all the body systems
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
epidermis
outer layer of skin, protection
dermis
middle layer of skin, connective tissue, glands, blood vessels
subcutaneous tissue
deepest layer, insulation and cushioning
apocrine glands
sweat glands active in stress and puberty
eccrine glands
sweat glands for temperature regulation
arrector pili msucles
cause goosebumps
melanocytes
produce melanin
hair
protection and insulation
nails
protection and enhance fine motor skills
integumentary functions
protection, fluid balance, absorption, synthesis of vitamin D, sensation, thermoregulation, immunity, excretion
nasal cavity
warms, humidifies, filters air
pharynx
passage connecting nose, larynx, mouth, and esophagus
larynx
airway, house vocal box
trachea
main airway connecting larynx, and bronchi
bronchi
airways branches into primary, secondary, and tertiary level
bronchioles
transitional airways for gas exchange
alveolar ducts and sacs
functional units for gas exchange
pleura
protective lung lining, reduce friction and maintains negative pressure
respiratory gas exchange
provide oxygen to body, remove carbon dioxide
respiratory filtration
clean air before reaching lungs
respiratory humidification
add moisture to prevent lung dryness
respiratory sound production
larnxy enables vocalization
respiratory protection
prevent foreign particles form entering deep airway
cardiovascular system
heart and blood vessels
heart
four chambers, right and left atria, right and left ventricles, function as double pump
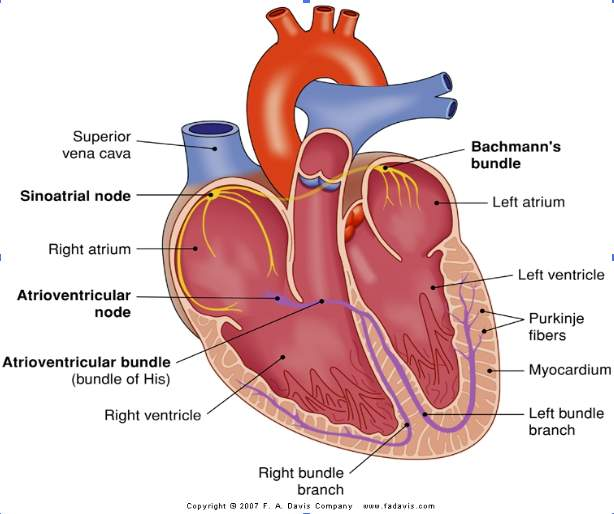
atria
right and left chambers pump blood into ventricles
left ventricle
pump blood to systemic circulation (body)
righ ventricle
pump blood to pulmonary circulation (lungs)
arteries
carry oxygen-rich blood away from heart
veins
return deoxygenated blood to heart
atrioventricular valve (AV)
tricuspid (right) and mitral (left)
semilunar valves
pulmonic (right) and aortic (left)
gastrointestinal system
digestive and urinary system
digestive system
stomach, small and large intestines, liver, pancreas, gall bladder, spleen
stomach
break down food, vitamin B1 absorption, secretes hydrochloric acid to begin digestion
small intestines
primary site for digestion and nutrient absorption
large intestines
absorb sodium and water
liver
metabolize nutrients, produce bile and clotting factors, detoxify drugs and alcohol, convert glucose to glycogen, store vitamins
pancreas
produce insulin, glucagon, digestive enzymes
gall bladder
store and concentrate bile
spleen
store red blood cell (RBCs), produce RBCs and macrophages
urinary system
bladder and kidneys
bladder
store urine
kidney
remove waste, regulate blood pressure, and produce erythropoietin ( stimulate RBC production)
female genitourinary system
mons pubic, labia majora/minora, clitoris, urinary meatus, skenes glands, vaginal introitus, vagina, bartholins galnds, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, kidneys
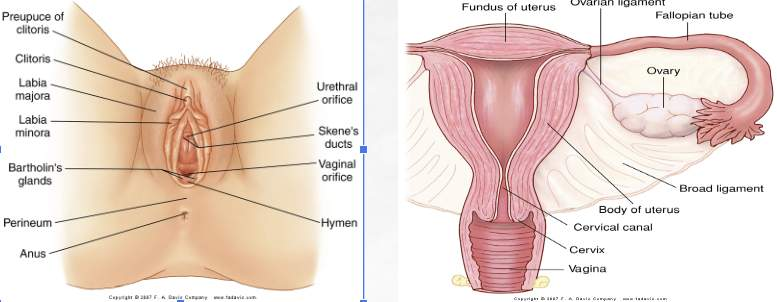
mons pubis
Subcutaneous pad over the symphysis pubis for protection.
