Evolution: the evidence pt 2. (7)
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
What is the theory of Evolution
• Things evolve | populations change over time
• Evolution usually happens gradually | populations change over hundreds to thousands of years
• Speciation occurs | one species splits into two or more species
• All species share common ancestry | splitting of lineages from one ancestral form
• Much of evolutionary change was caused by natural selection | the sole process producing adaptation, the ‘appearance’ of design
When does speciation usually occur?
In isolation and no gene exchange between species
What is the DNA difference between chimps and humans?
1-4%
When did humans and apes split?
5-7 million yrs ago
What are hominins
human side of split since the human and chimp common ancestry
What does a cladogram show?
See what is closely related and distantly related
Diverged in the distant past --> distantly related
What is a karyotype?
organized profile of an individual's chromosomes, displaying their number, size, and shape, often presented as a laboratory-produced image
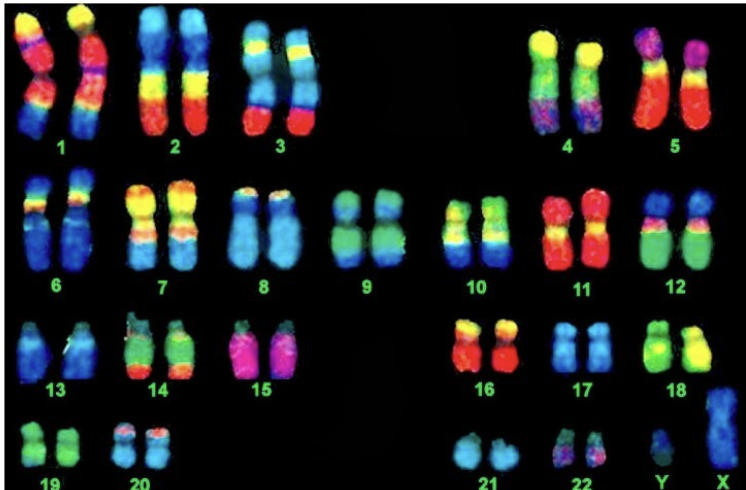
What is the difference between chimps and humans in karyotype?
humans- 23 pairs of chromosomes (46)
Chimps- 24 pairs of chromosomes (48)
What is one prediction of what happened to the extra chromosome between humans and chimps?
It was lost, we didn’t need those genes
Unlikely prediction
Unlikely to lose tons of genes --> usually conserved (doesn't code much but still need them)
What is Prediction 2 of what happened to the extra chromosome between humans and chimps?
•A Creator distributed the genes differently, didn’t need as many chromosomes
unlikely
What is Prediction 3 of what happened to the extra chromosome between humans and chimps?
• There was a fusion event
most likely
What causes a formation event?
Mutations can occur
Chromosomal rearrangment:
chromosomes may not align correctly , replicated incorrectly, or break apart —> might lead to death (some important genes were messed up) —>changes does not manifest in population
Death doesn’t always occur
What is the evidence for a fusion event?
conservation of gene structure/order
all same genes are basically there (arranged by nucleotides) --> fusion events probable
common ancestry
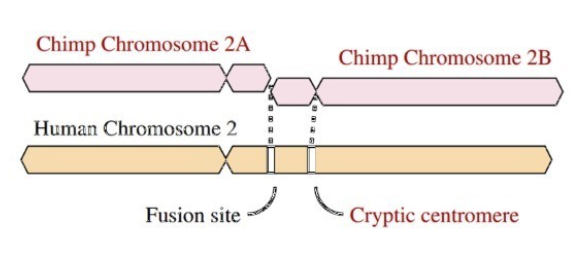
What happened to the extra chromosome between humans and chimps?
