Week 2 ABO blood group system
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
ABO blood group system
react at body temp (37C)
responsible for severe hemolytic transfusion reactions
able to activate classical complement cascade
Pre-transfusion testing
ABO typing is one of the first testing done before a transfusion
recipient and donor must be typed
to avoid giving the wrong blood type due to mistyped or incorrectly drawn specimen
compare current blood type to historical
if none then draw 2nd
another tech re-types current
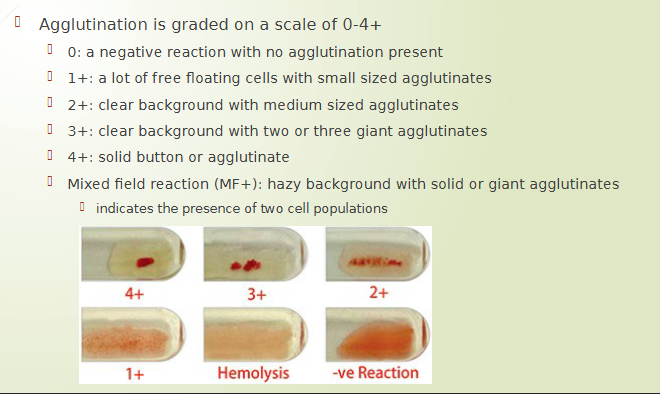
grading agglutination in tube testing
graded on a scale of 0-4+
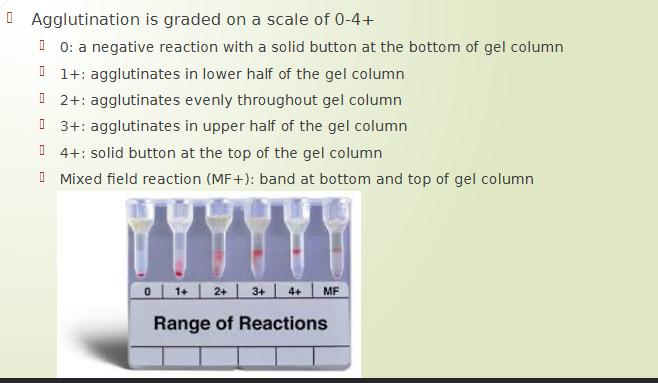
Grading agglutination in Gel testing
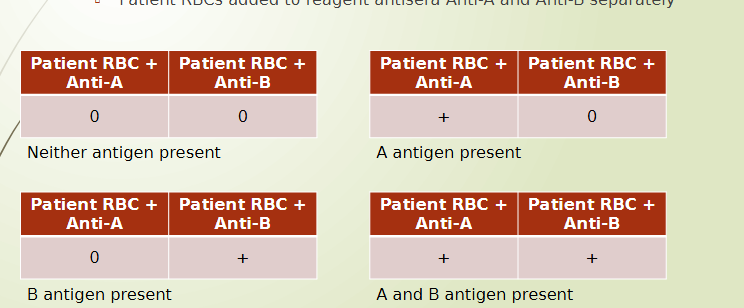
ABO testing - forward type
patient RBCs mixed with reagent antisera (antibody)
determines which antigens present on patient RBC
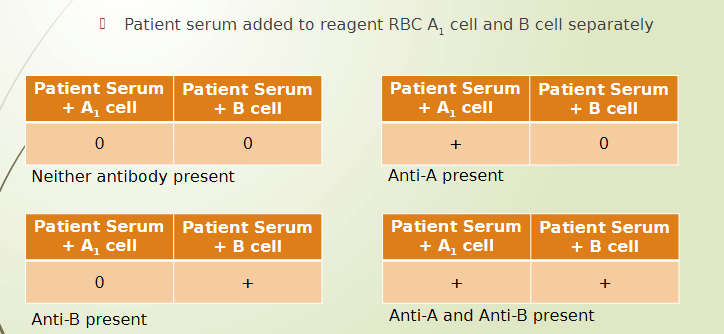
ABO testing - reverse type
patient plasma/serum mixed with reagent RBC (A1 cells and B cells)
Determines which antibody
present in patient serum
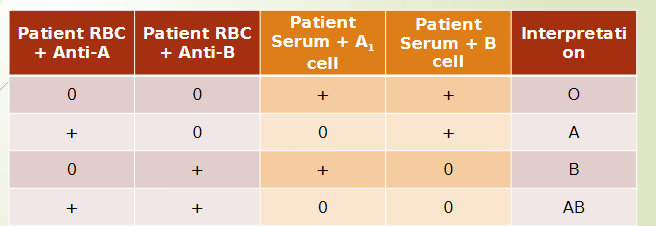
ABO testing chart
ABO discrepancy
why test the forward and reverse group?
