Atoms and Modern Atomic theory
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
atom
the smallest particle into which an element (matter) can be divided. Made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons
theory
an explanation for a range of hypotheses and observations that have been supported through testing.
Democritus
Greek philosopher, proposes first idea of the atom--that you'd eventually reach a piece of matter that you couldn't cut in half anymore.
Dalton
English scientist and teacher (late 1700s), proposes first 3-part atomic theory: 1. everything is made of atoms, 2. atoms of the same element are exactly alike and atoms of different elements are different, 3. atoms join together to make new substances (compounds). Also proposed the first atomic model--a sphere
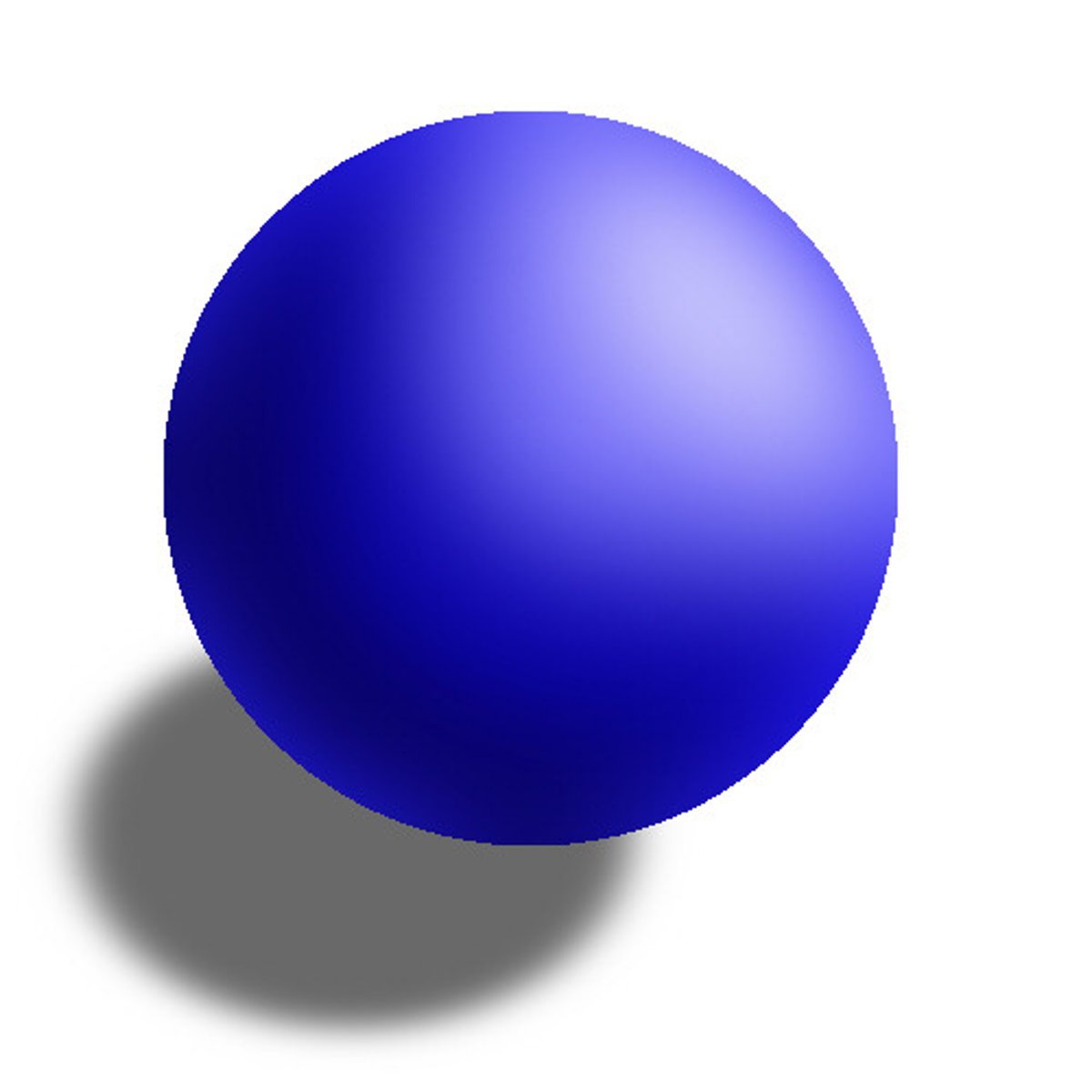

model
a representation of an object or system that is either too large or too small to be observed in the science lab.
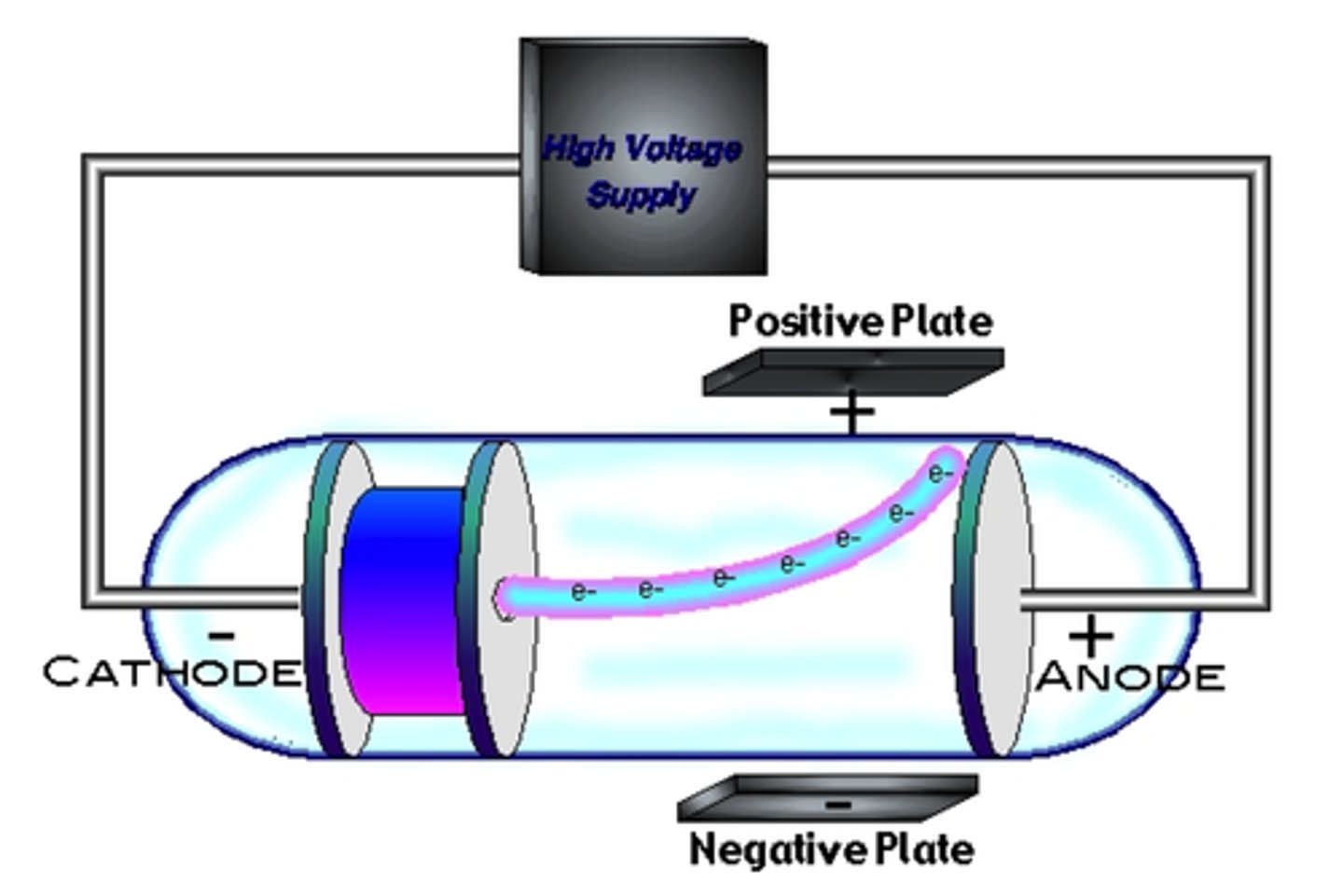
Thomson
Discovers the electron in 1897. JJ Thomson uses a cathode ray tube to make a beam bend using positive charges. Plum-pudding model
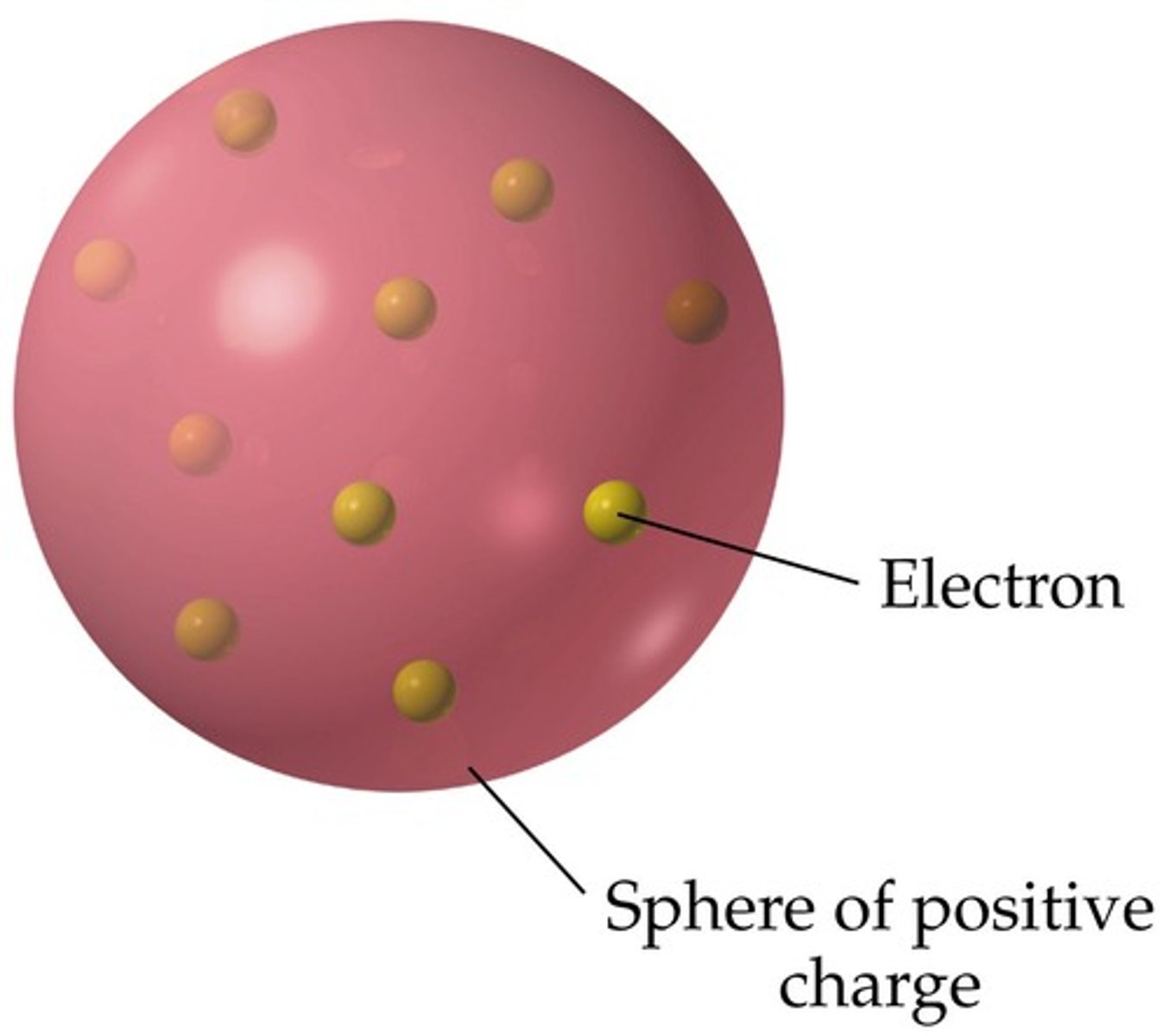
Plum pudding model
JJ Thomson's model: the atom consists of mostly positive material and the electrons are spread around the surface of the positive material. More like chocolate chip cookie dough/ice cream today.
electron
the very small negatively charged particles of an atom, move around the nucleus of the atom.
