B2.3 Cell specialization SL (copy)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
How is a zygote formed?
Fusion of m + f gametes
What produces unspecialised cells?
After fertilization
Embryo
Ball of undifferentiated (unspecialised) stem cells
Produced when zygote undergoes mitosis several times (to produce genetically identical cells)
Differentiation
Process by which unspecialised cells become specialized for specific functions by acquiring specific structures
Unspecialised develop into specialised cells
What determines what type of tissue unspecialised cells will form?
Their location in the embryo
What is common betw all cells in the body?
Same genome
Are gene expression patterns the same across all cell types?
No
GE patterns are diff in diff cell types
What affects gene expression in an early stage embryo?
Gradients
Eg chemical gradients- morphogens
Influence which genes activated / suppressed in embryonic cells
Morphogens
Signalling molecules that form conc gradients in an embryo + control patterns of gene expression
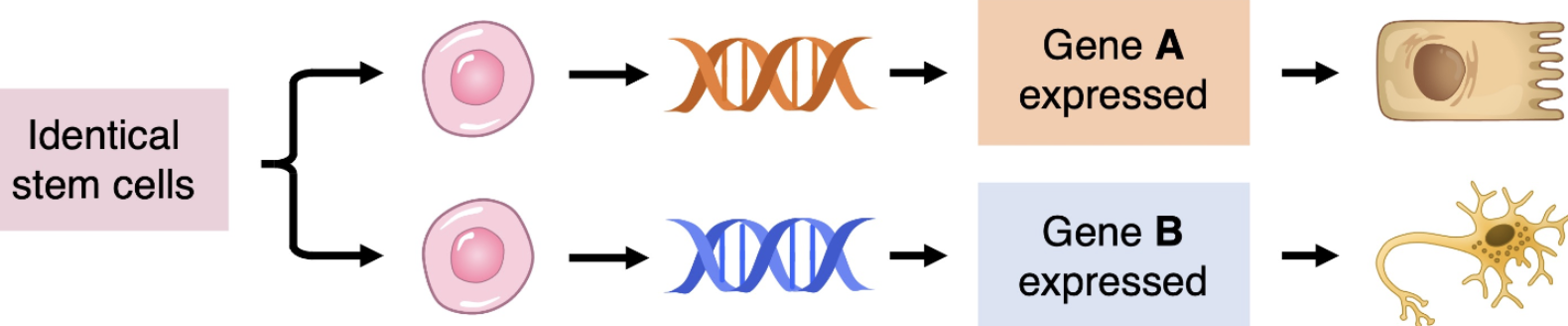
Impact of gradients on gene expression within an early-stage embryo
In early embryo, morphogens are distributed unevenly
Cells in diff positions within the gradient are exposed to diff concs
Varying concs trigger diff patterns of gene expression
Leads to cell differentiation
What happens to cells closer to where morphogens get releaed?
Get higher concs of morphogen → activates more genes
2 properties of stem cells
Capacity to:
Divide endlessly
To make more stem cells
Differentiate along diff pathways
Potency
The capacity to differentiate along diff pathways to become specialized
Endless self-renewal
Stem cell = unspecialized
But can go thru numerous cycles of cell division while maintaining the undifferentiated state
Stem cell niches
Locations that have SC in high concs
Provide an environment that allow SC to regenerate +/ differentiate
Location of stem cell niches in adult humans
Bone marrow
Hair follicles
Proliferation
Rapid increase in cell number
Function of stem cell niches in adult humans
SC niche can:
Maintain the cells
Promote their proliferation + differentiation
3 diff potencies of cells
Toti
Pluri
Multi
Totipotent
Can differentiate into any cell type
Including extraembryonic cells
Stem cells in early-stage animal
Pluripotent
Can differentiate into many (not all) body cell types
Not extraembryonic cells
SC in early-stage animal embryos soon become pluripotent
Multipotent
Can form a limited range (few) cell types
SC in adult tissue (eg bone marrow → blood cells)
Aspect of specialisation
Cell size
Cells have diff sizes, shapes functions
Closely related to function
Cell shapes in humans
Male gamete (sperm)
Female game (egg)
RBC
WBC
Neuron
Striated muscle fibres
Male gamete (sperm)- long + narrow
Female game (egg)- huge + rounded
RBC- 8μm (small), biconcave disc shape
WBC- larger, grow from 10-30μm when activated
Neuron- large cell body, long axon
Striated muscle fibres- long, multinucleated
Cell sizes in humans
Male gamete (sperm)
Female game (egg)
RBC
WBC
Neuron
Striated muscle fibres
RBC
WBC
Sperm
Egg
Neuron
Striated Muscle fibres
What limits cell size?
SA:V
What does the exchange of materials across a cell surface depend on?
Its area
What does the need for exchange of materials depend on (metabolism)?
Its volume
What happens to SA:V as a cell grows + why?
SA:V decreases bc V increases faster than SA
What does it mean if cells have a higher SA:V?
More efficient exchange → higher metabolism
Bc can exchange materials (O2, nutrients, waste) more efficiently across cell membrane
Models
Simplified versions of complex systems
Small cells = higher SA:V so more efficient. So why aren’t all cells as small as possible?
Need the correct no. + types of organelles to complete their specific roles
Risk of low SA:V (large cells)
If metabolic rate exceeds the rate of exchange of vital materials + wastes
Cell will eventually die
Why do growing cells tend to divide?
To remain small → can maintain high SA:V suitable for survival
Equation for a cube:
SA
V
SA = SA of 1 face x 6
V = LWH
Why are egg cells large?
So it contains all the nutrient materials needed for the early development of the embryo
Why are sperm cells small?
Easy to move (need less energy)
Why are RBC small + flexible?
Need to squeeze thru narrow capillaries
Adaptations of RBC
Small
Flexible
No nucleus – more space for haemoglobin
Biconcave – larger SA:V
Why are WBC larger than RBC?
So WBC can carry out phagocytosis on pathogens
Why are neurons long?
Allows for communication betw spinal cord + other distant parts of the body
How many nuclei do striated muscle fibres have?
Multinucleated
Stem cell
An undifferentiated cell which can give rise to more cells of the same type + differentiate along diff pathways
2 types of stem cells in humans
Embryonic
Adult