OBGYN EOR
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
167 Terms
MCC of secondary amenorrhea
pregnancy
primary vs. secondary amenorrhea
Primary amenorrhea is the absence of menarche by 14 or 16
Secondary amenorrhea is the cessation of menstruation for 3 cycles or 6 months in females previously menstruating normally.
AUB differential
PALM COEIN
PALM-COEIN
P: Polyp
A: Adenomyosis
L: Leiomyoma
M: Malignancy/hyperplasia
C: Coagulopathy
O: ovulatory dysfunction
E: Endometrial
I: Iatrogenic
N: Not yet classified
parabasal epithelial cells
atrophic vaginitis
pH of atrophic vaginitis
>5
tx w/ topical estrogen
MC location for fibroids
intramural
intermenstrual bleeding
metrorrhagia
endometrial thickness of ____ is considered thickened in premenopausal pts
15
>____ endometrial thickness is considered thickened in postmenopausal females
>4
MCC oligohydramnios
rupture of membranes
first line tx for AUB
Combo hormonal therapy→ suppresses GnRH and pituitary FSH/LH →suppresses ovarian folliculogenesis and LH surge therefore prevents ovulation
combo OCP are protective against which cancers?
endometrial and ovarian
slight inc. risk for breast
RF for PCOS
genetics
obesity
impaired glucose tolerance/DM
metabolic syndrome
epilepsy/antiepileptic drugs
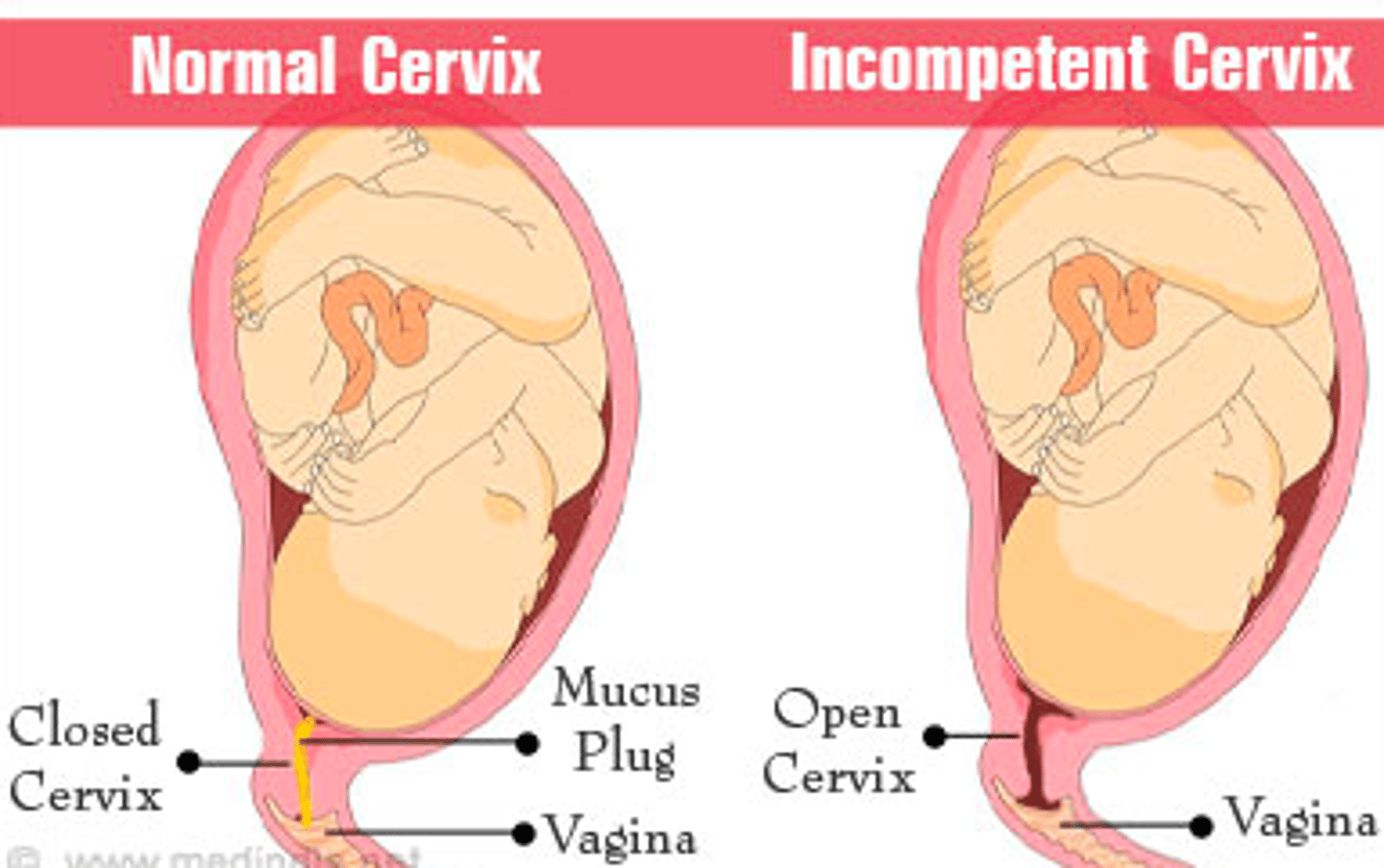
risk factors for cervical incompetence
congenital- DES exposure, bicornate uterus
acquired- inflammation, infection, cervical trauma, cone biopsy, multiple gest, late 2nd trimester abortion, LEEP
hormonal- relaxin
genetic - Ehlers Danlos, marfan
which hormone is disproportionately secreted in PCOS?