can have discrepancy between results
don’t match
ABO cannot be interpreted until discrepancy is resolved
transfuse group O if emergency and can’t wait for resolution
ABO antibodies
begin to develop at 4 months
production is stimulated when exposed to substances in nature that are chemically similar to A and B antigen
stays constant after peaking 5-10
titer could decrease in elderly
usually IgM antibodies
some O types produce an additional antibody (anti-A,B) that has dual specificity for A and B antigen (usually IgG)
preferentially agglutinates RBC at room temp or colder
activate complement at body temp
ABO antigens
newborn RBCs do have ABO antigens
not fully developed
half the amt of antigens on newborn RBCs
by 2-4 years, antigen completely developed
# of antigen sites stays constant once developed
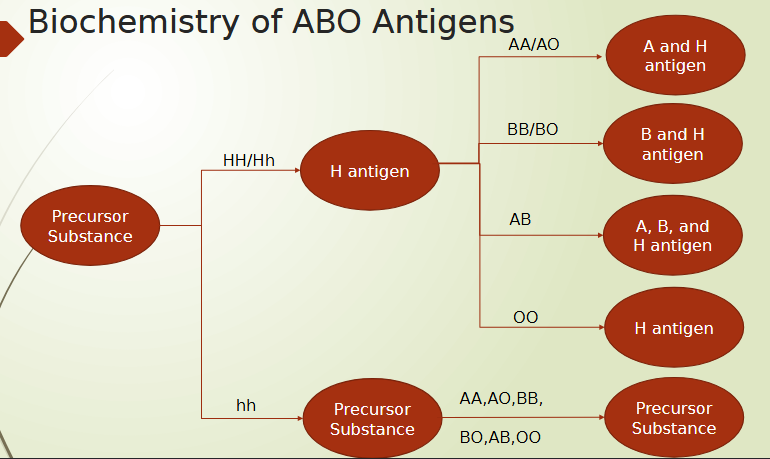
Genetics of ABO antigens
A, B, O are major alleles
located on chromosome 9
A/B are co-dominant
O allele is an amorph
doesn’t produce a detectable antigen
genes located on chromosome 19 are important in A and B antigen production
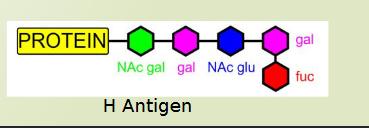
gene for H antigen
biochemistry of ABO antigens
A and B antigens are the last sugars at the end of a long chain of sugars stemming from RBC membrane
H antigen is the precursor to A and B antigens
last sugar added to the oligosaccharides before A and B antigen
A and B antigen production depend on the presence of H antigen
Formation of H antigen
greater than 99.9% of population of H antigen gene
H gene (HH or Hh) encodes L-fructosyltransferase to add L-fucose molecule to type-2-precursor substance on RBC
Type O individuals will have highest amt of H antigen present
Bombay phenotype (Oh)
hh genotype
H antigen is not formed
looks like an O phenotype even if A and/or B genes are inherited
will develop Anti-H whereas typical O have H antigen
IgM clinically significant antibody that binds complement and reacts at 37C
Lacks H antigen
Ulex europaeus
lectin used for testing
O + Anti-H = +
Bombay + Anti-H = negative
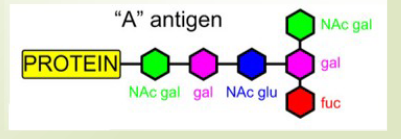
Formation of A antigen
A gene (AA/AO) encodes N-acetylglucosaminyl transferase to add a N-acetyl-D-galactosamine molecule in to H antigen
The N-acetyl-D-galactosamine with the H antigen is the A The N-acetyl-D-galactosamine with the H antigen is the A antigenantigen
Need A and H genes
strong and converts most H antigen to A
