Immunology SOLO 2
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
What are some preanalytical variables that could affect the results of lab testing in the immunology department?
specimen type
delayed testing
excessive heat
bacterial contamination
stron acid/base solutions
hemolysis, lipemia, icterus
complement inactivation
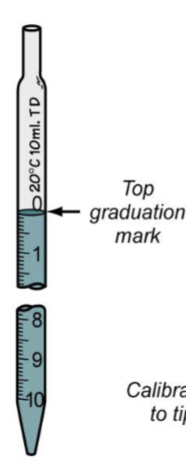
Identify the type of pipette
graduated
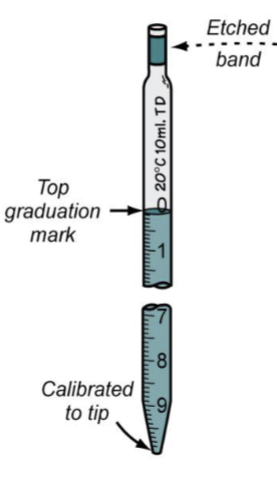
Identify the type of pipette
Serologic
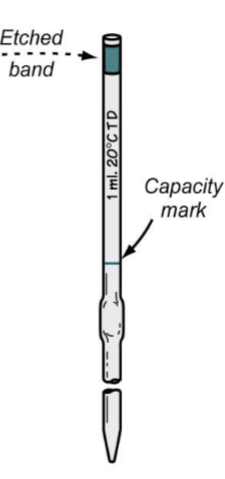
Identify the type of pipette
Ostwald
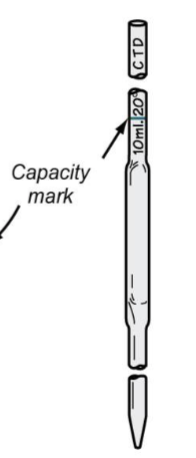
Identify the type of pipette
Volumetric
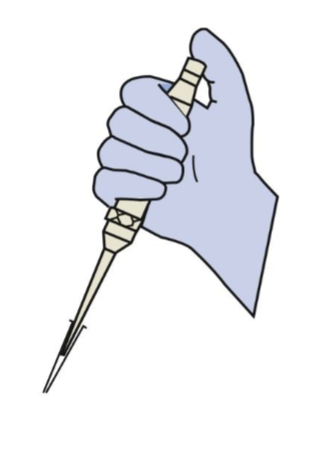
Identify the type of pipette
Automatic micropipette
Antibody titer
refers to the concentration of an antibody
acute phase specimen
serum from one with a current infection for which bacterial or viral specific immunoglobulins are measured
convalescent phase specimen
serum from one who has recovered from an infectious disease and considered to be especially rich in antibodies against the infectious agent
How can a current infection be revealed through analyzing acute phase and convalescent phase specimens of a patient?
increase in patients antibody titer of two doubling dilutions (four fold) OR
an acute of 1:8 and convalescent of 1:32
Precipitation
combination of soluble antigen with antibody to produce a visible insoluble complex
agglutination
specific insoluble antigens aggregate to form larger visible clumps when the corresponding specific antibody is present in the serum
