Function: Mediate adherence of bacteria to cell surface, sex plus during conjugation.
Spore formation is ONLY possible is what type of bacteria? Why is the formation of spores important/beneficial?
What is the composition of a spore?
Gram Positive Only
Function: Resistant to dehydration, heat, and chemicals.
Composition: Keratin-like coat; dipicolinic acid; peptidoglycan.
Capsule will be composed of what on bacteria? What is the benefit of a capsule?
Function: Protects against phagocytosis
Composition: Organized, discrete polysaccharide layer (except Bacillus anthracis, which contains d-glutamate)
Glycocalyx
Function: Mediates adherance to surfaces, especially foreign surfaces (e.g., indwelling catheters)
Composition:Loose network of polysaccharides
Periplasm
Space between the cytoplasmic membrane and outer membrane in gram-negative bacteria
(peptidoglycan in the middle)
Gram Neg only
Accumulates components exiting gram neg cells, including hydrolytic enzymes (β-lactamases)
Outer membrane (gram negatives)
Gram Neg Only
Function:
1. Endotoxin: Lipid A induces TNF and IL-1; O polysaccharide is antigenic
2. Most OMPs are antigenic
Porins: transport across outer membrane
Composition:
1. Outer Leaflet: endotoxin lipopolysaccharide [LPS/LOS]
2. Embedded proteins: porins and other outer membrane proteins (OMPs)
3. Inner Leaflet: phospholipids
Cell wall and Gram Stain
Composition: Peptidoglycan is a sugar backbone with peptide chains cross-linked by transpeptidase
Function: Net-like structure give rigid support, protects against osmotic pressure damage.
Gram Stain:
Thick peptidoglycan layer retains crystal violet = gram +
Thin peptidoglycan layer turns red or pink with counterstain = gram -
Cytoplasmic Membrane
Composition: Phospholipid bilayer sac with embedded proteins (PBP's) and other enzymes.
Lipoteichoic acids (gram Pos+ only) extend from membrane exterior.
Function: Site of oxidative and transport enzymes
PBPs involved in cell wall synthesis
Lipoteichoic acids induce TNF and IL-1
Plasmid
-Contains a variety of genes for antibiotic resistance, enzymes, and toxins
-Composed of DNA
Gram-positive spherical (coccus) bacteria
-Staphylococcus (clusters)
-Streptococcus (chains, pairs)
Gram-positive rod (bacillus) bacteria
-Bacillus
-Clostridium
-Corynebacterium
-Gardnerella (gram variable)
-Lactobacillus
-Listeria
-Mycobacterium (acid fast)
-Propionibacterium
Gram-positive branching filamentous bacteria
-Actinomyces
-Nocardia (weakly acid-fast)
Gram-negative spherical (coccus) bacteria
-Moraxella catarrhalis
-Neisseria
Gram-negative rod (bacillus) bacteria Enterics
Enterics:
1. Bacteroides
2. Campylobacter
3. E. coli
4. Enterobacter
5. Helicobacter
6. Klebsiella
7. Proteus
8. Pseudomonas
9. Salmonella
10. Serrate
11. Shigella
12. Vibrio
13. Yersinia
Gram-negative rod (bacillus) bacteria Respiratory and Zoonotic
Respiratory:
1. Bordetella
2. Haemophilus (pleomorphic)
3. Legionella (silver stain)
Zoonotic:
1. Bartonella
2. Brucella
3. Francisella
4. Pasteurella
Pleomorphic gram-negative bacteria
-Chlamydiae (Giemsa)
-Rickettsiae (Giemsa)
Spiral gram-negative bacteria
Spirochetes:
-Borrelia (Giemsa)
-Leptospira
-Treponema
No cell wall bacteria
Mycoplasma, Ureaplasma (contains sterols, which do not gram stain)
These bugs do not Gram stain well:
Too thin to be visualized.
1. Treponema
2. Leptosipra
Cell wall has high lipid content; mycolic acids in cell wall
detected by carbolfuchsin in acid- fast stain).
1. Mycobacteria
No Cell Wall
1. Mycoplasma
2. Ureaplasma
Primarily Intracellular
1. Legionella pneumophila (silver stain).
2. Rickettsia
3. Chlamydia ( lacks classic peptidoglycan because of low muramic acid)
4. Bartonella
5. Ehrlichia
6. Anaplasma
What is seen with dark-field microscopy and fluorescent antibody staining?
