carboxylic acids and esters
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
general formula and naming esters
general formula: R-COO-R’
RHS: prefix
LHS: suffix
acidity of carboxylic acids
weak acids - only partially dissosciates
solubility of carboxylic acids
soluble in water because they can hydrogen bond to water molecules
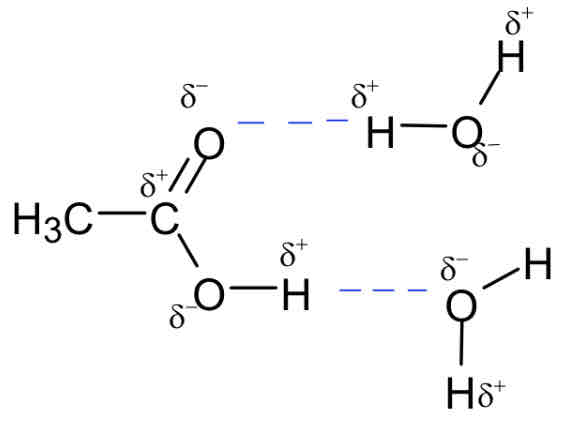
Salt formation reactions of carboxylic acids
Acid + metal —> salt + hydrogen
Acid + alkali —> salt + water
Acid + carbonate —> salt + water + CO2
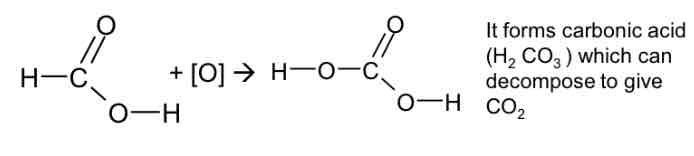
Oxidation of methanoic acid
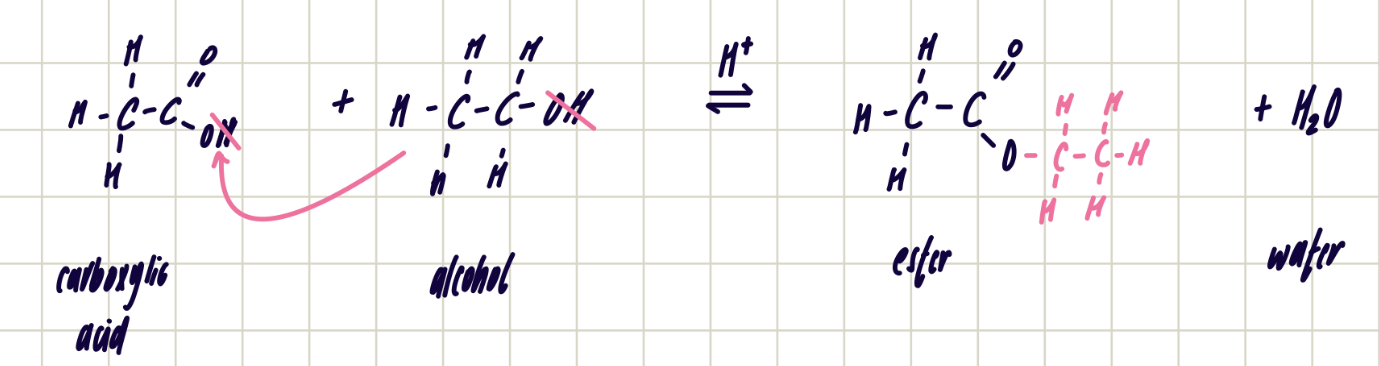
forming esters reagents, conditions and equation
esterification/condensation reaction
carboxylic acid + alcohol ——> ester + water
H2SO4 catalyst
heat under reflux
hydrolysis of ester with acids
ester + water ——> carboxylic acid + alcohol
