HN204 Lecutre 20 ILO's
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Large intestine
The final part of the digestive system where water is absorbed and waste is prepared for elimination.
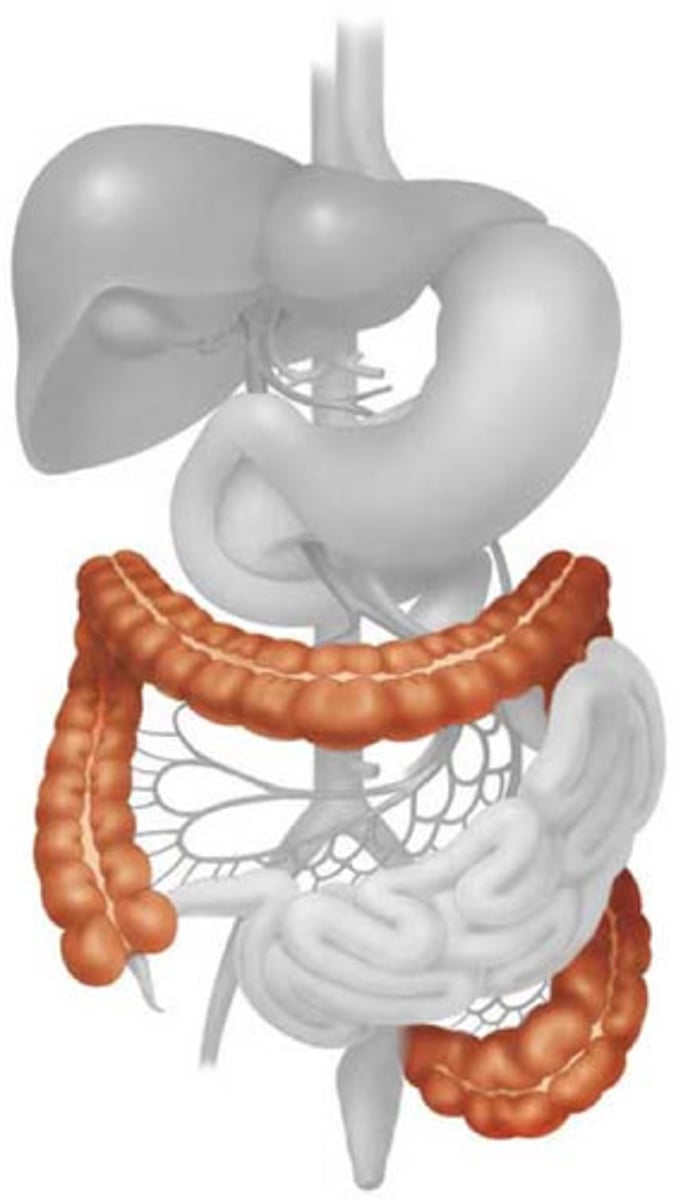
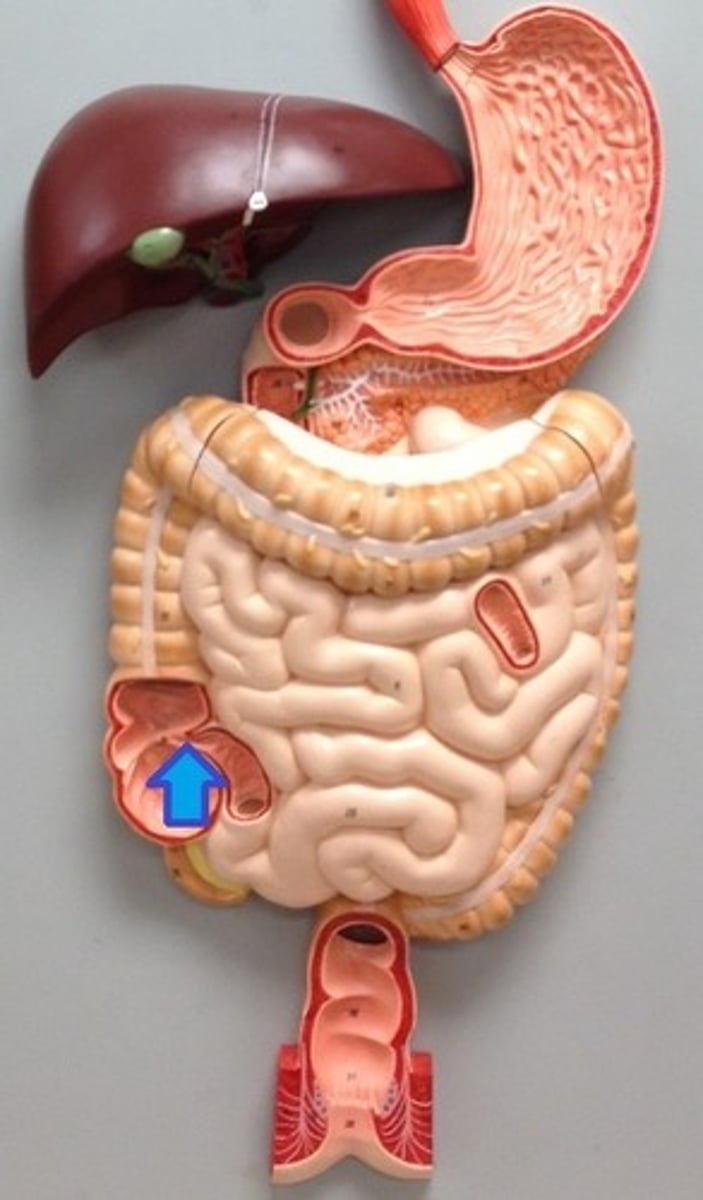
Cecum
The pouch connected to the junction of the small and large intestines.
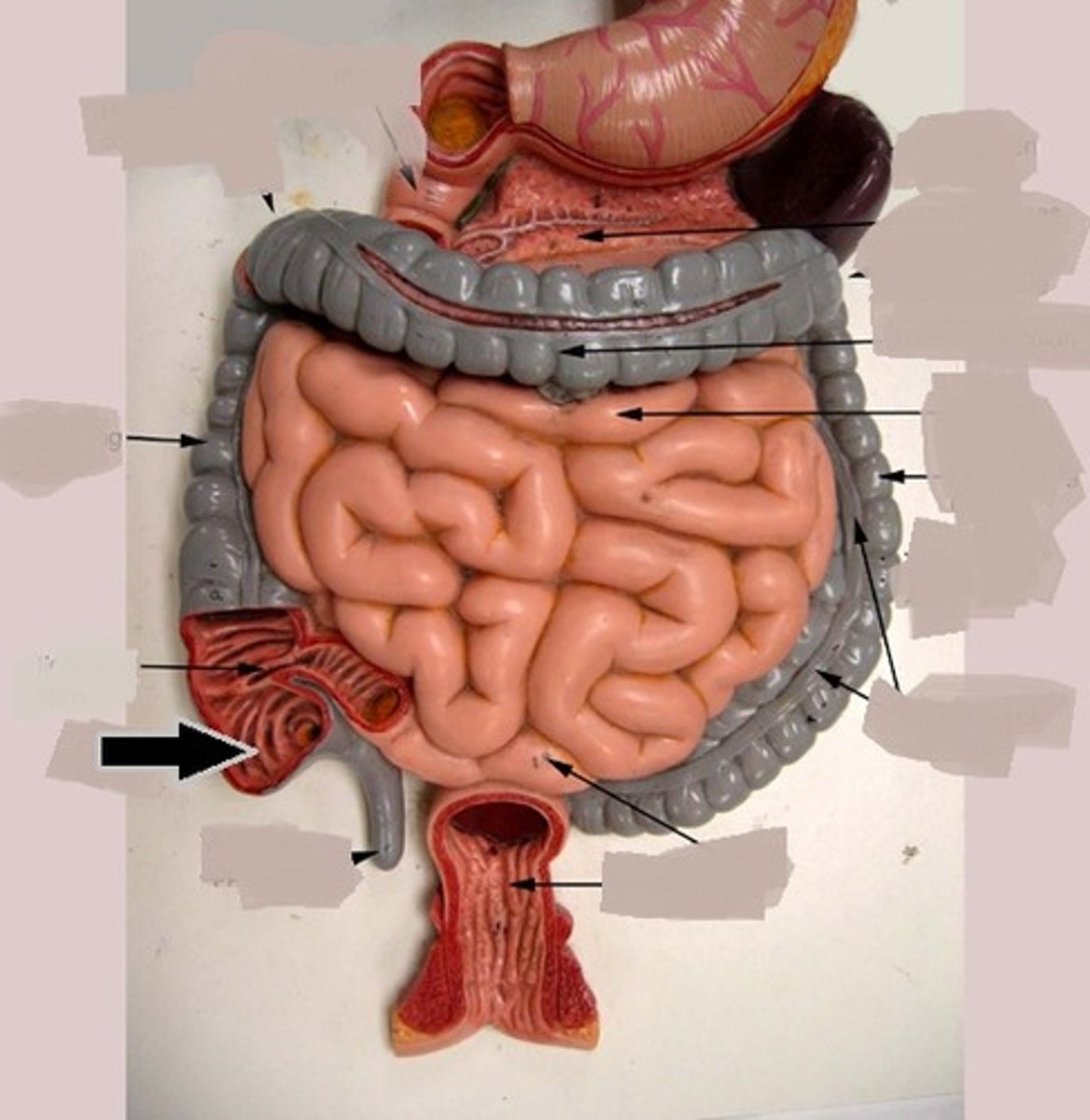
Ascending colon
The part of the colon that ascends on the right side of the abdomen.
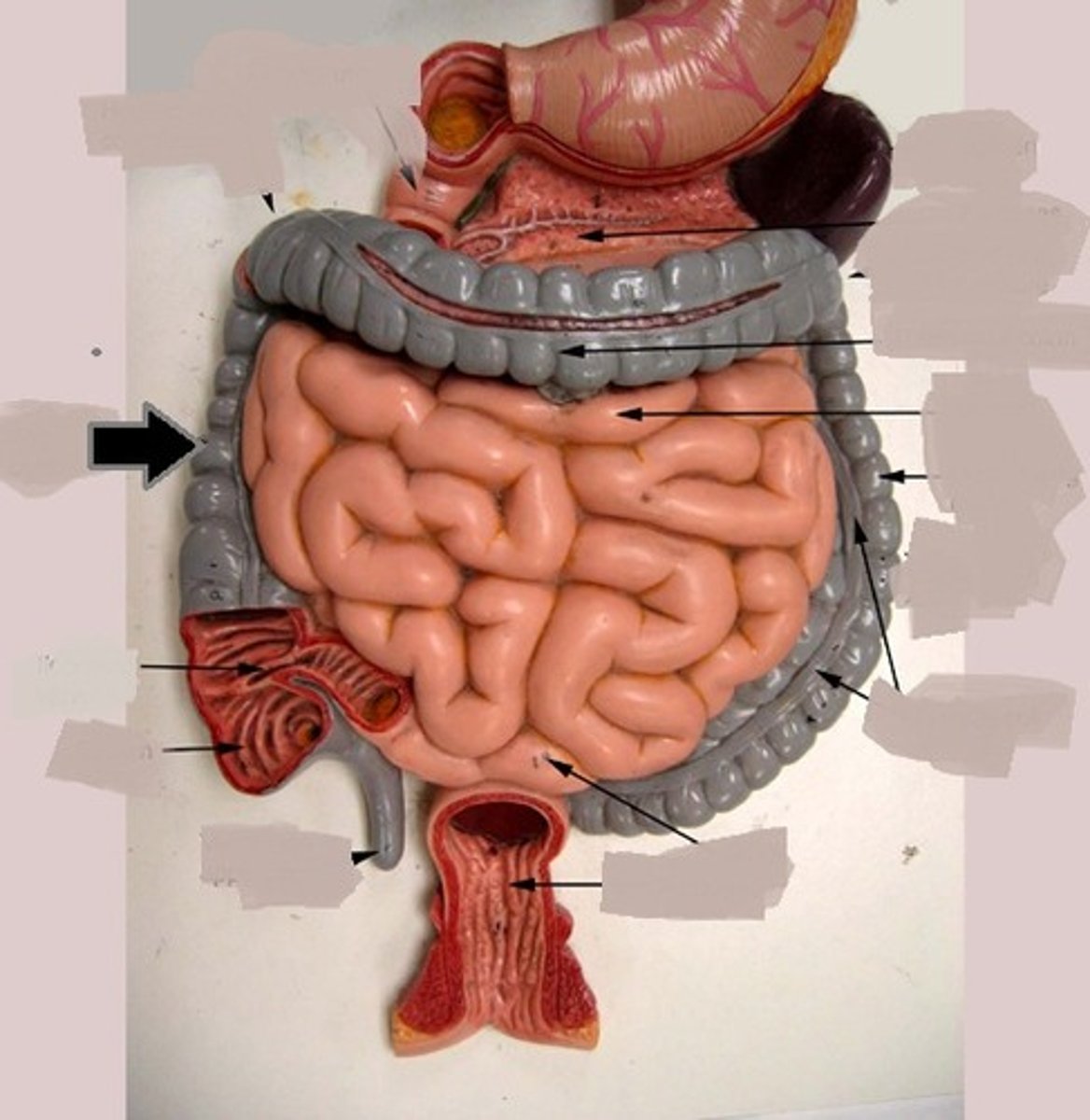
Transverse colon
The part of the colon that runs horizontally across the abdomen.
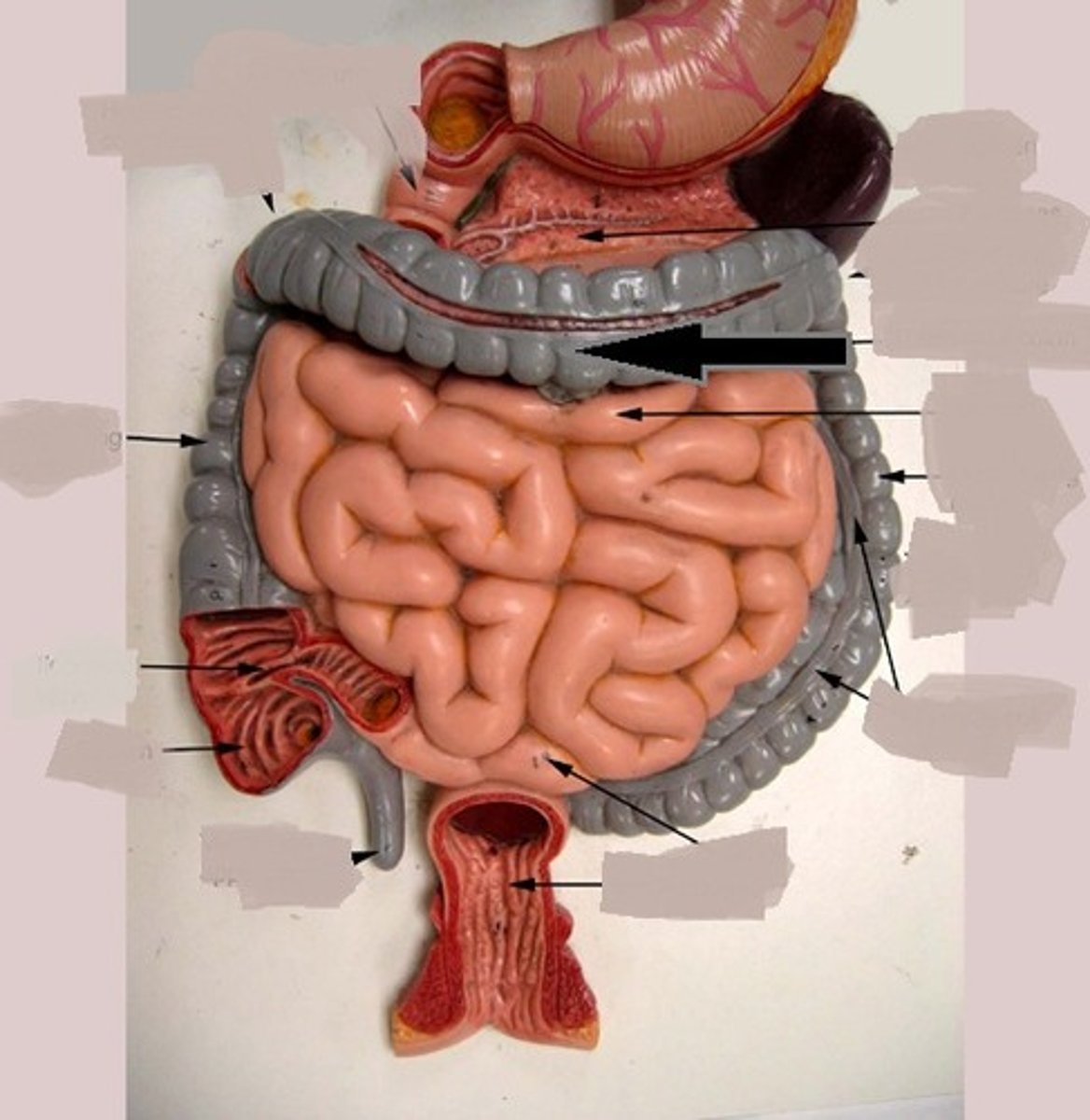
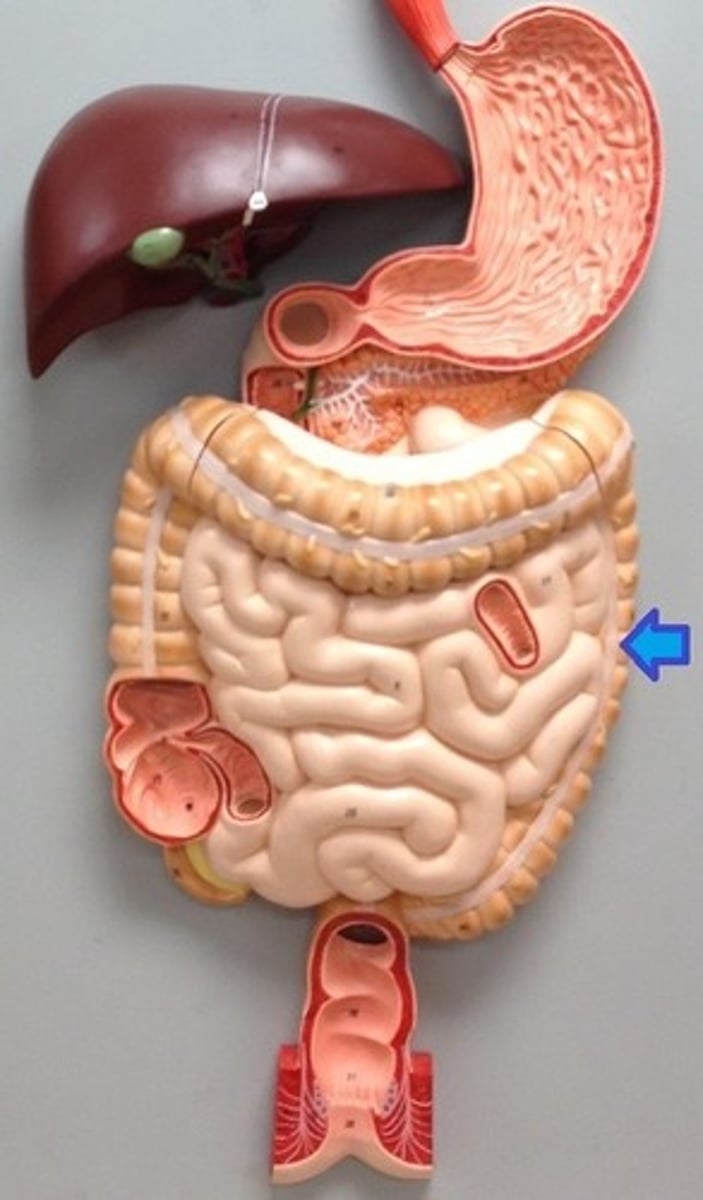
Descending colon
The part of the colon that descends on the left side of the abdomen.
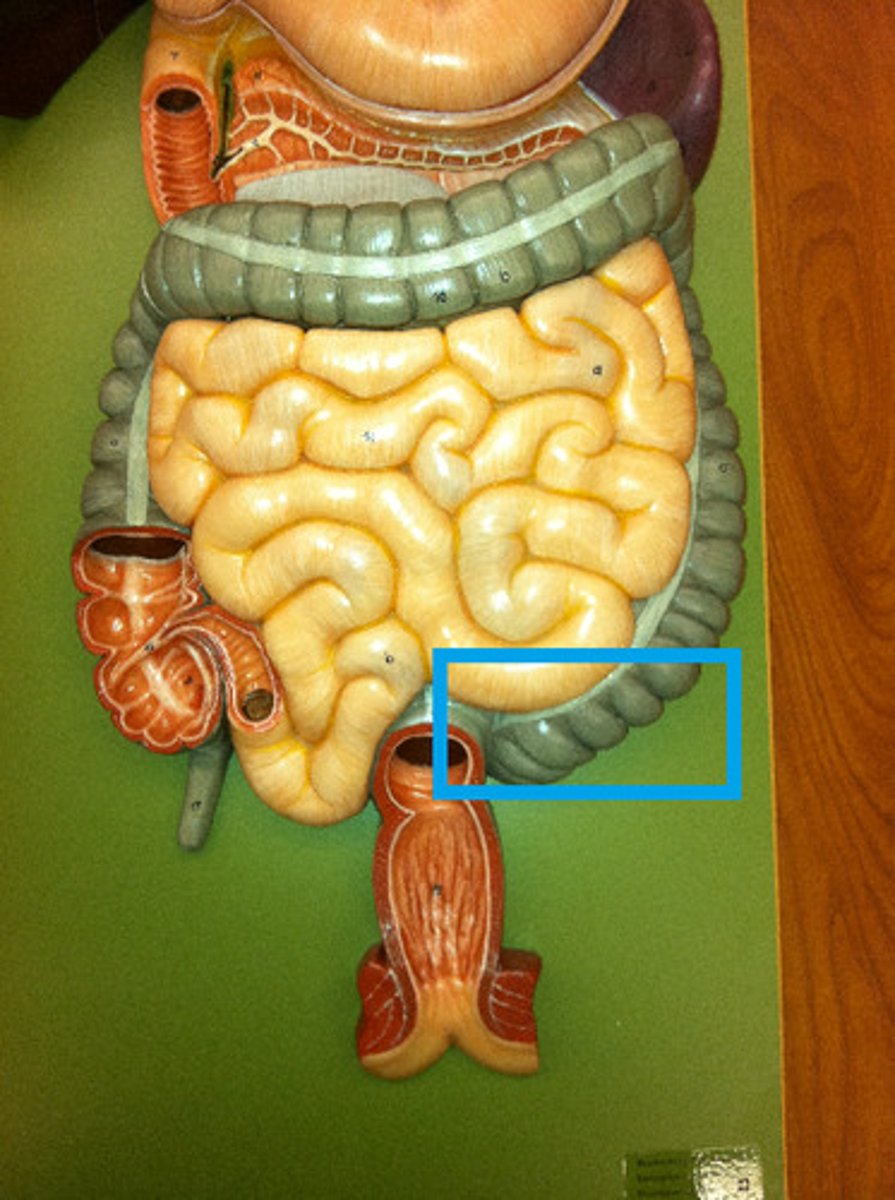
Sigmoid colon
The S-shaped last part of the colon leading into the rectum.
Rectum
The final section of the large intestine, terminating at the anus.
Anal canal
The terminal part of the digestive tract, leading to the anus.
Anus
The opening at the end of the digestive tract through which waste leaves the body.