Treponemes are seen with FTA-ABS
Giemsa staining
Chlamydia, Borrelia, Rickettsia, Trypanosomes, Plasmodium
PAS (periodic acid-Schiff)
Stains glycogen, mucopolysaccharides
Used to diagnose Whipple disease (Tropheryma whipplei).
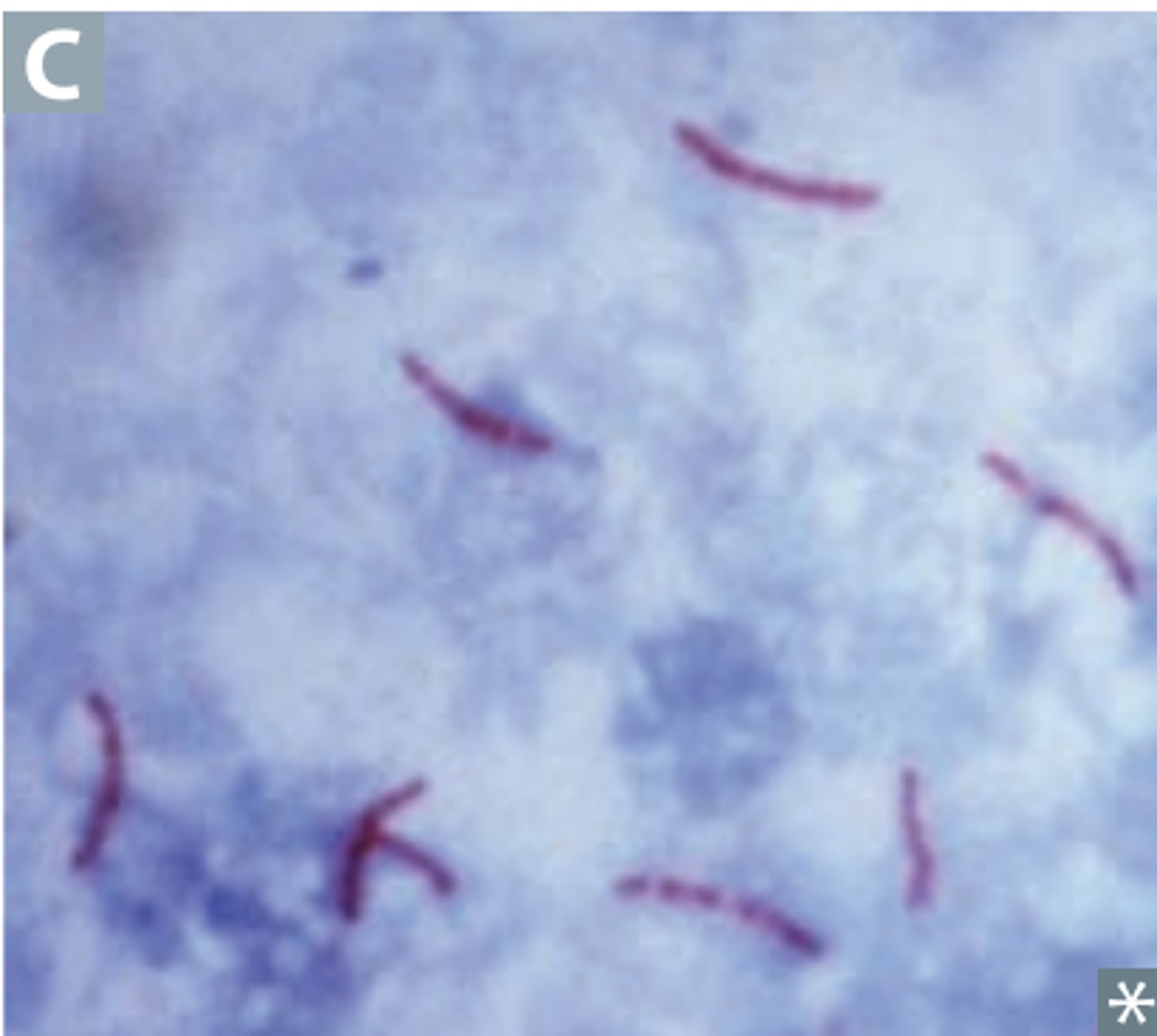