reagents: dilute HCl
condition: heat under reflux
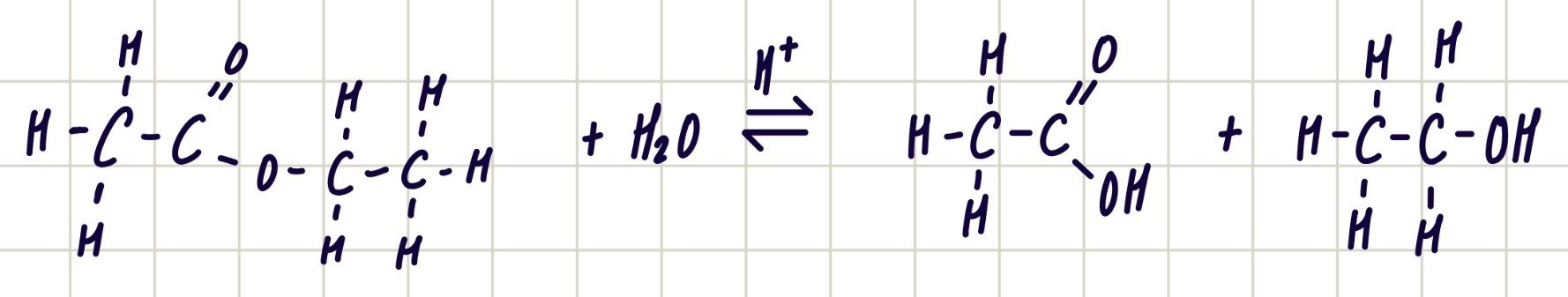
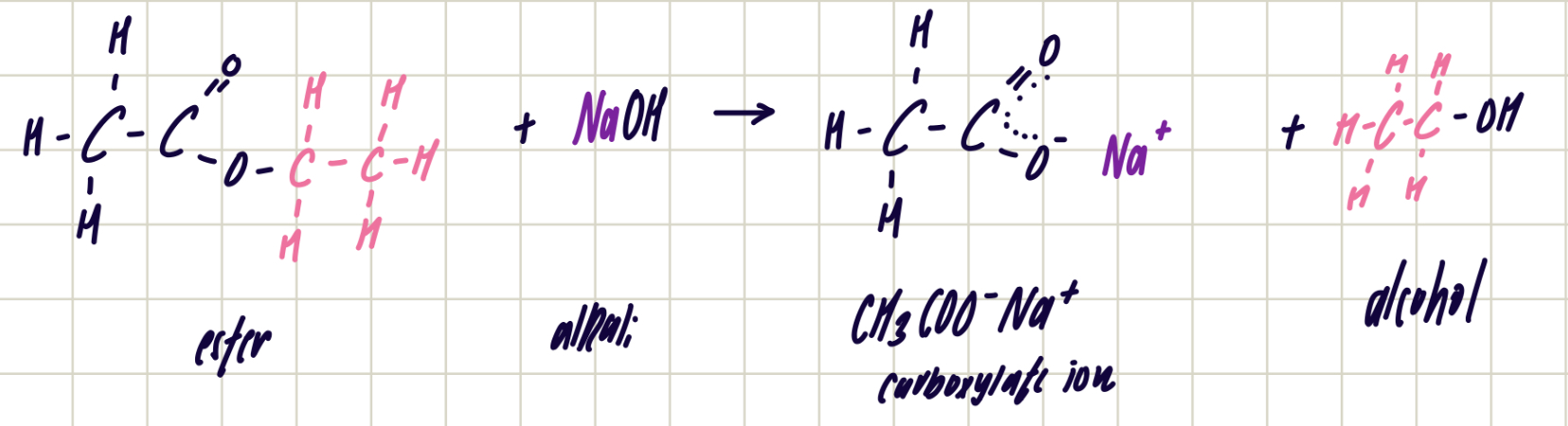
hydrolysis of esters with alkali - sapponification
ester + alkali ——> carboxylate ion + alcohol
reagent: excess, aqueous, dilute NaOH
condition: heat under reflux
Fats and soaps
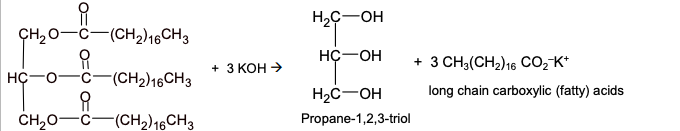
Fats and soaps are esters of glycerol and long chain carboxylic acids (fatty acids)
vegetable oils and animal fats can be hydrolysed to give soap, glycerol and long chain carboxylic acids
Glycerol
forms hydrogen bonds very easily and is readily soluble in water
used in cosmetics, foods and glues
Soap
long chain carboxylic (fatty) acids produced by the hydrolysis of fats
the polar CO₂⁻ end is hydrophilic and mixes with water
the long non-polar hydrocarbon chain is hydrophobic and mixes with grease
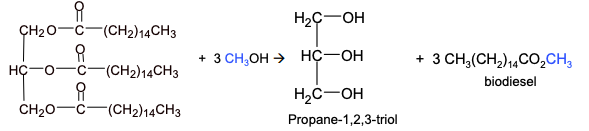
