AP Human Geography Unit 5 (Agriculture)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
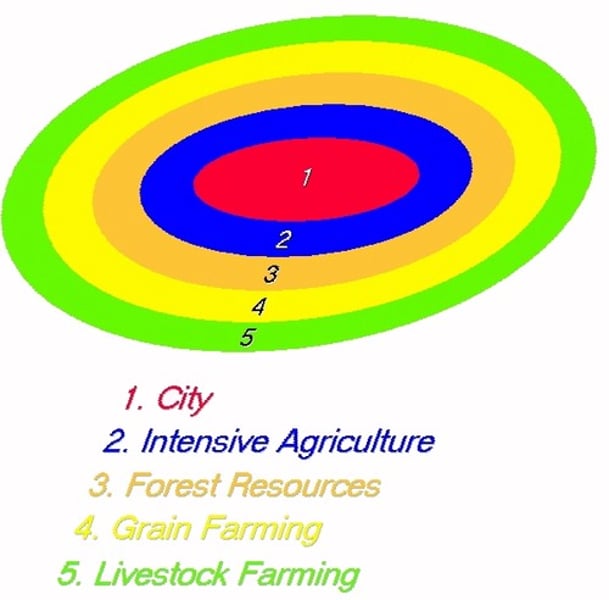
Von Thunen's Model
Transportation costs (weight & distance) and land value determines where farmers must be in relation to the market
Subsistence Farming
produces food that is needed to survive on a daily basis to a person, family or village

Commercial Farming
farming of products for sale off the farm (mostly done in more developed countries, requires use of machinery)

Breadbasket
US & Canadian prairies states, know for producing a lot of bread

First Agricultural Revolution (Neolithic Revolution)
Took place 10,000 years ago in 8,000 BCE. Allowed humans to become more sedentary and avail themselves of a more reliable source of food (shift from being primarily hunting/gathering societies to ones that planted crops for food) - changed human history.
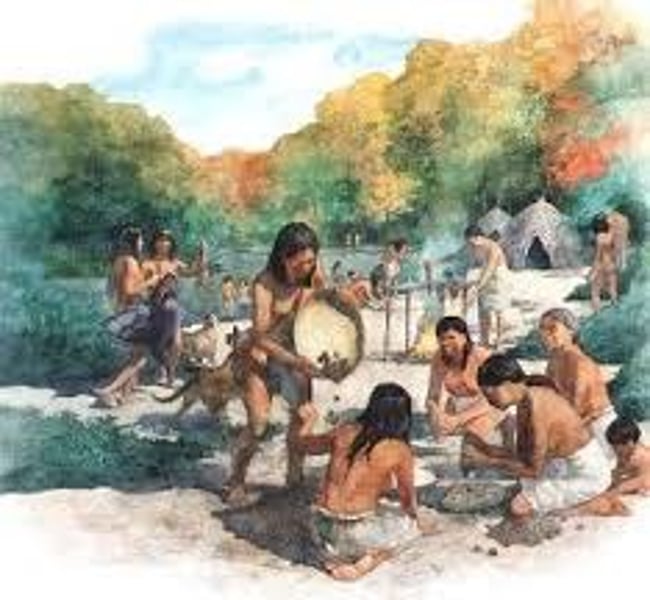

Second Agriculture Revolution
Occurred during the Industrial Revolution during 1750-1850 in more developed world. Uses technology provided by the Industrial Revolution as means to increase production and distribution of products.
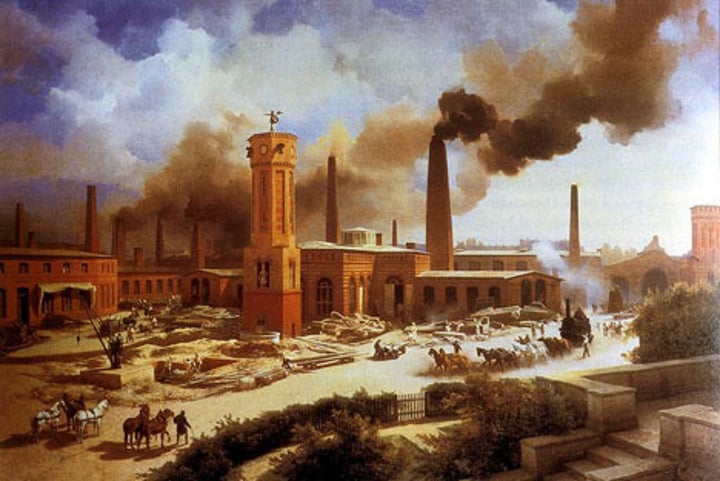