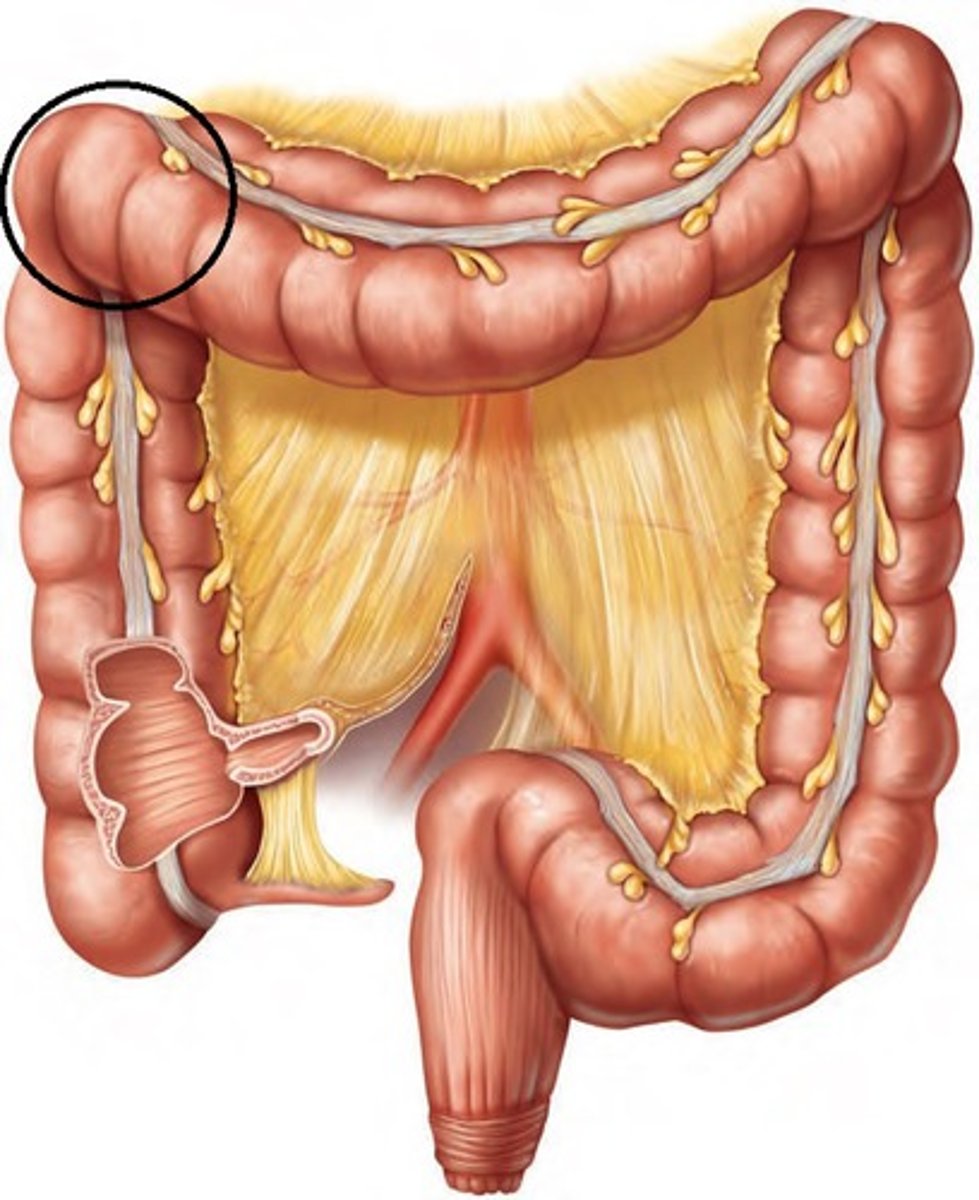
Teniae (taeniae) coli
Three longitudinal bands of muscle that run along the length of the colon.
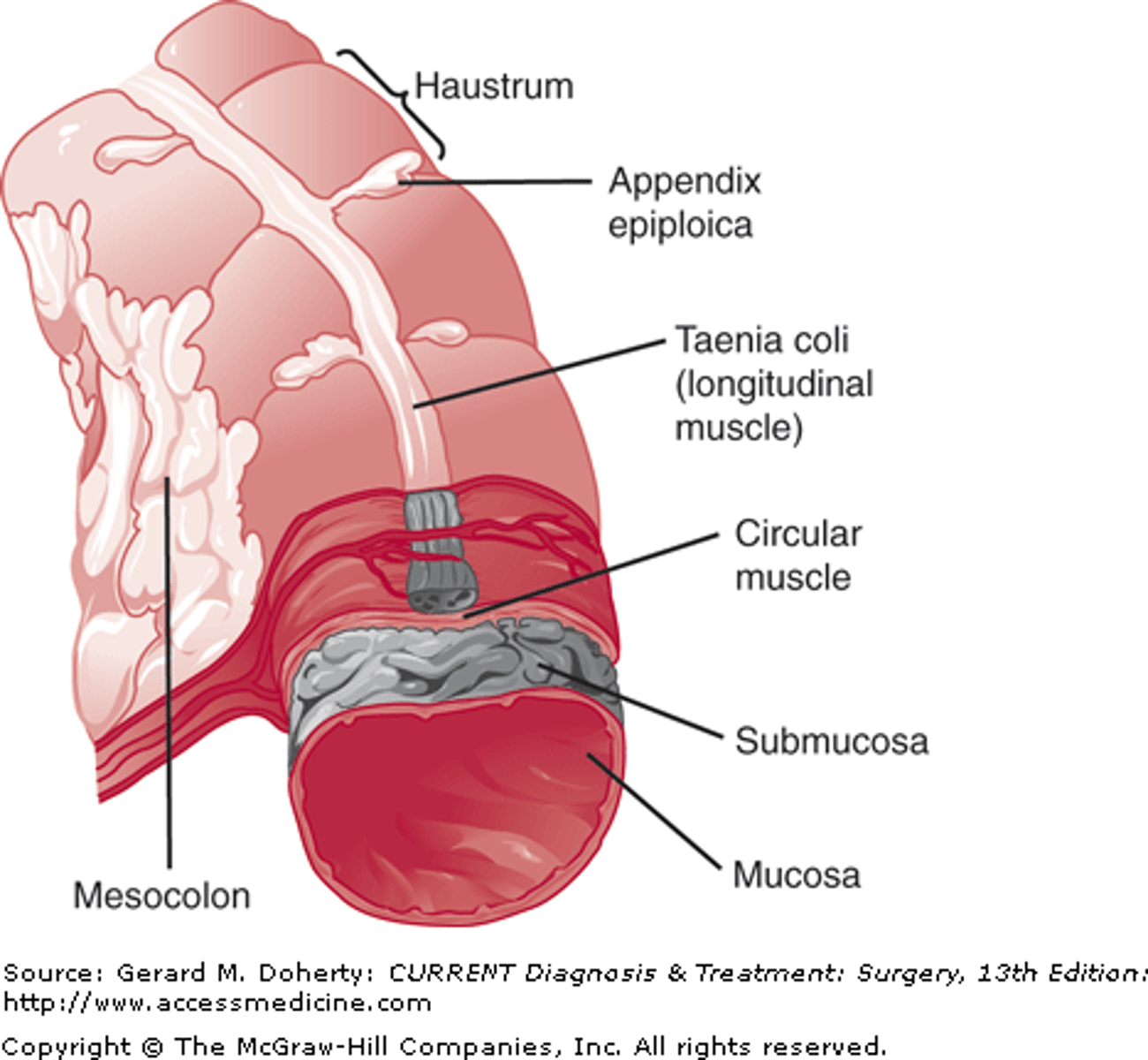
Haustra
Pouches or sacculations in the colon that allow for expansion and contraction.
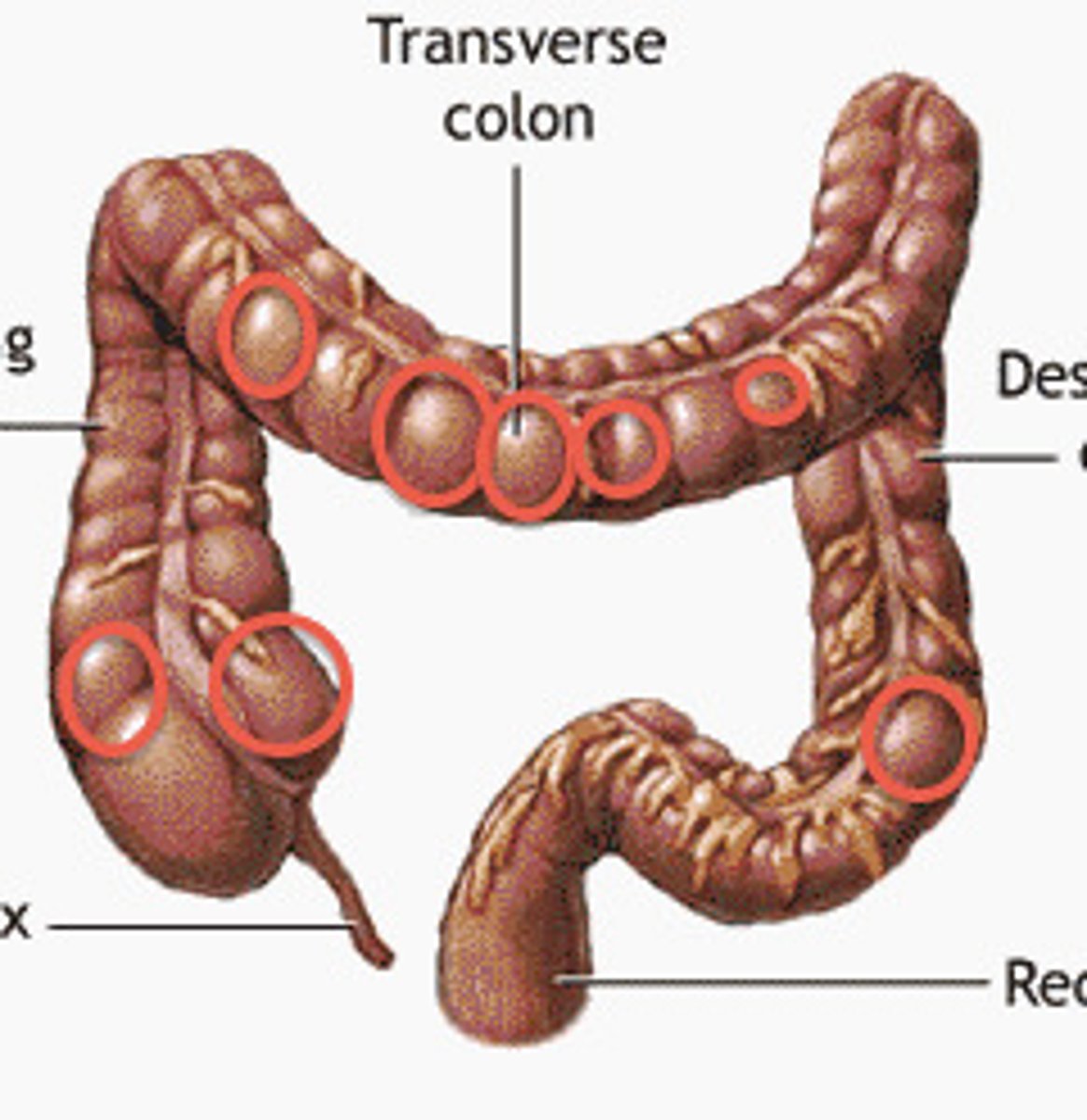
Epiploic appendages
Small pouches of fat that hang from the colon.
Omental appendices
Fatty tissue projections along the colon.
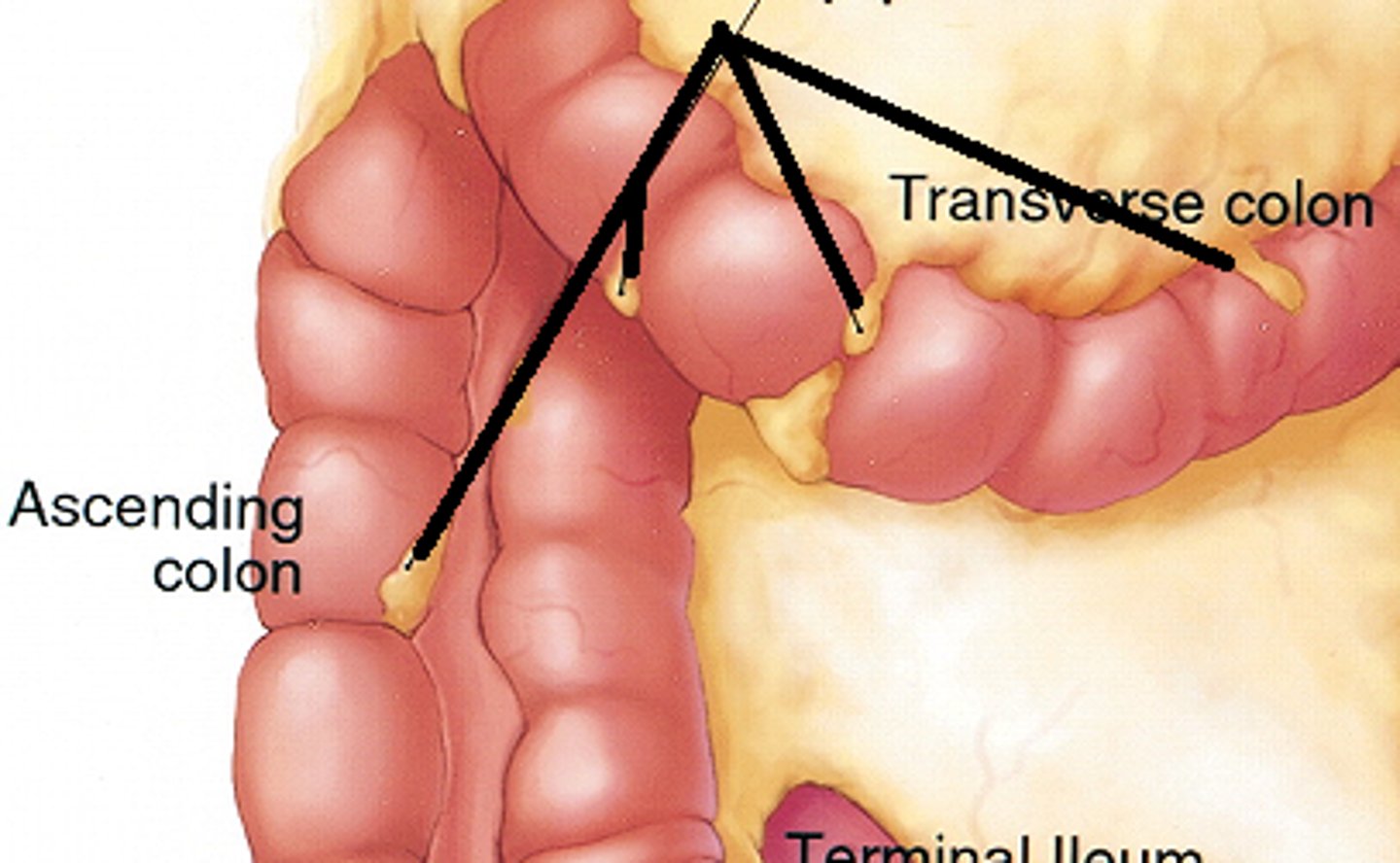
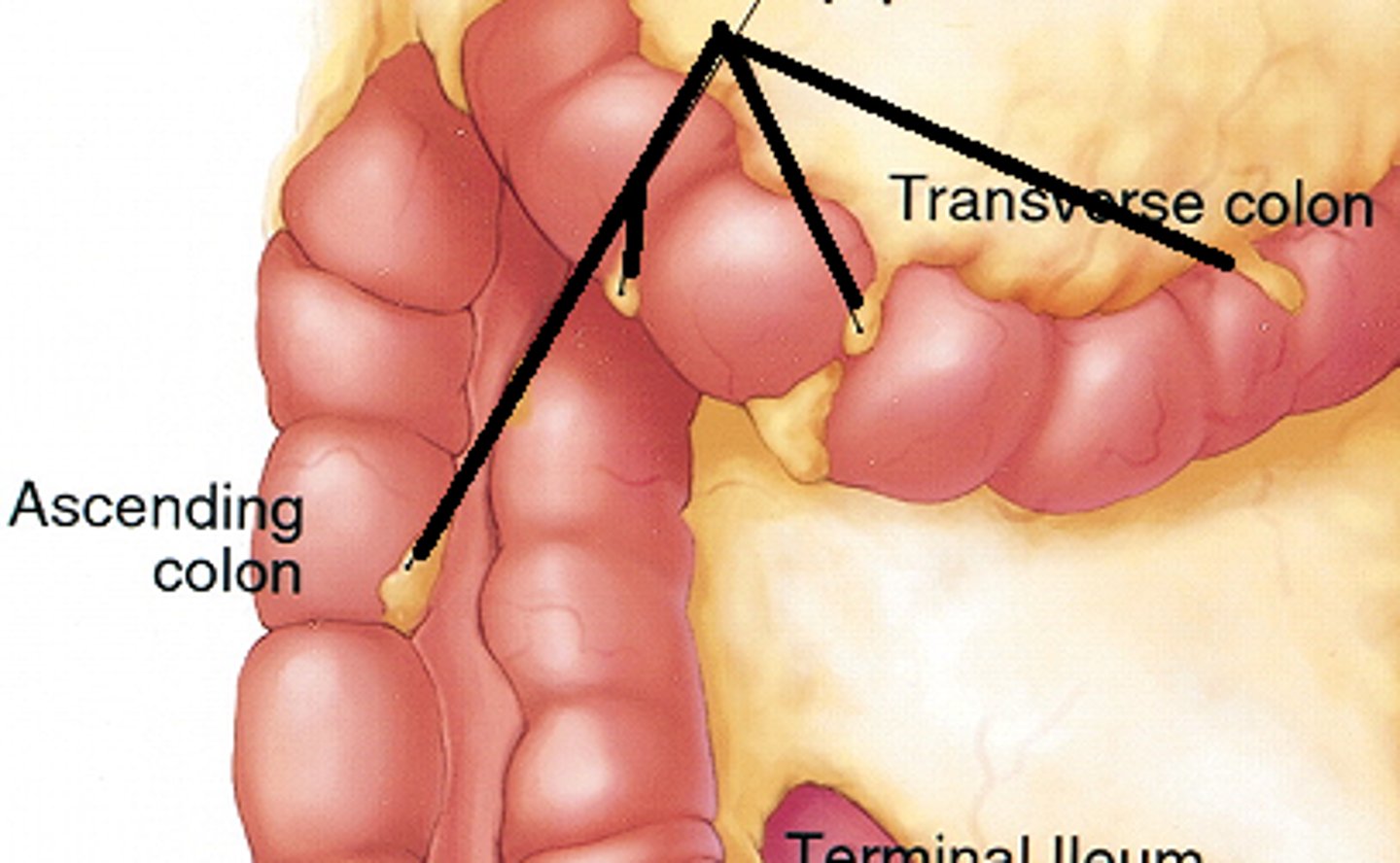
Ileocecal valve
The valve that separates the small intestine from the large intestine.
Right colic flexure
The bend in the colon between the ascending and transverse colon.
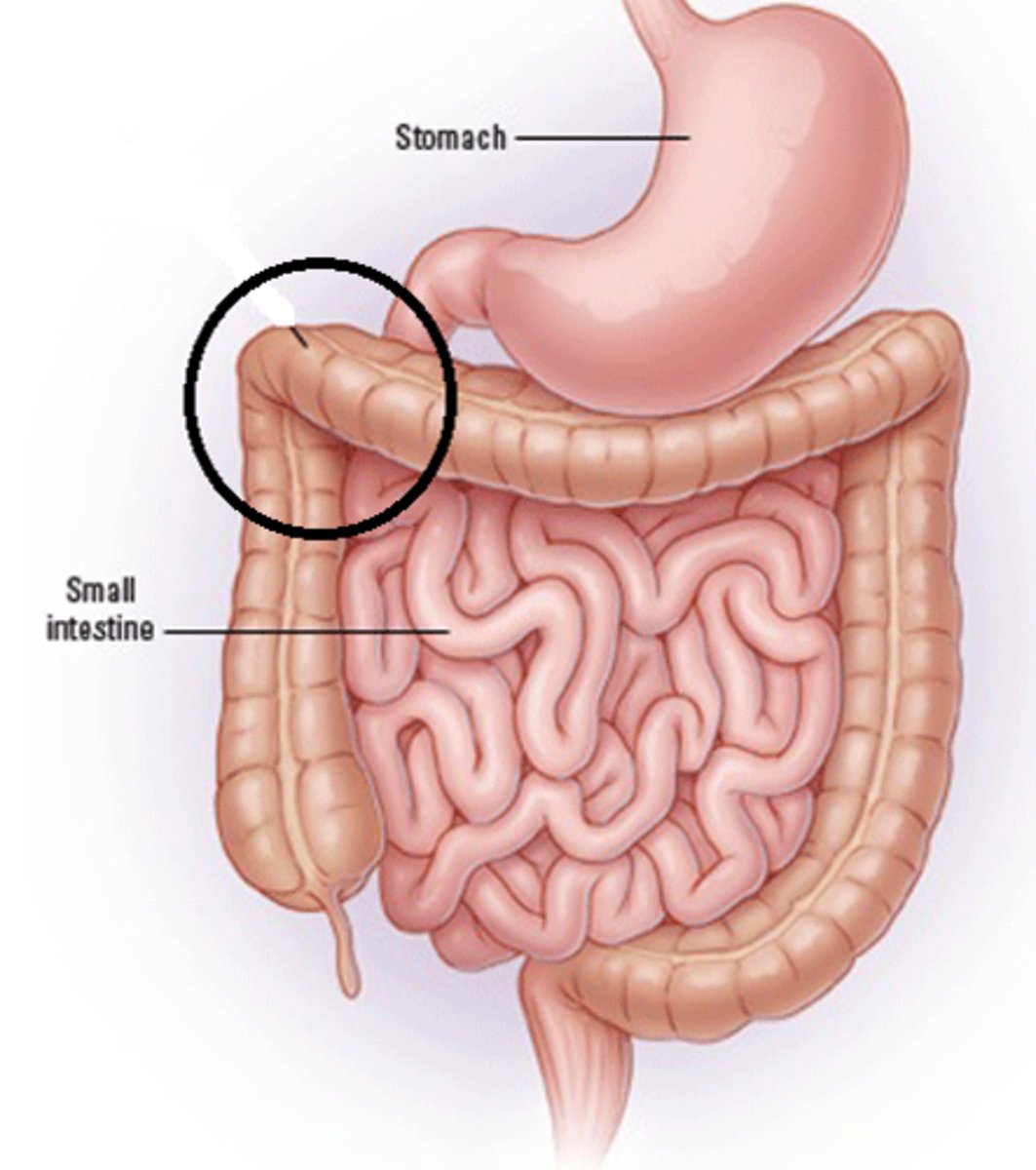
Hepatic flexure
The bend in the colon located near the liver.
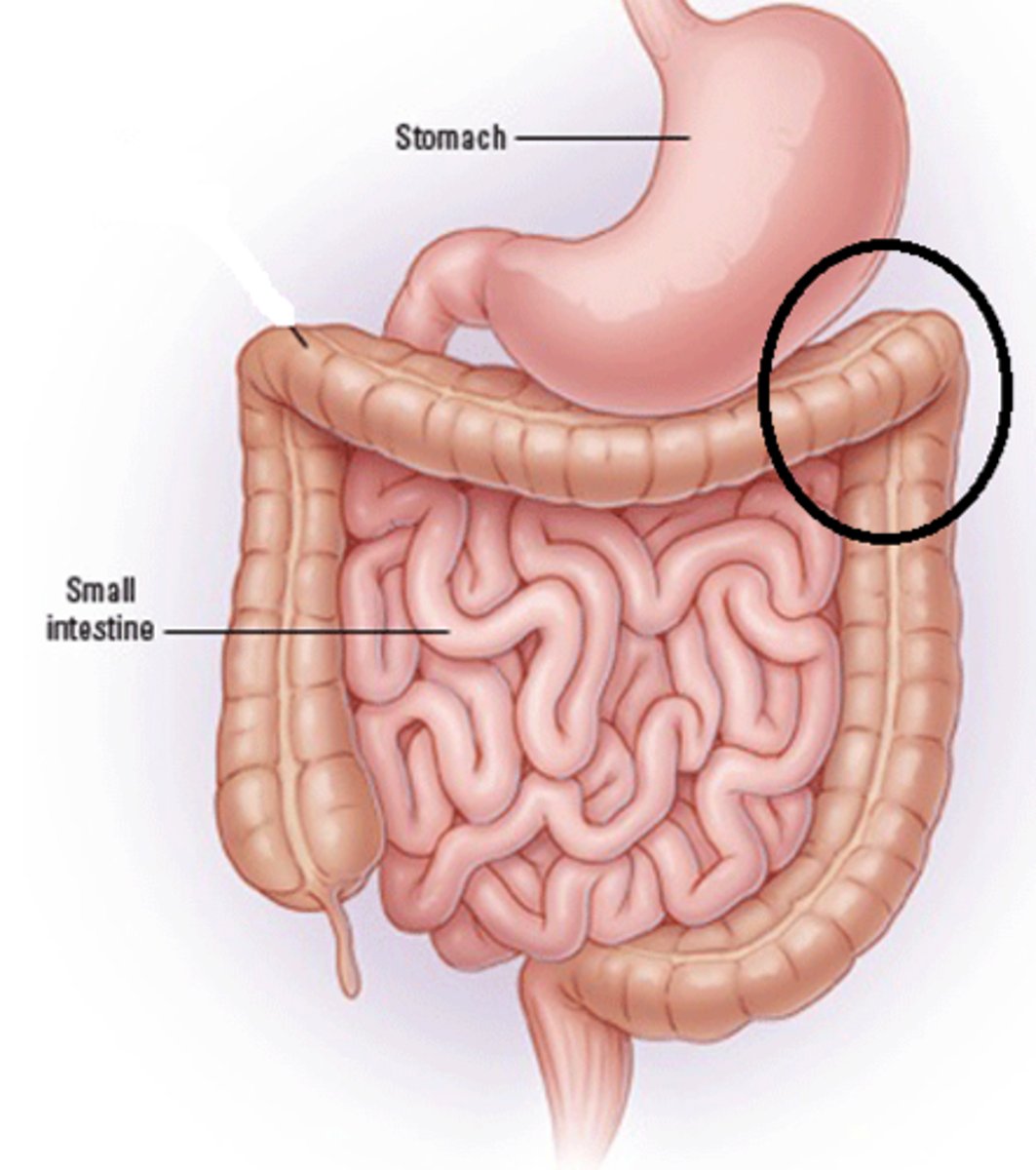
Left colic flexure
The bend in the colon between the transverse and descending colon.