Biodiesel
biodiesel is a mixture of methyl esters of long chain carboxylic acids
vegetable oils can be converted to biodiesel by a reaction with methanol in the presence of a strong alkali catalyst
it can be argued that the biodiesel produced from the method is classed as carbon-neutral
bc any CO2 given off when the biofuel is burnt would’ve been extracted from the air by photosynthesis when the plant grew
however this argument doesn’t take into account
the energy needed to irrigate the plants, extract the oil or heat the reaction with the methanol mixture
if the energy for any of these processes comes from fossil fuels than the biodiesel produced cannot be considered carbon neutral
also doesn’t take into account the effect on land available for food production
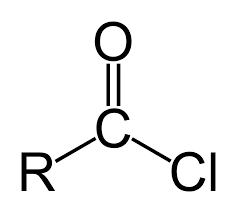
acyl chloride
suffix: -oyl chloride
much more reactive than carboxylic acids
explain why ethanoyl chloride reacts readily with nucleophiles
large charge on carbonyl carbon atom since its bonded to both O and Cl
nucleophiles have electron pairs which can be donated
acid anhydride
suffix - anoic anhydride
similar reactivity to acyl chlorides
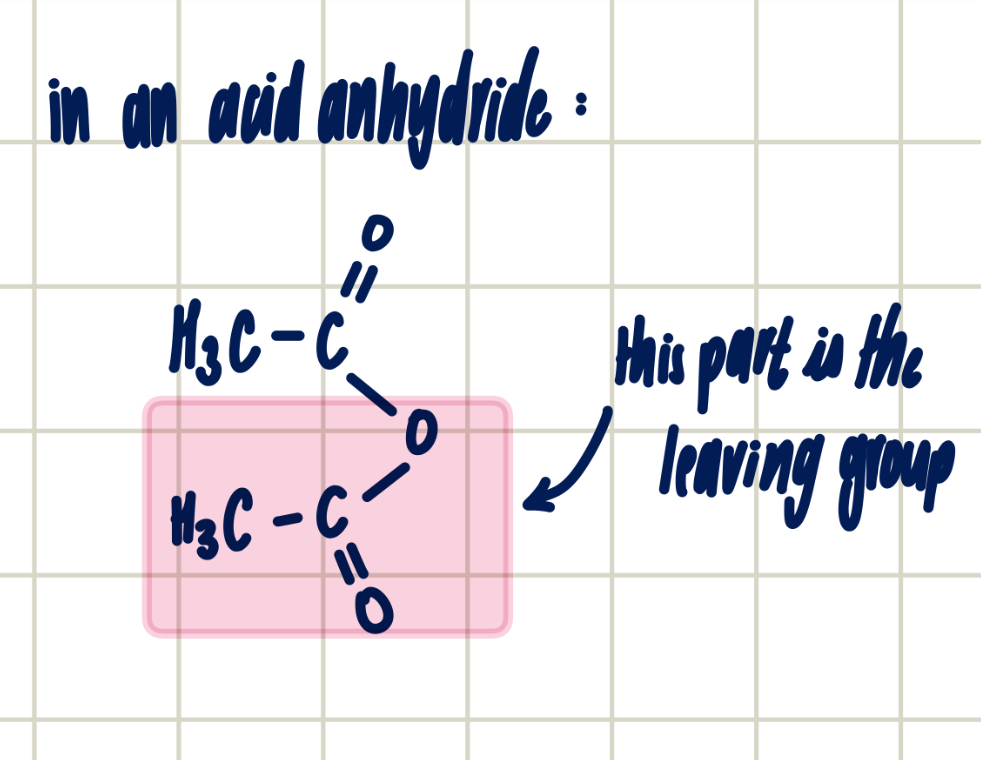
reasons for using acid anhydride over acyl chloride
acyl chloride has violent reaction
toxic HCl gas released when acyl chloride used
less corrosive
Reaction of acyl chloride and water
acyl chloride + water ——> carboxylic acid
nucleophilic addition-elimination
reagent: water
conditions: room temperature
observations: HCl (g) - white steamy fumes
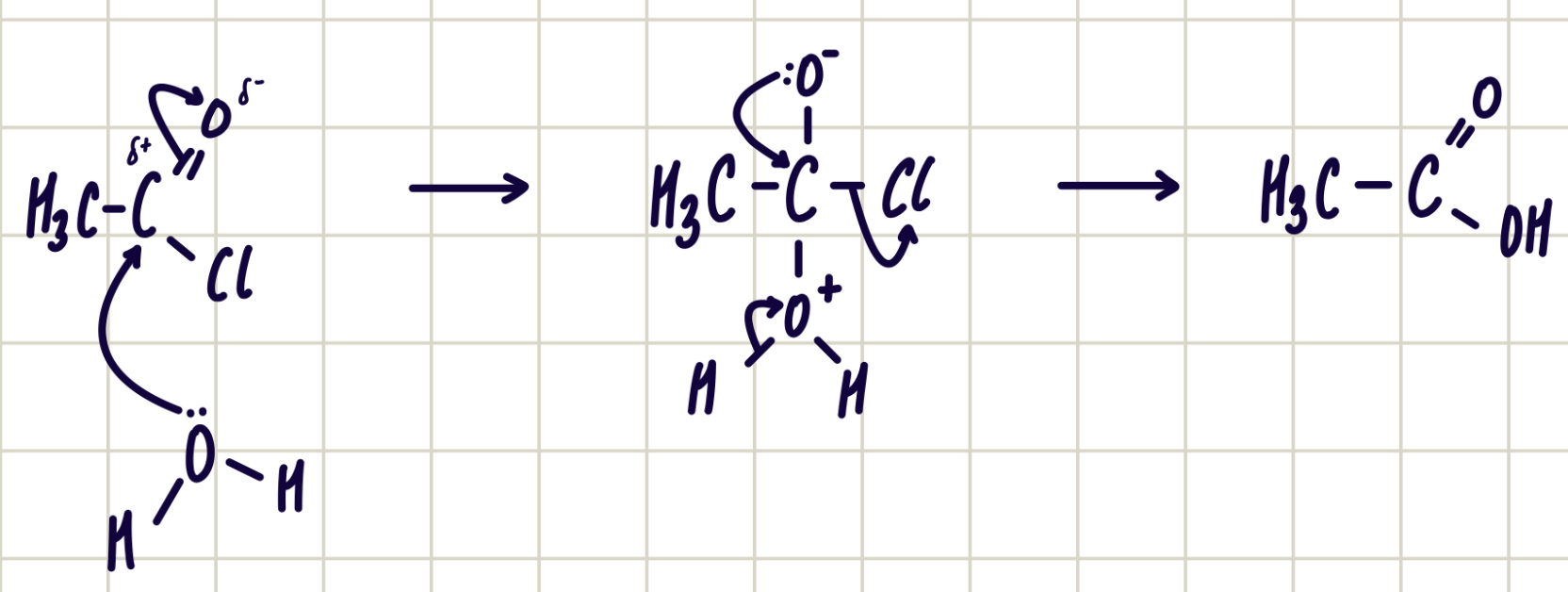
Reaction of acid anhydride and water
acid anhydride + water —> carboxylic acid
nucleophilic addition-elimination
reagent: water
conditions: room temp.