Human chromosome (2) and chimp chromosome: in the past --> telomerase (end of chromosomes) fused together between 2A and 2B
One lineage humans: fusion event --> happened only once
Individual survived (all genes there but just rearranged)
Arrangement was very adaptive --> passed through generations until all humans have 23 chromosome pairs
Fusion event happened before ancestors started radiating around the world (5-6 million years ago)
What are primates?
members of order of mammals
distinguished by large brains, nails instead of claw,
front facing eyes,
opposable thumbs in some
What should we see in fossil records if evolutionary theory is true?
First detectable traces of life on earth should be simple forms and only later would more complex forms appear
Why should life get more complex as time goes on?
more time for organisms to develop adaptations and variation
Does life always get more complex?
No
What is a fossil?
remains of a once living orgnaims preserved in sedimentary rock
When do fossils occur?
when organismal features are preserved long after death
How complete is the fossil record?
Incomplete
Why is the fossil record incomplete?
• Soft-bodies preserved less than hard
Rare species even rarer
Lack of sedimentation
Highly dependent on conditions – few were fossilized
What is permineralization?
Organism is buried, filled with mineral rich waters, turns tissue to stone; in some cases, in exceptional detail (cellular level)
What allows for multiple fossils to be captured at once?
Mass extinction event
What conditions allow for fossils to form?
Found in anoxic/anarobic environment (no oxygen):
Usually wet depressed area
Organism quickly covered in mud, clay that blocks oxygen in that space --> limits what could decompose
Animal tissues change form organic to stone (inorganic) (individual cells are replaced)
What are trace fossils?
fossils of trails
preserve record of anatomy and behavior
Why is it important to cover organism quickly with sediment for fossil to form?
limits what bacteria/ other organisms can decompose of the body
What groups rarely form fossils?
bacteria
single celled eukaryotes
How are plants/wood petrified?
Earthquake / volcanoes bury’s forest
Organic tissue (plant tissue) --> converted to stone
How does wood petrification help discover Earth’s history?
count the rings
see what environmental conditions were back then
size, color, width, etc change based on environmental factors around them
What is the Messel Shale?
gap in earth that opens to cavern filled with mud, dirt, clay
hot bed for fossils
Why the Messel Shale a hot bed for fossils?
animals drop in gap —> creates layer cake of animals and sediments
well preserved conditions —> imprint of fur remains
Deeper you go the older the animals
What does resin/sap turn into?
amber
Is amber a form of permineralization?
No
How do fossils form with sap?
resin and sap flow out of tree —> collects overtop of insect
falls into anoxic environment —> turns into amber
Within fossils, what usually stays intact?
hard parts
DNA often does not remain intact —> but some DNA proteins can still be analyzed
What are the strengths of fossils?
show evolutioning linkages through dinosaurs
What fossils have been preserved from the recent times?
Baby mammoth – 40,000 ya
Otzi – 3300 BCE
Tollund Man 405-380 BCE
How does ice preserve fossils?
organic material can be preserved (ex: collect food last eaten)
slows down decomposition
How was the Tollund Man preserved?
Imbedded in peep bog (very acidic)
Thrown in bog --> preserved in acidification of bog
Not undergoing perminierlization--> will decompose and is not a rock currently
What is a geological timescale?
series of time divisions that mark Earth’s long history
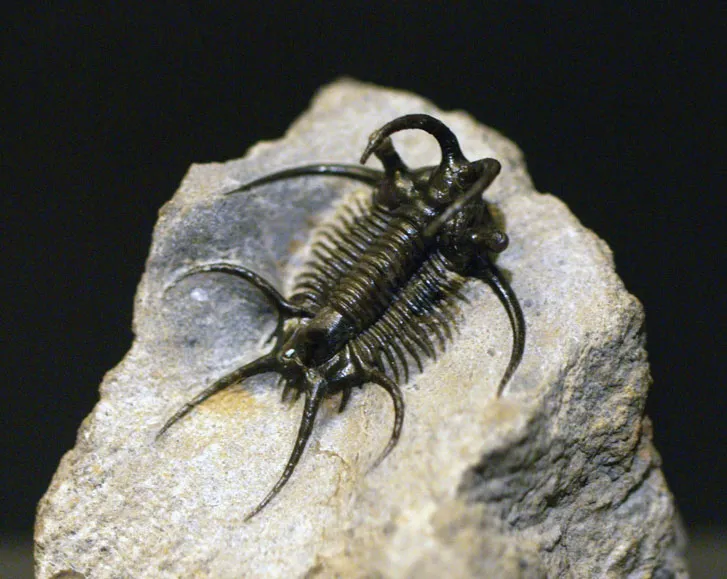
What can be found at the bottom of an open face rock/mountain?