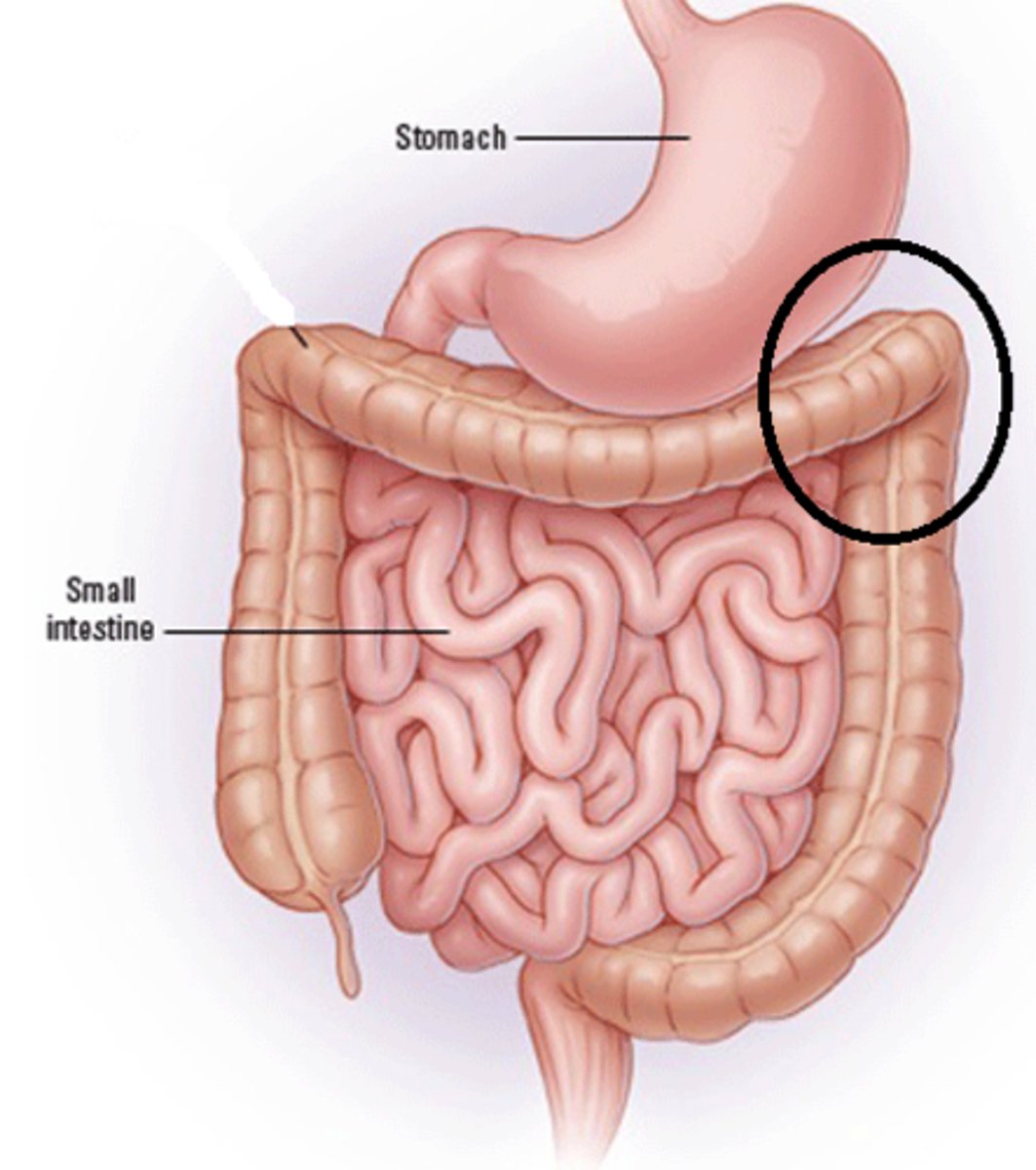
Splenic flexure
The bend in the colon located near the spleen.
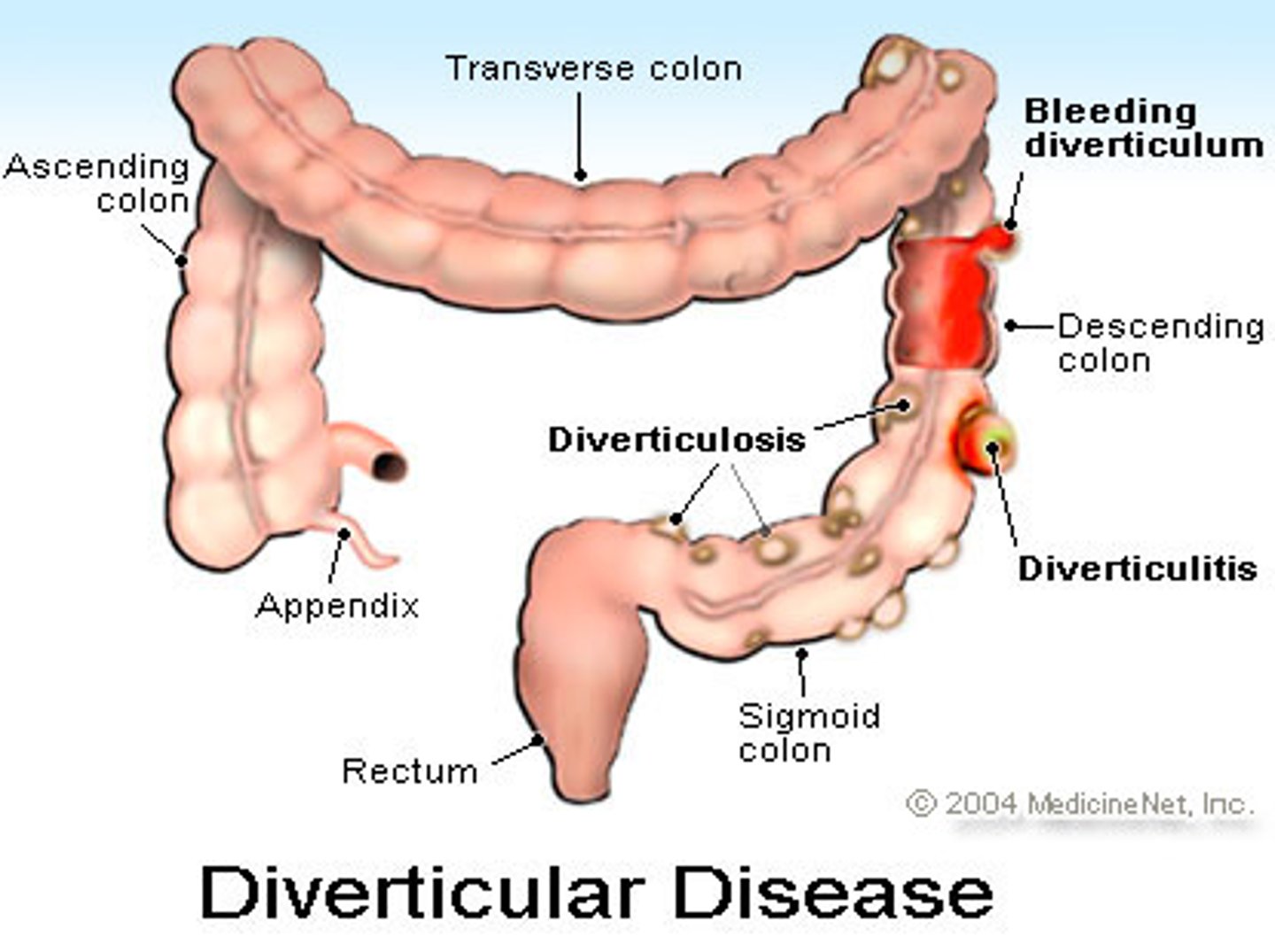
Diverticulosis
The presence of diverticula in the colon without inflammation.
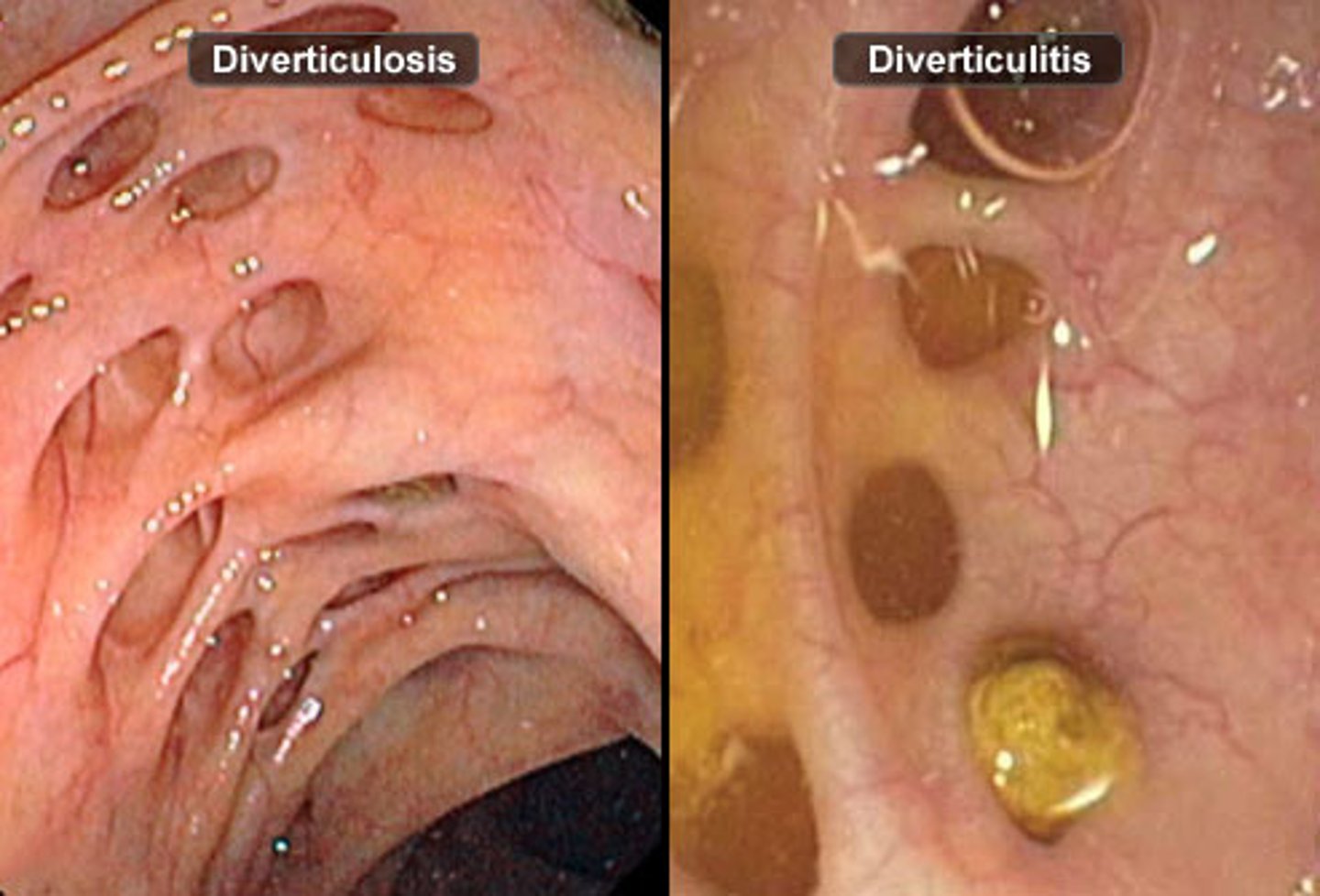
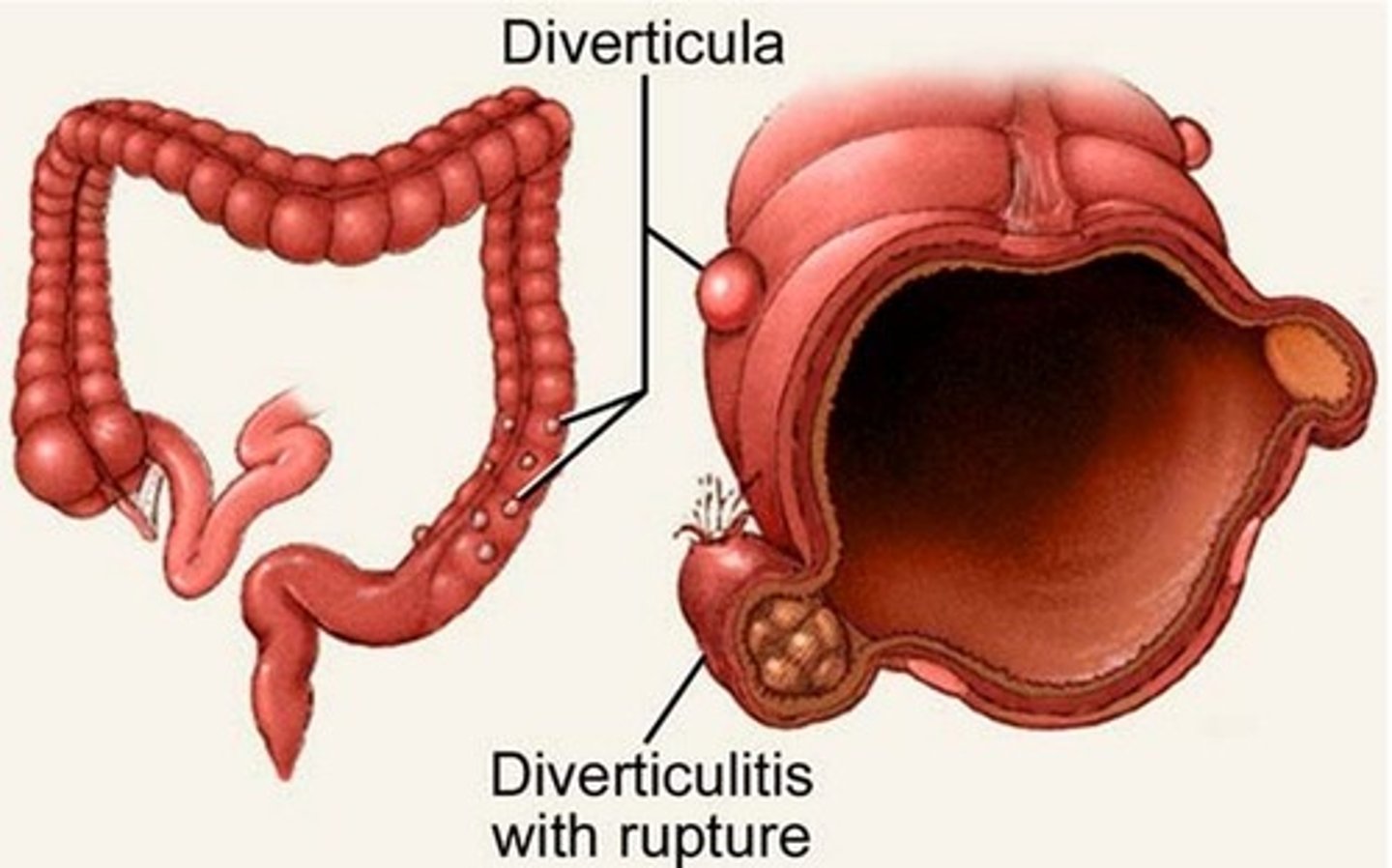
Diverticulitis
Inflammation of diverticula in the colon.
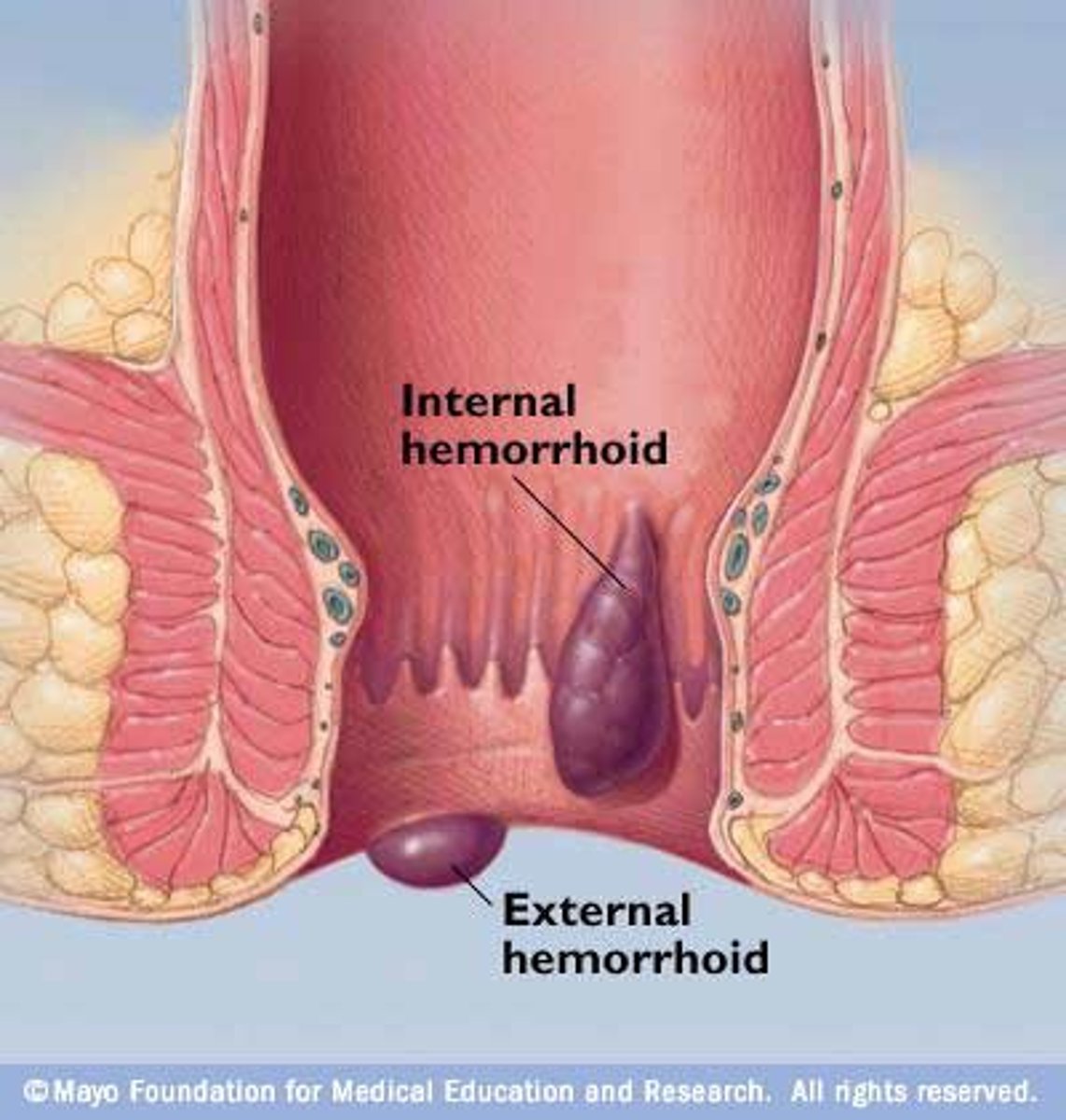
Hemorrhoids
Swollen veins in the lower rectum or anus.
Diverticula
Small bulging pouches that can form in the lining of the digestive system.
Accessory organs
Organs that assist in digestion but are not part of the digestive tract.
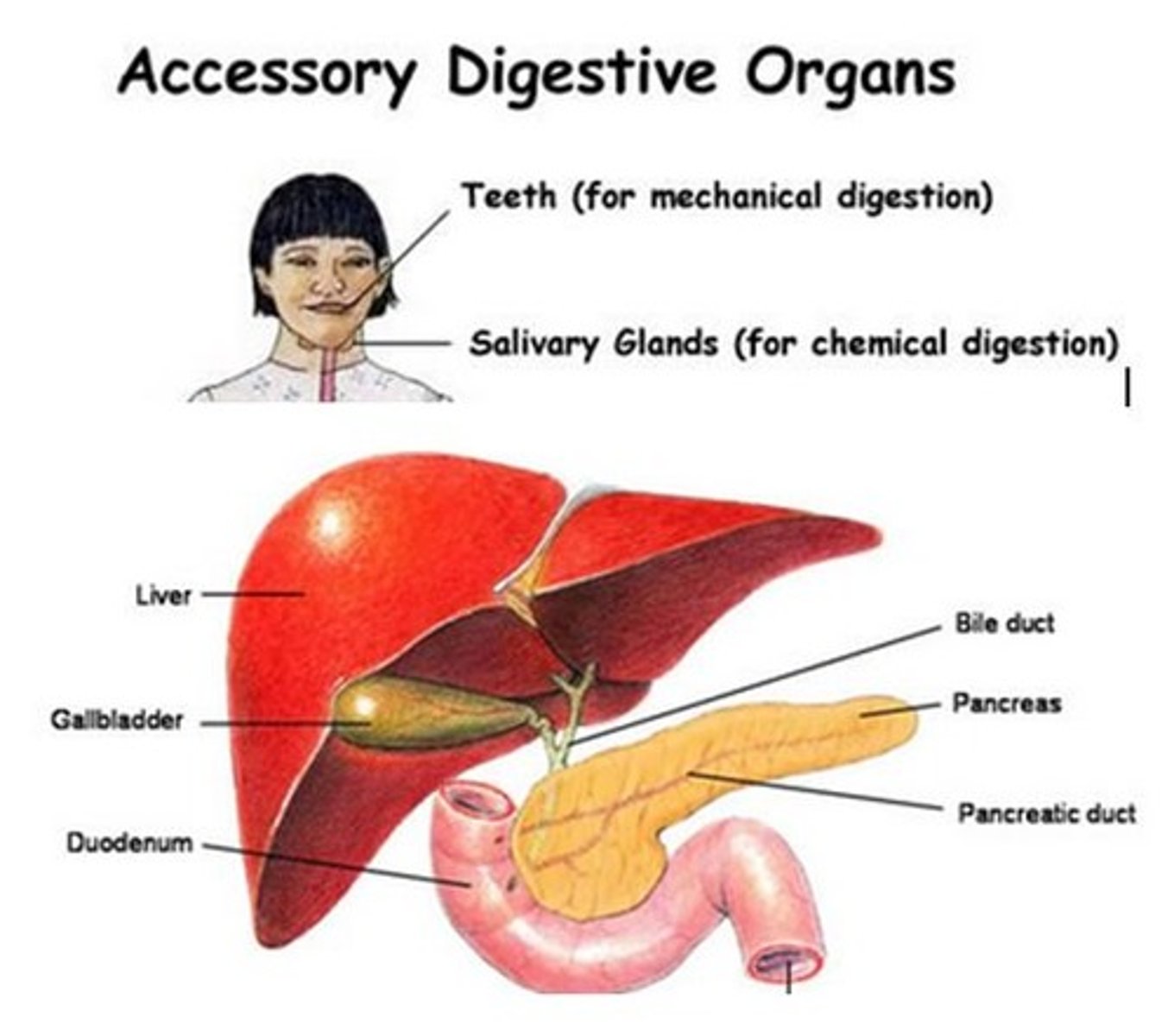
Bile
A digestive fluid produced by the liver that helps in the digestion of fats.