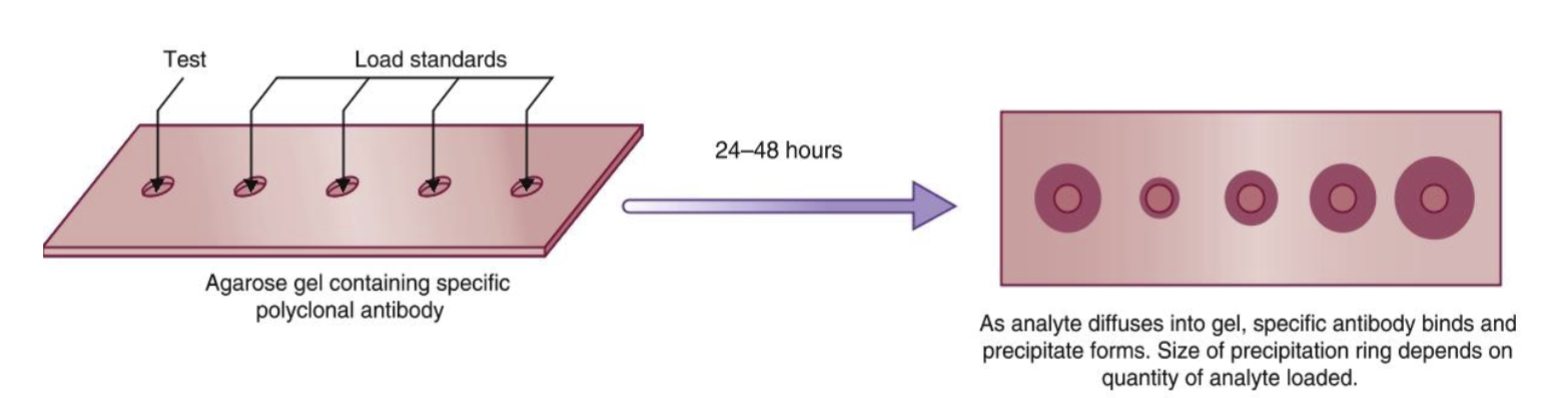
Name the technique
Single/ radial immunodiffusion
Name the technique
Double immunodiffusion or Ouchterlony
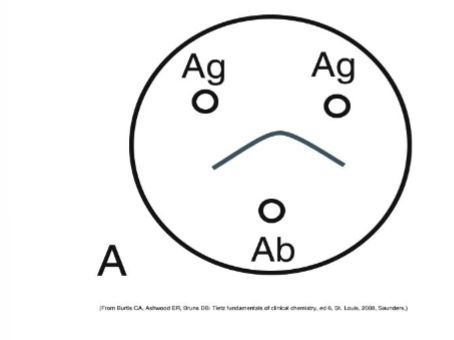
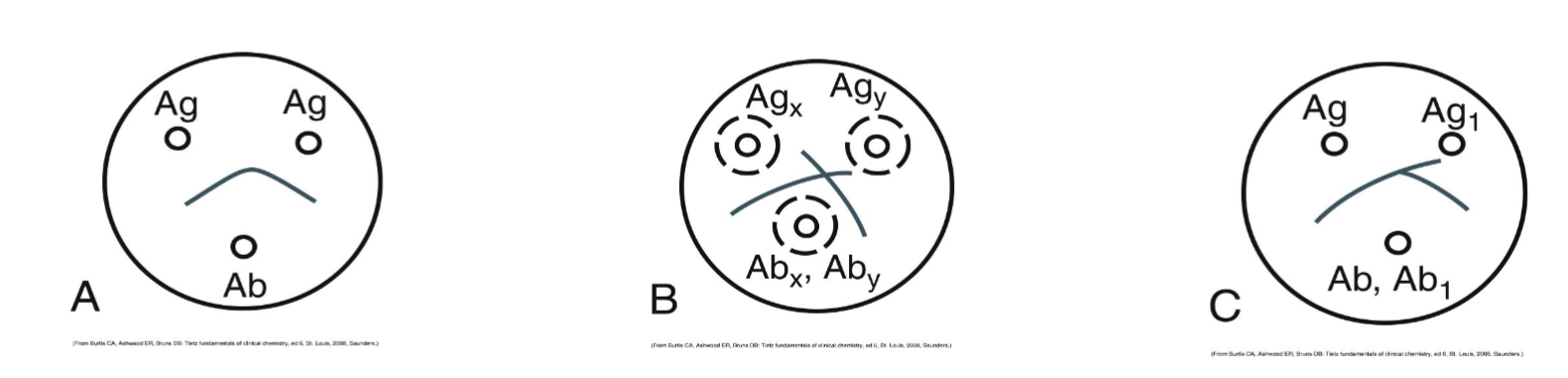
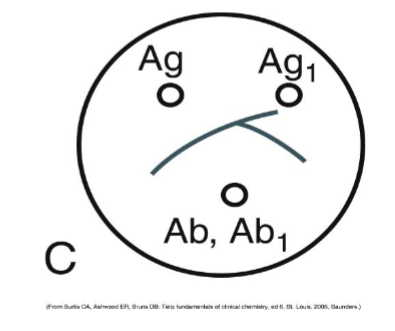
This is a reaction of:
Identity
This is a reaction of:
non-identity
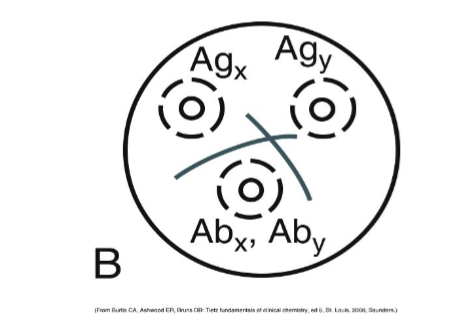
This is a reaction of:
partial identity
inhibition agglutination
detects patient antigen
the blocking of agglutination is the principle of the test
Reverse passive agglutination
detects antigen (CRP, fibrinogen)
antibody is attached to a carrier particle
direct bacterial agglutination
detects patient antibody
antigen is naturally on the particle itself
the binding of patient antibody to antigen in a bacterial suspension causes the bacteria to clump togenther in visible aggregates
passive agglutination
detects patient antibody
a carrier such as RBCs is used to adsorb soluble antigen onto their surfaces
the RBCs then agglutinate in the prescence of antiserum specific for the adsorbed antigen
What are the two phases of hemagglutination?
sensitization
lattice formation
Sensitization
physical attachment of antibody molecules to antigens on erythrocytes
Lattice formation
occurs when antigen particles and antibodies crosslink to form bridges
What are some ways to reduce the zeta potential in hemagglutination reactions?
centrifugation
enzyme pretreatment of RBCs
addistion of colloids
What is the purpose of using anti-human globulin in hemagglutination reactions, such as the direct antiglobulin test?
