lab practical 2
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
what type of bacteria traps the crystal violet-iodine complex, which results in the purple color?
gram positive
in what type of bacteria does the thinner peptidoglycan and outer membrane allow the complex to be washed out, resulting in the pink color?
gram negative
is blood agar enriched, selective, or differential?
differential and enriched
blood agar ingredients
sheep’s blood
is macconkey agar enriched, selective, or differential?
selective (enteric gram-negative) and differential (ability to ferment lactose)
macconkey agar ingredients
selective- crystal violet and bile salts
differential- substrate lactose and pH indicator neutral red
is ccna enriched, selective, or differential?
selective (gram positive) and differential (hemolysis)
ccna ingredients
selective- colistin (polymyxin b) and naladixic acid (both antibiotics)
differential- 5% sheep’s blood
is s+s agar enriched, selective, or differential?
selective (enteric gram-negative) and differential (ferment lactose and reduce sulfates)
s+s ingredients
selective- bile salts, brilliant green dye
differential- neutral red pH
is msa enriched, selective, or differential?
selective (halotolerant organisms) and differential (ferment mannitol)
msa ingredients
selective- 7.5% nacl
differential- substrate mannitol (sugar alcohol) and pH indicator phenol red
5 steps for unknown isolation
observation of mixed culture by gram staining
obtain isolated colonies
use colony morphology/gram stain to distinguish your pathogen from your contaminant and identify pure colonies
inoculate a stock slant with bacteria from an isolated and pure colony
confirm the purity of your stock slants
iodine purpose
mordant
iodine step
2
safranin purpose
counterstain
safranin step
4
crystal violet purpose
primary stain
crystal violet step
1
ethanol purpose
decolorizer
ethanol step
3
heat fix purpose
adheres the bacteria to the slide surface
kills most microorganisms without destroying structural features
enables many stains to better penetrate or react with the microorganisms
heat fix step
6
drying purpose