made of mud
deposited by sea 500 mil yrs ago
contains oldest fossils of arthropods called trilobites

What can be found in the middle of an open face rock/mountain?
red=limestone
deposited by oceans 335 million yrs ago
traps marine fossiles
What can be found at the top an open face rock/mountain?
white beds = terrestrial land
deposited 260 million years ago
find footprints of vertebrate animals
how are geological strata arranged?
• Oldest = Deepest
Geological processes may move strata after formation
Fossils in particular strata represent relative age
What is an isotope?
each of two or more forms of the same element that contain equal numbers of protons but different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei
What is radiometric dating?
Dating ancient materials using the decay of radioisotopes as a yardstick
What gives absolute age?
Radiometric age
What do fossils in particular strata represent?
relative age
What is half-life?
The time it takes for an amount of a substance to reach half its original value. Radioactive half-life is the time it takes for half of the atoms in a given sample of a substance to decay.
What isotopes are used for radiometric dating?
Recent (-50,000 years) - Carbon, 14C
Far back (millions of years) – Potassium-Argon
Older (millions to billions years) – Uranium –> Lead
How is Uranium 235/238 used for radioactive dating?
at Half- life turns Uranium turns into lead
Find proportion in fossil and estimate how much was in that environment when it was alive
used to time calibrate
What is the process of radiocarbon dating?
Sun emits cosmic radiation --> excites neutrons--> collides with elementals in atmosphere (oxygen, nitrogen, carbon etc)
Neutrons collide with Nitrogen 14 (14N) (most common in atmosphere) —> kicks out protein —> turns it into Carbon 14
Carbon 14 in atmosphere connect with oxygen --> forms CO2
CO2 absorbed by plants and photosynthesis to create energy
Plants absorb Carbon 14 (formerly nitrogen)+ oxygen
Something eats plan --> carbon 14 is now part of the animals (tissues and bones metabolized)
Animal dies or plant dies and buried —> 14C decays to more stable 14N
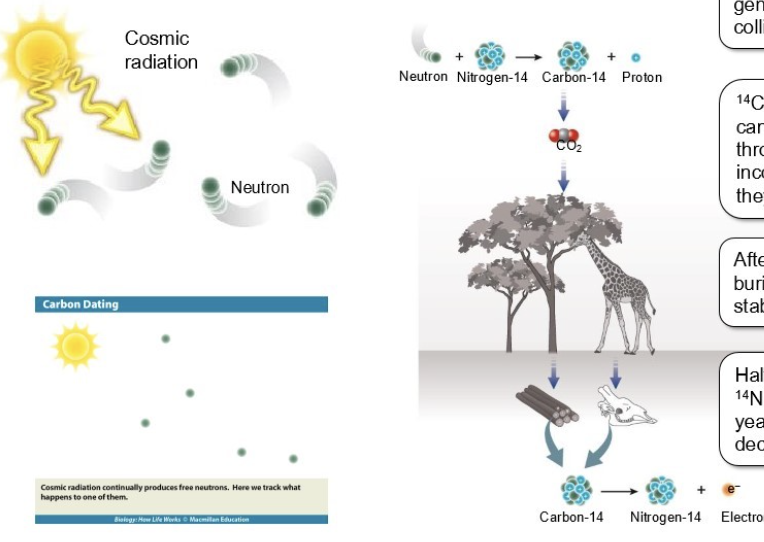
What is 14C half-life?