observations: nvc
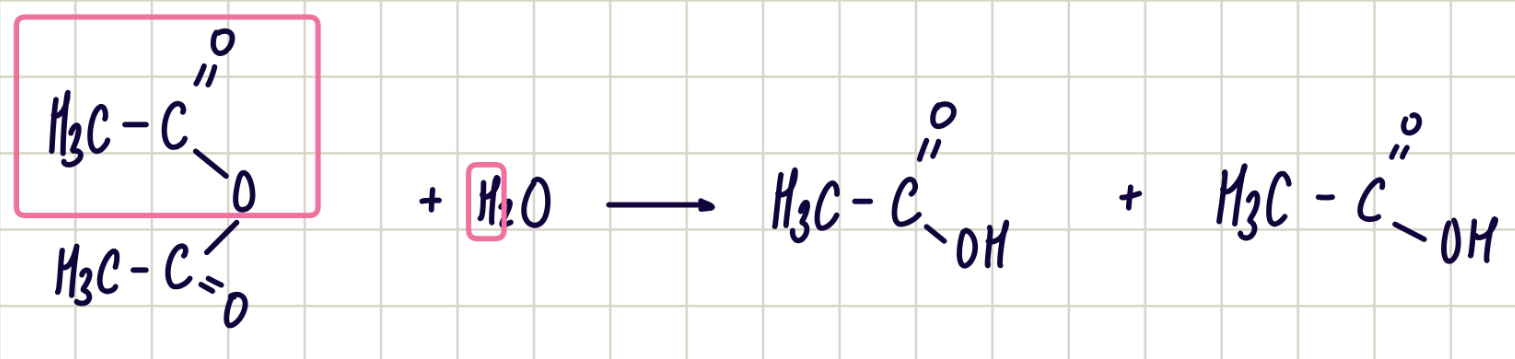
Reaction of acyl chloride and alcohol
acyl chloride + alcohol ——> ester
nucleophilic addition-elimination
reagent: alcohol
conditions: room temperature
observations: HCl (g) - white steamy fumes
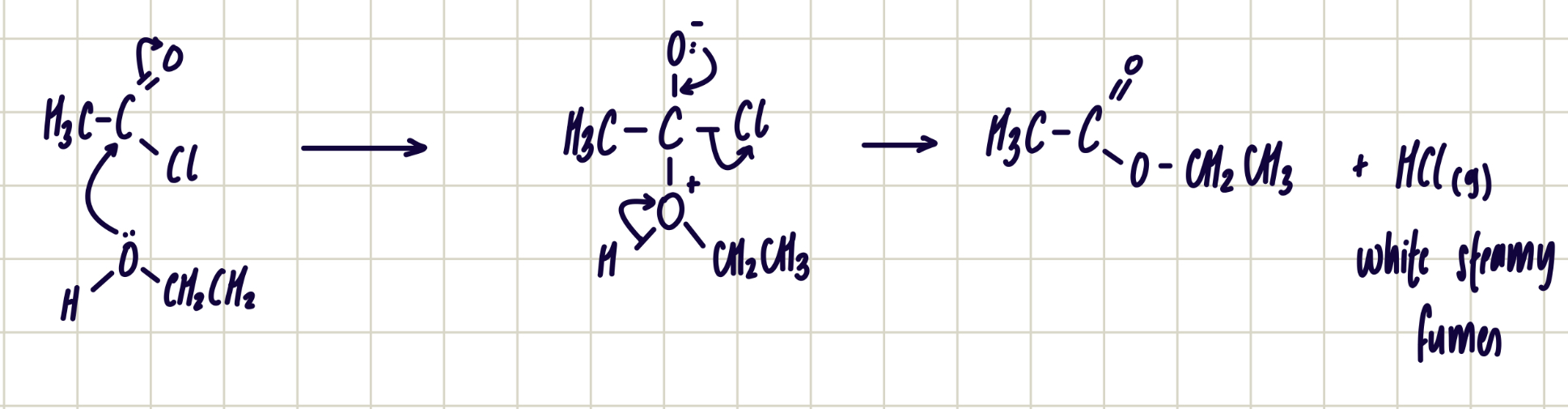
Reaction of acid anhydride and alcohol
acid anhydride + alcohol ——> ester
nucleophilic addition-elimination
reagent: alcohol
conditions: room temperature