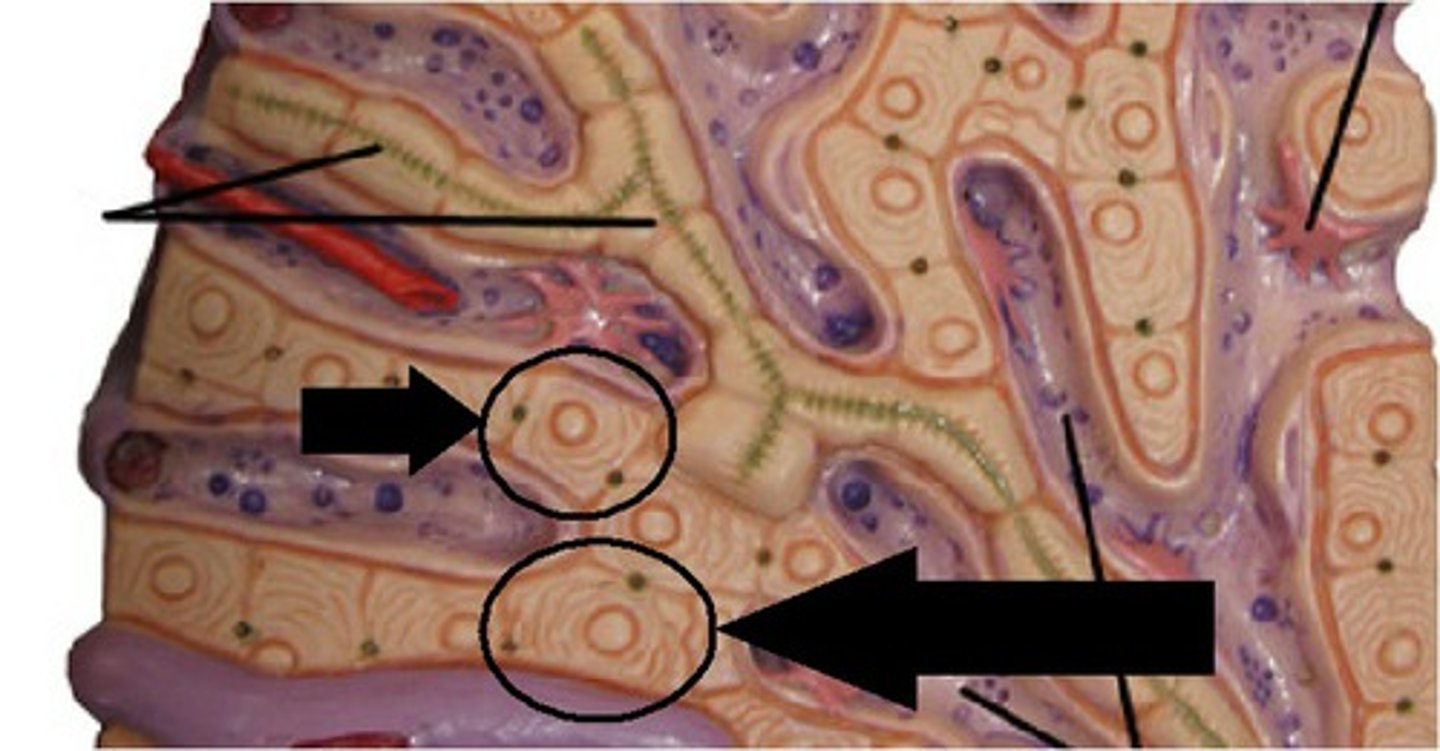
Hepatocyte
The main functional cells of the liver.
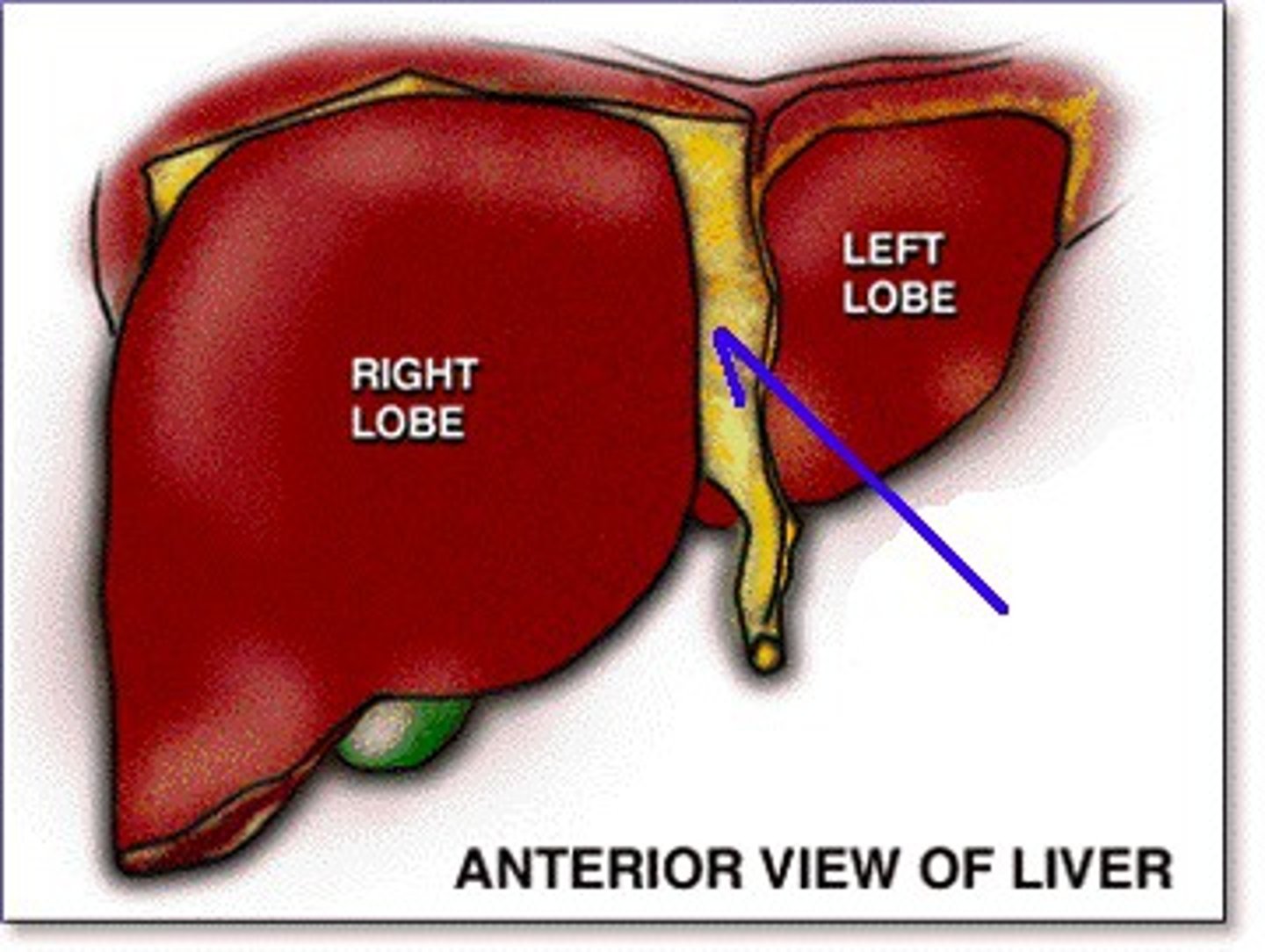
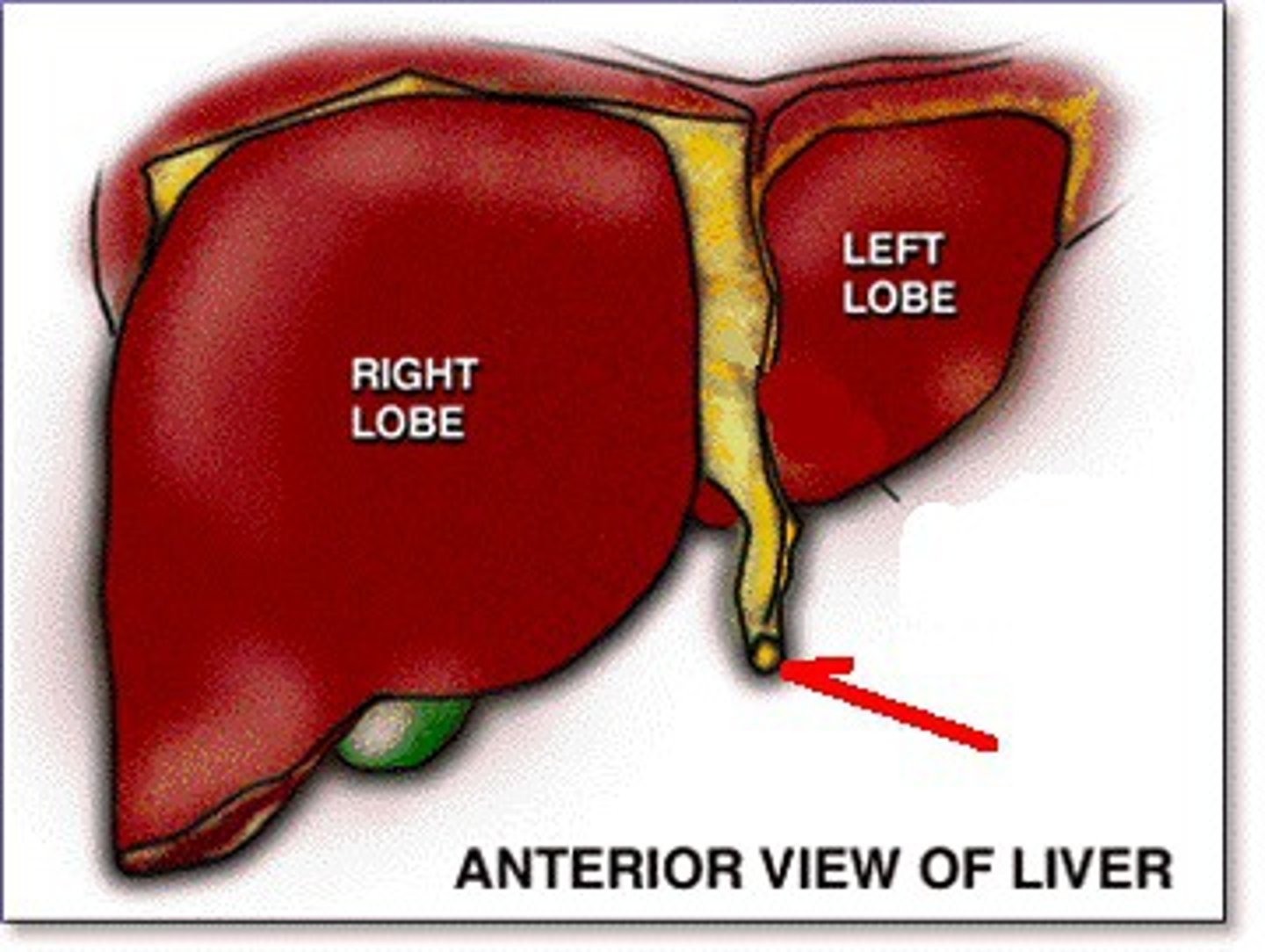
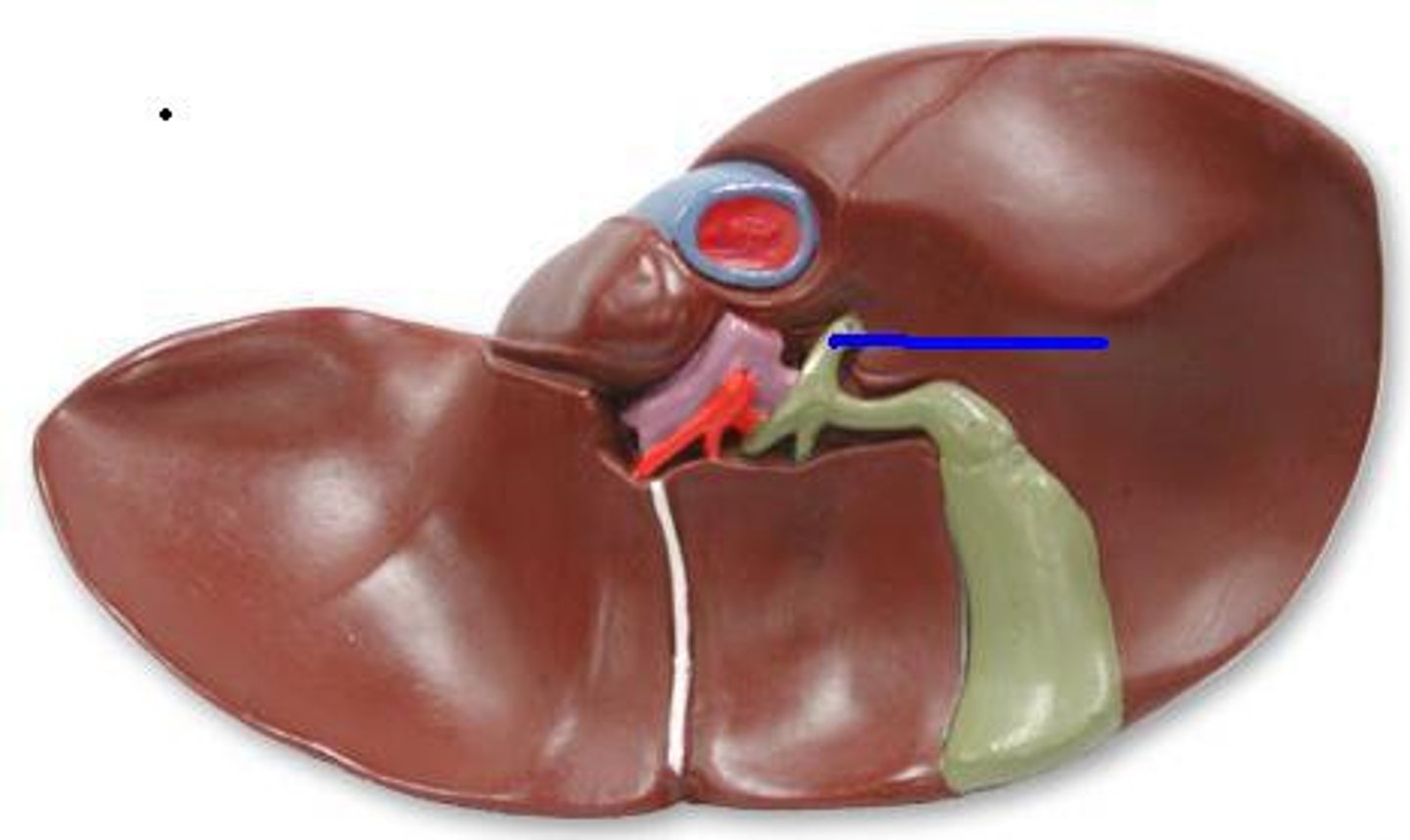
Liver right lobe
The larger lobe of the liver located on the right side.
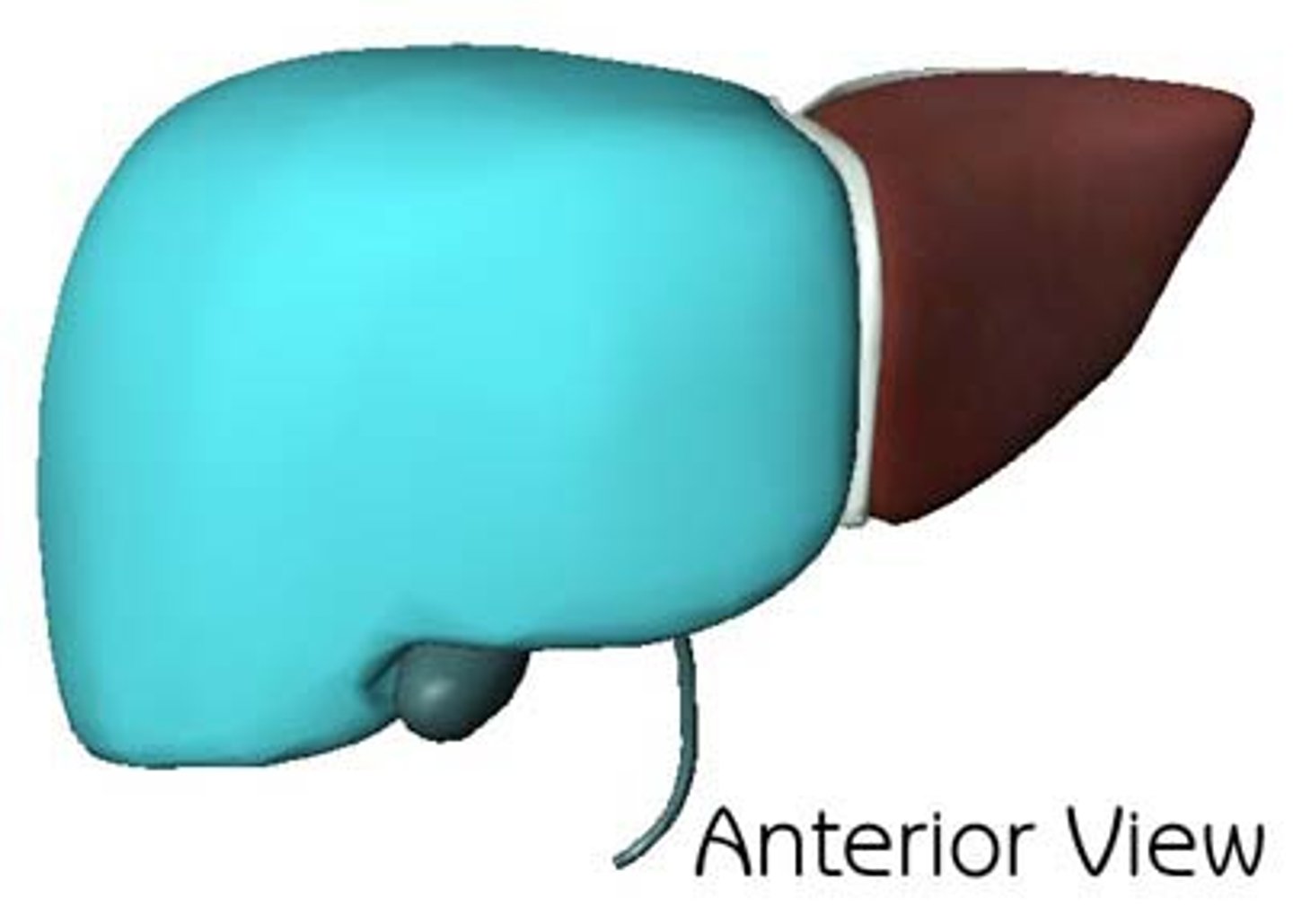
Liver left lobe
The smaller lobe of the liver located on the left side.
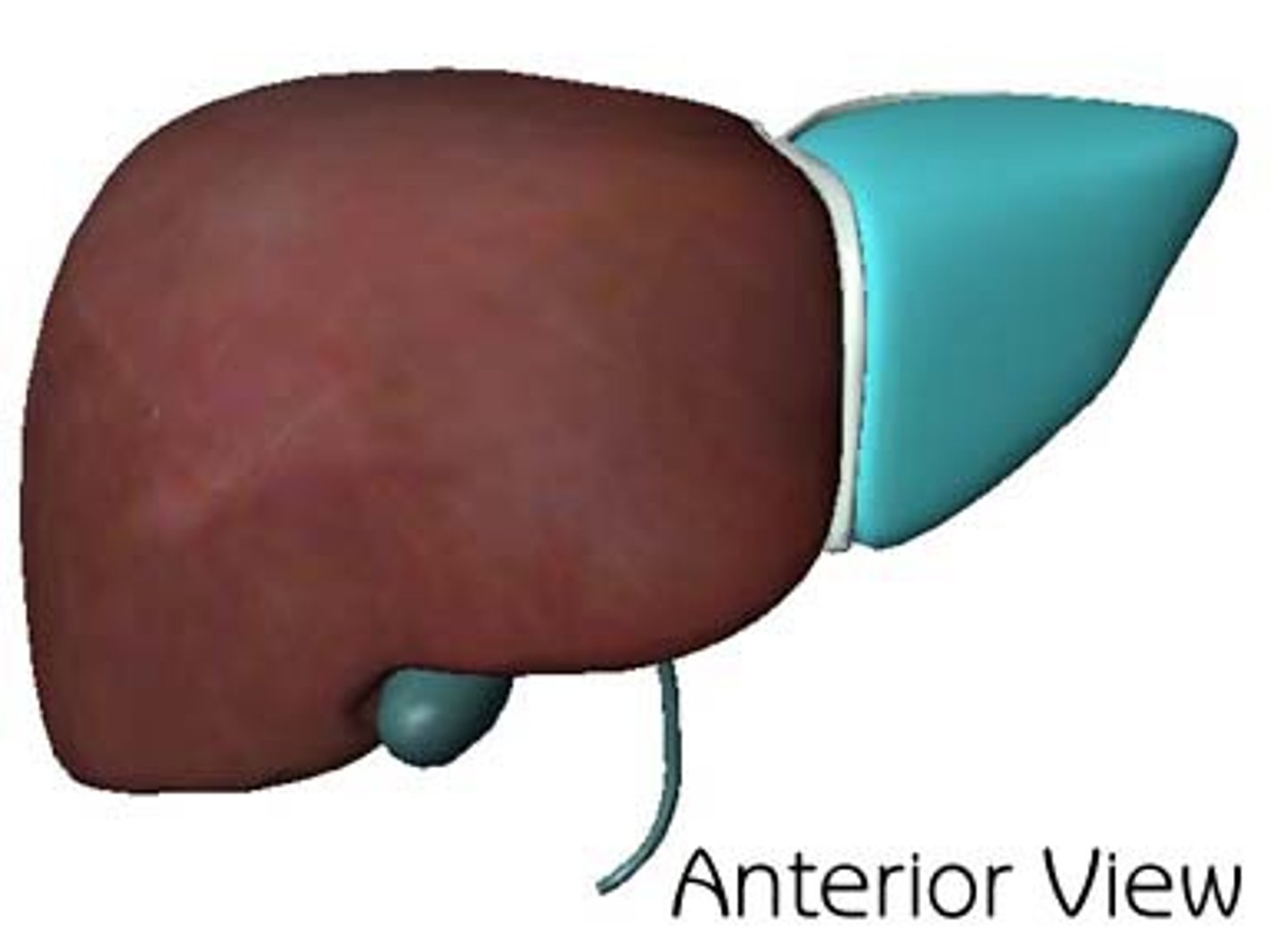
Falciform ligament
A ligament that attaches the liver to the anterior abdominal wall.
Quadrate lobe
A lobe of the liver located on the inferior surface.