AHG froms crosslinks between antibodies that are bound to antigens on a carrier surface to make the reaction visible
Which region of MHC fenes codes for some of the complement components and cytokines?
Class III
Which region of MHC genes control HLA-A,B,C antigens found on most nucleated cells, which function to present endogenous antigen to CD8 lymphocytes?
Class I
Which region of MHC genes code for DP, DQ, and DR antigen expressed primarily on B cells, macrophages, other antigen presenting cells, and function to present exogenous antigen to CD4 lymphocytes?
Class II
HLA nomenclature “N”
null allele
non-function protein
HLA nomenclature “L”
lower than normal cell expression
HLA nomenclature “S”
soluble protein not found on cell surface
HLA nomenclature “Q”
questionable
allele may no affect normal expression
HLA nomenclature “C”
cytoplasmic protein not present on the cell surface
HLA nomenclature “A”
aberrant expression
uncertain if protein is expressed
HLA B27
Ankylosing spondylitis
HLA DQ2 and HLA B8
celiac disease
HLA DR2
Narcolepsy, Goodpasture’s syndrome and multiple sclerosis
What is the primary consideration in assessing whether an organ donor is acceptable for given patient?
HLA matching
Which tissue type is most and least immunogenic in transplants?
Bone marrow and cornea
What are some disease treatable by stem cell transplant?
acute/chronic leukemias
myelodysplastic syndromes
stem cell disorders
myeloproliferative disorders
lymphoproliferative disorders
phagocyte disorders
platelet abnormalities
allograft
graft between genetically different recipient and donor of the same species
autograft
graft transferred from one position to another in the same individual
syngraft
graft transplanted between different bu identical recipient and donor
xenograft
graft between individuals of different species
Hyperacute graft rejection
within minutes
humoral mediated
preformed cytotoxic antibodies to donor antigens
accelerated graft rejection
2-5 days
cell mediated
previous sensitzation to donor antigen
acute graft rejection
7-21 days
cell mediated
development of allogenic reaction to donor antigens
chronic graft rejection
later than 3 months
cell mediated
disturbance of host-graft tolerance
What is graft vs host disease?
occurs when immunocompetent T lymphocytes are transfused from a donor to an immunodeficient recipient
What are the requirements to develop GVHD?
source of immunocompetent lumphocytes
human leukocyte antigen differences between patient and donor
inability to reject donor cells
What is the most effective method of preventing GVHD for blood transfusion?
irradiating the blood components
What are the five categories of vaccines?
live attenuated
inactivated
subunit, recombinant, polysaccharide, and conjugate
toxoid substances
nucleic acid
Subunit, recombinant, polysaccharide and conjugate vaccine treated diseases
Haemophilus influenzae type B
Hepatitis B
HPV
whooping cough
pneumococcal disease
meningococcal disease
shingles
Live attenuated vaccine treated diseases
measles
mumps
rubella
rotavirus
smallpox
chickenpox
yellow fever
inactivated vaccine treated diseases
hepatitis A
influenza
polio
rabies
toxoid vaccine treated diseases
diphtheria
tetanus
nucleic aicd vaccine treated diseases
SARS-CoV-2 virus
Which agency regulates vaccine products?
Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER)
What are three specific requirements that the FDA has for vaccines?
produce protective immunity with only minimal side effects
be immunogenic enough to produce a strong and measurable immune response
be stable suring its shelf life with potency remaining at the proper level
What is Guillain-Barre syndrome?
caused by surgery, infection, or immunization
Disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks nerves
myelin sheath becomes damaged and prevents nerves from transmitting signals to the brain, causing weakness, numbness, or paralysis
Serologic testing
an assay involvin serum constituents
immunologic testing
testing related to antigens and antibodies
HLA crossmatching methods
ELISA and flow cytometry
classic was complement dependent cytotoxicity
Preventative AIDS vaccine
HIV negative individuals to prevent HIV infection
Therapeutic AIDS vaccines
HIV positive individuals to improve the immune system
Pathogens adapted for biological warfare include:
smallpox
anthrax
plague
tularemia
brucellosis
Q fever
botulinum toxin
staphylococcal enterotoxin B