Astronomy Exam 3
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
Density between stars
less dense than the best vacuum we can make on earth—very few atoms.
Interstellar Dust
dust particles are roughly the size of the wavelength of visible light, so it is mostly blocked, but infared radiation (just larger) go right through—results in a dark cloud with “reddish” stars at edges
Preferential scattering
happens at the edges of a dust cloud, or at the horizon at sunset: most blue light is scattered, and red light (at a longer wavelength than dust particles) sometimes makes it through
Interstellar gas
90% hydrogen, 9% helium
Types of nebulae
Emission nebulae= glows reddish due to the radiation from a hot star within the cloud
Dark nebulae= dust cloud
Reflection nebulae=light from surrounding stars bounces off cloud particles to create blue color due to preferential scattering
Dark nebulae
Very cold
Absorb visible light
Emit radio waves
Have strong CO emission lines
Sculpting of dust lanes
radiation blows back less dense dust and leaves just the unique shape of the high-density dust within it
Importance of atomic hydrogen in interstellar gas
when the hydrogen transitions from the electron and proton being in “parallel spin” to “anti-parallel” spin, which reduces it’s energy—causing a lower energy wavelength longer than the typical size of interstellar dust particles.
So, this hydrogen radiation reaches earth unaffected by stellar debris
Molecular Clouds
regions of interstellar gas between 10-20 K, where density is a bit higher due to most gas particles are molecules—only longer wavelength radio waves can escape
Molecular Clouds
H2 (molecular hydrogen)
CO (carbon monoxide)
H2O (water
H2CO (formaldehyde)
The last 3 emit radio waves as they are created by chemical processes within the clouds—called “Tracer molecules”
Ratio of Hydrogen to tracer molecules in molecular clouds
1 billion: 1
Molecular cloud complexes
huge groups of molecular clouds, 10s of parsecs across
Triggers star formation
Some kind of external event causes a molecular cloud to lose it’s hydrostatic equilibrium and gravity dominates over heat, causing it to contract and collapse on itself.
Seven stages of stellar evolution
1)Interstellar Cloud—begins to collapse and fragment
2) & 3) Contracting Cloud fragment—temp and density increases rapidly
4) Protostar—shrinks as density and temp increase to 1,000,000 K, ignites the proton-proton chain
5) Protostellar Evolution—outward directed pressure grows, heat escapes and contraction slows, luminosity decreases, gas is ionized and temp continues to increase. Strong winds result in bipolar flow and ejects matter perpendicularly
6) Newborn Star—10 million years after stage 4, radius decreases and temp increases. Proton-proton chain begins producing helium, luminosity less than the sun, and radiation is absorbed by dust and reemitted as infrared
7) Main Sequence Star—hydrostatic equilibrium reached, energy emitted is stable
Brown Dwarfs
“Failed stars” whose original fragments were too small, so hydrostatic equilibrium was achieved before temp became high enough to start nuclear fusion—very cool and smaller
Star clusters
a group of stars that all formed from the same parent cloud
Open cluster
type of star cluster that is loose and irregular (often found on Milky Way disc)
Associations
star clusters that are smaller than open clusters, but more spread out and expanding
Globular clusters
spherical star clusters with millions of stars, not found in Milky Way, lack upper-main sequence stars and are the oldest ones
Average lifetime of a star
10 billion year
How stars maintain hydrostatic equilibrium
Due to law of reciprocity:
1) Small decreases in central temp lead to small decreases in pressure—so star contracts and heats
2) Small increase in central temp, increase in pressure, star expands and cools
Hydrogen Shell Burning
nuclear fusion is relegated to the outer surroundings of the core as unburnt helium builds up in the core and less hydrogen is produced there
Red Giant Branch
Star’s core shrinks and the outer layer expand and cool. It’s luminosity increases due to increased surface area. (stage 9)
Subgiant Branch
Process leading up to stage 9—star’s core cools and shrinks
Helium flash
Stage 10: attempted ignition of the helium in the star when it’s temp has gotten hot enough again after being a Red Giant, but it does not have enough hydrogen fuel. The flash only lasts a few hours. Star reaches equilibrium
Asymptotic Giant Branch
Stage 11: star becomes a Red Giant again! hydrogen burning shell and a helium burning shell
Planetary Nebula
Stage 12: Planetary nebula occur, as it contracts and increases pressure in the core. Outer layers are blown off to form nebula.