observations: nvc
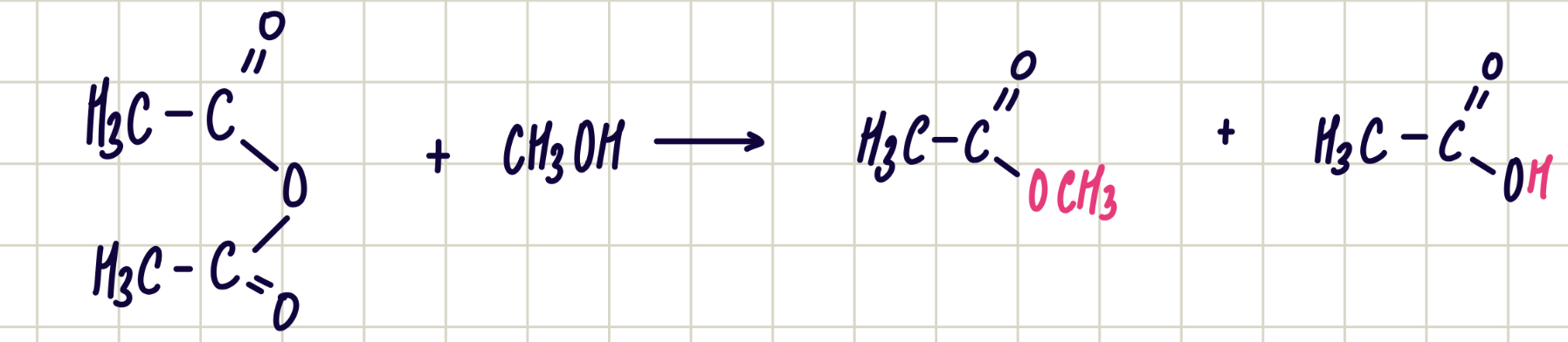
Reaction of acyl chloride and ammonia
Acyl chloride + ammonia —> primary amide
Nucleophilic addition-elimination
Reagent: ammonia
Conditions: room temp
Observations: white smoke of NH4Cl is given off
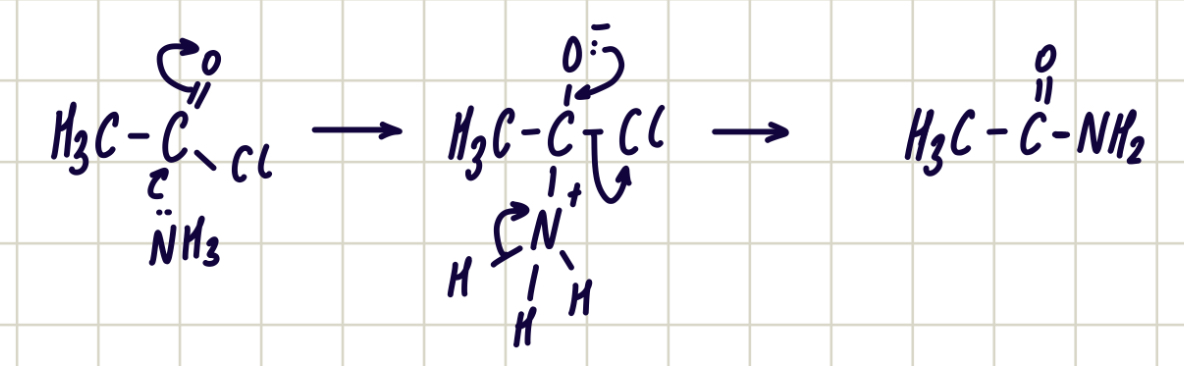
Reaction of acid anhydride and ammonia
Acid anhydride + ammonia —> primary amide
Nucleophilic addition-elimination
Reagent: ammonia
Conditions: room temp.