Ziehl-Neelsen (carbol fuchsin)
Acid-fast bacteria
1. Nocardia
2. Mycobacteria - stains mycelia acid in cell wall
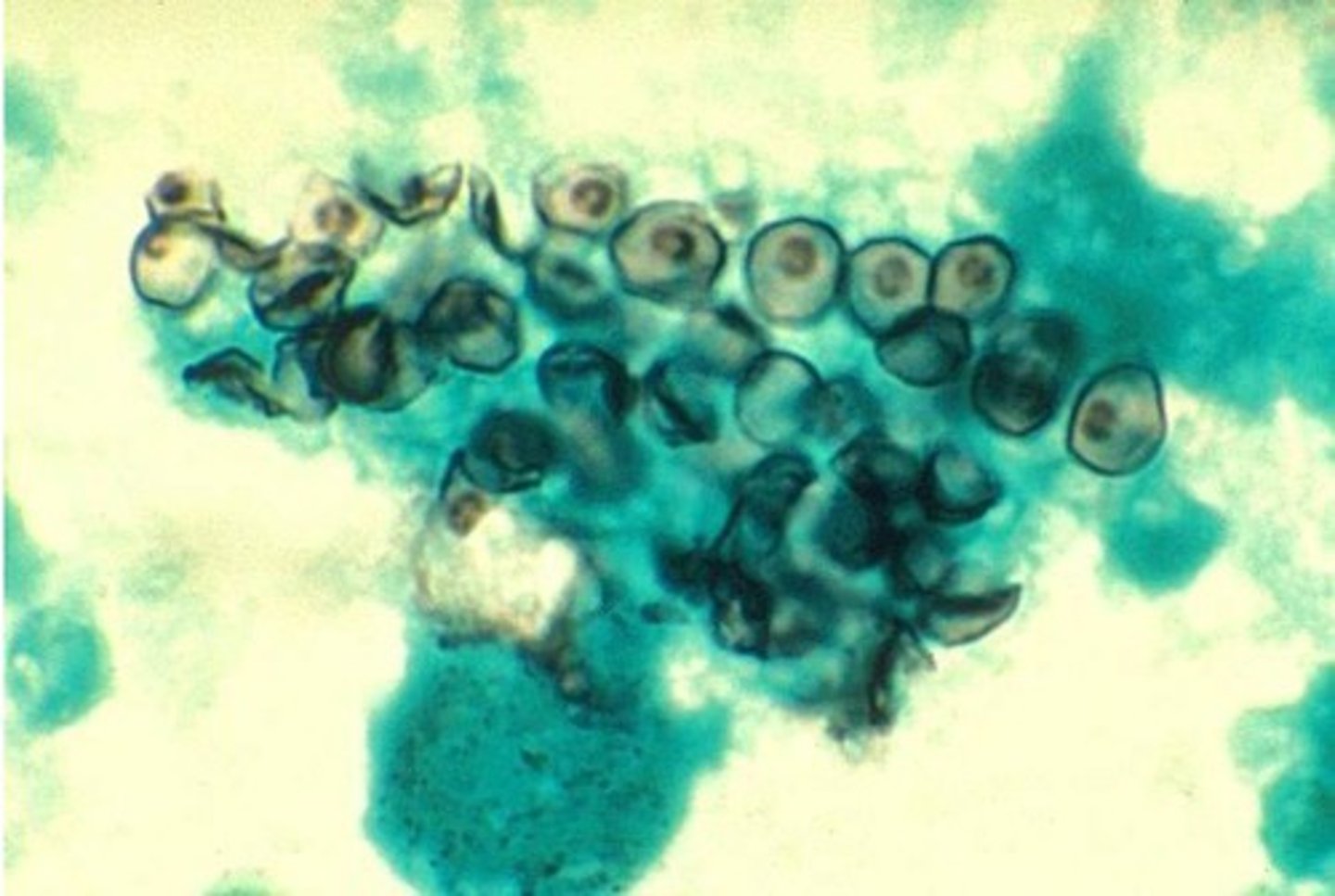
Protozoa
1. Cryptosporidium oocysts
-Alternative is auramine-rhodamine stain for screening (inexpensive, more sensitive but less specific).