14 C turns in 14N in 5730 yrs
in another 5730 yrs, half of remaining 14C decays to 14N and so on
how is radiocarbon dating used?
The level of 14C in plants and animals when they die approximately equals the level of 14C in the atmosphere at that time
Gives template : how much Carbon 14 in fossil --> how much carbon existed in the past in the atmosphere --> can link to time period that it would have been alive
What has radiocarbon dating directly compared with?
Directly compared with known year-by-year data from tree-ring data (~13,000 years),
ocean and lake sediments, corals and stalagmites (now ~55,000 years)
What does the level of 14C in plants and animals show?
The level of 14C in plants and animals when they die approximately equals the level of 14C in the atmosphere at that time.
What is the error in Uranium-lead radioactive dating?
2 million years in 2.5 billion yrs
How were rocks in the beginning of Earth formed?
Bacterial appear 3.5 billions years ago
Rock formed by bacteria growing and exuding slime --> gets covered in mud --> fossilzes --> creates rock
What are planktonic diatom (rhizosolenia)?
free floating algae in ocean
have a support scaffolding system
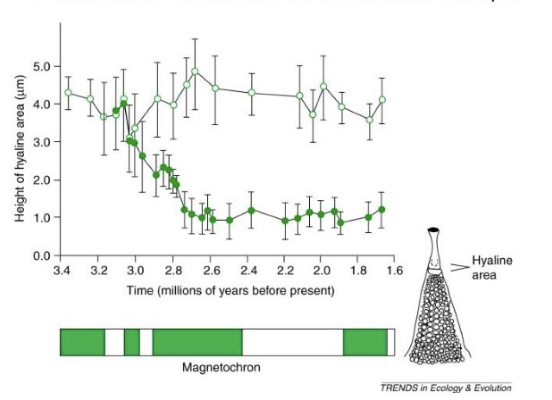
How did rhizosolenia diverge?
Magnetic cores of the Earth flip once in a while —> changes environment (weather, ocean structure)
Causes sediment columns to diverge
one stays at 4mm
others go down to 1mm
What were early horses (Hyracotherium) like?
lived in America
Lived in forests
size of foxes
had fingers
eat soft vegetation
How did the modern form of a horse form?
Marshal’s reconstruction
leave the forest —> speciation in more open environment
How did leaving the forest speciate early horeses?
Fingers become less valuable --> better for one hoof (no need to creep around roots)
Become larger to avoid predators
Change mouth --> molars become flat (eating grasses and not bugs on trees)
Become even larger --> leave north America to Russia and Asia
Increased Diversity in that region
What happened to the New World horses?
ice age wiped out horses in North America
only lived in Asia
How did modern horses return to NA?
Horses came back through colonization after being extinct
only domesticated left
No wild horses left (except one artificial kept?)
Only Eqqus
What shape does changes in species occur in?
branching pattern (not linear)
different distinct groups going extinct and others going on
What should transitional forms show?
connections between modern groups with their common ancestor
What traits do intermediate species show?
traits of both the common ancestor and new descendent
ex: transitional form of birds and dinosaurs —> structure similar to birds and dinosaurs
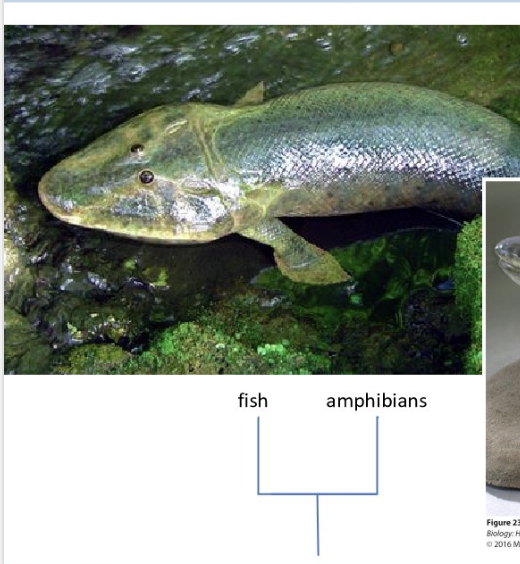
Where did terrestrial salamanders come from?
became terrestrial from marine ancestor
What does Tiktaalik show?
