AP Huge Unit 3: Cultural Patterns & Processes
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Culture
The mix of values, beliefs, behaviors, & material objects that form a people’s way of life
Cultural Trait
A single aspect of a given culture or society
Cultural Attitudes
Concepts & ideas in a society that are shaped by cultural opinions, beliefs, & perspectives
Relocation Diffusion
Occurs when migrating individuals or groups bring an idea or practice from their old homeland to their new homeland
Expansion Diffusion
Ideas or practices spread in snowballing process (includes Hierarchical, Stimulus, & Contagious)
Hierarchical Diffusion
When ideas leapfrog from one influential person, community, or place to another, bypassing other people, communities, or rural areas
Stimulus Diffusion
Occurs when a specific trait is rejected, but the unifying idea is accepted (ex: McDonald’s)
Contagious Diffusion
Involves rapid spread of cultural ideas or traits through a population, often through direct contact & interaction
Centripetal Forces
Forces that bring people together and unite a neighborhood, society, or country
Centrifugal Forces
Forces that threatens the cohesion of a neighborhood, society, or country
Time-Space Convergence
The phenomenon whereby the introduction of new transportation technologies progressively reduces the time it takes to travel between places (“shrinks” the world)
Material Culture
Physical, visible objects made & used by members of a cultural group
Non-Material Culture
intangible elements, including norms, beliefs, values, myths, & symbolic meanings that can be passed down within a given society
Popular Culture
Heterogeneous, influenced by urban areas, and quick to adopt new technologies
Folk/Local Culture
Homogeneous, connected to local land, pass traditions, slow/resistant to change, more regionally distinct
Taboo
Practices that are religiously or socially prohibited or discouraged
Ethnocentrism
An approach to understanding other cultures that evaluates them from the perspective of the observer’s culture
Xenophobia
The fear or dislike of anything that is perceived as being foreign or strange
Cultural Relativism
An approach to understanding other cultures that seek to understanding individuals and cultures from a wider perspective of cultural logic
Multiculturalism
Set of policies that promote active participation & inclusion of minority groups in national histories, national policies, and cultural institutions with goal of embracing differences within the society
Sequent Occupance
Refers to the fact that many places have been controlled or affected by a variety of groups over a period of time, groups have reshaped the functions or meanings of those places, leaving behind layers of meetings
Placelessness
Feeling resulting from standardization of built environment, occurs when local distinctiveness is erased, and many places end up with similar cultural landscapes
Cultural Landscape
Made up of geographic patterns of cultural traits and practices - includes physical, industrial, agricultural, & architectural features
Agricultural Landscape
Evoke a sense of place through architecture
Physical Landscape
All the natural, physical surroundings that create & shape the places we are living in or examining
Urban Ethnic Landscapes
Ethnic cultural landscapes appear in urban settings, can be exclusive like in ethnic neighborhoods
Linguistic Landscapes
Signs, billboards, graffiti, and other displays can reveal locally dominant languages, bilingualism, linguistic oppression, and more
Religious Landscapes
Places such as sacred spaces or places that are more secular
Sacred Spaces
Natural or human-made sites that possess religious meaning worthy of devolution, loyalty, fear, or esteem
Secular
Less influenced by religion
Secularization
Process where religion becomes less dominant force in everyday life than in the past
Pidgin Language
A trade language characterized by a very small amount of vocab that is derived from languages of at least two or more groups in contact
Creole Language
A languages made by languages that are combined and has a fuller vocab than pidgen, becomes a native language
Creolization
Linguistic process where languages converge and create new languages & forms of communication
Lingua Franca
Language of communication & commerce spoken across a wide area where it is not a mother tongue
Imperialism
Motivating impulse to control greater amounts of territory
Colonization
The act of formally controlling a foreign territory (becomes known as a colony)
Empire