White Dwarf
The core of the blown—off neublae: it can’t become hot enough for fusion of elements heavier than oxygen to take place, so it becomes a white dwarf as it slowly cools down over billions of years. Any luminosity comes only from heat.
Black dwarf
eventually, a white dwarf gets dimmer and cooler, and eventually stops glowing. Like a dark coal in space.
Novas
usually in a double star system—the white dwarf pulls the outer atmosphere of it’s main sequence companion into its orbit and it forms a bright accretion disk with explosive hydrogen burning. Causes a brief, sudden flare up of brightness, and then dimming again. Some novas cycle several times.
Higher mass star’s on H-R Diagram
loop back and forth going upward and right—luminosity stays relatively stable but radii and temp go up and down
Red Supergiant
very high mass stars achieve this—fuse heavier elements like magnesium, silicon, neon, and iron in the inner core
Photodisintegration
as a red supergiant dies and implodes, temps reach 10 billion K and individual photons break iron into smaller and smaller nuclei until only protons and neutrons remain
Main sequence Turnoff
the high-luminosity end of a star’s journey on the main sequence on an H-R diagram
Supernova
occurs when a supergiant’s core collapses and blasts all overlying material into space with a luminosity billions of times brighter than the sun’s in it’s entire lifetime
Type I supernova
Carbon-Detonation Supernova: little hydrogen, and it’s light curve shows a sharp rise of intensity followed by a gradual decline
Type II Supernova
hydrogen rich, and include a plateau in their light curve for a few months after reaching max luminosity—they leave remnants in space, and often result in neutron stars/black holes
Neutron star
can sometimes result from a Type II supernova, if the ball of ultra compressed neutrons in the very center of the core remains after the implosion
Properties of a neutron star
—tiny (size of a city)
—very massive (more than the sun!)
—rotate every fraction of a second
—very strong magnetic field
—can be pulsars
Pulsar
a neutron star that periodically flashes it’s radio radiation towards earth
Lighthouse model
model for pulsars—two hot spots on either side of neutron star diagonal to the rotation axis, as it rotates we get “flashes” of radio waves coming towards our spot in space
Pulsar wind
hot, x-ray emitting gas flowing out of neutron star’s equator at the speed of light
Pulsar/ neutron star relationship
all pulsars are neutron stars, but not all neutron stars are pulsars (due to old age and diminishing magnetic field or rotation rate)
Neutron star binaries
neutron stars (including pulsars) that are in a binary system—can exhibit X-ray activity
X-Ray bursters
occurs on or near neutrons that are part of a binary system—neutron star pulls material from companion’s surface and forms an accretion disk for several seconds as nuclear fusion sputters up and then dies down
Pulsar planets
some millisecond pulsars (very fast ones) who exist in globular clusters show Doppler Shifts and regular intervals that indicate the pull of several planets OUTSIDE our solar system on them
Gamma Ray Bursts
fireballs in space beyond our galaxy that produce expanding superhot jets of gas emitting gamma ray radiation for a brief time—afterglow occurs as fireball expands and cools again. occur about once a day
Theories on Gamma Ray Bursts
1) they are the result of a binary neutron star system in which they merge
2) they are hypernovas in which the core itself collapses, causing a black hole with an erupting accretion disk
Black holes
when neutron stars (whose main sequence mass was more than 25 suns) compress beyond the “set limit” of 3x the sun’s mass, they exert such an intense gravitational pull on their surroundings that any light, radiation or information of any kind from it disappears.