India ink
Cryptococcus neoformans (mucicarmine can also be used to stain thick polysaccharide capsule red).
Silver stain
Fungi (e.g., Coccidioides, Pneumocystis jirovecii)
Legionella
Helicobacter pylori
H. influenzae special culture requirements
Chocolate agar: Factors V (NAD+) and X (hematin)
N. gonorrhoeae, N. meningitidis special culture requirements
Thayer-Martin agar:
-Vancomycin inhibits gram+ organisms
-Trimethoprim and Colistin inhibits gram(-) organisms except Neisseria
- Nystatin inhibits fungi
"Very Typically Cultures Neisseria"
B. pertussis special culture requirements
Bordet-Gengou agar (Bordet for Bordetella)
-potato
Regan-Lowe medium
-charcoal, blood, and antibiotic
C. diphtheriae special culture requirements
Tellurite agar
Löffler medium
M. tuberculosis special culture requirements
Lowenstein-Jensen agar
M. pneumoniae special culture requirements
Eaton agar - requires cholesterol
Lactose fermenting enterics special culture requirements
MacConkey agar - fermentation produces acid, causing colonies to turn pink
E. coli special culture requirements
Eosin-methylene blue (EMB) agar
-Colonies with green metallic sheen
Legionella special culture requirements
Charcoal yeast extract agar buffered with cysteine and iron
Fungi special culture requirements
Sabouraud agar
"Sam's a fun guy!"
What are aerobes? Examples?
Use an O2-dependent system to generate ATP
Examples include:
1. Nocardia
2. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
3. MycoBacterium tuberculosis
Reactivation of M. tuberculosis (e.g., after immunocompromise or TNF-α inhibitor use) has a predilection for the apices of the lung, which have the highest Po2.
What are anaerobes? Examples?
Can't grow in the presence of O2
Examples include:
1. Fusobacterium
2. Clostridium
3. Bacteroides
4. Actinomyces.
They lack catalase and/or superoxide dismutase and are thus susceptible to oxidative damage. ("Anaerobes Frankly Can't Breathe Air")
Generally foul smelling (short-chain fatty acids), are difficult to culture, and produce gas in tissue (CO2 and H2)
Anaerobes are normal flora in GI tract, typically
pathogenic elsewhere
AminO2glycosides are ineffective against anaerobes because these antibiotics require O2 to enter into bacterial cell.
Obligate intracellular bugs
Rickettsia, chlamydia, coxiella
Rely on host ATP.
Facultative intracellular bugs
Salmonella, Neisseria, Brucella, Mycobacterium, Listeria, Francisella, Legionella, Yersinia pestis.
Encapsulated bacteria
1. Streptococcus pneumoniae
2. Haemophilus influenzae type B
3. Neisseria meningitides
4. Escherichia coli
5. Salmonella
6. Klebsiella pneumoniae
7. Group B Strep.
Their capsules serve as an antiphagocytic virulence factor.
Capsular polysaccharide + protein conjugate serves as an antigen in vaccines.
How are encapsulated bacteria killed?
They are opsonized, and then cleared by spleen.
Asplenics have decreased opsonizing ability and thus increased risk for severe infections.
Give S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, N. meningitidis vaccines.
Encapsulated bacteria vaccines
Some vaccines containing polysaccharide capsule antigens are conjugated to a carrier protein, enhancing immunogenicity by promoting T-cell activation and subsequent class switching.
A polysaccharide antigen alone cannot be presented to T cells
Pneumococcal vaccine
PCV (pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, i.e., Prevnar)
PPSV (pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine with no conjugated protein, i.e., Pneumovax)
H. influenzae type B vaccine
Conjugate vaccine
Meningococcal vaccine
Conjugate vaccine
Urease-positive organisms
Cryptococcus
H. pylori
Proteus
Ureaplasma
Nocardia
Klebsiella
S. epidermis
S. saprophytic.
Potentiate struvite (ammonium magnesium phosphate) stones.
Urease hydrolyzes urea to release ammonia + CO2 which increases pH to become alkaline
Catalase-positive organisms
Catalase degrades H2O2 into H2O and bubbles of O2 before it can be converted to microbicidal products by the enzyme myeloperoxidase.