must be done before heat fixing to prevent the microorganisms from being boiled and destroying structural features needed for staining
drying step
5
both purple and pink stained, with same morphology- pure or mixed?
pure
pure or mixed- both purple and pink stained rods and cocci
mixed
only purple rods- pure or mixed?
pure
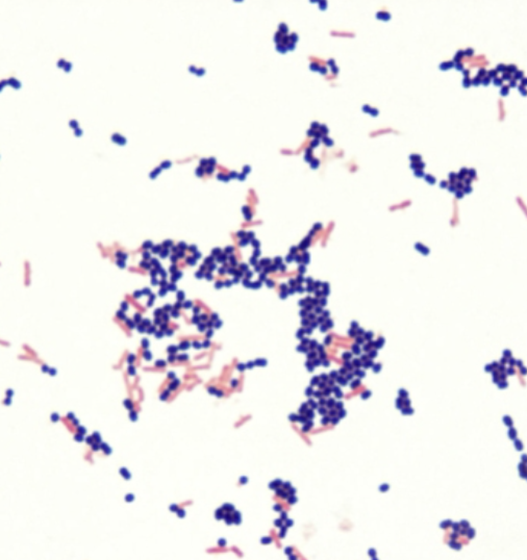
gram stain, gram reaction, shape, arrangement
gram positive cocci clusters
gram negative single rods
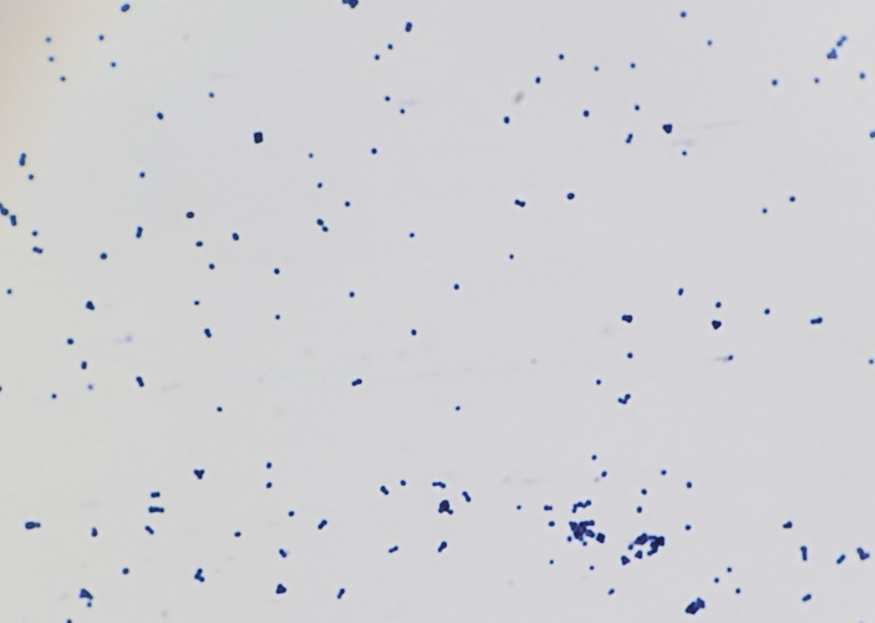
shape, gram type, arrangement; is it a pure culture?
gram positive single cocci; pure
what aseptic techniques are needed for identifying unknown organism?
why are aseptic techniques important?
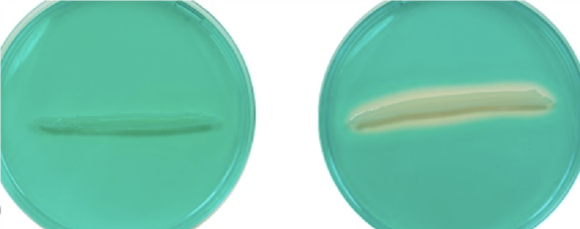
identify test. positive or negative? what identification pathway are these tests a part of?
DNAse; negative, positive; gram positive
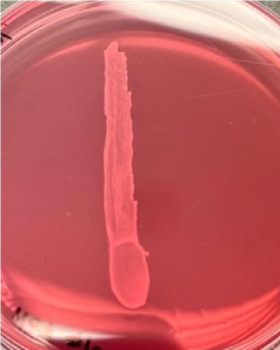
identify test. positive or negative? what identification pathway are these tests a part of?
identify test. positive or negative? what identification pathway are these tests a part of?
mannitol salt agar (msa); organism can ferment mannitol; gram positive
how to know if a test is catalase positive?
it bubbles
would you use a catalase test on gram negative or gram positive organisms?
gram positive
what does the catalase test stand for?
based on how organisms detoxify hydrogen peroxide; differentiates staphylococcal (+) from streptococcal/enterococcal (-)
what tests would you use for a gram positive, catalase negative organism?
Blood agar, SXT antibiotic, BEA slant, PYR Broth
what test would you use for a gram positive, catalase positive organism?
Mueller Hinton Agar plate; Novobiocin antibiotic disk; DNAse Agar plate; Mannitol Salt Agar plate; PYR broth
what test would you use for a gram negative organism?
Triple-Sugar Iron (TSI) slant; Microgen GNA-ID panel
beta hemolysis
complete lysis- complete clearing of blood around colonies
alpha hemolysis
partial lysis; greenish-gray/yellow around colonies
gamma hemolysis
no hemolysis; no change in medium
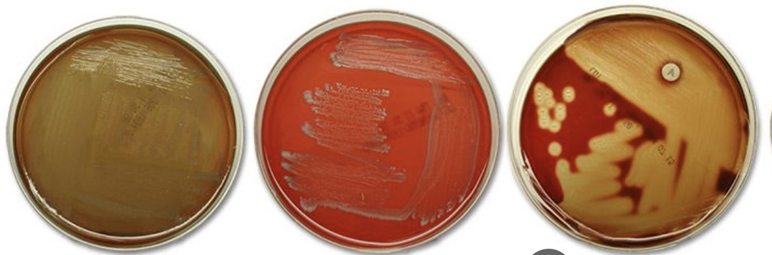
identify the hemolysis
what does well 7 test for? how do you interpret the results?