subgroups of A antigen
often discovered if there is an ABO discrepancy
don’t need to differentiate unless
Most prominent A1 + A2
make up 99% of A individuals
A1 - 80%
A1 gene
causes the N-acetylgalactosaminyl transferase to be produced in high amt
convert 4x the number of antigen sites compared to A2
A2 gene
differs from A1 by the ability to develop anti-A1
1-8% A2 and 22-35% A2B develop anti-A1
Less common subgroups
A3, Am, Ax, Ael
could be a neg result with anti-A antisera
some Anti-A,B antisera reagents are better at picking up weak subgroups
increased expression of H antigen as the A antigen expression decreases
A3 can have mixed field reaction with anti-A human source antisera used
Ax usually agglutinates with anti-A,B weakly and no reaction with anti-A
absorption/elution are techniques used to show the presence of weaker subgroups on RBC
Anti-A1 in subgroup
IgM naturally occurring antibody
tends to react under 37C
forms in patients w/o A1 antigen
Lectin Dolichos biflorus will only bind A1 antigen
subgroups other than A1 won’t agglutinate
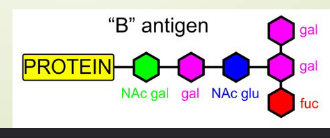
Formation of B antigen
B gene (BB/BO) encodes D-galactosyltransferase to add a D-galactose molecule to H antigen
D-galactose with H antigen is B antigen
need B and H genes
converts less H antigen to B antigen compared to A
Formation of Group AB
Group AB contain the A and B genes that encode N-acetylgalactosaminyl transferase and D-galactosyltransferase to add a N-acetyl-D galactosamine and a D-galactose molecule to H antigen
Need the A, B and H genes
N-acetylgalactosaminyl transferase and D-galactosyltransferase both converting H antigen to A and B
Has the least amount of H antigen of the ABO blood types
biochemistry of ABO antigens
H antigen concentration
adding A and B antigens to RBC membrane decreases the amt of H antigen present
inversely proportionate relationship
effects ability to detect H antigen
Anti-H can develop occasionally in patients with low amt of H antigen
A1 A1B
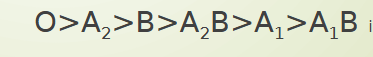
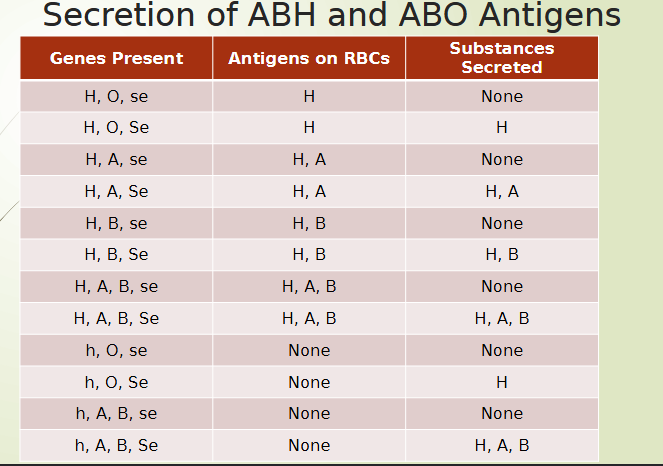
Secretion of ABH
secretor gene (Se and se alleles) found on chromosome 19
responsible for ABH soluble substances found in body fluids
80% of population are secretors (SeSe or Sese)
encodes L-fucosyltransferase to add L-fucose molecule to type-1-precursor substance
^ found in secretory tissues
secretion of ABH and ABO antigens