Observations: nvc
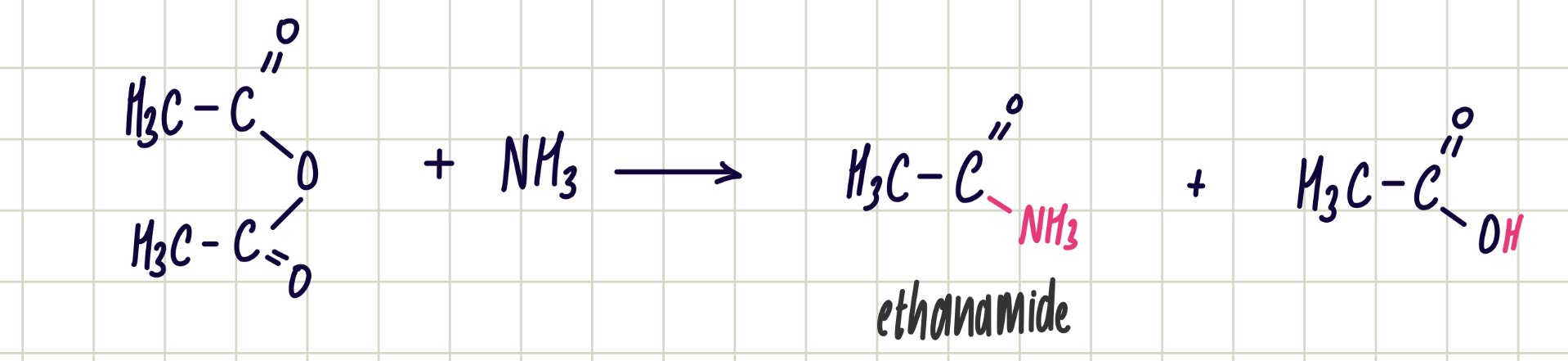
Reaction of acyl chloride and primary amines
Acyl chloride + primary amine —> secondary amide
Nucleophilic addition-elimination
Reagent: primary amine
Conditions: room temp.
Observation: nvc
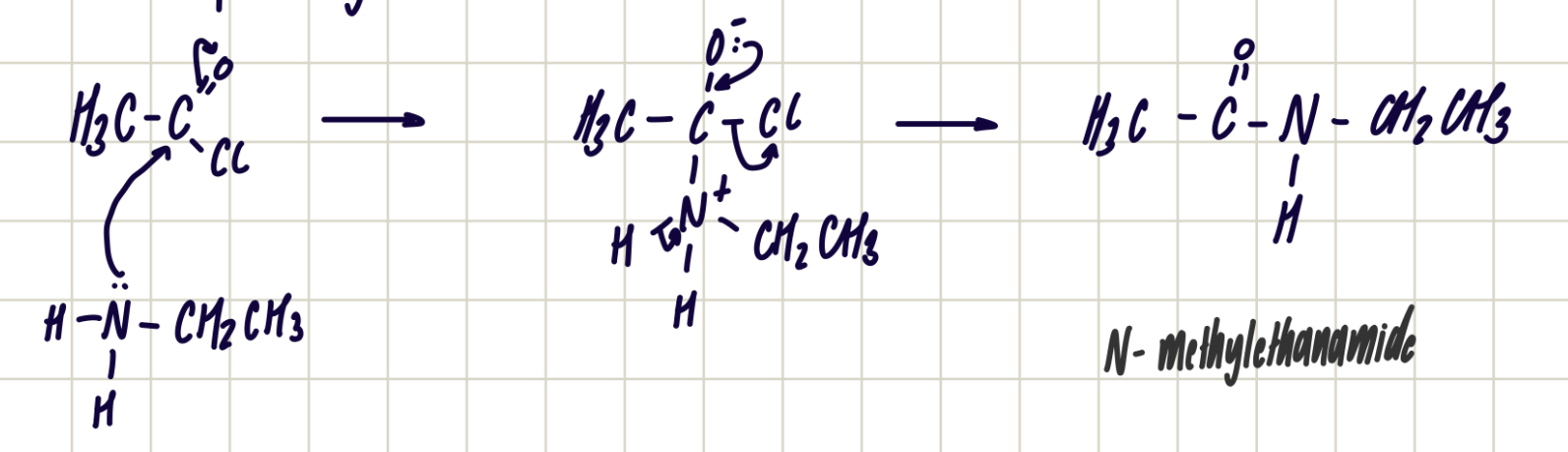
Reaction of acid anhydride and primary amines
Acid anhydride + primary amine —> secondary amide
Nucleophilic addition-elimination
Reagent: primary amine
Conditions: room temp.