Black hole’s escape speed
would be faster than the speed of light—thus, nothing in existence could escape being pulled into the black hole, and no information would exist about it. It is invisible and uncommunicative, with only a single point of gravity betraying it
Schwarzchild radius
the radius a specific object would need to compress to to become a black hole (every object has one)
Event horizon
the imaginary sphere “demarking” the edges of a black hole event—nothing from within that sphere’s surface can be perceived in any way
Michelson-Morely findings
the speed of light is always the same, no matter the relative position of the measurer or the source
What can explain black holes
only Einstein’s theory of general relativity ( integrated from his special relativity, and assuming that spacetime is curved, and gravitational pull is not a real agent).
Black holes
any matter that enters the event horizon of a black hole will be flattened, torn apart, disappear, and be unable to every get out
Gravitational redshift
photons passing nearby a black hole’s event horizon do not slow down, but lose energy—causing their wavelengths to become smaller and smaller, eventually going off the known spectrum past radio. Theoretically, light emitted from on the event horizon itself would be red-shifted to infinitely long wavelengths
Horizontal branch
part of the H-R diagram when large mass stars move from burning hydrogen to burning helium—but not yet carbon
Andromeda galaxy
the nearest galaxy to ours (800 thousand pcs away)—with similar disk, bulge, and halo.
Variable stars
stars whose luminosities change significantly over short periods of time—often the result of binary systems, but sometimes intrinsic to the star itself
Pulsating variable stars
like RR Lyrae and Cepheid— stars that vary cyclically in their luminosity
RR Lyrae stars
pulsating variable stars that are on the low (er) mass end of the horizontal branch—so have started core helium burning—with regular pulses every 0.5-1 day. They have a luminosity of ~ 100x the sun
Cepheid stars
pulsating variables that pulse in a “sawtooth pattern” and have very different periods between pulses (anywhere from 1-100 days)
Period-luminosity relationship
used to infer luminosity of Cepheid stars:
those that vary slowly have the highest luminosity, and those that vary more quickly have lower luminosities.
Discovery of the galactic halo
knowing that many RR Lyrae stars are in globular clusters, were able to map out distances of all known globular clusters and found that they lie on a sphere surrounding the milky way galaxy
Galactic center
not the sun! it is the saggitarius constellation, about 8 K pcs away from the sun
Dust/gas distribution in Milky Way
virtually NONE in galactic halo—in bulge and disk, very common
Population I stars
Stars in the galactic disk—younger, brighter and bluer with more heavy elements
Population II stars
stars in the galactic halo and bulge= older, redder stars with less heavy elements
Differential Rotation of Galaxy
when looking at the area of the galaxy around our sun—stars to the upper right and lower left are blueshifted (moving TOWARDS the sun) and the stars in the lower right and upper left are redshifted (RECEEDING from the sun)
Rotation of Galaxy
in bulge and halo, stars do not share the same differential rotation patten of the disk. Each of them has a random orbit, all filling up a 3D spherical volume
Spiral Arms
pinwheel like sturctures originating close to the galactic bulge (one of which contains our solar system)—each one is 30K pcs across and filled with emission nebulae, O- and B- type stars, and open clusters
Spiral Density Waves
coiled compression waves that move through the arms of the galactic disk, squeezing gas clouds and triggering star formation
Theories on the cause of Spiral Density Waves
1) instabilities in gas near the galactic bulge
2) Gravitational effects of nearby galaxies
3) Elongated shape of the galactic bulge itself
Formula for mass of Milky Way
total mass (s.m)= orbit size (AUs)³// orbital period (yrs)²
Mass of Milky Way
4x 10^11 solar masses, with half of the matter in the Galaxy existing as dark matter beyond the luminous galactic disk
Dark Halo
the extensive region of dark matter surrounding the inner Galactic Halo (with the ancient stars)—accounts for half the Galaxy’s mass
Dark Matter
has mass but emits no electromagnetic radiation, has no detectable elements, and cannot be accounted for by black holes because there simply aren’t enough of those
Subatomic Particle Theory
Dark matter is made up of subatomic particles which were produced in huge amounts during the Big Bang (Creation). They must:
-have mass
-but NOT interact with normal matter or else we would see it
Gravitational Lensing
Explains ½ of galactic dark matter—when looking at an invisible object far away, a dim foreground object will become suddenly brighter when passing in front of it —a way to “see” the effects of dark matter indirectly
Observation of Galactic Center
cannot see visually because interstellar material obstructs our view—must use RADIO and INFARED
Innermost Parsec of Milky Way
densely populated by (in order):
- a cluster of 1 million stars
-huge dust-rich clouds
-400 pc rotating ring of molecular gas
-Saggitarius A region of strong radio waves and powerful magnetic field lines
-Hot X-ray emitting gas from “supernova-like” remnant
-1 pc ring of star-forming molecular gas with streams of matter spiralling inward
-An accretion disk that accelerates particles into “cosmic rays” which is caused by………
-A several MILLION solar mass supermassive Black Hole!