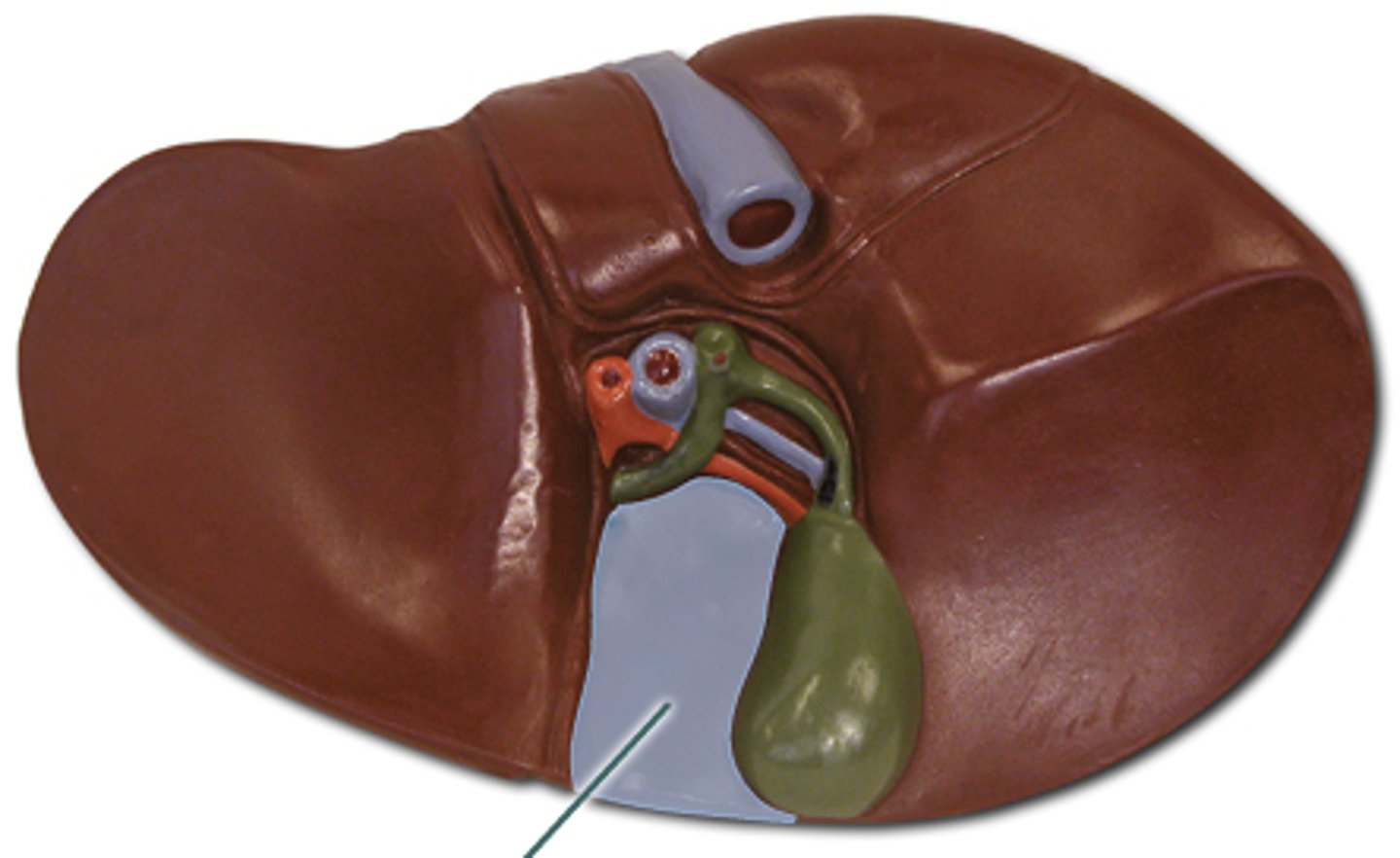
Caudate lobe
A lobe of the liver located posteriorly.

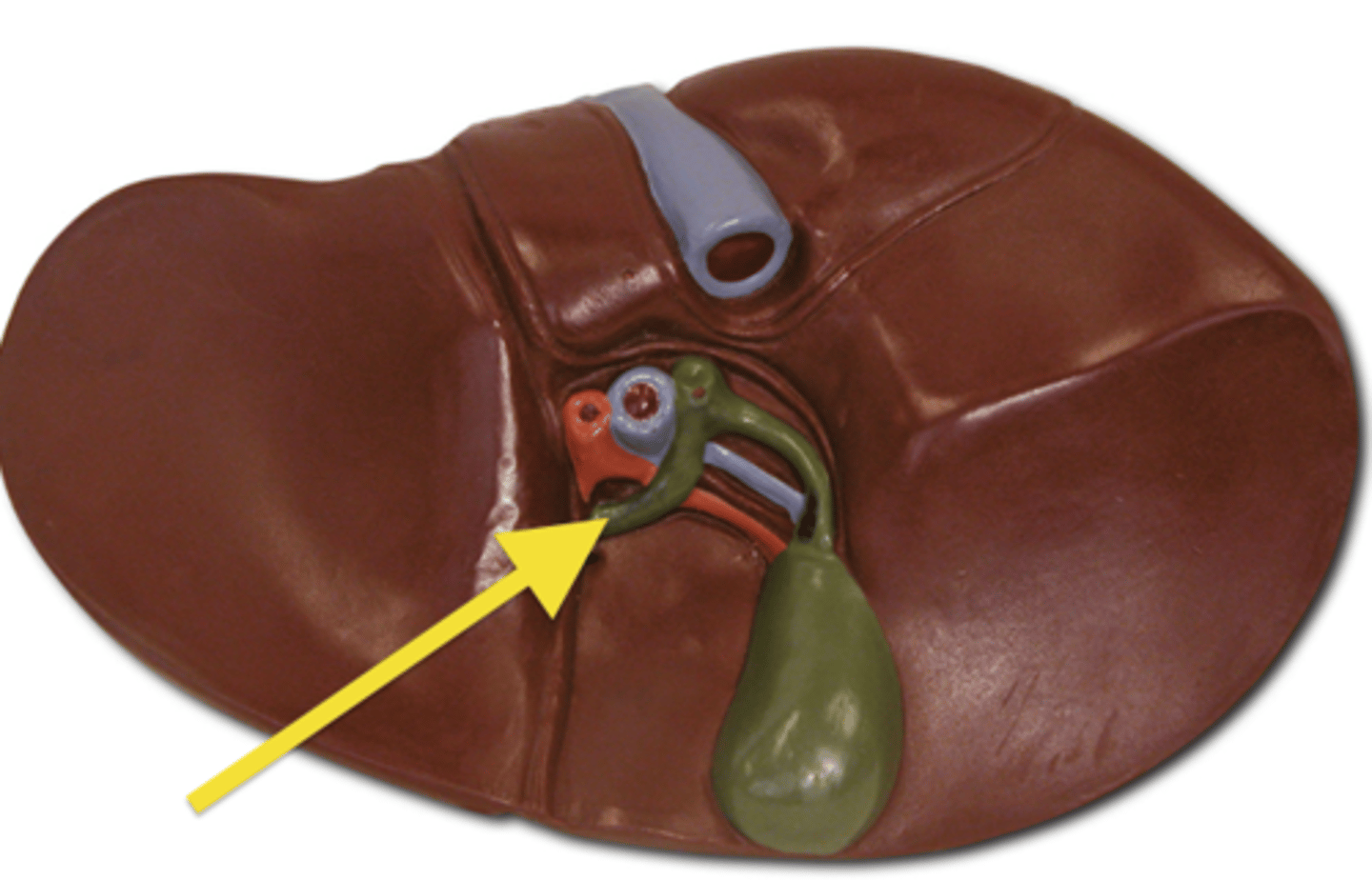
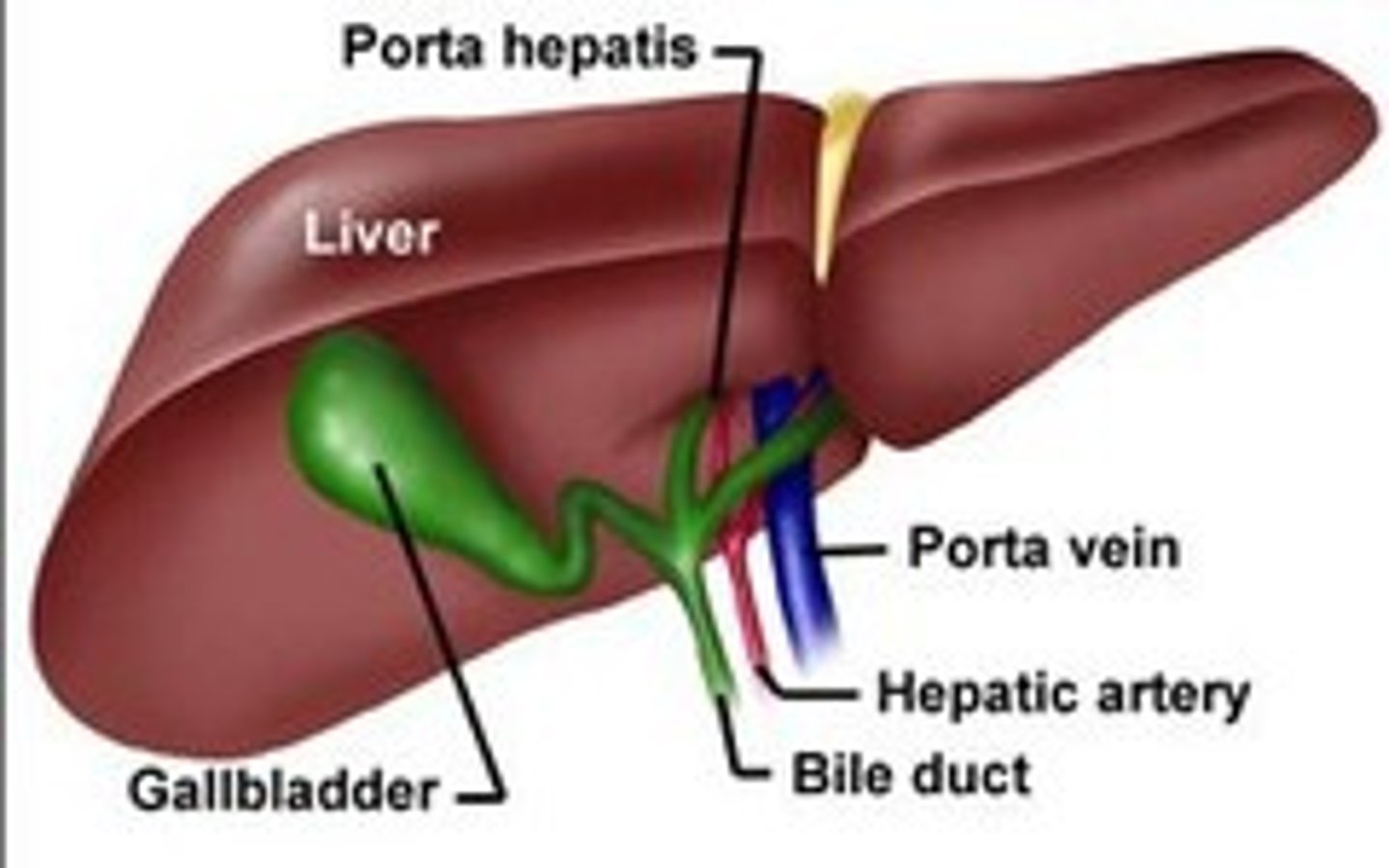
Porta hepatis
The area of the liver where blood vessels, ducts, and nerves enter and exit.
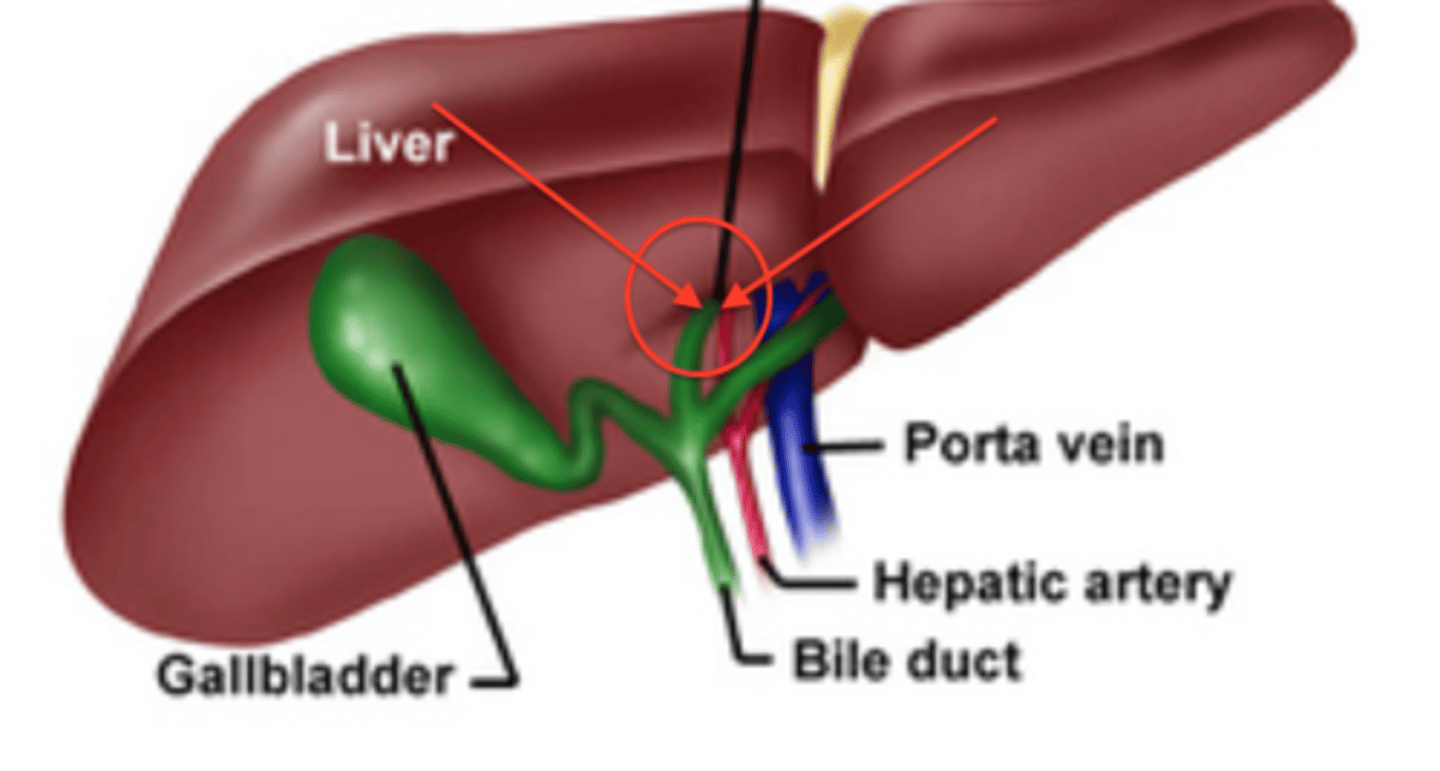
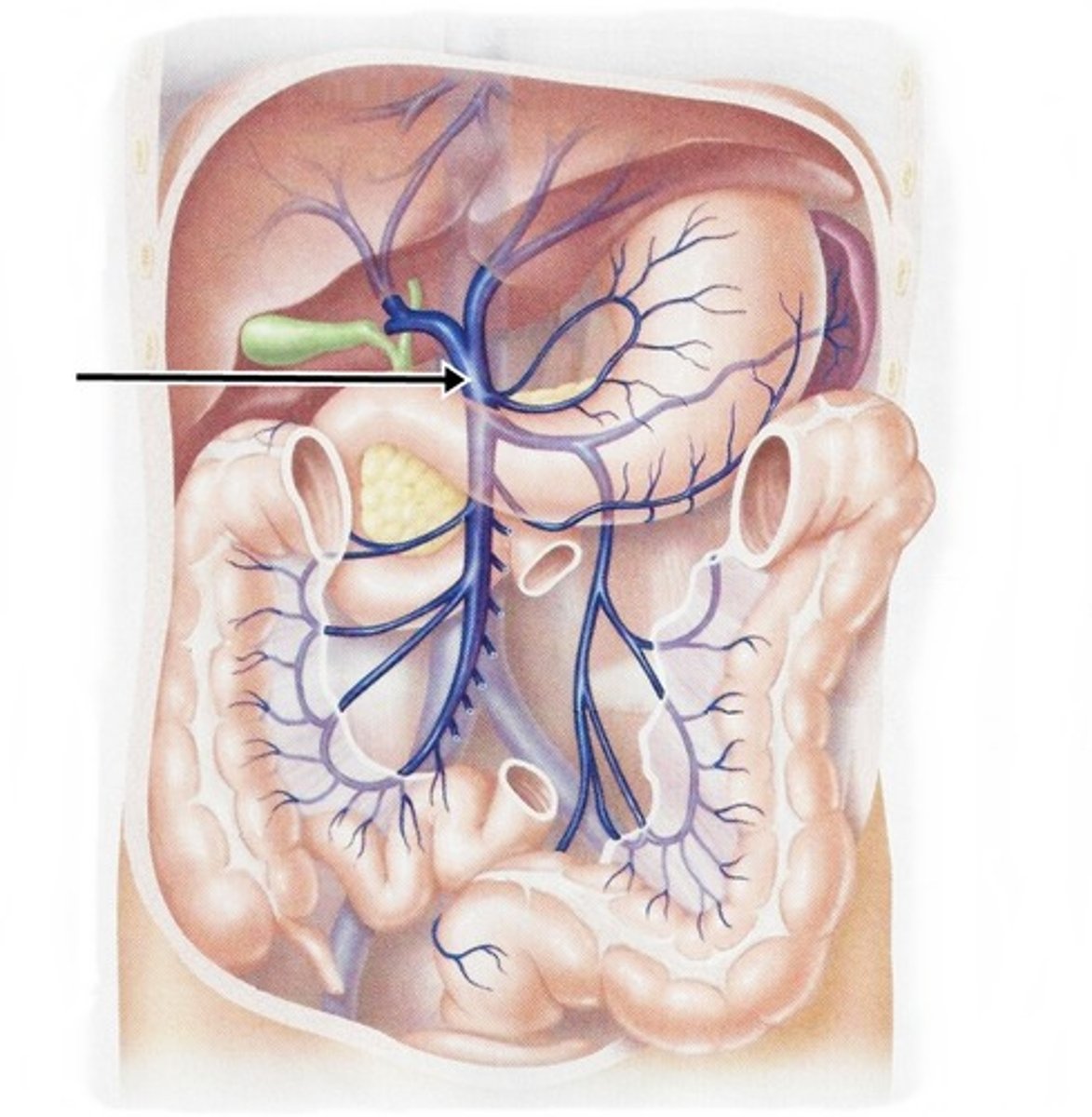
Hepatic portal vein
The vein that carries blood from the digestive organs to the liver.
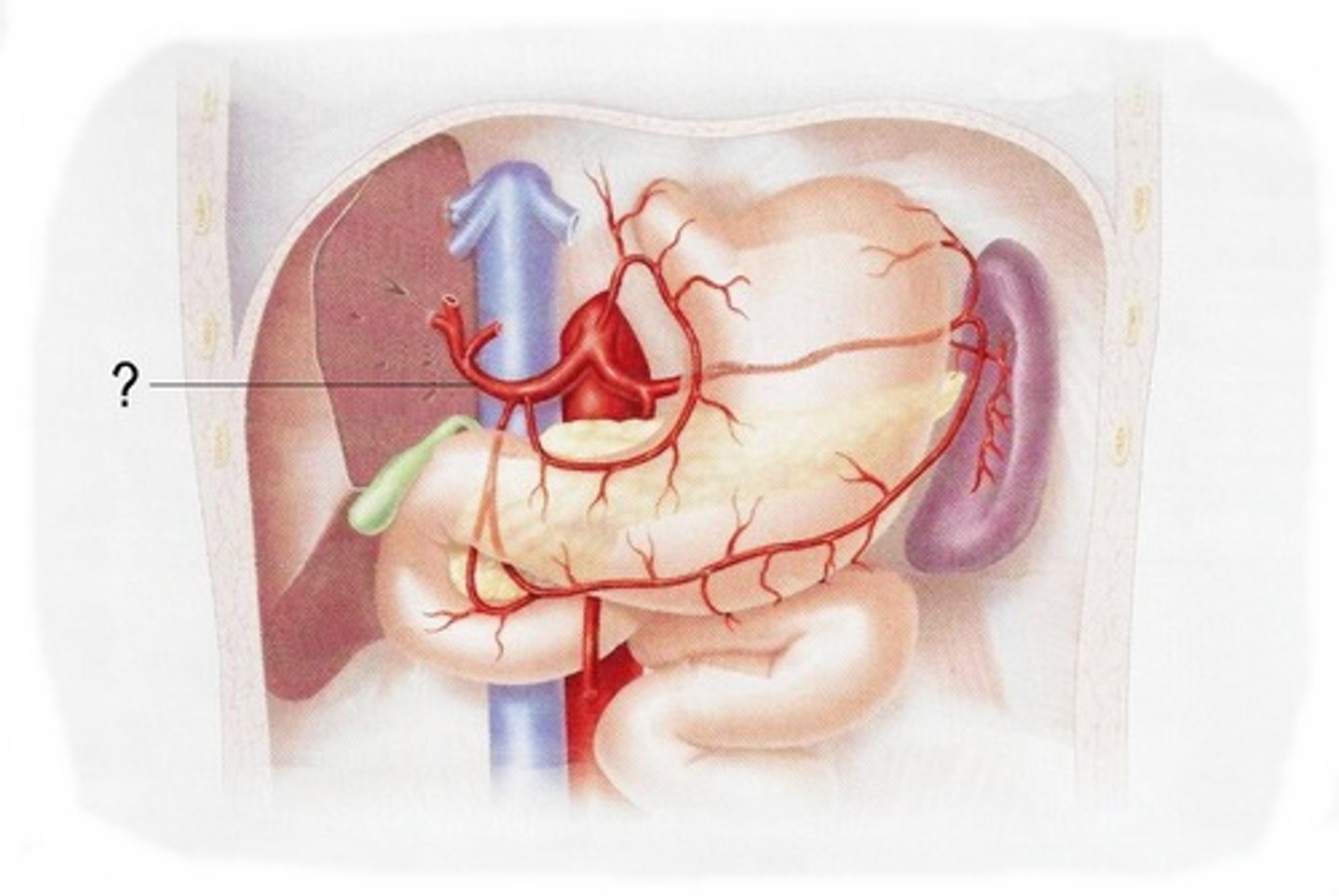
Hepatic artery proper
The artery that supplies blood to the liver.
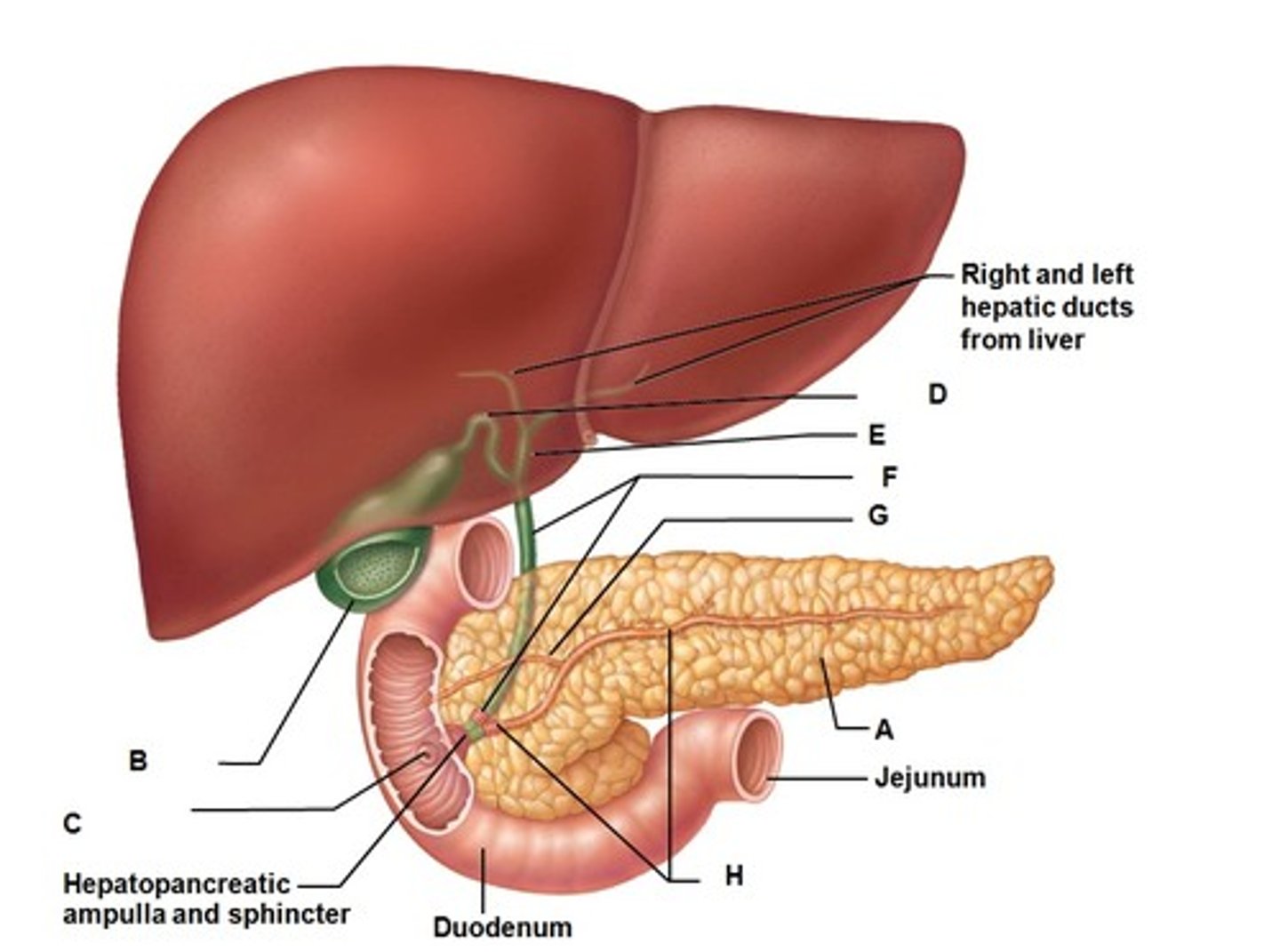
Right and left hepatic ducts
Ducts that drain bile from the right and left lobes of the liver.
