Biology - Musculoskeletal System
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Functions of the Skeleton
support
protection
movement
shape
manufacture of blood components
Axial Skeleton
consists of the skull, spine, ribs and sternum (breastbone)
Spine
made up of 33 bones called vertebrae
7
number of vertebrae in cervical (neck) region of spine
12
number of vertebrae in thoracic (chest) region of spine
5
number of vertebrae in lumbar (back) region of spine
5
number of vertebrae in sacrum (hip) region of spine
4
number of vertebrae in coccyx (tail) region of spine
True Ribs
the top seven ribs attached to the breastbone
False Ribs
ribs 8,9,10 are attached to each other at the front of the chest by cartilage
Floating Ribs
the bottom two ribs, which are only attached to the spine
Appendicular Skeleton
composed of the limbs (arms and legs), the pectoral (shoulder) girdle, and the pelvic (hip) girdle
Pectoral Girdle
consists of the collarbone (or clavicle) and the shoulder blade (or scapula)
Pelvic Girdle
is composed of two halves of the hip joined to the sacrum
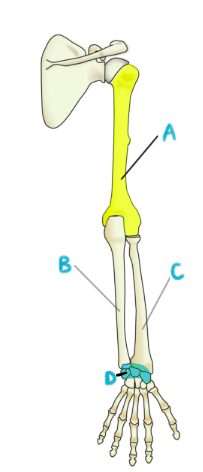
A: humerus
B: ulna
C: radius
D: carpals
name the bones of the arm
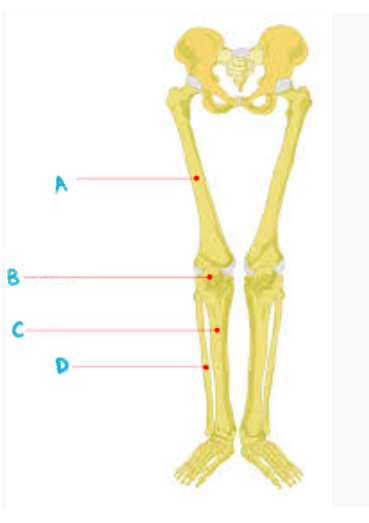
A: femur
B: patella
C: tibia
D: fibula
name the bones of the leg
Cartilage
covers the ends of bones, is composed of the protein collagen
Functions of Cartilage
acts as a shock-absorber
allows friction-free movement
Epiphysis
head of long bone
Diaphysis
shaft of long bone
Compact Bone
hard and strong
→ gives strength and flexibility to the bone
Spongy Bone
more porous
→ has hollow spaces containing bone marrow
→ makes blood cells
Medullary Cavity
a hollow tube located at the centre of the shaft of a bone
→ contains bone marrow
Osteoblast
a bone-forming cell
Growth Plate
the area between the epiphysis and the diaphysis in a long bone within which bone growth occurs
Ossification
cartilage is formed and turned into bone
→ occurs in the growth plate
Osteoclast
a bone-digesting cell
Joint
where two or more joints meet
Immovable Joints
joints in the skull and pelvic girdle
Slightly Movable Joints
joints between the vertebrae in the upper spinal column
Synovial Joints
include ball and socket, and hinge joints
Synovial Fluid
produced in movable joints to lubricate and reduce friction
Ball and Socket Joints
joints in the shoulder and hip
→ allow movement in all directions
Hinge Joints
joints in the elbow and knee
→ allow movement in one direction only
Ligaments
strong, fibrous, slightly elastic tissues that connect bone to bone
Tendons
strong, flexible, inelastic fibres that connect muscle to bone
Arthritis
a disorder that results in inflammation of joints
may be prevented by reducing damage to joints in sports
treated by rest, exercise, drugs and surgery
Antagonistic Pair
two muscles that have opposite effects to each other
Biceps
is a flexor
→ closes the joint
Triceps
is an extensor
→ opens the joint