Rutherford
1909, Rutherford (Thomson's student) discovers the nucleus through his gold foil experiment. Creates new atomic model.
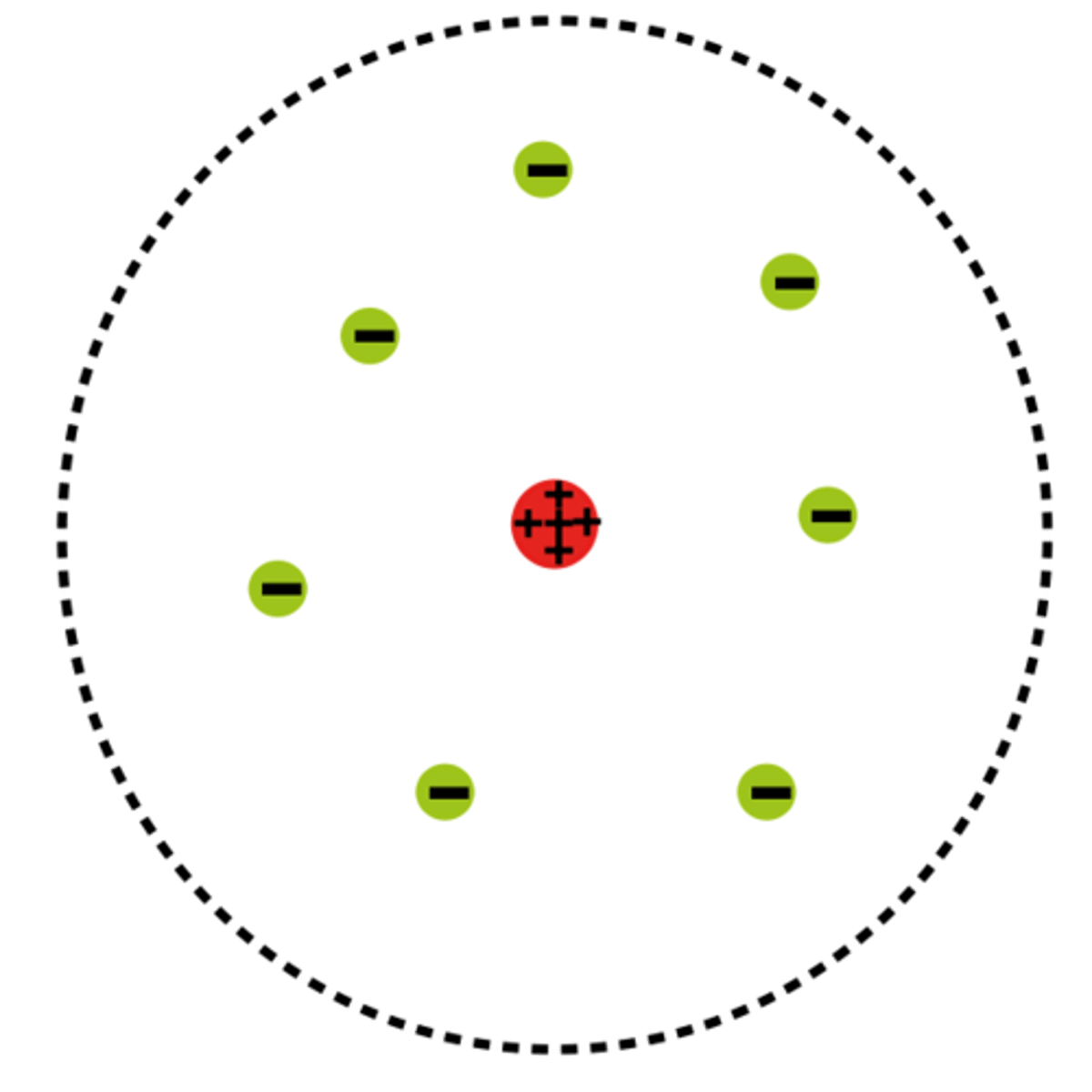
nucleus
the small, densely packed and positively charged center of the atom. Made up of protons and neutrons
Bohr
1913 Niels Bohr suggests that electrons travel in very definite paths around the nucleus and at different levels. Still a very common model due to its simplicity.