Central Balck Hole
studied by looking at Sgr A*, a compact, relatively low-energy nucleus (still 1 millionX sun) around 10 AU across, powered by the supermassive black hole whose event horizon is only .08 AU across
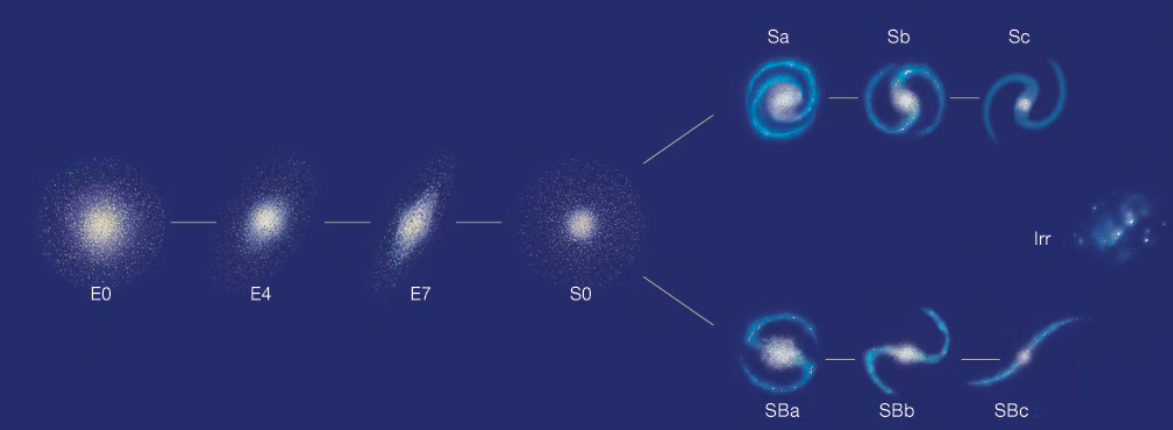
Hubble Classification Scheme
classifies galaxies according to appearance:
-Spiral galaxies (Milky Way, Andromeda)
-Barred Spirals
-Ellipticals
-Irregulars
Barred Spiral Galaxies
spiral arms extend from the ends of the huge “bar” of interstellar matter crossing the galaxy: SBa are smallest, SBc are largest
Elliptical Galaxies
no spiral arms or visible disk—just a dense central nucleus and an ellipse shaped ring of stars and interstellar matter—E0= most circular, up to E7, most elongated. They range hugely in size
Irregular Galaxies
a “catch-all” category for all other galaxies
-rich in matter/ young blue stars
-lacks defined structure
-small ones most common
-often found close to “parent galaxy”
-2 subclasses
Irr I Galaxies
irregular galaxies that look like misshapen spirals that contain a lot of gas, dust, supernovas (ongoing star formation) and blue stars
Irr II Galaxies
very rare, with explosive/filamentary appearance—could be result of near collision between two “normal” systems
Hubble Sequence
a diagram of all types of galaxies as outlined by Edwin Hubble:
Standard candles
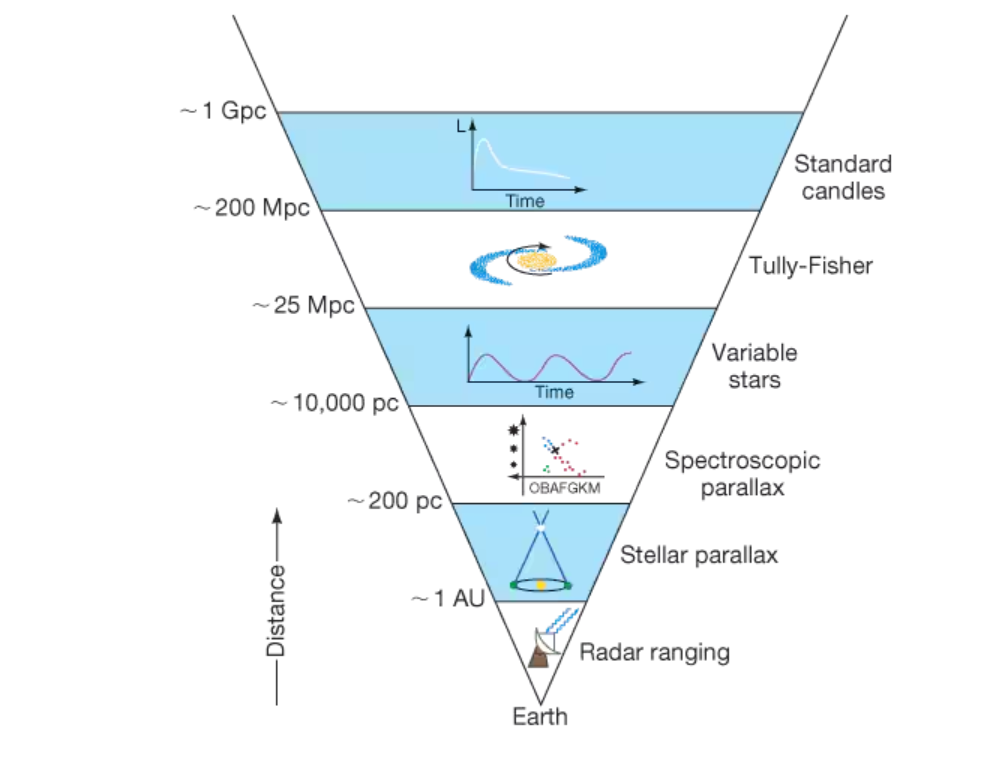