Third Agricultural Revolution (Green Revolution)
(latter half of the 20th century) corresponded with exponential growth occurring around the world - also called the Green Revolution - involves the use of biotechnology (genetic engineering) and expanded use of fertilizers.

Intensive Subsistence Agriculture
More intense style of subsistence farming (more work needed to obtain same level of production). Used in the developing world largely in parts of Asia. Maximizes every piece of land by double & triple cropping, and not wasting any land - no animal grazing.

Green Revolution
involves the use of biotechnology (genetic engineering). Also called the third agricultural revolution.

Mediterranean Agriculture
practiced in climate that has dry summer and cool, moist winter (grapes, dates, olives) - around Mediterranean Sea, parts of California and southern Australia
Desertification
overgrazing of land led to encroaching deserts within arid regions (Southern Sahara regions have experienced loss of farmland to expanding desert)

Transhumance
the action or practice of moving livestock from one grazing ground to another in a seasonal cycle, typically to lowlands in winter and highlands in summer.

Double Cropping
growing of two crops per year to double the harvest - used in Asia and other parts of the world to maximize land use

Boserup Thesis
It states that agricultural methods and productivity of food depend on the size of the population. Indications: 1: if population increases, larger workforce so more food produced. 2: if population increases, mechanization occurs, more food produced as more effective means found of producing high yields of food through use of machinery. 3: if population increases, increased use of fertilizers results, so as to produce more food for the growing population.

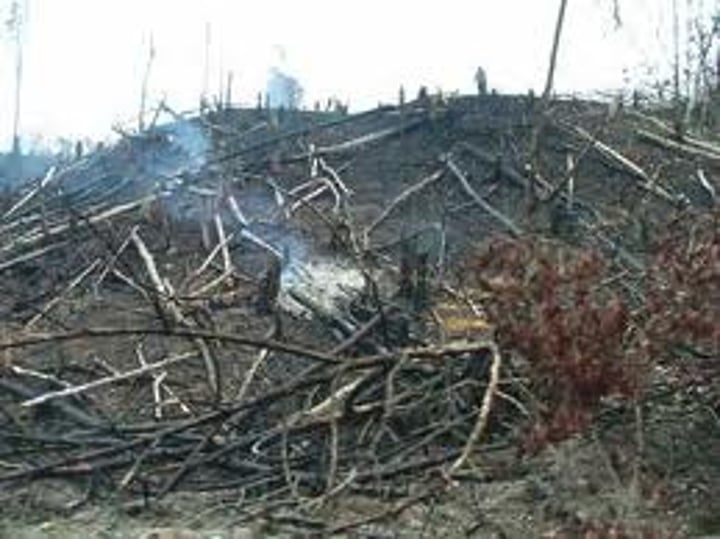
Shifting Cultivation
Slash and Burn agriculture - clear land of vegetation (usually by burning) and use land until nutrients in field are depleted (scars the landscape). Use of land only 2-3 years. Very damaging to the environment but used to support most of the world's people in the developing world