People with chronic granulomatous disease (NADPH oxidase deficiency) have recurrent infections with certain catalase ⊕ organisms.
Examples: Nocardia, Pseudomonas, Listeria, Aspergillus, Candida, E. coli, Staphylococci, Serrate, B Cepacia, H. Pylori
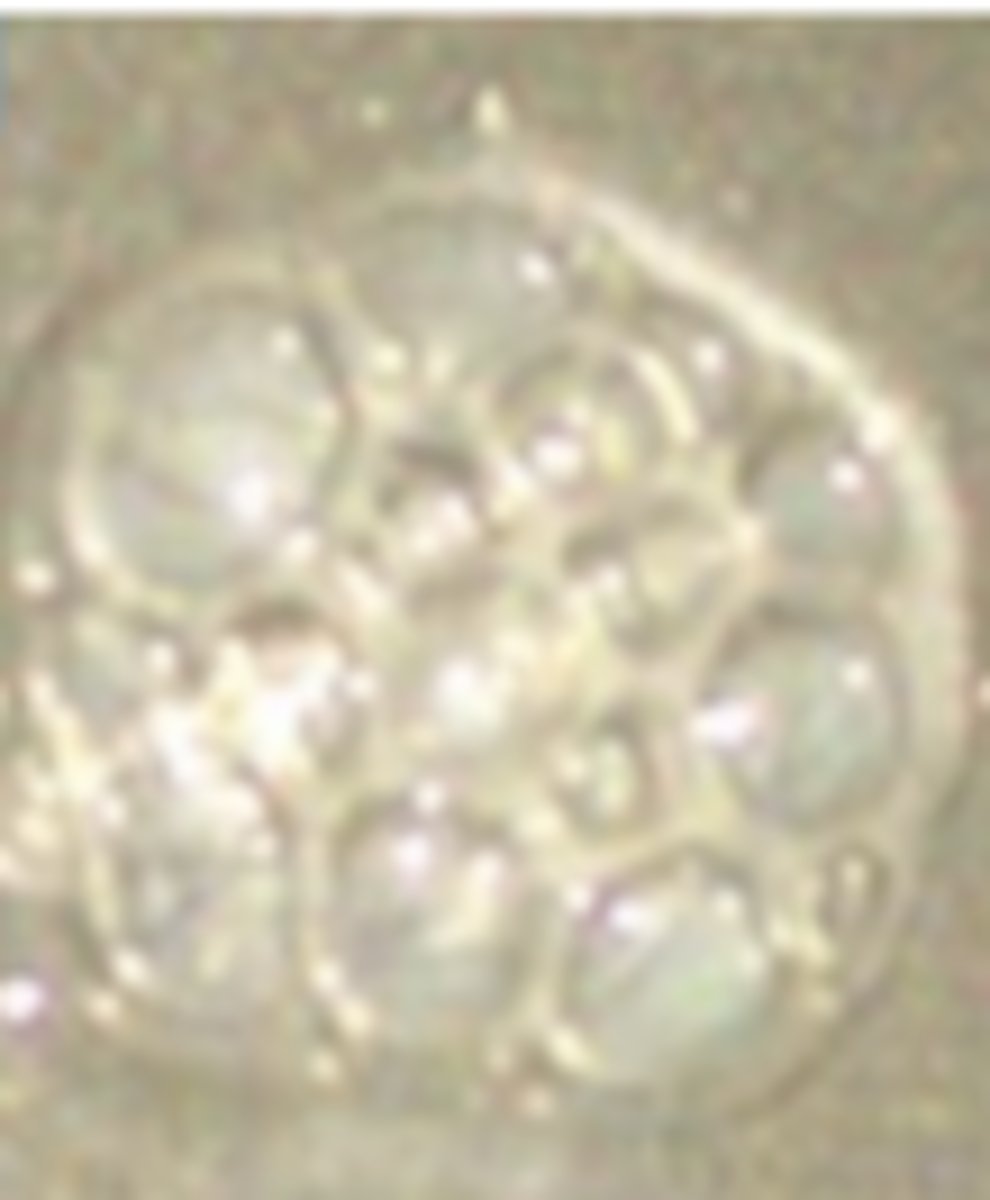

Actinomyces israelii pigment
Yellow "sulfur" granules, which are composed of filaments of bacteria
"Israel has yellow sand"
S. aureus pigment
Yellow pigment
Aureus (latin) = gold
Pseudomonas aeruginosa pigment
Blue-green pigment
"Aerugula salad is green"
Serratia marcescens pigment
Red pigment
"Think red maraschino cherries"
Staph epidermidis biofilm location
Catheter and prosthetic devices
Viridian's Streptococci (S. Mutans, S. Sanguinis) biofilm location
dental plaques
infective endocarditis
P. aeruginosa biofilm
Respiratory tree colonization in cystic fibrosis patients, contact lens-associated keratitis
Nontypeable unencapsulated H influenza biofilm
Otitis Media
Bacterial virulence factors
These promote evasion of host immune response.