labia majoria/minora
Folds of adipose (body tissue) and connective tissue; protect and lubricate external genitalia.
clitoris
Erectile tissue for sexual stimulation
urinary meatus
opening to urethra (duct for urine)
vaginal introitus
opening for vagina
vagina
muscular tube for copulation, birth canal, and menses (blood from menstruation)
bartholin’s glands
Secretes alkaline mucus to improve sperm viability and motility.
cervix
end of uterus extending into vagina
uterus
hollow, muscular organ, site for fertilized egg, protect fetus
fallopian tubes
passage for ovum to uterus
ovaries
produce ova, estrogen, and progesterone
kidneys
filter and excrete waste products
male genitourinary system
scrotum, testes, vas deferens, spermatic cord, seminal vesicles, bulbourethral gland, prostate, epidiymis, kidney, ureter, bladder, urethra, penis, glans penis, inguinal area
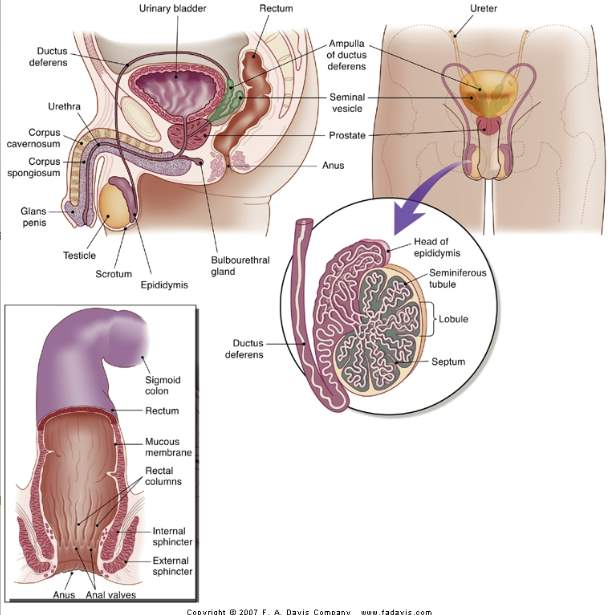
scrotum
sac that contains and protect testes
testes
produce sperm and testosterone
vas deferens
duct from epididymis to ejaculatory duct
spermatic cord
protective sheath around vas deferens
seminal vesicles
produce 70% of semen
bulbourethral gland
secrete lkaline substance to neutralize vaginal secretions
prostate
produce 20% semen
epididymis
store sperm until mature
kidney
filter blood and remove waste
ureter
tube connecting kidney to bladder
urethra
passageway for urine elimination
penis
male sex organ and urine elimination
glans penis
important for sexual arousal
inguinal area
canal for vas deferens from srotum through abdominal muscles, contains lymph nodes
musculoskeletal system
bones
206 bones, provide structure and protection, produce blood cells and store calcium
muscles (650)
enable movement and positioning, produce heat
joints
articulation points, range of motion (ROM)
tendons
connect muscle to bone
ligaments
connect bone to bone
cartilage
support and shapes, shock absorber
bursae
sacs filled with synovial fluid (cushion and reduce friction)
types of joints
pivot
condyloid
ball and socket
hinge
plane/gliding
saddle
sutures