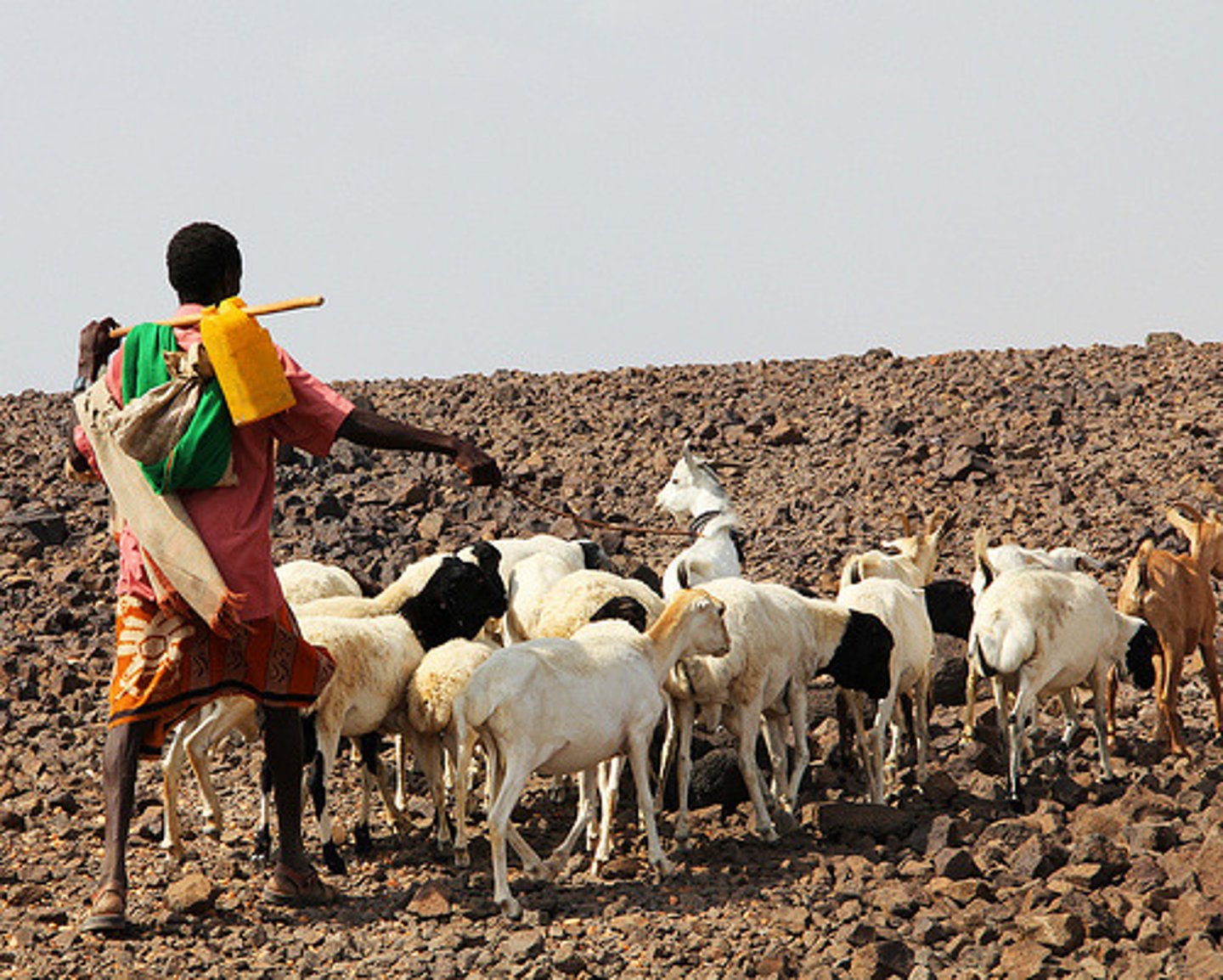
Pastoral Nomadism
Involves moving animals on a seasonal basis to areas that have necessary vegetation & water to meet the needs of animals. Done in arid climates in North Africa and Central Asia. Mostly goats, sheep, camels. People survive off of the milk products of the animals & rarely meat products.

Intertillage
clearing between the rows in the field through the use of hoes, rakes and other manual equipment. Does not till flat the agricultural land preventing the loss of valuable top soil.

agriculture
deliberate modification of the Earth's surface through the cultivation of plants and animals
crop
any plant cultivated by people
Hunter-Gatherer
Before the invention of agriculture-man obtained the food they needed by hunting animals and gathering available agricultural products.
Colombian Exchange
refers to a period of cultural and biological exchanges between the New and Old Worlds. Exchanges of plants, animals, diseases and technology transformed European and Native American ways of life. Beginning after Columbus' discovery in 1492 the exchange lasted throughout the years of expansion and discovery.
Enclosure Movement
was the legal process in England during the 18th century of enclosing a number of small landholdings to create one larger farm. Once enclosed, use of the land became restricted to the owner, and it ceased to be common land for communal use.
Dietary Energy Consumption
the amount of food that an individual consumes. Measured in calories / kilocalories.
Food security
Exists when all people, at all times, have physical and economic access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life
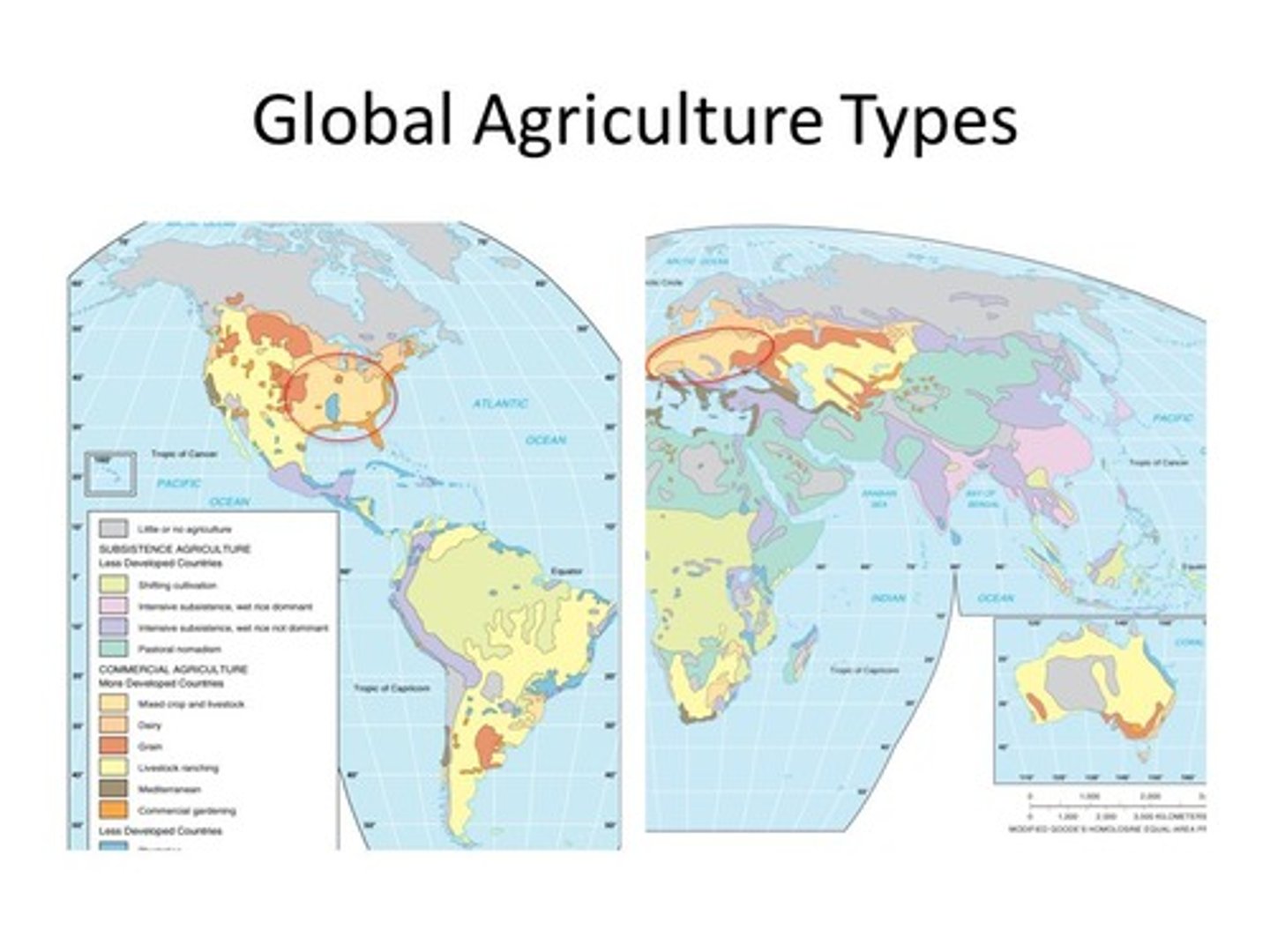
Derwent Whittlesey's Agricultural Regions
Divides the world into 11 agricultural regions based on agricultural products & climate
Swidden
A field created by slash-and-burn agriculture (involves the cutting and burning of plants in a forest or woodland)
Potash
Mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water-soluble form to be used as a fertilizer.
Sawah
The flooded field to produce wet rice used in Indonesia
Paddy
A field flooded and used for growing wet rice.
crop rotation
the system of varying successive crops in a definite order on the same ground, especially to avoid depleting the soil and to control weeds, diseases, and pests.
plantation
Commercial agriculture largely in the developing world on which crops such as coffee, sugar, and tobacco are cultivated by resident labor.
agribusiness
Large scale agricultural production done in the developed world. Includes agrichemicals, breeding, crop production (farming and contract farming), distribution, farm machinery, processing, and seed supply, as well as marketing and retail sales.
Truck Farming / Market gardening
The production of some vegetable crops on an extensive scale in regions especially suited to their culture primarily for shipment to distant markets.
Undernourishment
dietary energy consumption that is consistently below the minimum requirement for maintaining a healthy life and carrying out light physical activity.
Kilocalorie / calorie
A unit of energy. In nutrition and everyday language, calories refer to energy consumption through eating and drinking, and energy usage through physical activity.
milkshed
The ring surrounding an urban area where milk can be supplied without spoiling
Winter Wheat
A wheat crop planted in the fall and harvested in the beginning of the summer. It is able to survive winter under a blanket of snow as it establishes roots before the winter comes. Common in warmer grain producing areas.
Spring Wheat
Grain planted in the spring and harvested in the summer. Common in areas where winter is too harsh for winter wheat.
horticulture
growing of fruits, vegetables, flowers and tree crops. Common in Mediterranean farming.
Ranching
Commercial grazing of livestock for meat over an extensive area.
Feedlot
an area or building where livestock are fed and fattened up
Pampas
An area in Argentina where ranching is common. Has a dry, arid climate.
Cash Crops
Crops produced on a farm to be sold for profit.
Luxury Crops
Non-subsistence crops such as tea, cocoa, coffee, and tobacco.
Fallow
land plowed but left unplanted for a period in order to restore its fertility as part of a crop rotation or to avoid surplus production.
Aquaculture / aquafarming
the rearing of aquatic animals or the cultivation of aquatic plants for food.
Dr. Norman Borlaug
The Father of the Green Revolution / genetically modified agriculture. He received his Ph.D.in plants pathology and genetics from the University of Minnesota in 1942. In 1944 he was sent to Mexico as a plant pathologist in order to stop the "rust", a fungal disease affecting wheat leaves and grains. There, working in the fields with the farmers and the laborers, by taking wheat and cross-breeding it, he developed new seeds that yielded more and were more disease resistant. In the early 50's, the improved wheat seeds made Mexico self-sufficient. In the early 60's the improved wheat seeds were shipped to India.
Genetically Modified Foods
Foods produced from organisms that have had changes introduced into their DNA using the methods of genetic engineering.
Organic Agriculture
production of food without chemical fertilizers or pesticides. Sustains the health of soils, ecosystems and people. It relies on ecological processes, biodiversity and cycles adapted to local conditions.
Sustainable agriculture
agricultural practices that preserve and enhance environmental quality through the use of sensitive land management, limited use of chemicals and integration of crops and livestock.