LH >> FSH
LH binds within ovaries and leads to hypersecretion of androgens
MC presentation of PCOS
oligomenorrhea
what commonly needs to be supplemented in pregnant pt with PCOS?
progesterone → plays an important role in implantation and inhibition of uterine contractions in pregnancy
Rotterdam criteria
PCOS
string of pearls on US
PCOS
how to differentiate anovulatory vs. ovulatory AUB
ovulatory is cyclic
fibrocystic breasts or fibroadenoma: fluctuates with menses?
fibrocystic
fibrocystic or fibroadenoma: tender?
fibrocystic
Most common breast cancer
IDC
ductal carcinoma with eczematous nipple lesion
paget's disease
breast cancer hormonal therapy ONLY used in post-menopausal women
aromatase inhibitors → anastrozole, letrozole
useful in ER-positive
tx indicated in HER2 overexpression
monoclonal abs
risk factors for umbilical cord prolapse
low birth weight, multiparity, polyhydramnios, prolonged labor, long umbilical cord, preterm gestation, malpresentation, pelvic deformities, and external fetal anomalies.
Malpresentation of the fetus includes transverse lie, oblique lie, breech presentation, or unstable lie.
breast cancer hormonal therapy used in pre-menopausal women
SERM → tamoxifen
adverse effects of tamoxifen
hot flashes
uterine bleeding
venous thrombosis
endometrial cancer
breast cancer screening modalities
mammogram = best in >40 y/o
US = best in <40 y/o
adverse effects of aromatase inhibitors
thromboembolism
*osteoporosis*
MI
arthralgia
why might SERMs (tamoxifen, raloxifen) be preferred in post-menopausal women for breast cancer prevention?
if they have osteoporosis
HPV vaccine schedule
<15 y/o = 2 dose series given at 0 and 6-12 months
15+ y/o = 3 dose series. Given 0,1-2, and 6 months apart.
MC etiology of breast abscess
S. aureus
treatment for breast abscess
I & D and antibiotics (e.g. cephalexin)
abx for breast abscess
dicloxacillin or cephalexin
if MRSA then TMP-SMX DS or clindamycin
MC cervical cancer
SCC
HPV strains assoc with cervical cancer
16, 18, 45
clinical manifestations of cervical cancer
usually asymptomatic
- post coital bleeding = MC sx
- irregular/heavy period
- watery discharge
- advanced dz = pelvic pain, back pain, bladder/rectal dysfunction
premature cervical dilation
incompetent cervix
tx for incompetent cervix
cerclage and bed rest
or
weekly injection of 17 alpha-hydroxyprogesterone
diagnosis of infertility
hysterosalpingography- helps evaluate tubal patency or abnormalities
first line meds for ovulation induction
letrozole or clomiphene
most effective method of emergency contraception
copper IUD → must be inserted within 5-7 days after unprotected sex
contraindications to combo OCP
- ischemic heart dz
- hx of DVT, PE, stroke
- breast cancer
- migraine w/ aura
- smokers if >35
- severe HTN
Adverse effect of depo shot
bone weakness and osteoporosis d/t calcium loss → don't use more than 2 yrs
what causes ovulation?
LH surge
what causes dysmenorrhea?
excess prostaglandins→ cause increased uterine wall contractions
treatment for PMDD
lifestyle mod
SSRIs
OCPs
risk factors for fibroids
-increasing age (>35)
-early menarche
- nulliparity
-obesity
-black ethnicity (5x)
-family history
sx of fibroids
pelvic pressure
bleeding
painful irregular periods
cannot lose weight
infertility/miscarriages
which GYN tumors are estrogen dependent and therefore may increase in size with relation to menstrual cycle?
fibroids
also inc. in size during pregnancy, anovulatory states
most used imaging modality for dx of fibroids
transvag US → focal heterogenic hypoechoic mass or masses with shadowing
1st line tx for fibroids
Combined estrogen-progestin contraceptives, a progestin-releasing intrauterine device, and tranexamic acid
most effective nonsurgical tx for fibroids
GnRH analogs (leuprolide, nafarelin) → usually used near menopause or to shrink fibroids prior to hysterectomy/myomectomy
HOWEVER this is 2nd line
surgical TOC for fibroids in women who want to PRESERVE fertility
myomectomy
biggest risk factor for endometritis
c-section
infection of the pregnancy endometrium (decidua)
endometritis
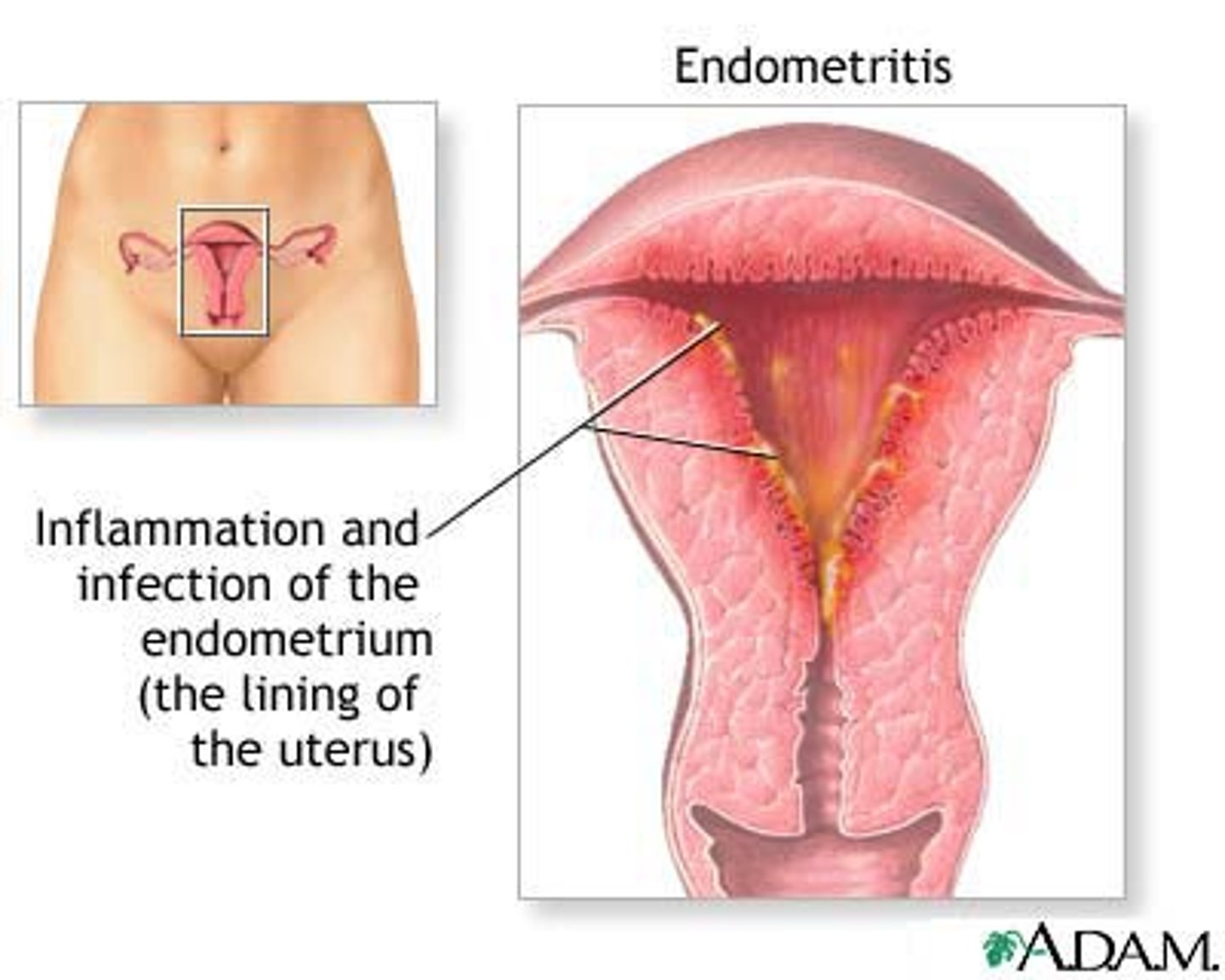
sx of endometritis
1. Fever > 38 (after first 24 hrs, for 2 of 10 post-partum days)
2. Uterine tenderness + abd pain
3. Foul smelling (persistent vag discharge) +/- leukocytosis
Caused by polymicrobial infection.
tx for endometritis
gentamicin + clindamycin +/- ampicillin
what abx may be given before c-section to prevent endometritis?
first gen cephalosporin → cefazolin
when are sx of endometriosis better?
estrogen stimulated → symptoms improve during pregnancy and after menopause
MC site of endometriosis
ovaries
risk factors for endometriosis
prolonged estrogen exposure → nulliparity, late first pregnancy, early menarche, short menses
other: fhx, prolonged/heavy menses
what may reduce risk of endometriosis?
- exercise >4 hrs/week
- higher parity (more kids)
- late menarche (after 14)
- longer duration of lactation
classic triad of endometriosis
Cyclic premenstrual pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia
may have: dyschezia, abnormal bleeding, back/abd pain/pressure, infertility
initial imaging of choice for endometriosis
pelvic US (to rule out other dx)
definitive diagnosis of endometriosis
Laparoscopy with biopsy
first line tx for endo
- ovulation suppression → OCP
most sensitive initial test for menopause
FSH assay, >30 = menopause
LH will also be increased, estrogen decreased
raloxifene or tamoxifen: endometrium agonist
tamoxifen → therefore inc. risk of endo cancer
raloxifene is antagonist
risk factors for endometrial cancer
obesity, nulliparity, infertility, late menopause, diabetes mellitus, PCOS, unopposed estrogen stimulation, HTN, gallbladder disease, tamoxifen use.
Grades of uterine prolapse
Grade 0: Normal
Grade 1: descent into upper 2/3 of vagina
Grade 2: cervix approaches introitus
Grade 3: The lowest part is more than 1cm below the introitus, but not fully descended
Grade 4: Full descent with eversion of the vagina
pelvic organ prolapse risk factors
vaginal birth
obesity
prior pelvic surgery
advancing age
heavy lifting or straining
genetic predisposition
connective tissue disorders.
MC type of ovarian cyst
follicular
MC type of ovarian tumor
epithelial carcinoma
MC type of endometrial cancer
adenocarcinoma
tx of ovarian cyst
if <8 cm: supportive → rest, NSAIDs; may resolve
>8cm or persistent → laparoscopy/laparotomy
abrupt onset of unilateral lower quadrant abd pain; often sharp and focal and often occurring during sex or strenuous physical activity
ruptured ovarian cyst
initial test of choice for ovarian torsion
US with doppler
definitive is surgical exploration
thin, gray-white discharge
BV
what is the pH in BV?
>4.5
positive whiff test
BV
first line in BV
metro or clinda (both safe in preg)
clue cells
BV
AKA epithelial cells covered by coccobacilli
sexually transmitted flagellated protozoan
trichomonas
copious frothy yellow-green discharge
trich
cervical petechiae
Strawberry cervix→ Trichomoniasis
tx for trich
metro
treat partners
spontaneous abortion is a pregnancy that ends before ___ weeks
20
when is mifepristone/misoprostol indicated for elective abortion?
<10 weeks+6 days
When can D&C be done?
up to 12 weeks
when can D&E (evacuation) be done?
15.5-22 wks
triad of PID
1. abd tenderness
2. cervical motion tenderness
3. adnexal tenderness
PLUS 1 of the following:
- temp, wbc >10000, pelvic abnormality on bimanual/US, ESR/CRP inc. abnormal cervical or vaginal mucopurulent discharge or cervical friability
pelvic tenderness, cervical motion tenderness, purulent discharge
PID
MC etio of PID
chlamydia
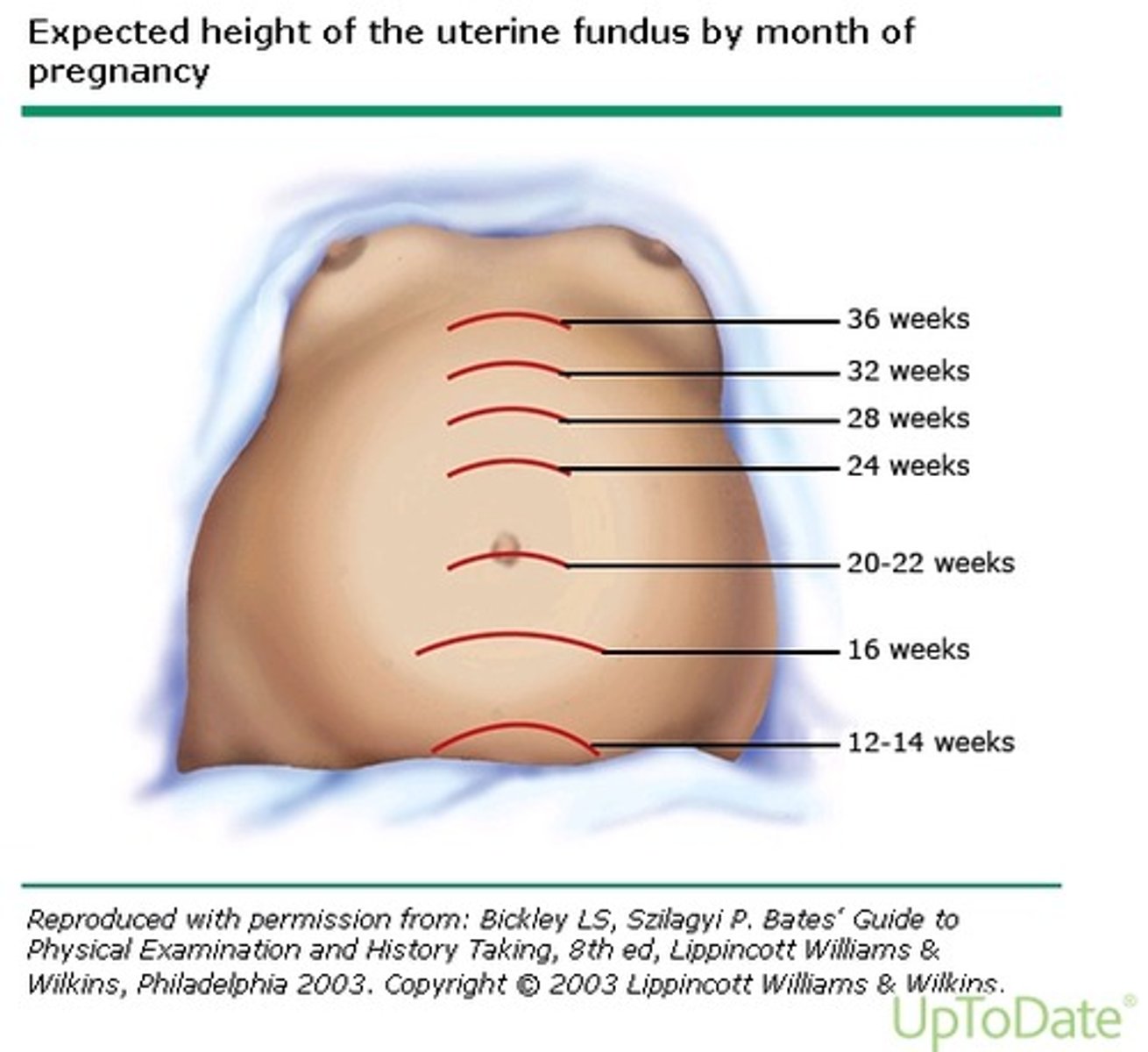
fundal height measurements
12 wks - pubic symphysis
16 wks -midway between pubis and umbilicus
20-22 wks - umbilicus
38 wks - xiphoid process
how soon can urine b-hCG detect pregnancy?
14 days
which sign: uterus softening after 6 weeks
ladin's