Thermodynamics & Calorimetry
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
1
New cards
Collision Theory
reactants need to combine w/ enough energy and in proper orientation in order to react
2
New cards
effective collision
a collision that results in a chemical reaction
3
New cards
law of conservation of energy
energy cannot be created or destroyed
4
New cards
kinetic energy
energy used for motion
5
New cards
potential energy
stored energy- when reactants collide
6
New cards
activated complex
unstable phase while reaction is occurring
7
New cards
enthalpy
the amount of energy(heat) being stored in bonds of a compound.
Note: products & reactants almost always have an absorption release of enthalpies
Note: products & reactants almost always have an absorption release of enthalpies
8
New cards
endothermic reaction
* when products have a higher enthalpy
* reaction in which energy is absorbed
* reaction in which energy is absorbed
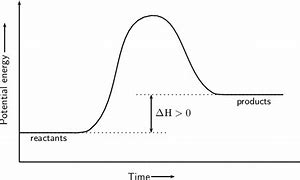
9
New cards
exothermic reaction
* reaction in which energy is released
* when products have a lower enthalpy
* when products have a lower enthalpy
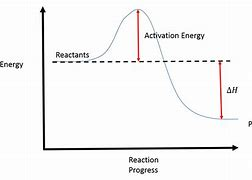
10
New cards
specific heat
substance ability to resist temperature change
11
New cards
high specific heat
requires a lot of energy to inc. or dec. in temperature
12
New cards
Calorimetry Equation
mcΔT
13
New cards
Q
heat (joules)
14
New cards
M
mass (grams) \*if not in grams, convert
15
New cards
C
specific heat (j/gC)
16
New cards
T
temperature (C)
17
New cards
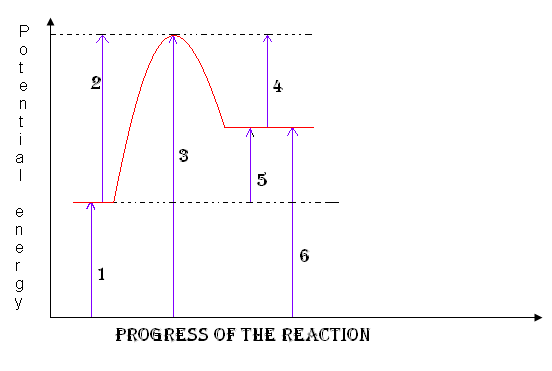
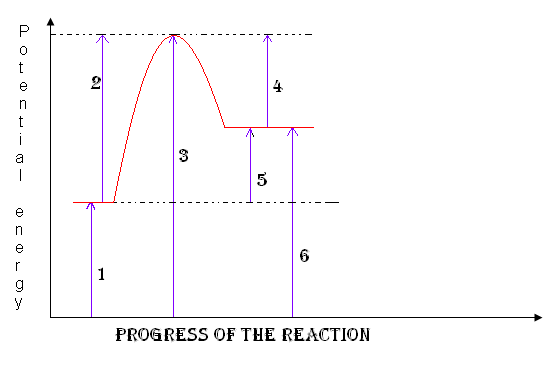
reactants
1
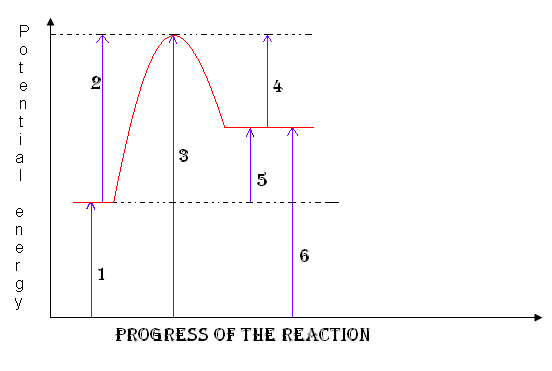
18
New cards
products
6
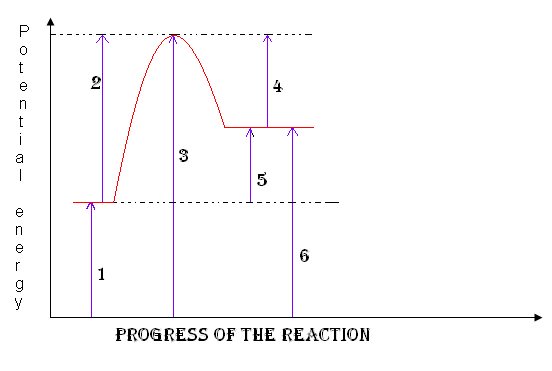
19
New cards
activation complex
3
20
New cards
Heat of the reaction
5
21
New cards
Q of absorbed
Q of released =
22
New cards
Q of released
Q of absorbed =
23
New cards
\-Q
if energy is lost (__Q)
24
New cards
\+Q
if energy is absorbed (__Q)
25
New cards
ΔH (delta H)
change in variable
H final-H initial
H final-H initial
26
New cards
\-ΔH
exothermic H
27
New cards
\+ΔH
endothermic H
28
New cards
potential energy (hold together)
there is a specific amount of energy holding together H2 & O2
29
New cards
potential energy
When the particles collide, Kinetic Energy becomes ______
30
New cards
5 things to increase rate of Effective collision
* temperature (changes energy & likelihood, speed & rate)
* pressure (decrease in volume, more collisions)
* surface area (increase # of particles for collisions)
* presence of catalyst
* concentration (likelihood of collisions is higher bc more molecules)
* pressure (decrease in volume, more collisions)
* surface area (increase # of particles for collisions)
* presence of catalyst
* concentration (likelihood of collisions is higher bc more molecules)
31
New cards
no, sometimes they bounce off because:
* not enough energy
* did not collide in the right spot
* not enough energy
* did not collide in the right spot
Do molecules always react when they collide?
32
New cards
they collide
why do molecules react?
33
New cards
entropy
the amount of disorder in a system
naturally increases (easier to create disorder than order)
naturally increases (easier to create disorder than order)
34
New cards
least entropy
particles in solids stay in place: rigid, fixed shape, fixed volume (____entropy)
35
New cards
most entropy
gas particles move freely & randomly (____ entropy)
36
New cards
least particles
least disorder (solid)
37
New cards
most particles
most disorder (gas)
38
New cards
S
entropy
39
New cards
entropy equation
ΔS = S final - S initial
40
New cards
spontaneous
* uses energy to create reaction
* once reaction starts, continues on own
* these reactions can possibly take a long time
* once reaction starts, continues on own
* these reactions can possibly take a long time
41
New cards
non spontaneous
* needs a constant source of energy
42
New cards
\-ΔG
spontaneous reaction
43
New cards
which thermic is more favorable
exothermic (more spontaneous)
44
New cards
which ΔS is more energetically favorable
\+ΔS
45
New cards
\+ΔS
inc. in entropy
46
New cards
\-ΔS
dec. entropy
47
New cards
Exothermic + inc entropy (-ΔS) =
ALWAYS SPONTANEOUS
48
New cards
Endothermic + dec. entropy =
NEVER SPONTANEOUS
49
New cards
gibbs free energy equation
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS