biology - specialised cells, microscopes and maths
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
specialised cells
Define: Specialised cell
Cells adapted to carry out a particular function in the body.
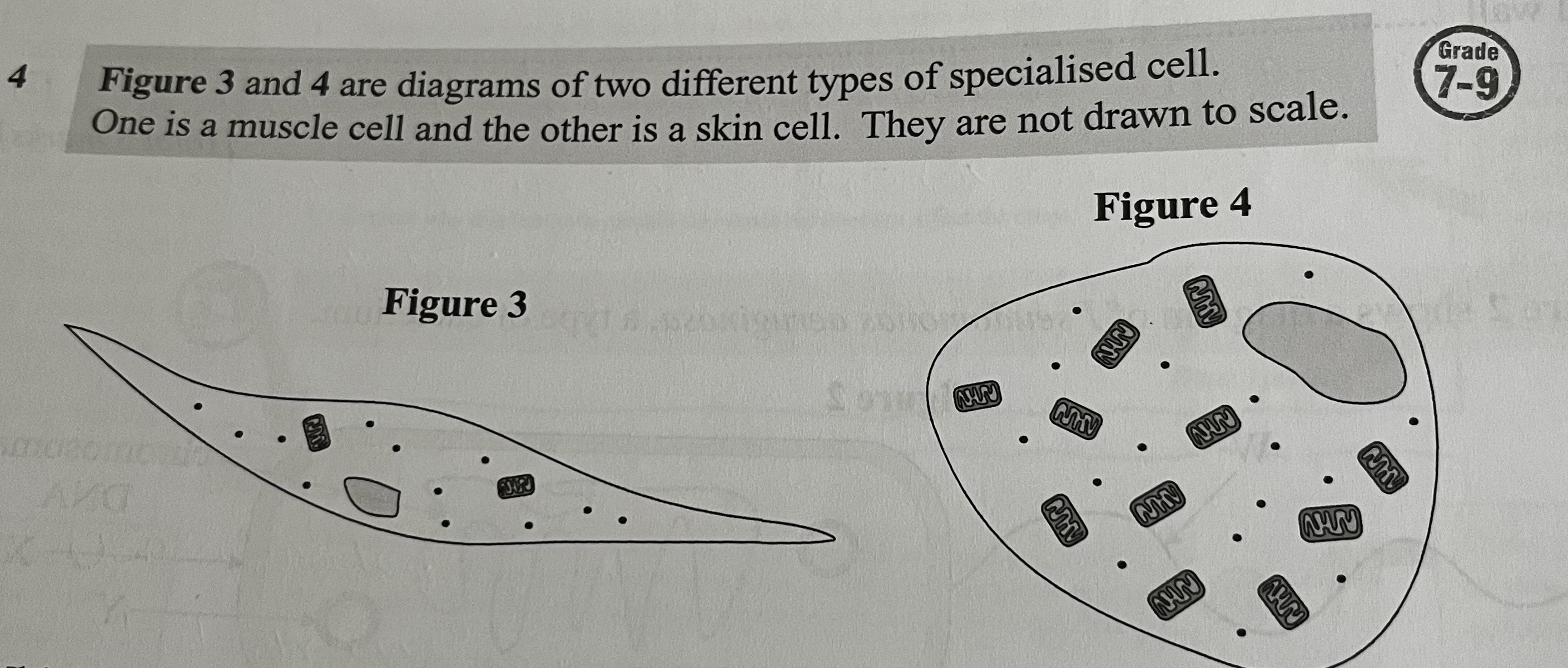
Which cell is more likely to be a muscle cell? Explain your answer.
Figure 4 since it contains more mitochondria. Muscle cells require a lot of energy to contract so will need lots of mitochondria as this is the site of respiration which transfers energy to the cell.
What are cilia?
Microscopic hairs that sway to move substances/particles (eg. lungs, nose and throat to move mucus and trapped dirt up and out of the airways)
flagellum
a tail that allows the cell to move
microscopes and magnification
Define: Magnification
The size of the image compared to the real size of the object.
A microscope has three different objective lenses - x4, x10 or x40. Which lens should a students select first when viewing her cells?
x4
Name the 2 types of microscopes.
ligh and electron microscopes
The microscope has two lenses.
An eyepiece lens with x10 magnification.
An objective lens with x40 magnification.
What is the total magnification of the microscope?
x400
State what can be added to a slide to make plant cells more visible.
Stain/dye such as iodine.
State the equation to calculate: Image size.
Image size = Actual size x Magnification
State the 2 equations to calculate: Magnification.
Magnification = Image size / Actual size or = Eyepiece x Objective Lens
State the equation to calculate: Actual size.
Actual size = Image size / Magnification
How many micrometres are in 1 mm?
1000
mathematics
how do you calculate surface area?
6a2
how do you calculate volume?
a3
in smaller organisms is the surface area:volume bigger or smaller?
bigger
formula for area of a triangle
½ x b x h