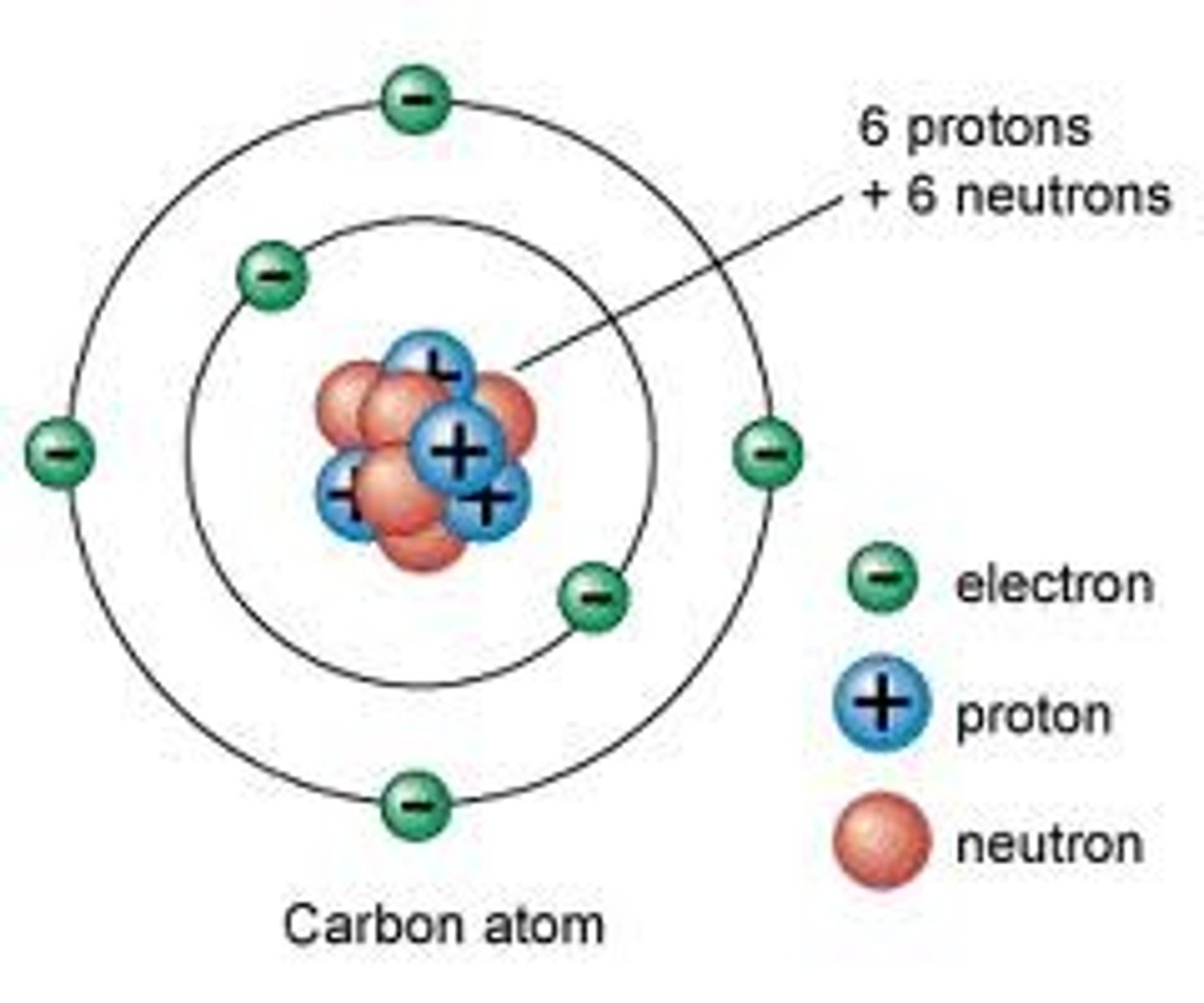
Modern Atomic Model
Schrodinger and Heisenberg were major contributors to the modern atomic model: THE ELECTRON CLOUD MODEL
electron clouds
regions surrounding the nucleus where the electrons are LIKELY to be but the exact location of the electron cannot be predicted.