Presence of beta-galactosidase activity; if well turns yellow, there is activity.
Presence of nitrate reductase; red indicates presence of nitrites (positive for nitrate reduction); zinc- red means negative for nitrite reduction, no color- positive for nitrate reduction
if a tsi slant has a black discoloration on the slant, does that mean it is acidic or alkaline?
acidic
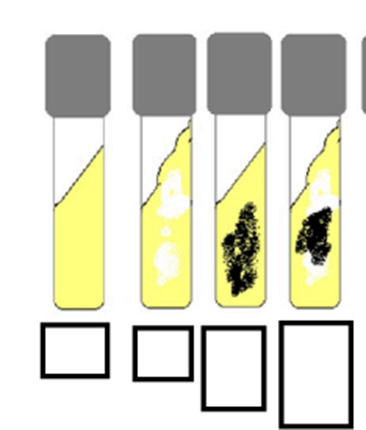
interpret the tsi
A/A, CO2 -, H2S -
A/A, CO2+, H2S -
A/A, CO2- , H2S+
A/A, CO2+, H2S+
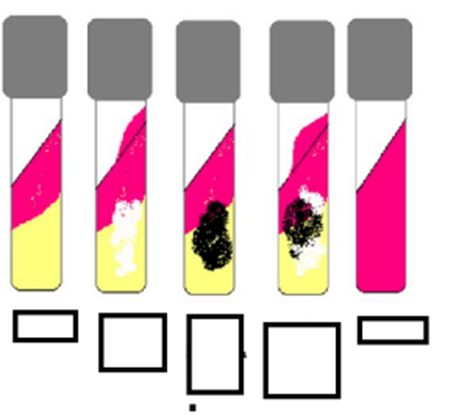

interpret the tsi
A/K, CO2-, H2S-
A/K, CO2+, H2S-
A/K, CO2-, H2S+
A/K, CO2+, H2S-
K/K, CO2-, H2S-
if your organism produces acid for both the butt and slant on a tsi slant but doesn’t grow pink (lactose fermenting) colonies on mac, why might this occur?
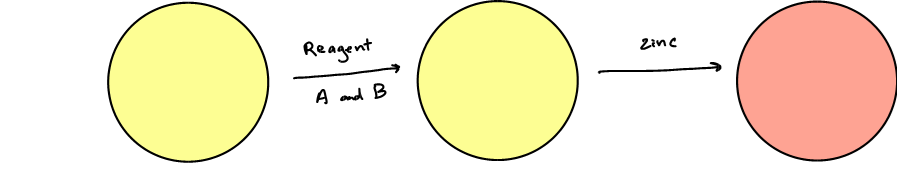

interpret nitrate well
Nitrate reduction negative
which wells on the gram negative test strip require reagents before reading?
8, 10, 12
what pH indicators are used within the different wells?
Bromthymol blue, phenol red,
describe the differences in methods and testing between a kirby-bauer test and an e-test
kirby-bauer test- assess bacterial sensitivity to antibiotic
e-test- determine a specific antibiotics’ minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)
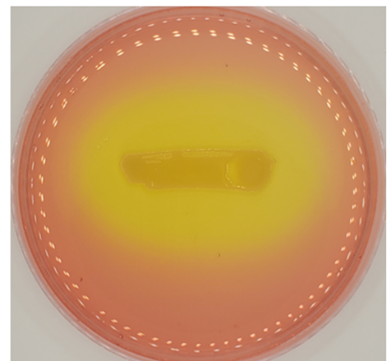
what is the zone of inhibition for the antibiotic?
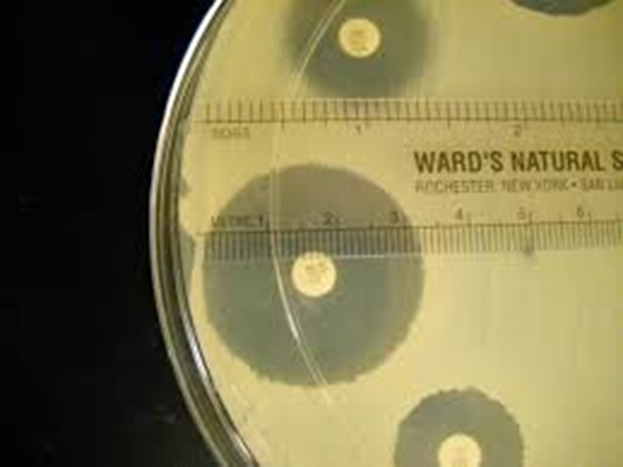
36 mm
what is the zone of inhibition for the antibiotic?
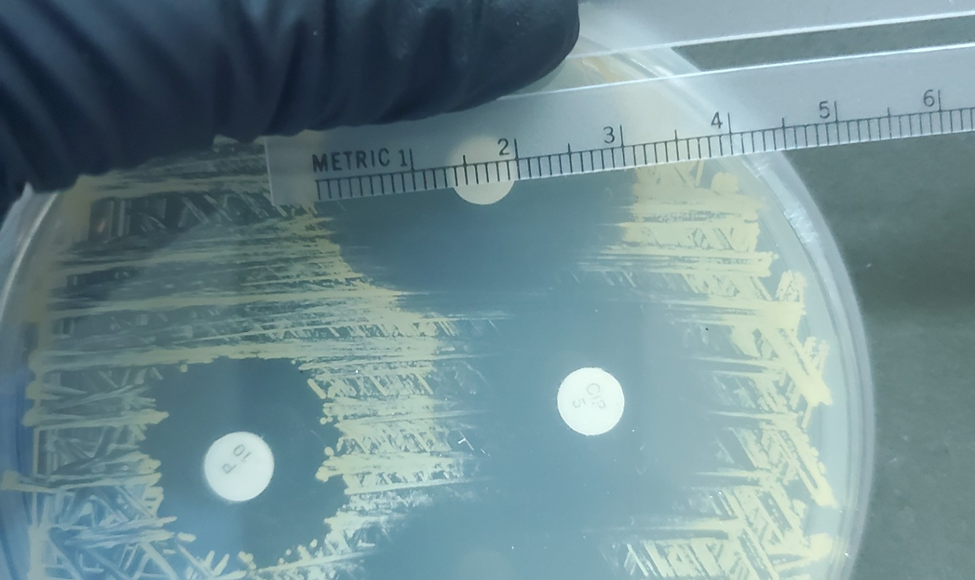

31 mm
how would you measure the zones of inhibition for this test? what is this test?
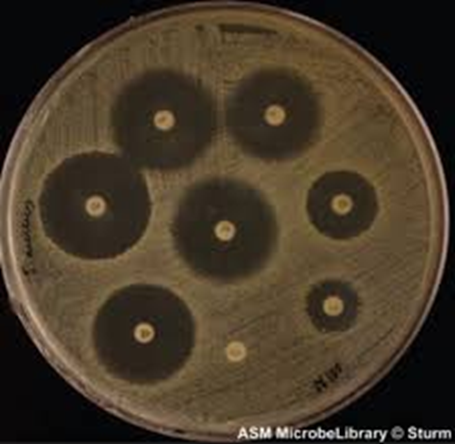
measure diameter when possible, measure radius and double if unable to measure diamter
why would e. coli and s. aureus show different sensitivity to the same beta-lactam antibiotic?
how does the structural difference between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria affect the zone of inhibition observed with different chemical agents, and why might a chemical be effective for disinfection but not antisepsis?
what is the difference between broad-spectrum and narrow-spectrum drugs?
what is the MIC for the given E-test? ug/mL

what is the MIC for the given E-test? ug/mL
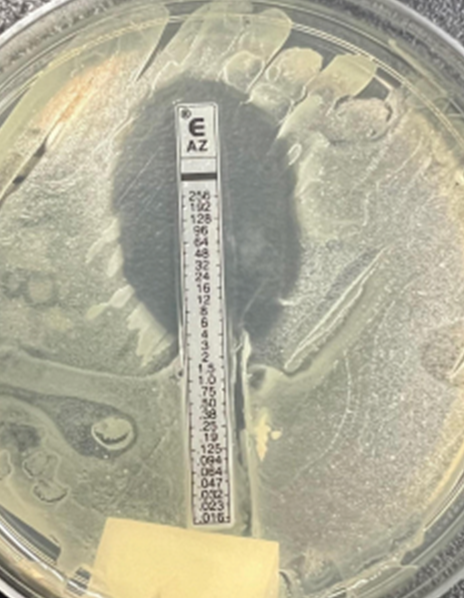
what is the minimal inhibitory concentration on the picture below?
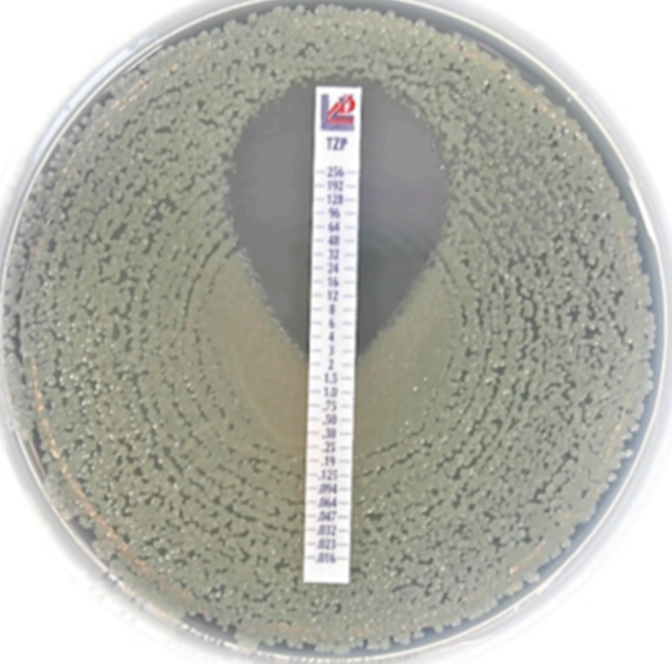
various chemical tests were tested on an organism. which chemical is most effective against the pathogen based on the following zones of inhibition?
· Chemical 1: 25 mm
· Chemical 2: 3.6 cm
· Chemical 3: 0.3 cm
· Chemical 4: 12 mm
given this disk diffusion assay, rank each chemical in terms of sensitivity.
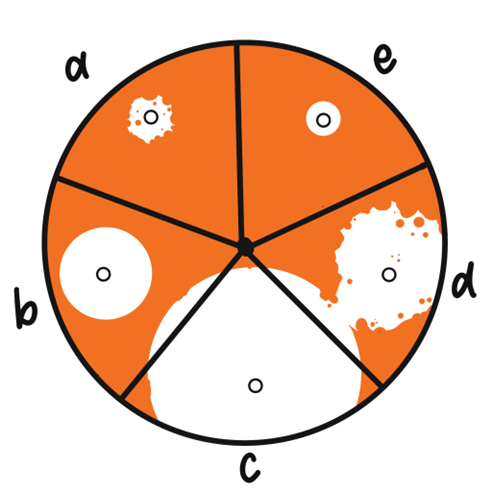
for the following chemical testing, which of the 3 bacterial species shown are most susceptible to the chemical?
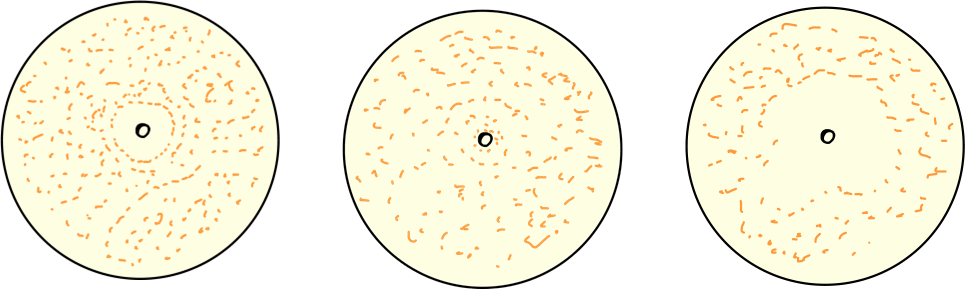
does gram reaction result determine the effectiveness that some chemicals will have against the bacteria? why?
what structures enable gram-negative bacteria to be more resistant, generally, to most chemical agents?
what chemical class impacted your bacteria the most? why do you think that is?
after placing filter disks on an agar plate, what happens to the chemical as it diffuses into the agar?
what are some environmental factors that affect the effectiveness of a chemical?
disinfection
antisepsis
sanitization
why might a chemical be effective for disinfection but not for antisepsis?
hydrogen peroxide class
oxidizing agent
when to use hydrogen peroxide
spores, fungus, strep, etc
ethanol class
when to use ethanol
cavicide class
when to use cavicide
bleach solution class
when to use bleach solution
mouthwash class
when to use mouthwash
what occurs to DNA in the thermocycler?
what is thermocycling and why is it important when running a PCR gel?
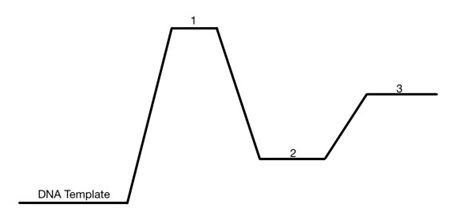
name the steps of PCR at numbers 1, 2, and 3 and the temperature that each step occurs at
why might no bands appear after running a PCR? how might this be avoided?
what was placed in the well before running the gel electrophoresis?
what are the approximate sizes of the bands in this gel?
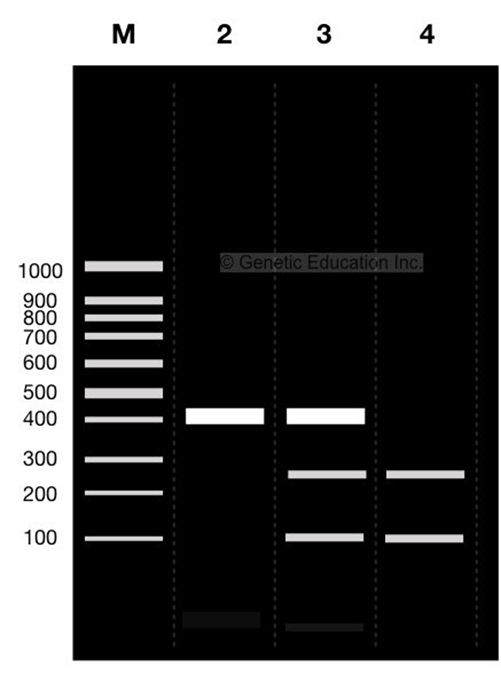
what are the approximate sizes of the bands in this gel?

what gene was amplified for our PCR reaction?
what advantage does 16S rRNA PCR have over traditional biochemical identification methods?
it is faster and more sensitive
thermocycler purpose
SybrSafe DNA dye purpose
16S rRNA primers purpose
why do fermented foods have longer shelf lives and are less prone to spoilage?
what is the first bacterial strain added during fermentation?
what is the second bacterial strain added during fermentation?