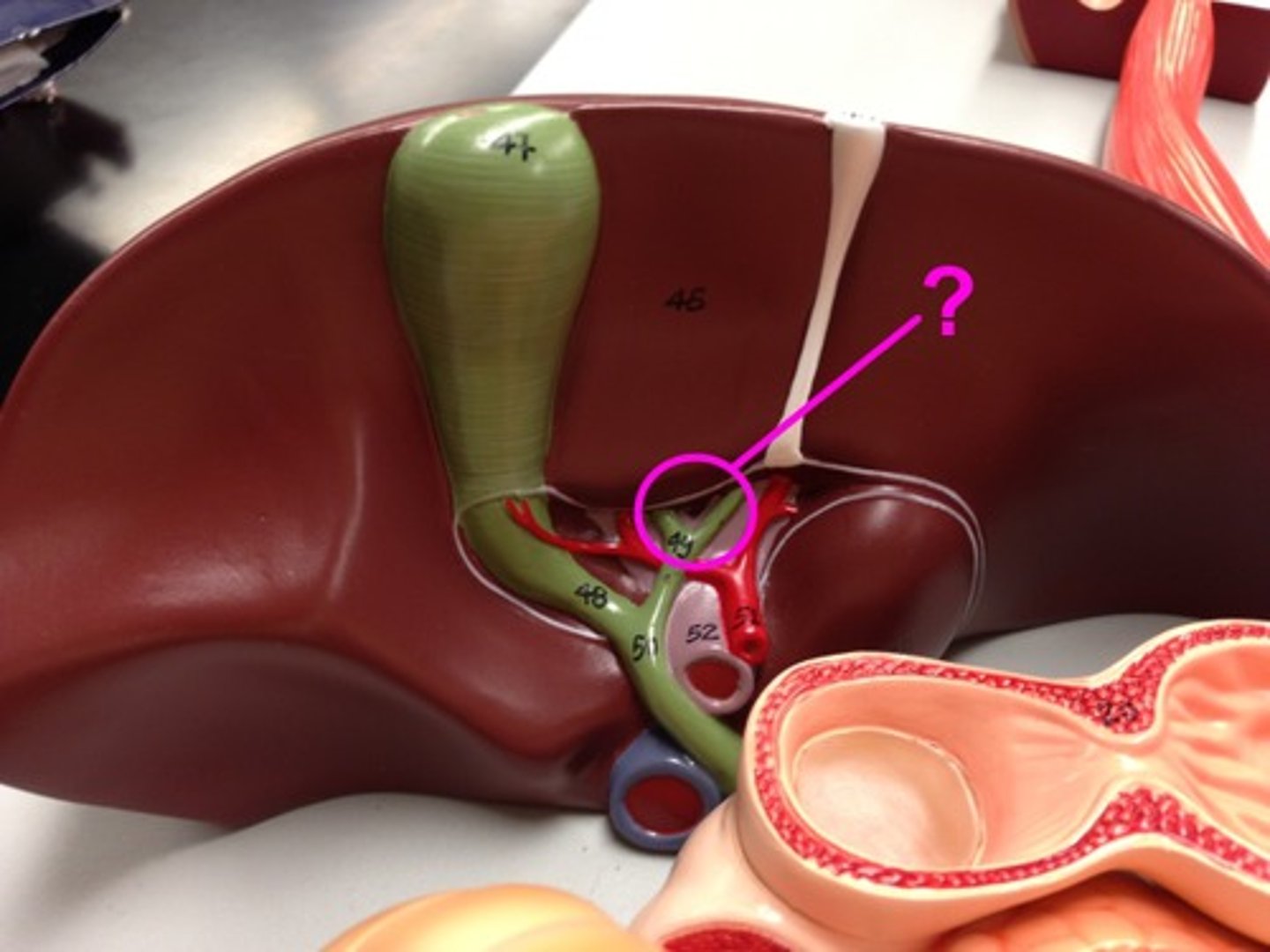
Common hepatic duct
The duct formed by the convergence of the right and left hepatic ducts.

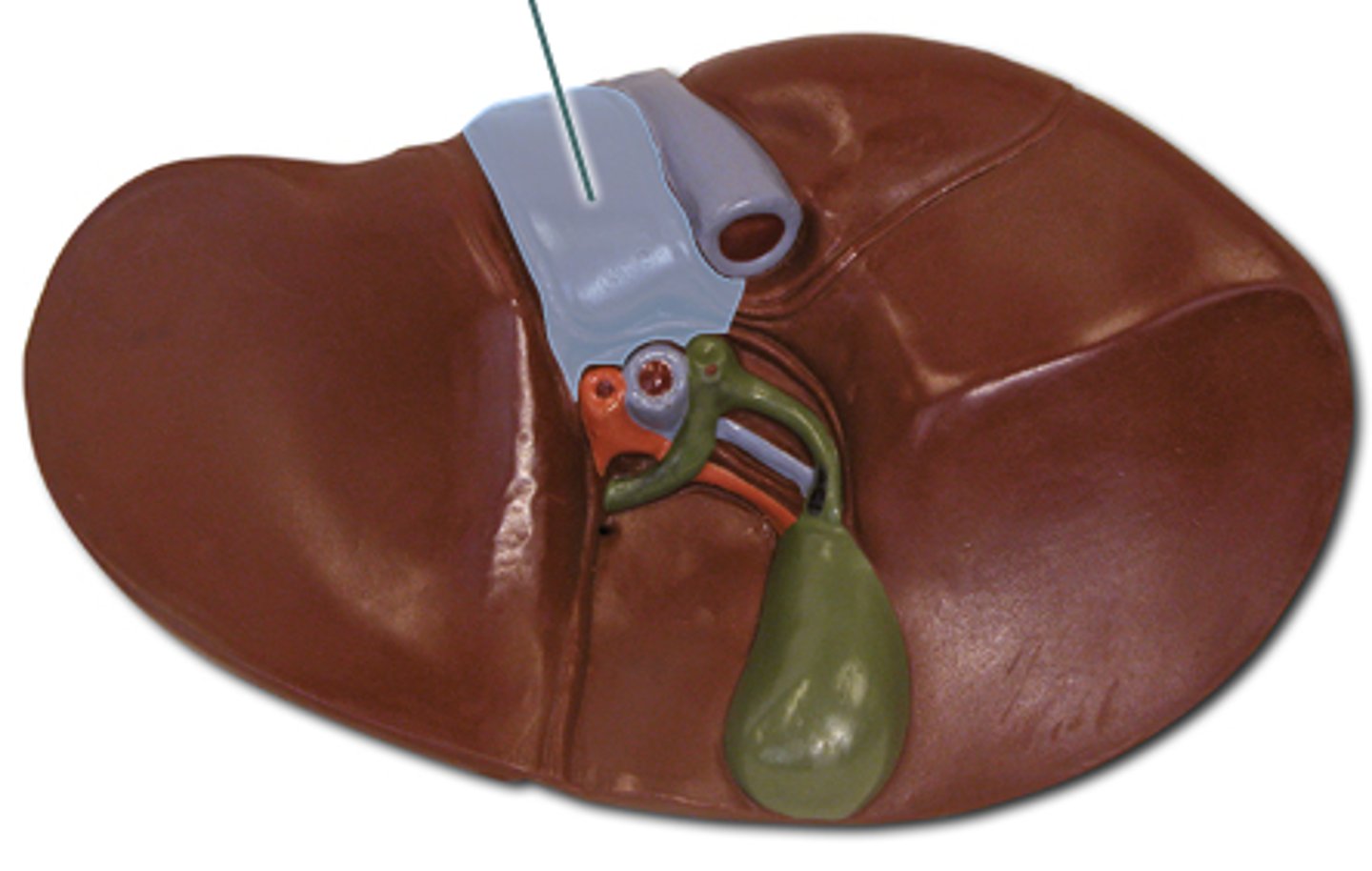
Round ligament
A remnant of the umbilical vein that runs along the falciform ligament.
Ligamentum teres
The fibrous remnant of the umbilical vein.
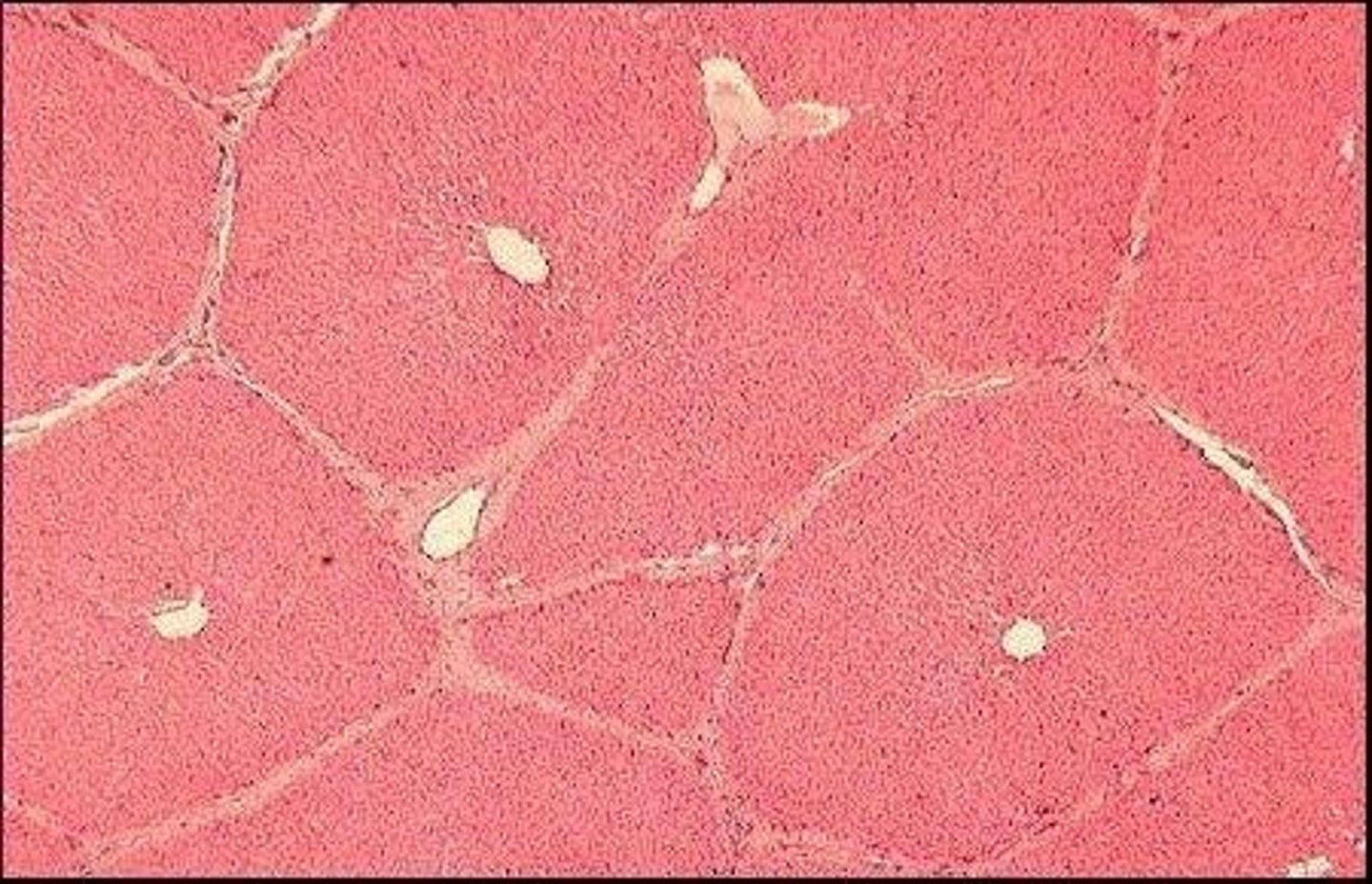
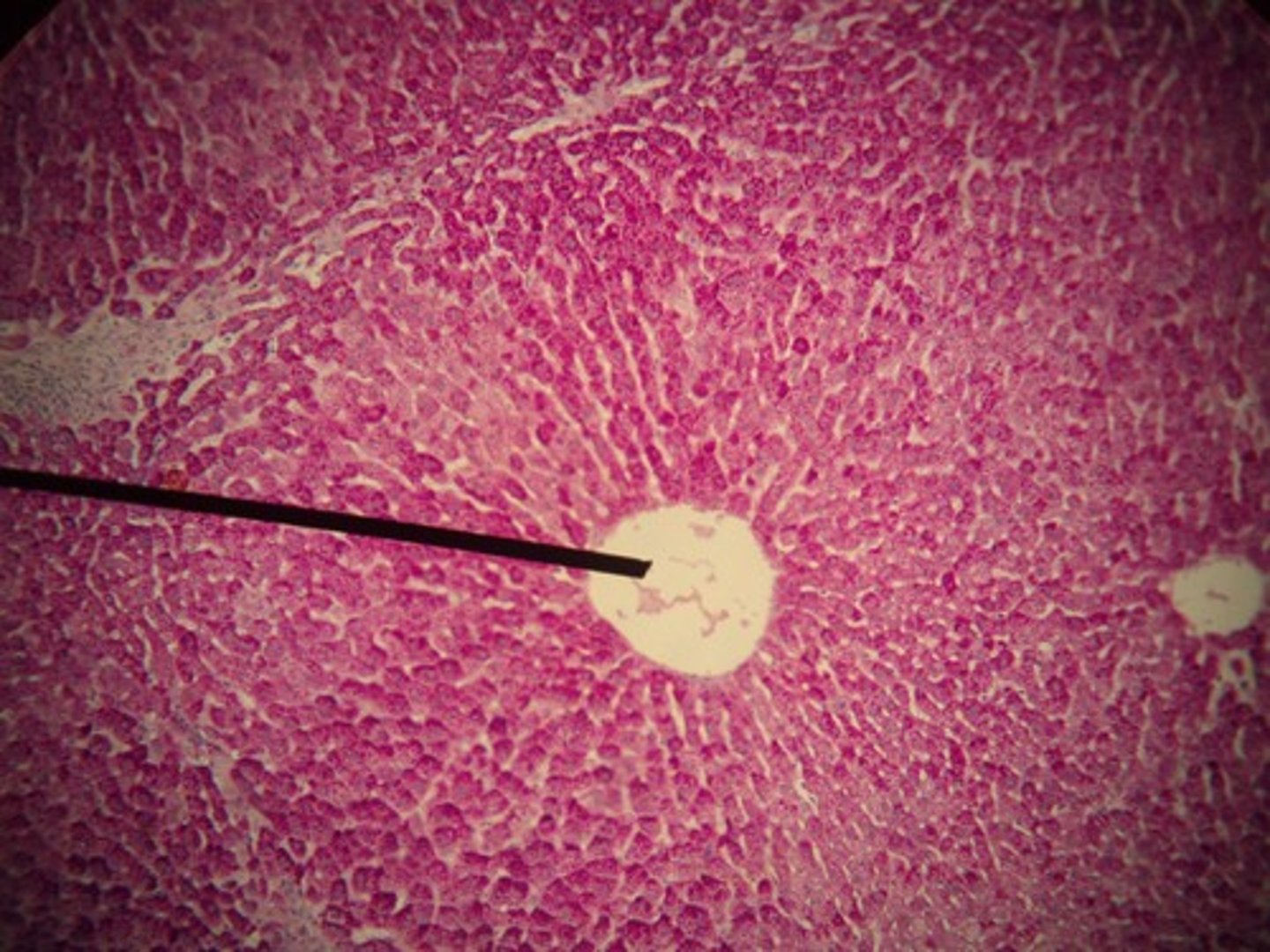
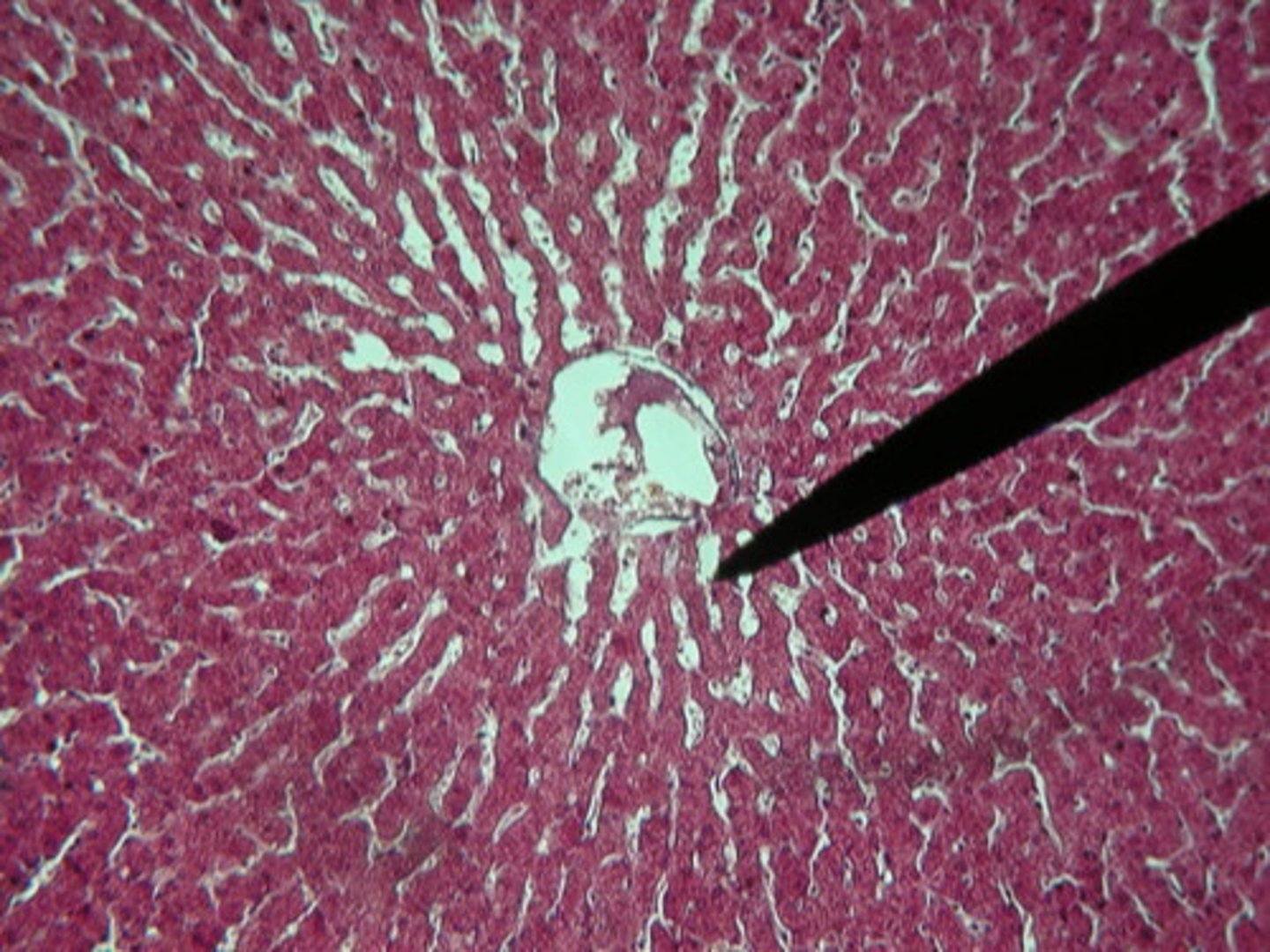
Liver lobules
The functional units of the liver.
Central vein
The vein that collects blood from the liver lobules.
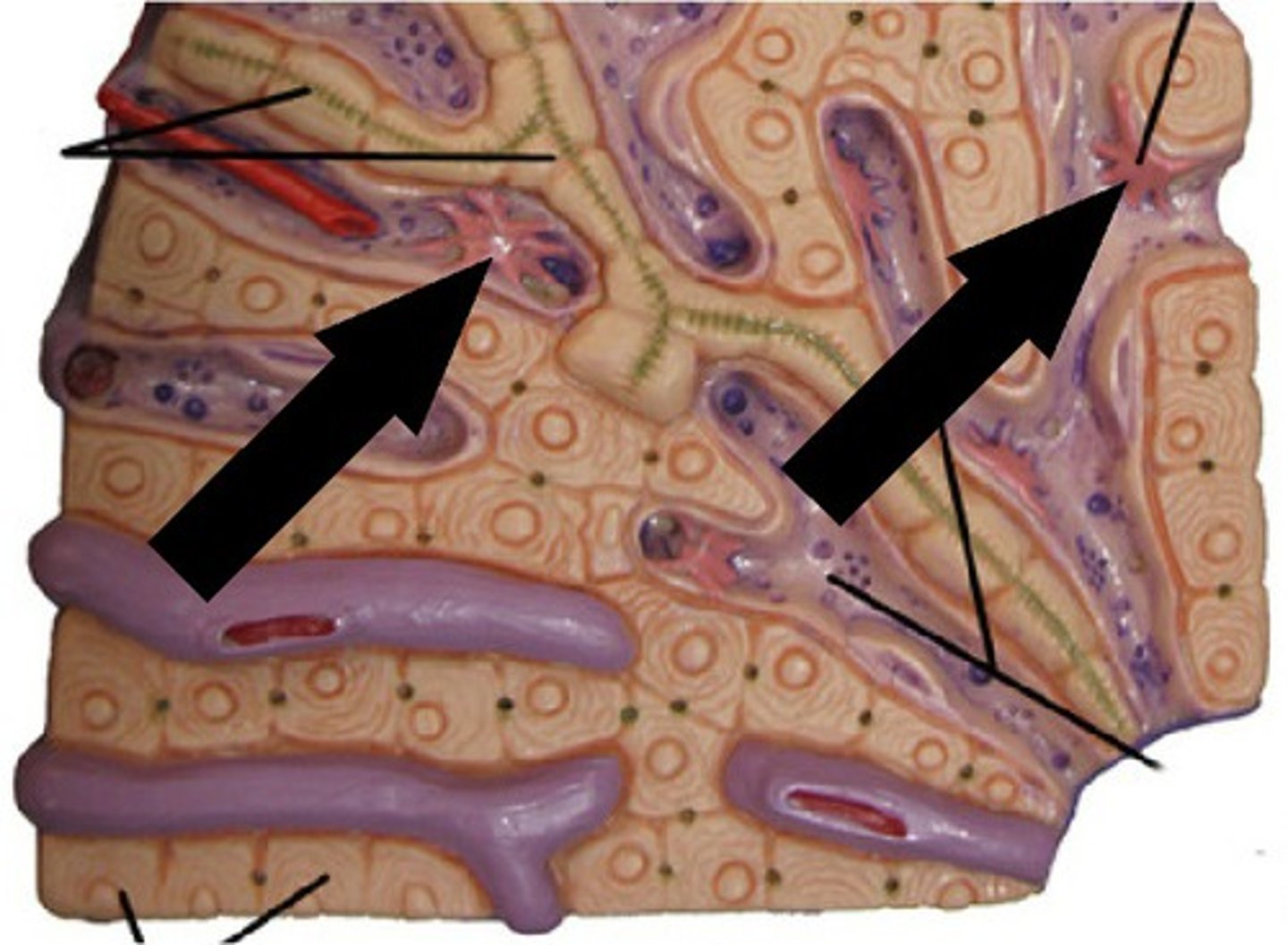
Portal triad
The structure containing a branch of the hepatic artery, a branch of the portal vein, and a bile duct.