A sovereign political entity that seems to expand beyond origin land to control more territory politically and/or economically
Genocide
The systematic killing of members of a racial, ethnic, or religious group
Ethnic Cleansing
The forced removal of an ethnic group by another ethnic group to create an ethnically consistent territory
Classification
Dividing societies into different groups & distinguishing between “us” and “them”
Symbolization
Naming different groups or distinguishing them through symbols, colors, or dress
Discrimination
A group holding power using law, custom, or political power to deny the rights of other groups
Dehumanization
One group denying the humanity of another group, often by reducing them to an animal or disease
Organization
When perpetrators create a plan for genocide and train and arm militias, may set up secret police to spy and arrest victims
Polarization
When moderate leaders and groups are eliminated, leaving a polarized society, propaganda is more widespread
Preparation
The process of preparing for mass murder. Leaders use euphemisms to hide their intentions, and people are trained to kill
Persecution
Victims are identified and separated from society. Leaders of the genocide draw up lists of people or communities targeted for death and deprive their victims of basic resources like water and food. Violent acts often begin at this stage
Extermination
The mass killing we know as genocide
Denial
Some may try to cover up evidence or refuse to acknowledge that genocide happened
Endangered Language
A languages not taught to children and not used actively everyday
Extinct Language
A languages that has only a few elderly speakers or no living speakers
Dialect
A regional variation of a languages that is understood by people who speak other variations of that language
The most spoken language in the world
English
The most spoken language in the world by natives
Mandarin
Cultural Convergence
The idea that cultures are converging and becoming more alike due to globalizing forces & trends
Glocalization
Adopting global practices to fit local cultural practices & preferences
Cultural Hearth
A focused geographic area where important innovations are born & form which they spread
Judaism Hearth
Southwest Asia
Hinduism Hearth
India
Christianity, Islam, & Judaism Hearth
Southwest Asia
Religion
Complex, interrelated set of cultural traits, beliefs, & rites
Monotheistic Religion
Relating to the belief in only one god
Language Family
A group of related languages that share a common ancestry
Indo-European Language Family
Largest & most widespread
Spoken in all continents, dominant in Europe, Russia, N & S America, Australia, and some parts of SW Asia & India
English, Hindi, Spanish, French, Bengali, Russian, Portuguese
Sino-Tibetan Language Family
Spoken in most of China & SE Asia
Mandarin, Cantonese, Tibetan, Burmese, etc
Afro-Asiatic Language Family
Orginated in Asia, but only spoken in Africa today
Semitic & hamitic languages, such as arabic
Universalizing Religions
A religion that actively seeks new members (through expansion diffusion, such as missionary or migration) & believes its message has universal importance and application
Most Common Universalizing Religions
Christianity, Islam, Buddhism
Ethnic Religions
A religion identified with a particular ethic or tribal group & doesn’t seek converts, spread mainly through relocation diffusion
Most Common Ethnic Religions
Judaism, Hinduism
The 5 Most Popular Religions
Christianity
Islam
Hinduism
Buddhism
Judaism
Atheists
Non-religious group that don’t believe in a God
Agnostics
Non-religious group that believes humans are not capable of knowing whether God exists
Universalizing Religions can be organized into
Branches → Denominations → Sects
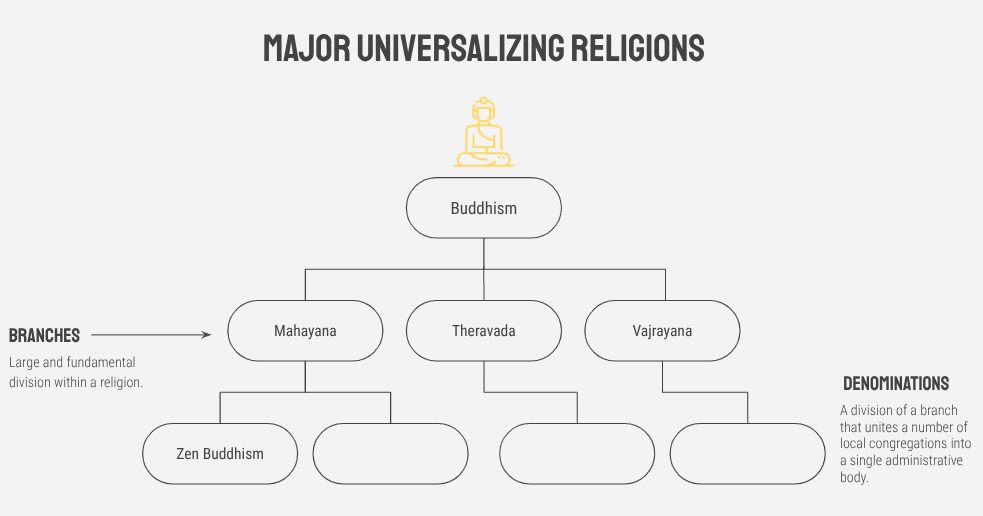
Toponyms
Names given to places
Acculturation
Occurs when an ethnic or immigrant group adopts enough of the ways the host society to be able to function economically & socially
Assimilation
Occurs when an ethnic or immigrant group blends in with host culture and loses many culturally distinctive traits
Transculturation
Notion that people adopt elements of other cultures as well as contribute elements of their own culture, thereby transforming both cultures
Cultural Syncretism
Can help explain complex patterns that emerge as multiple cultures affect one another to create new traits & cultural patterns
Syncretic Religions
Religions that combine elements of two or more different belief systems
Orthodox Religions
Religion that emphasizes purity of faith and is generally not open to blending with elements of other belief systems