Observations: nvc
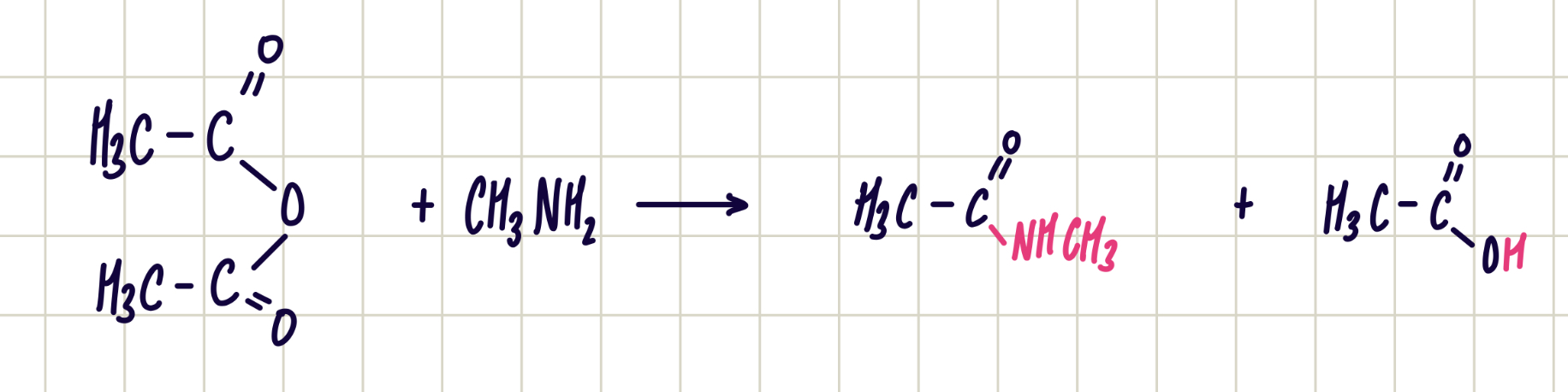
recrystallisation method with reasoning
Dissolve the impure compound in a minimum volume of hot solvent
The minimum volume is used to ensure the hot solution would be saturated (to obtain saturated solution) and to enable crystallisation upon cooling
Filter solution through filter paper quickly
To remove any insoluble impurities that will prevent crystals reforming
Allow solution to cool and crystals to form
cool solution increases yield of crystals
yield would be lower if solution was warm
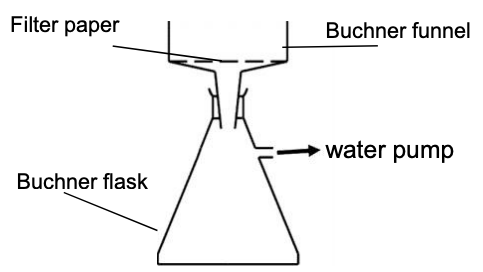
Filter off the pure product under reduced pressure
The water pump connected to the Buchner flask reduces the pressure and speeds up the filtration
Wash the crystals with distilled water
To remove soluble impurities
Dry the crystals between absorbent paper
Reasons for loss of yield in recrystallisation process
sample was still wet
sample lost during recrystallisation
product left in beaker or glassware
Buchner apparatus
How to determine purity using the melting point
measure the melting point using an oil bath:
heat the melting point tube in an oil bath, heating slowly near the melting point
if pure compound it will have a sharp melting point
State the most likely impurity to cause a compounds melting point to be slightly lower than the data-book value.
Give an improvement to the method so that a more accurate melting point can be obtained.
water
press the sample of crystals b/w filter paper