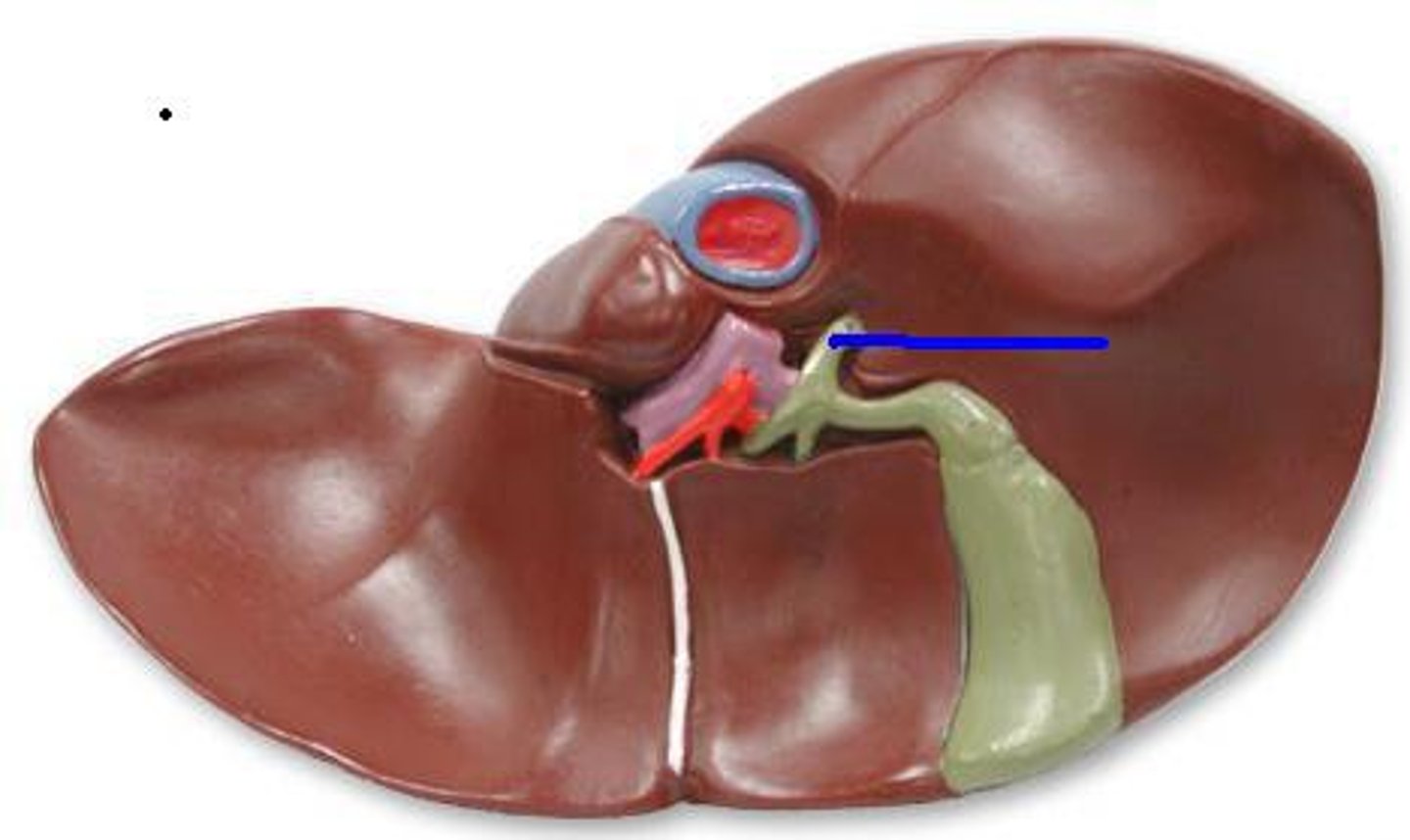
Bile duct
The duct that carries bile from the liver to the gallbladder and duodenum.
Liver sinusoids
Small blood vessels in the liver that allow for exchange between blood and liver cells.
Stellate cells
Liver cells involved in the storage of vitamin A and the production of extracellular matrix.

Stellate macrophages
Immune cells located in the liver that help in the removal of pathogens.
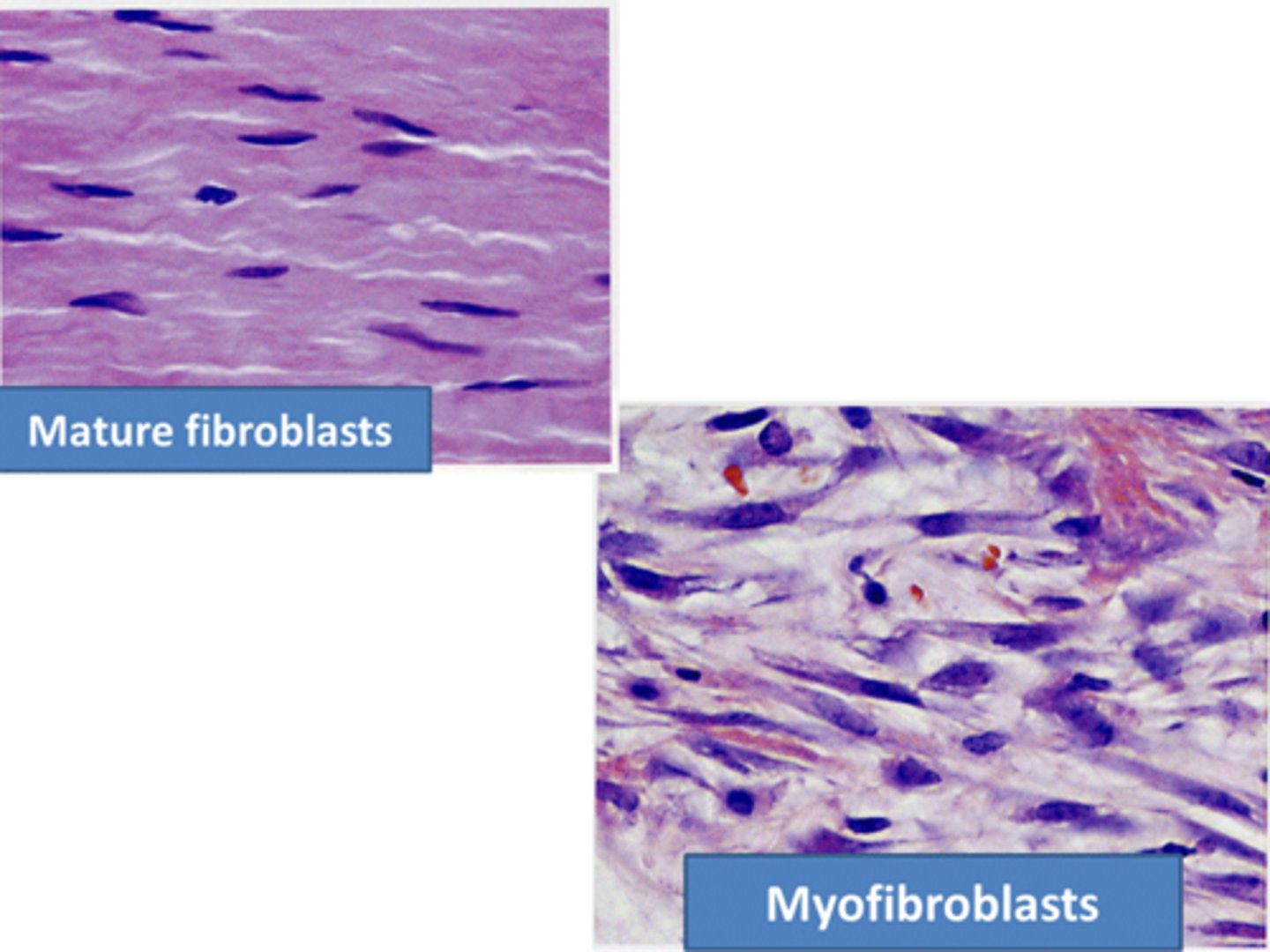
Myofibroblast
Cells that play a role in wound healing and fibrosis in the liver.
Gallbladder
The organ that stores bile produced by the liver.
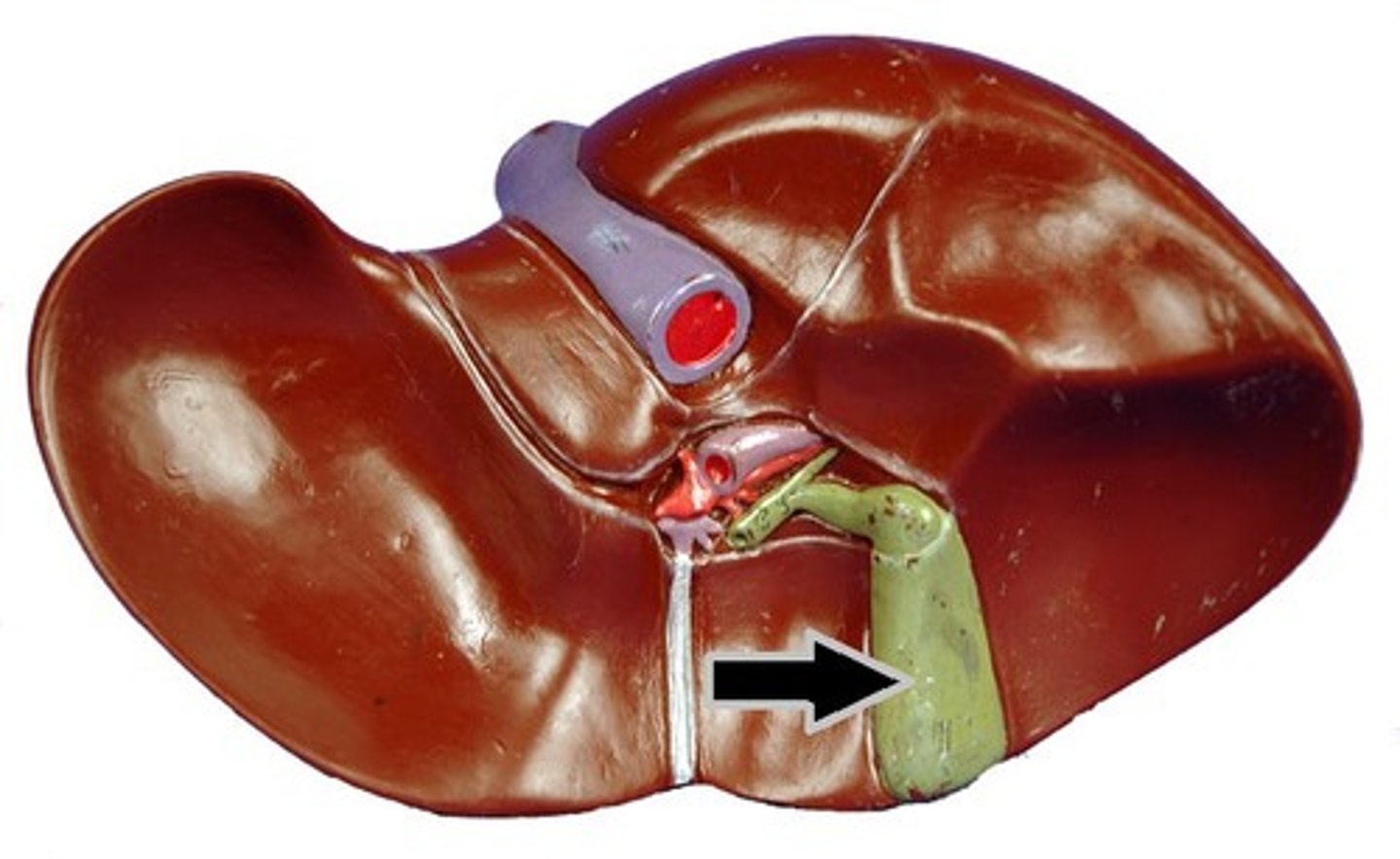
Gallstones
Small crystals that form from bile in the gallbladder.
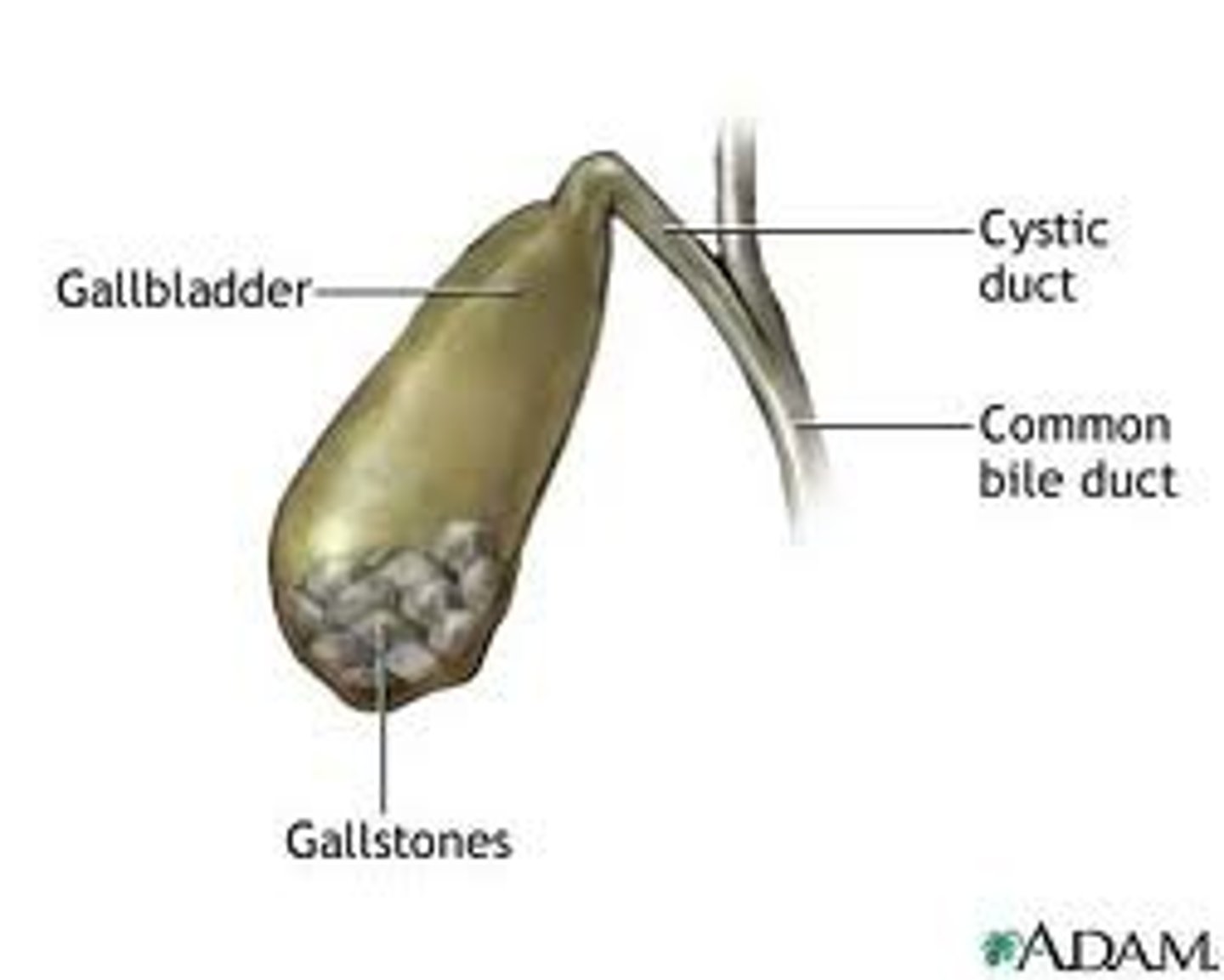
Cystic duct
The duct that connects the gallbladder to the common bile duct.
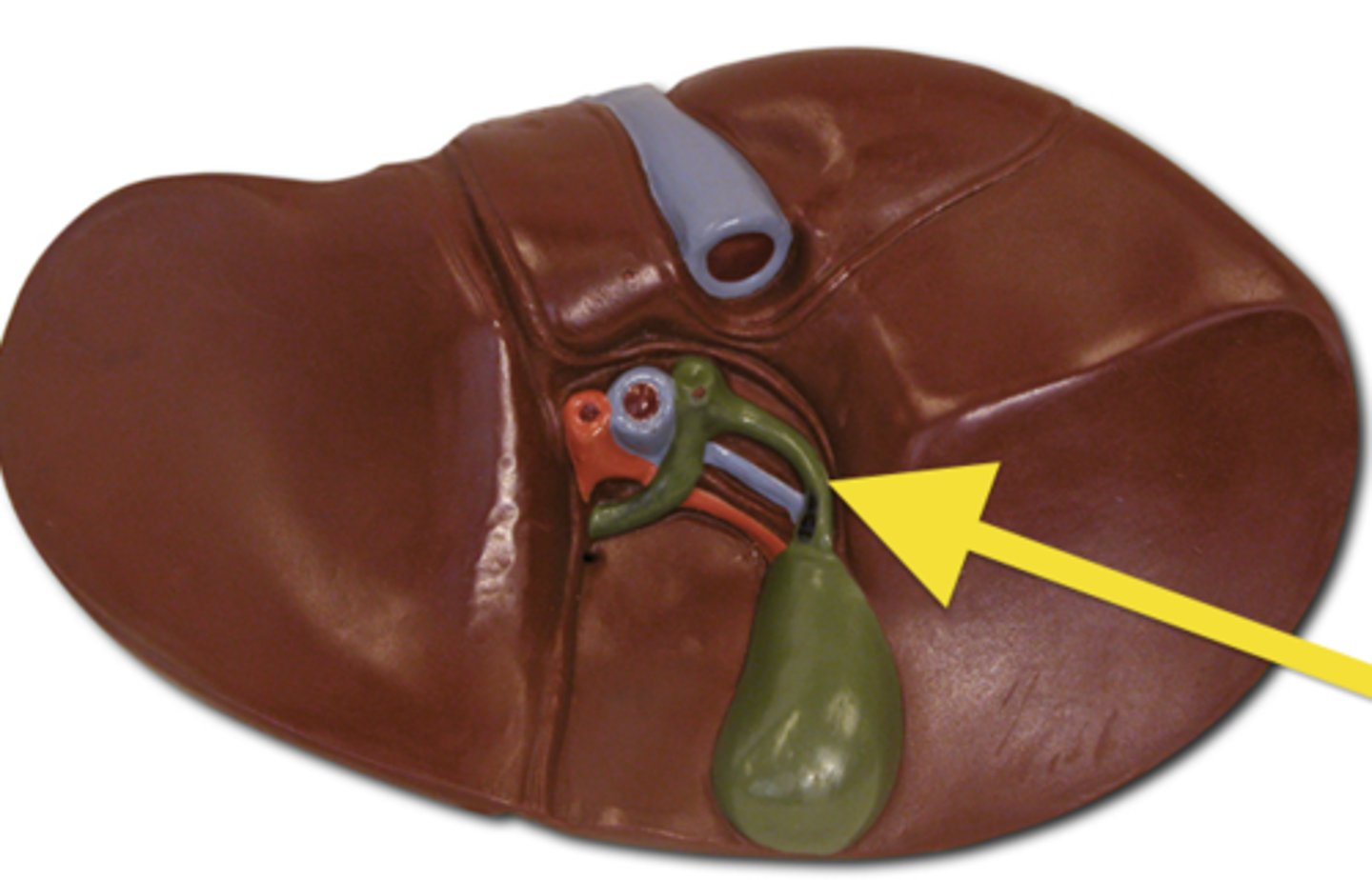

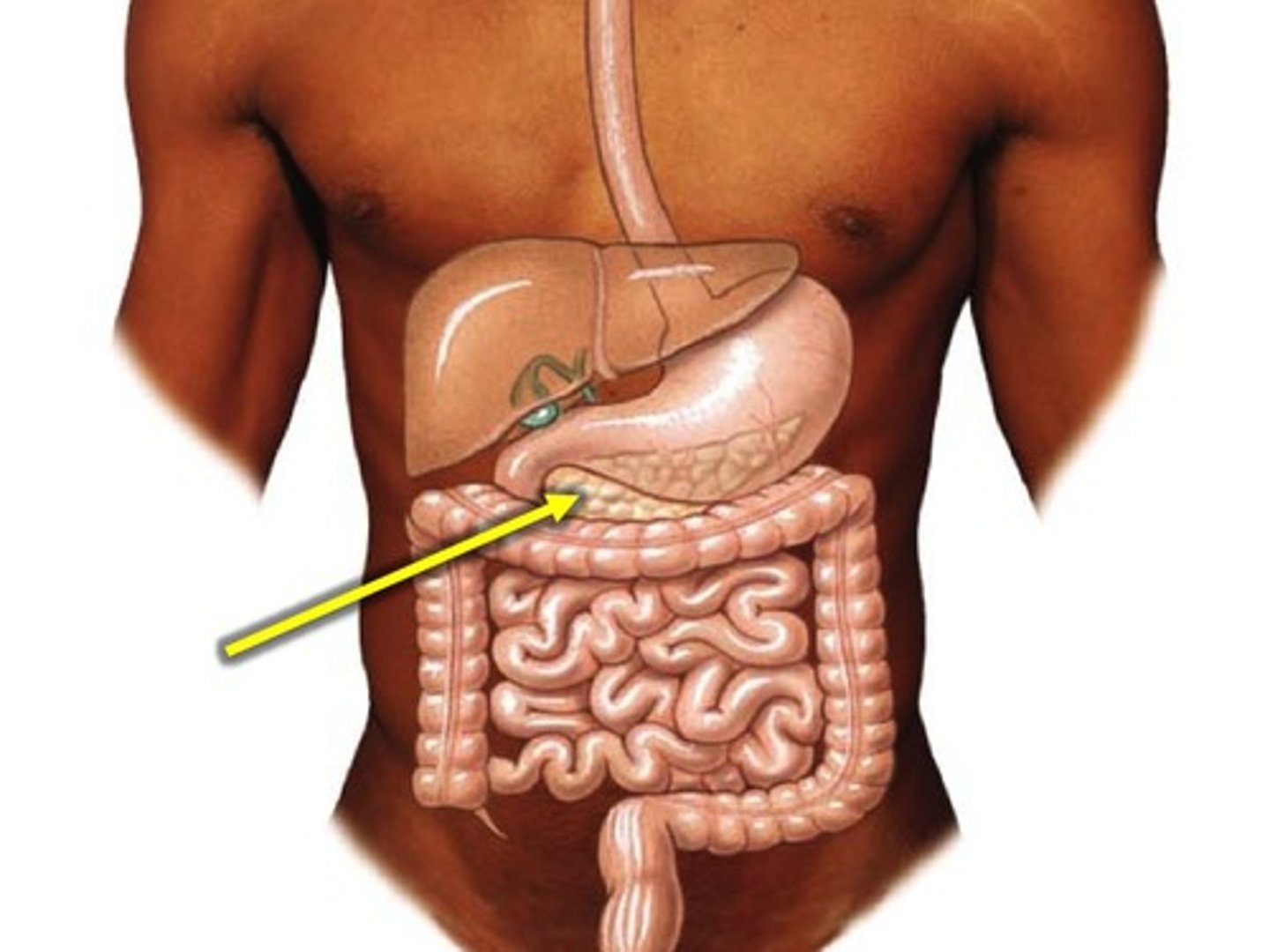
Pancreas
An organ that produces digestive enzymes and hormones like insulin.
Main pancreatic duct
The duct that carries digestive enzymes from the pancreas to the duodenum.
