Lesson 6.2: Understanding Federal, State, and Local Taxes
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards made from a presentation segment created as a lesson on federal, state, and local taxes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms

Taxes
How federal, state, and local governments primarily raise money to pay for schools, roads, and national programs
Raises or lowers aggregate demand as part of the government’s fiscal policy for cooling or growth
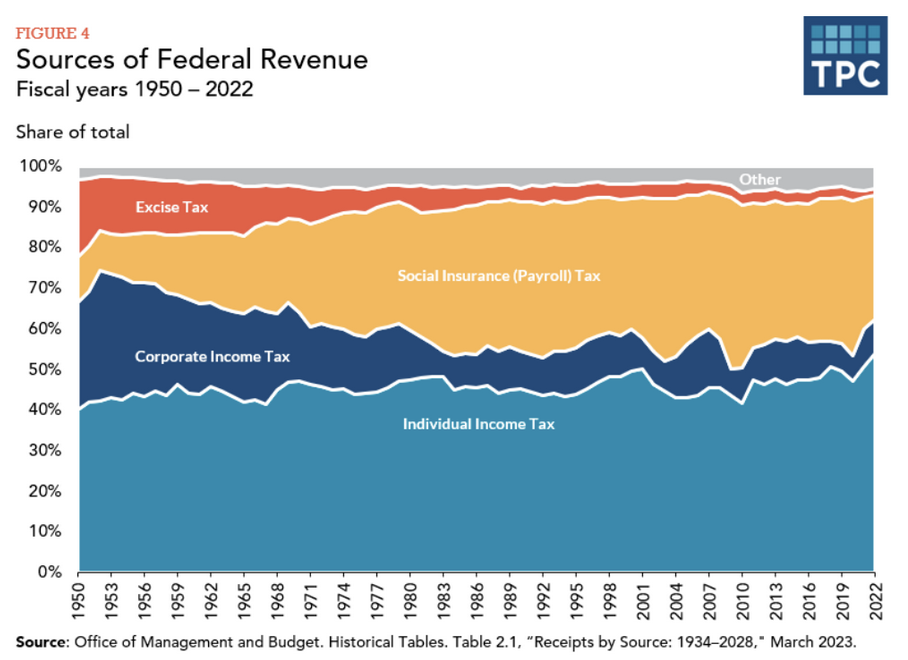
Government revenue
Money the government receives from taxes and other sources
About 84% of this comes from individual income taxes and payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare
About 11% of this comes from corporate income taxes
The remaining 5% comes from excise taxes, tariffs, fees, and other sources
Congress
The body of government given the power to “lay and collect taxes” according to Article I, Section 8 of the Constitution for:
The payment of debt
The common defense
General welfare
Cannot levy taxes on religious services, exports, or polls, as they were used to restrict voting in the past

Progressive tax
A tax structure that makes a person’s effective tax rate rise with their income level, as seen in the federal income tax
Serves as an automatic stabilizer to reduce tax burdens on the low income while increasing taxes on the higher income
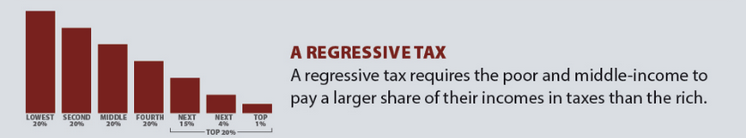
Regressive tax
A tax structure that makes a person’s effective tax rate fall with their income level, as seen in sales taxes
Higher income households spend a lower portion of their incomes on taxable goods and services

Proportional tax
A tax structure that makes a person’s tax rate the same across all income levels with minimal deductions or exemptions

Tax base
The income, property, good, or service that is subject to a tax; seen in the forms of personal earnings, company profits, real estate, and goods and services sold

Pay as you earn
A tax collection system where money is withheld from a paycheck throughout the year by employers to avoid a large tax bill during filing season
Taxable income
The income one earns (minus exemptions and deductions) that can be taxed
Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA)
Act that funds Social Security and Medicare through payroll withholdings and employer contributions
Corporate income tax
A progressive tax paid on corporate profits
Excise tax
A regressive tax on specific items, such as gasoline, cigarettes, and alcohol
Estate tax
A tax on the total value of an estate that changes year-by-year
In 2025, this applied to any estate worth over $13.99 million
Tariffs
Taxes on imported goods
Once one of the most important sources of federal revenue; today, they represent just a tiny share
Intended to protect American industries with better trade deals, lowered trade deficits, and increased government revenue
State revenue
Mostly in the form of:
Personal income taxes
Sales taxes
Excise taxes
Corporate income taxes
Charges (university tuition, tolls, park fees)
Federal funds (for healthcare and low-income programs; one-third of total revenue in many)
Funds are often passed on to lower levels
Local revenue
Revenue that goes to counties, cities, towns, and school and special districts for schools, emergency services, libraries, parks, and utilities in the form of:
Property taxes (largest contributor)
Sales taxes
Income taxes
Fees for utilities, land, and public resources
Intergovernmental transfers
Grant
A portion of money set aside to another entity for a designated program
The federal government offers these to states and localities for healthcare, income support, transportation, and education