a bright, easily recognizable object whose luminosity is known (like a planetary nebula or Type I Supernova)—which are used to estimate distances to very distant galaxies
Tully-Fisher Relation
obtaining an estimate of a galaxy’s luminosity from it’s rate of rotation, in order to calculate distance
Extragalactic distance ladder
Local Group
Our galaxy cluster—contains Milky Way and Andromeda as biggest members, plus 50 others
-over 1 Mpc in diameter
Virgo Cluster
galaxy cluster nearest (18 Mpc) to our Local Group
-3 Mpc across
-2,500 galaxies
Hubble Diagrams
plot galaxies’ recessional velocity away from us by their distance from us—shows us that all galaxies are part of a general motion away from us in all direction
Hubble’s Law
the rate at which a galaxy is receding from us is directly proportional to it’s distance from us
Hubble’s constant
recessional velocity= H0 x distance
H0= 70 km/s/Mpc
Active Galaxies
galaxies that look normal, but radiate large amounts of non-stellar radiation in the invisible spectrum
Starburst galaxies
previously normal galaxies that now have intense periods of star formation from an active galactic nuclei—include Seyfert, Radio, and Quasar galaxies
Seyfert galaxies
a type of starburst galaxy that resembles a normal spiral galaxy but has a nucleus up to 10X as bright as our entire galaxy—luminosity can halve or double within the span of a year. Most energy is in the infrared.