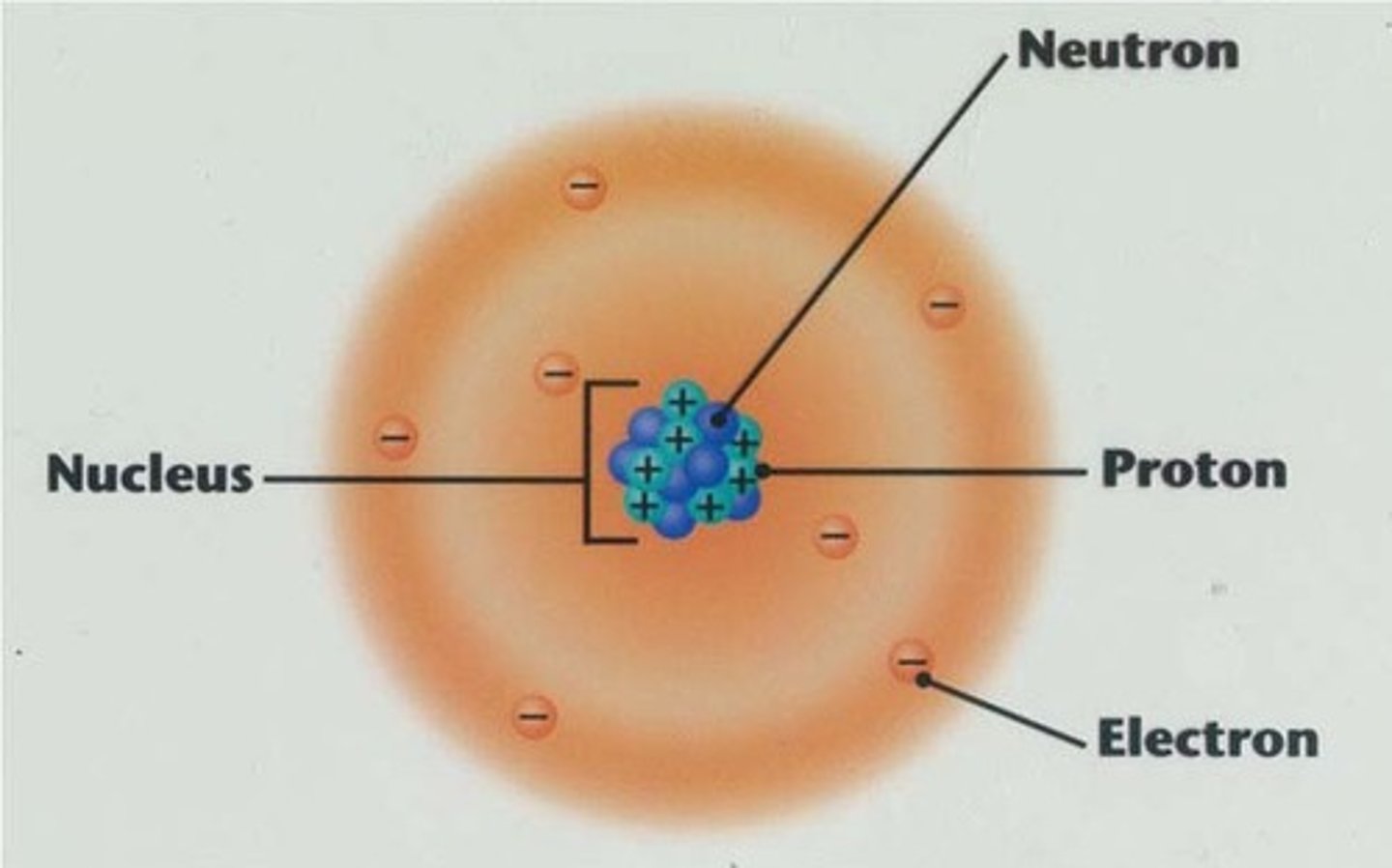
protons
the positively charged particles of the atoms.
atomic mass units
amu's the unit used to measure the mass of the atom. 1 proton has a mass of 1 amu, 1 neutron has a mass of 1 amu
neutron
neutral part of the atom, found in the nucleus, has a mass of 1 amu
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
mass number
the sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus
atomic mass
The average mass of all the naturally occurring isotopes of an element
isotope
An atom with the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons from other atoms of the same element.