Transitional early form of life leaving water
What is retrodiction?
Something that make sense only in light of evolution, but is not necessarily predicted by evolution
Which vestigial trait do wales have?
Hind limbs and pelvis
shows atavism?
What is atavism
Vestigial structure that showed its true form
reappearance of an ancestral trait that was lost during evolution
What vestigial structure shows in dolphins?
hind limbs
Some Dolphins have mutation where hind limbs actually grow (hind fins)
What are vestigial genes?
Dead genes (silent)
What does the human fetal yolk sac show?
Vestigial genes: genes to produce a yoc sac, but they are silent
humans have genes for making yolk proteins —> 3 genes —> they are nonfunctional (silenced)
human fetal yolk sac - empty
Why can’t humans make vitamin C?
vestigial character
Could get vitamin C from outside sources due to new diet —> NS said it was too expensive to create
What are endemic animals?
species that naturally occur only within a specific geographic area, such as an island, region, or country, and are not found anywhere else in the world
What is there a lack of in Oceanic islands?
mammals
Lord Howe, Galapagos
mammals on continental islands (Madagascar) but not oceanic islands
What species are more often found in oceanic islands?
endemic plants, birds, and insects
Why are there more endemic plants, birds, and insects on oceanic isands?
They are better at dispersal
What do mass extinctions enable?
provides evolutionary opportunities for survivors on a grand scale
When did the Earth form?
4.6 billions yrs ago
When was the first evidence of oxygen-rich environment?
proterozoic eon
2500 million years ago
When was the first evidence of life?
Archean eon
4025 million years ago
When was the first animal fossil appear?
proterzoic eon
680/541 million years ago
When was the first eukaryotic microfossile appear?
proterzoic eon
2000 million years ago
When was the Archean eon?
4 billion - 2.5 billion years ago
When is the first evidence of lfie?
Archean era
closer to 4 billion years ago
When was the proterozoic era
2.5 billion - 541 million years ago
What happened in the beginning of the Proterzoic era?
First eukaryotic microfossiles
What happened near the end of the proteerozoic eon?
major diversification of eukaryotic organisms
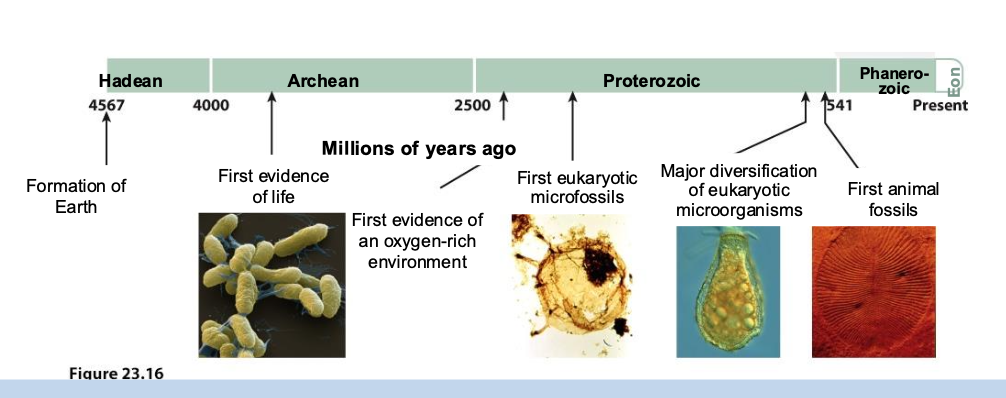
What happened near the very end of the proteerozoic eon?
first animal fossiles
When is the phanoerozoic era?
541 million yrs ago to now
What is biogeography?
the study of the geographic distribution of plants, animals, and other forms of life.
gives geographical data