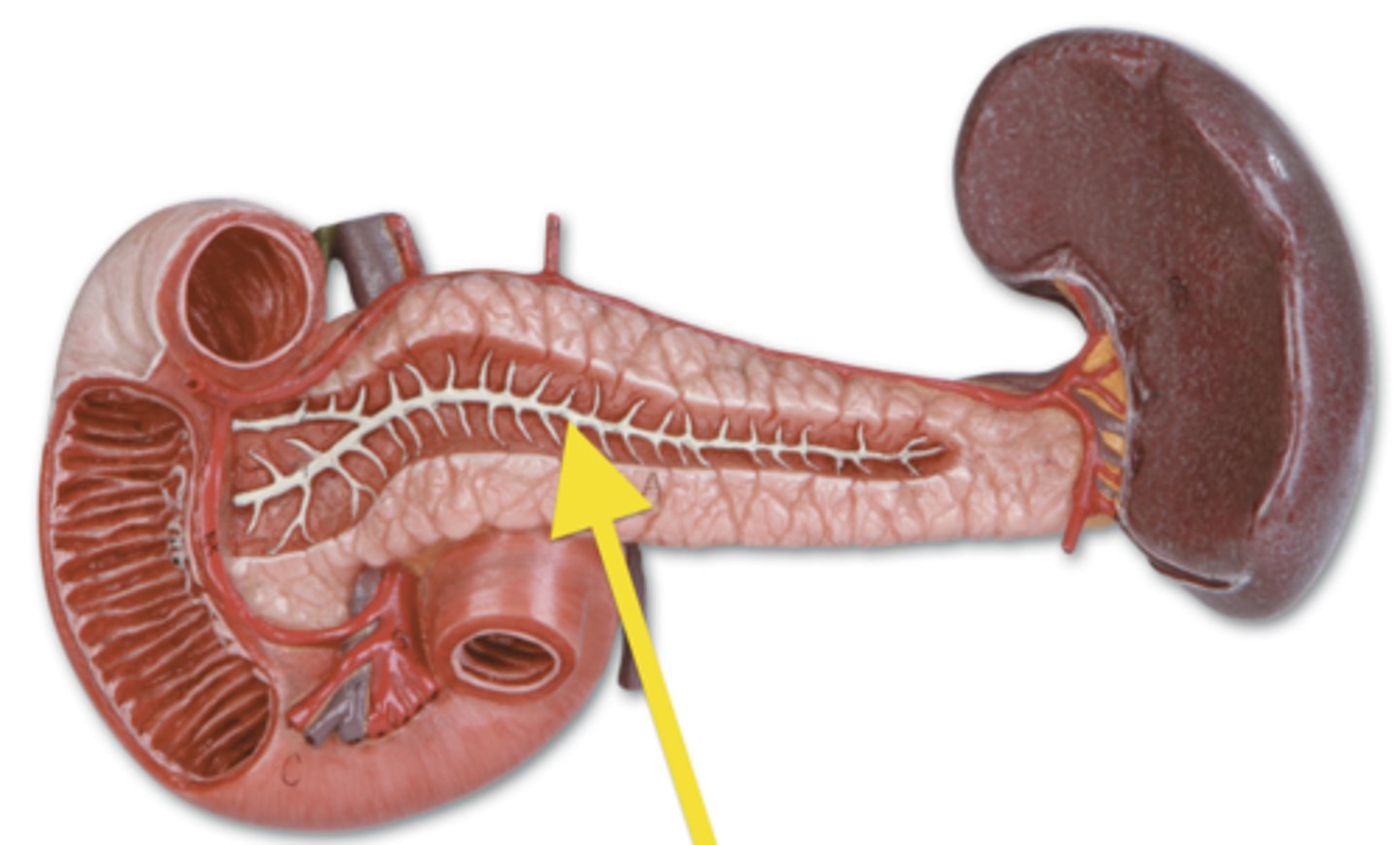
Accessory pancreatic duct
A secondary duct that may also carry pancreatic juices to the duodenum.
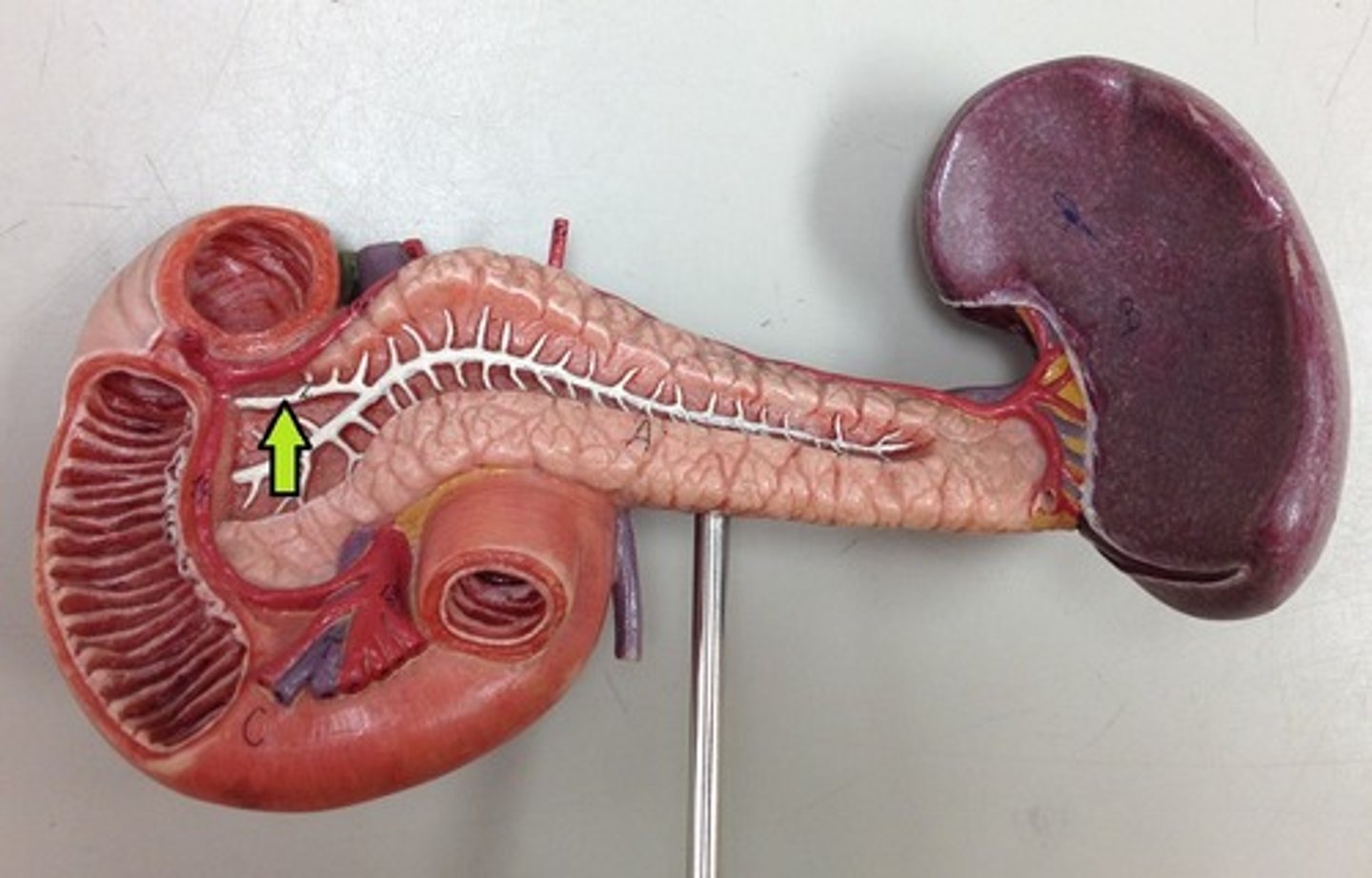
Pancreatitis
Inflammation of the pancreas.
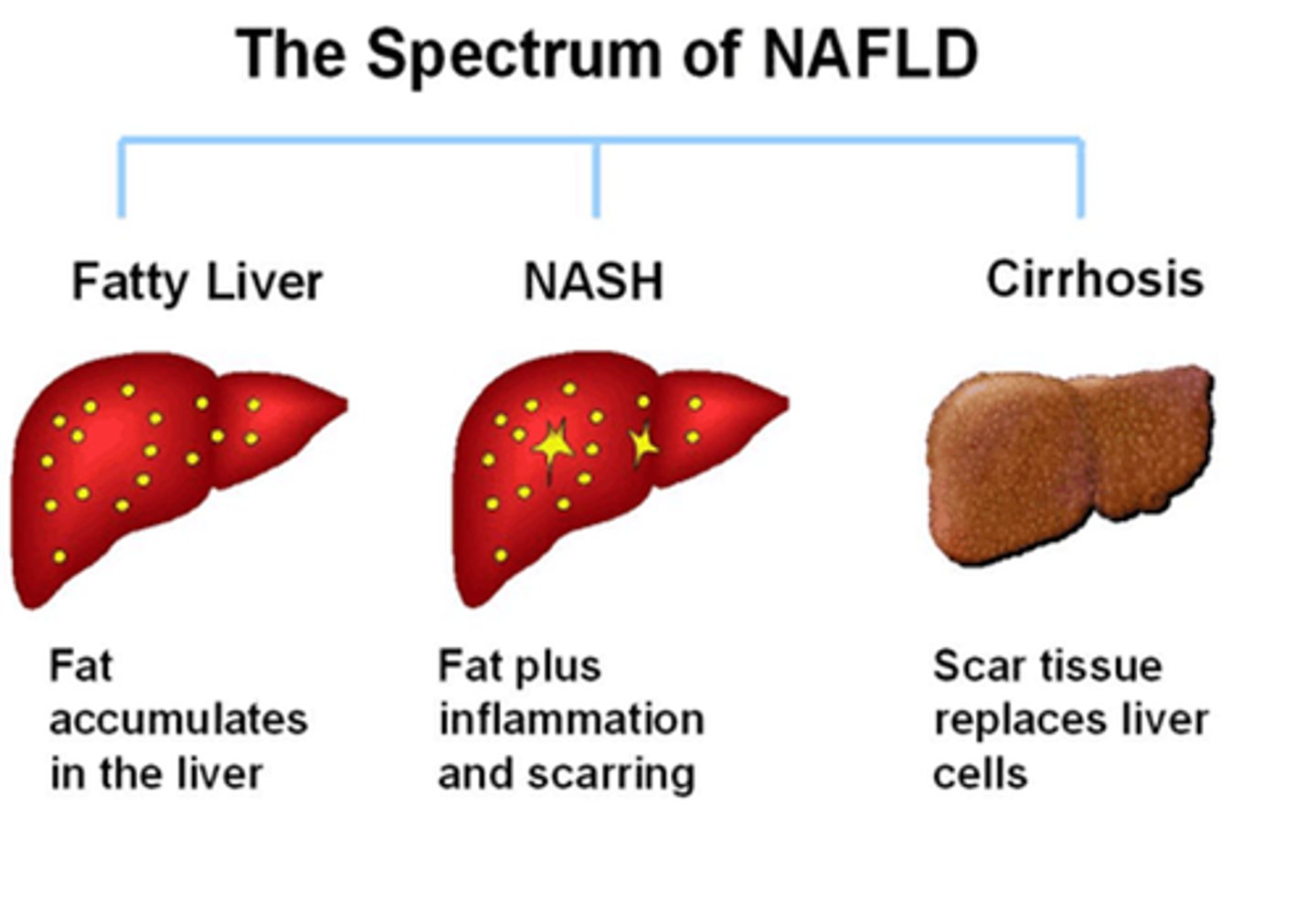
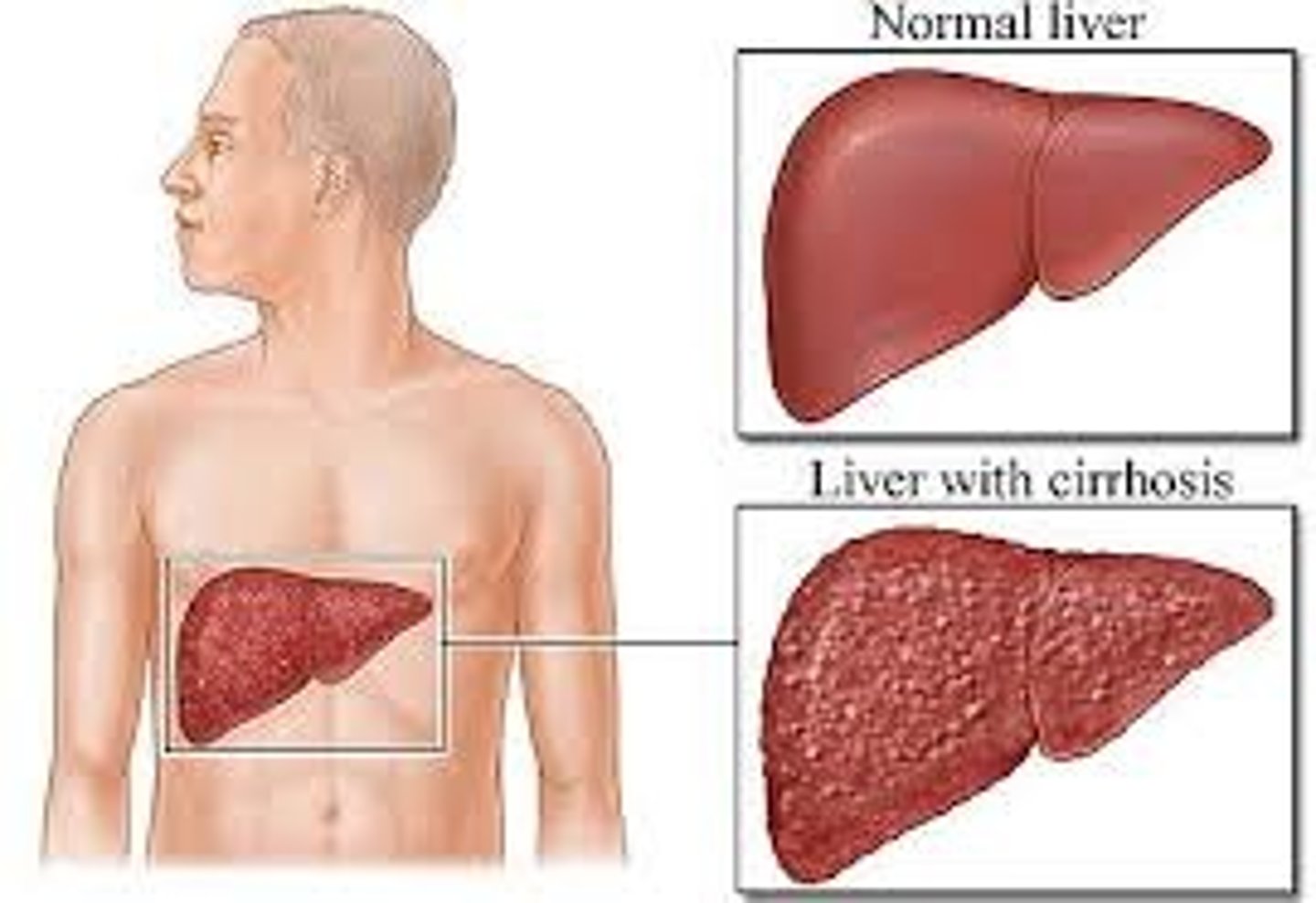
Cirrhosis
Chronic liver damage leading to scarring and liver failure.
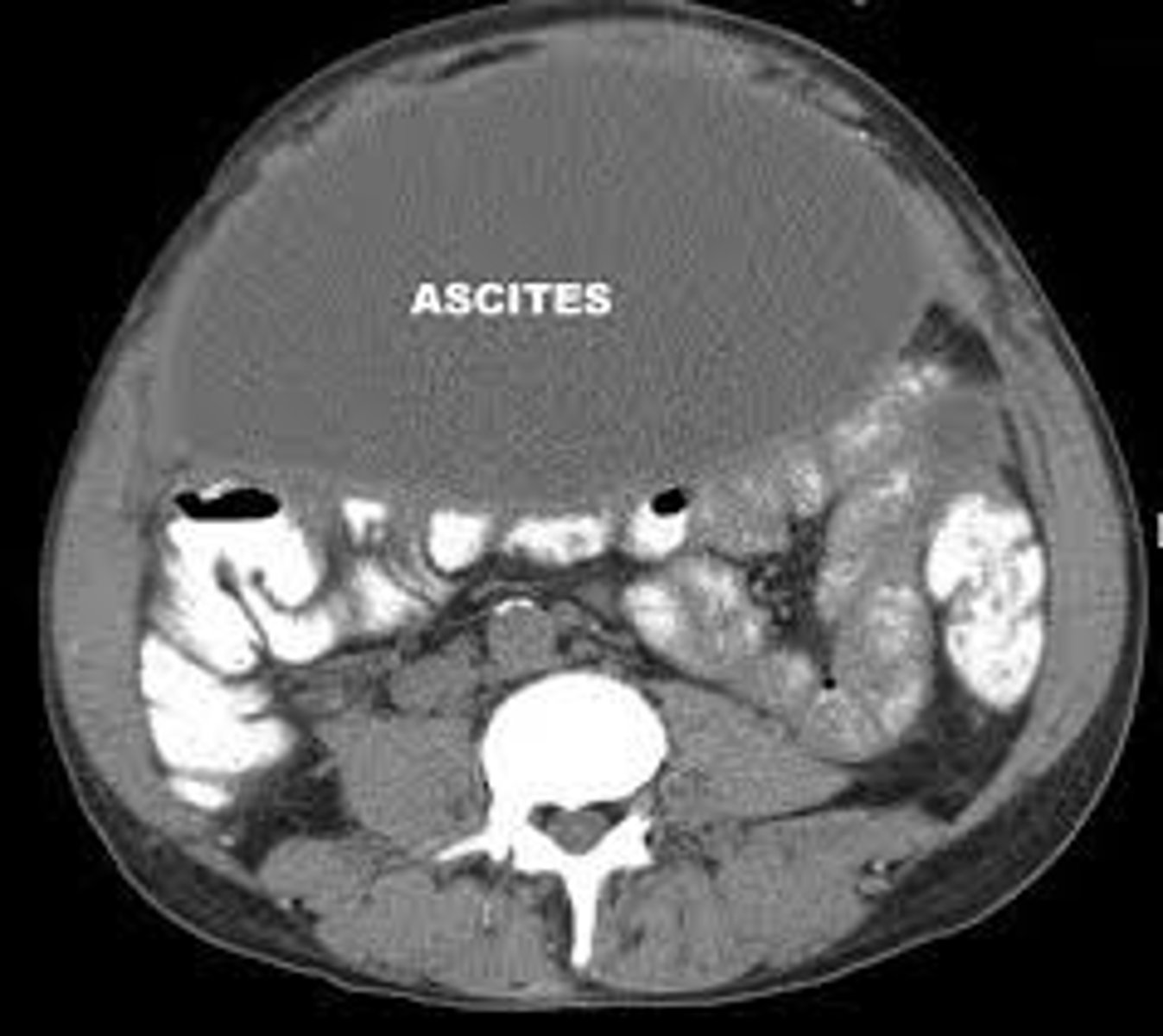
Ascites
The accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
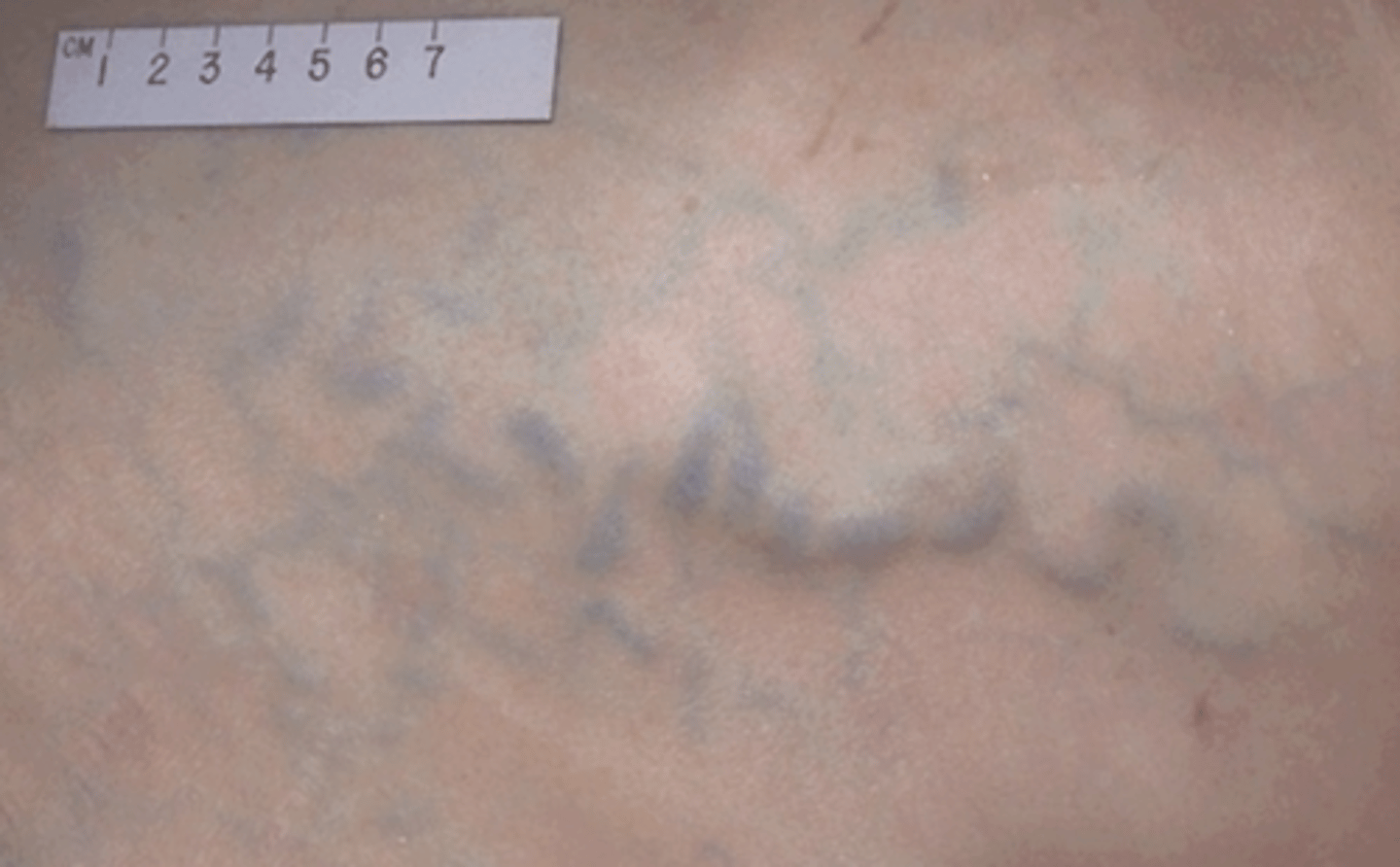
Periumbilical caput medusae
A condition characterized by distended veins around the navel due to portal hypertension.
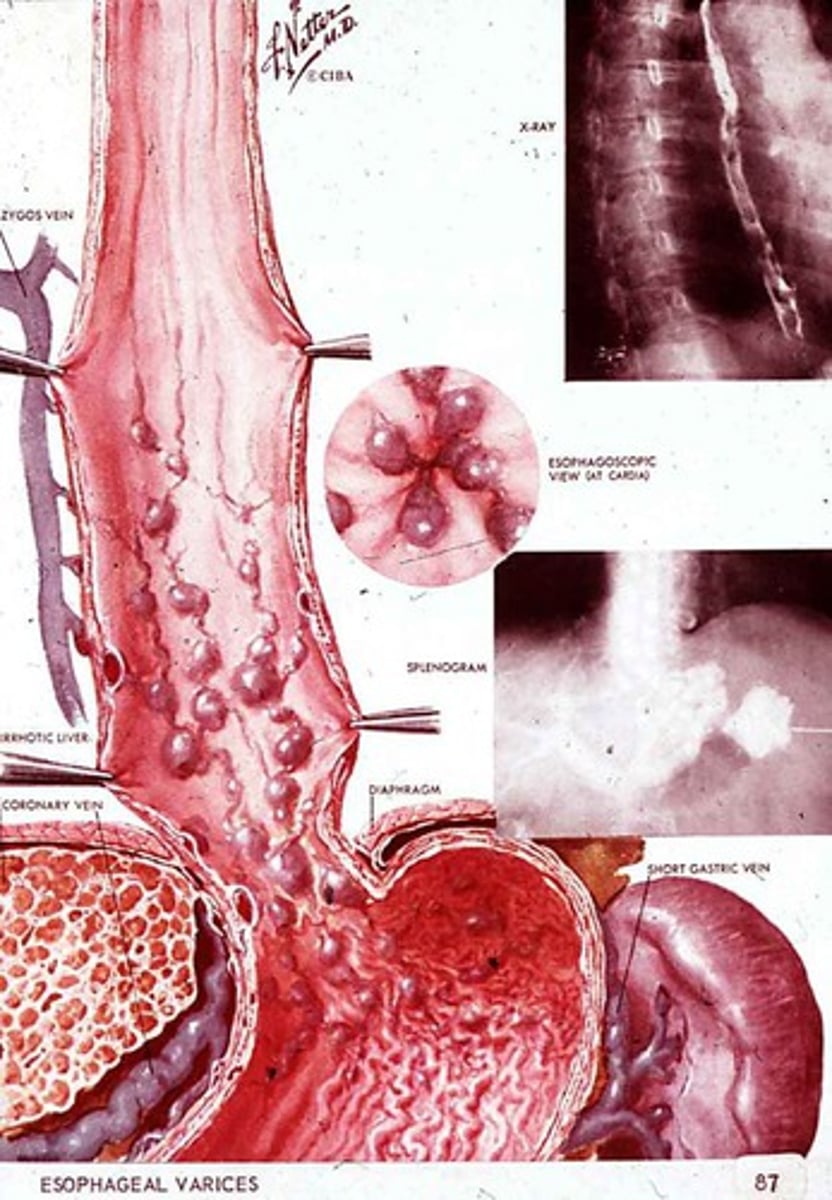
Esophageal varices
Enlarged veins in the esophagus that can rupture and cause bleeding.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
A condition characterized by excess fat accumulation in the liver not due to alcohol.
NAFLD
An acronym for Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.