Protein A
Binds Fc region of IgG. Prevents opsonization and phagocytosis. Expressed by S. aureus.
IgA protease
Enzyme that cleaves IgA
Secreted by S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae type B, and Neisseria (SHiN) in order to colonize respiratory mucosa.
M protein
Helps prevent phagocytosis. Expressed by group A streptococci.
Shares similar epitopes to human cellular proteins (molecular mimicry); possibly underlies the autoimmune response seen in acute rheumatic fever.
Type III secretion system
Also known as "injectisome."
Needle-like protein appendage facilitating direct delivery of toxins from certain gram-negative bacteria (e.g., Pseudomonas, Salmonella, Shigella, E. coli) to eukaryotic host cell.
Exotoxin source
Certain species of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
Exotoxin secreted from cell?
Yes
Exotoxin chemistry
Polypeptide
Location of exotoxin genes
Plasmid or bacteriophage
Exotoxin toxicity
High (fatal dose on the order of 1 μg)
Exotoxin antigenicity
Induces high-titer antibodies called antitoxins
Exotoxin vaccines
Toxoids used as vaccines
Heat stability of exotoxins
Destroyed rapidly at 60°C (except staphylococcal enterotoxin)
Typical exotoxin diseases
Tetanus, botulism, diptheria
Endotoxin source
Outer cell membrane of most gram-negative bacteria
Is endotoxin secreted from the cell?
No
Chemistry of endotoxin
Lipid A component of Lipopolysaccharide (structural part of bacteria; released when lysed)
Endotoxin Toxicity
Low
Fatal dose on the order of 100s of μg
Location of endotoxin genes
Bacterial chromosome
Clinical effects of endotoxin
Fever, shock (hypotension), DIC
Mode of action of endotoxin
Induces TNF, IL-1, and IL-6
Antigenicity of endotoxin
Poorly antigenic
Endotoxin vaccines
No toxoids formed and no vaccine available
Endotoxin heat stability
Stable at 100°C for 1 hr
Typical endotoxin diseases
Meningococcemia; sepsis by gram-negative rods
Corynebacterium diphtheriae exotoxin
Diphtheria toxin
Inhibits protein synthesis via inactivation of elongation factor (EF-2).
Presents as pharyngitis with pseudomembranes in throat and severe lymphadenopathy (bull neck)
Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin
Exotoxin A
inhibits protein synthesis via inactivation of elongation factor (EF-2)
Manifests itself in host cell death
Shigella spp. exotoxin
Shiga toxin (ST)
Inactivation of 60S ribosome by removing adenine from rRNA
Manifestations: GI mucosal damage --> dysentery; ST also enhances cytokine release, causing hemolytic- uremic syndrome (HUS)
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) exotoxin
Shiga-like toxin (SLT)
Inactivation of 60S ribosome by removing adenine from rRNA
Manifestations: SLT enhances cytokine release, causing HUS (prototypically in EHEC serotype O157:H7). Unlike Shigella, EHEC does not invade host cells
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) exotoxin
Heat-labile toxin (LT): overactivates adenylate cyclase (increasing cAMP) --> increasing Cl− secretion in gut and H2O efflux
Heat-stable toxin (ST): overactivates guanylate cyclase (increases cGMP) --> decreased resorption of NaCl and H2O in gut
Both increase fluid - presents as watery diarrhea
"labile in the Air (Adenylate cyclase), stable on the Ground (Guanylate cyclase)"
Edema toxin
Bacillus anthracis exotoxin
- Increase Fluid Secretion
Mimics the adenylate cyclase enzyme (increase cAMP)
Likely responsible for characteristic edematous borders of black eschar in cutaneous anthrax
Cholera toxin
Vibrio cholerae exotoxin
-Increases fluid secretion
Overactivates adenylate cyclase (increasing cAMP) by permanently activating Gs --> increasing Cl− secretion in gut and H2O efflux
Voluminous "rice-water" diarrhea
Pertussis toxin
Bordetella pertussis exotoxin
Inhibits phagocytic ability
Overactivates adenylate cyclase (increasing cAMP) by disabling Gi, impairing phagocytosis to permit survival of microbe
Whooping cough—child coughs on expiration and "whoops" on inspiration (toxin may not actually be a cause of cough; can cause "100-day cough" in adults)
Tetanospasmin
Clostridium tetani exotoxin
Inhibits release of neurotransmitter
Protease that cleaves SNARE (soluble NSF attachment protein receptor), a set of proteins required for neurotransmitter release via vesicular fusion
Spastic Paralysis, risus sardonicus, and "lockjaw"; toxin prevents release of inhibitory (GABA and glycine) neurotransmitters from Renshaw cells in spinal cord
Botulinum toxin
Clostridium botulinum exotoxin
Inhibits release of neurotransmitters
Protease that cleaves SNARE (soluble NSF attachment protein receptor), a set of proteins required for neurotransmitter release via vesicular fusion
Flaccid paralysis, floppy baby; toxin prevents release of stimulatory (ACh) signals at neuromuscular junctionsflaccid paralysis
ADP ribosylating A-B toxin
B (binding) component binds to host cell surface receptor, enabling endocytosis
A (active) component attaches ADP-ribosyl to disrupt host cell proteins
Examples: Botulinum, Tetanospasmin, Pertissis toxin, Cholera toxin, Edema toxin, Heat-labile toxin (LT), Shiga-like toxin (SLT), Shiga toxin (ST), Endotoxin A, Diphtheria toxin.
Alpha toxin
Clostridium perfringens exotoxin
Lyses cell membrane
Phospholipase (lecthinase) that degrades tissue and cell membranes
Manifests as a degranulation of phospholipids --> myonecrosis ("gas gangrene") and hemolysis ("double zone" of hemolysis on blood agar)
Streptolysin O
Streptococcus progenies exotoxin
-Lyses Cell Membrane
Protein that degrades cell membrane
Lyses RBCs; contributes to β-hemolysis;
host antibodies against toxin (ASO) used to diagnose rheumatic fever (do not confuse with immune complexes of poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis)
Toxic shock syndrome toxin (TSST-1)
Staphylococcus aureus exotoxin
Superantigen causing shock
Binds to MHC II and TCR outside of antigen binding site to cause overwhelming release of IL-1, IL-2, IFN-γ, and TNF-α ---> shock
Toxic shock syndrome: fever, rash, shock; other toxins cause scalded skin syndrome (exfoliative toxin) and food poisoning (enterotoxin)
Exotoxin A
Streptococcus pyogenes exotoxin
Superantigen causing shock
Binds to MHC II and TCR outside of antigen binding site to cause overwhelming release of IL-1, IL-2, IFN-γ, and TNF-α causing shock
Toxic shock syndrome: fever, rash, shock
Endotoxin
LPS found in outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria (both cocci and rod).
Composed of:
O antigen + core polysaccharide + lipid A (the toxic component)
Released upon cell lysis or by living cells by blebs detaching from the outer surface membrane (vs exotoxin which is actively secreted)
Endotoxin action
1. Activate macrophages(TLR4) ---> they secrete:
- IL-, IL-6 (fever)
-TNF-α (fever and hypotension)
- NO (hypotension)
2. Activates complement --> releases
- C3a (Hypotension, edema, histamine release)
- C5a (Hypotension, Edema, Histamine release, neutrophil chemotaxis)
3. Activates tissue factor -> coagulation cascade -> DIC
ENDOTOXINS
pneumonic
Edema
Nitric Oxide
Dic/Death
Outer Membrane
TNF-alpha
O-antigen+core polysacc + lipid A
eXtremely heat stable
IL-1 and IL-6
Neutrophil Chemotaxis
Shock