Microbio Lab Exam 1
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
order these: nm mm um
from smallest to largest
nm, um, m
order: fungi, protozoa, virus, and bacteria
from smallest to largest
virus, bacteria, protozoa, fungi
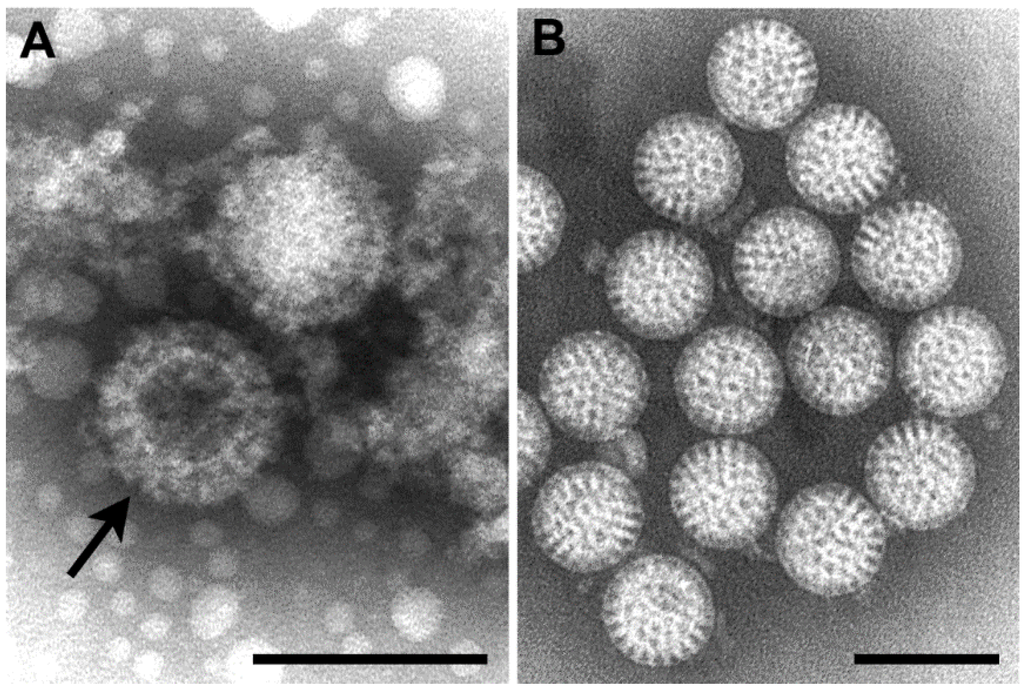
what microbe is this
virus

what microbe is this
bacteria
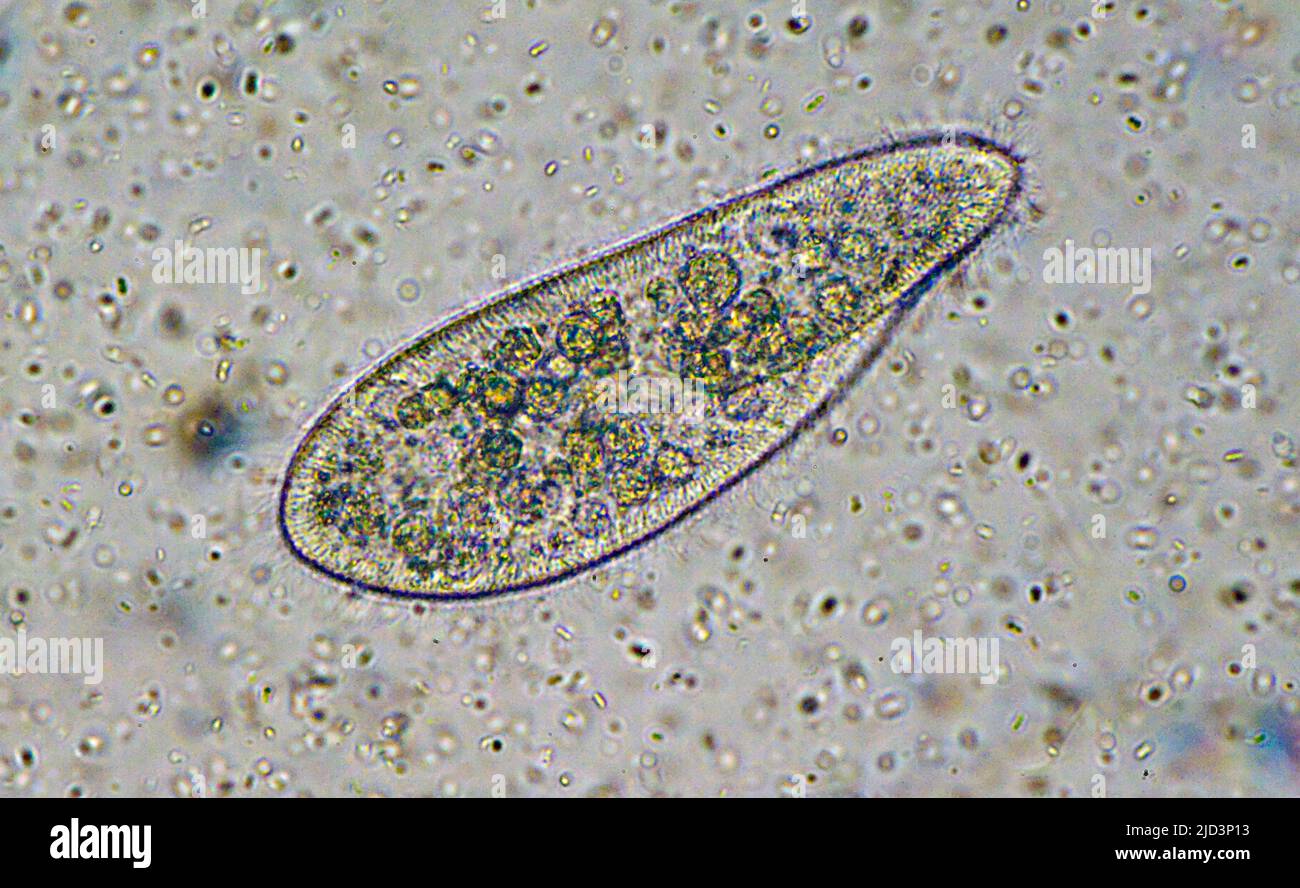
what microbe is this
protozoa
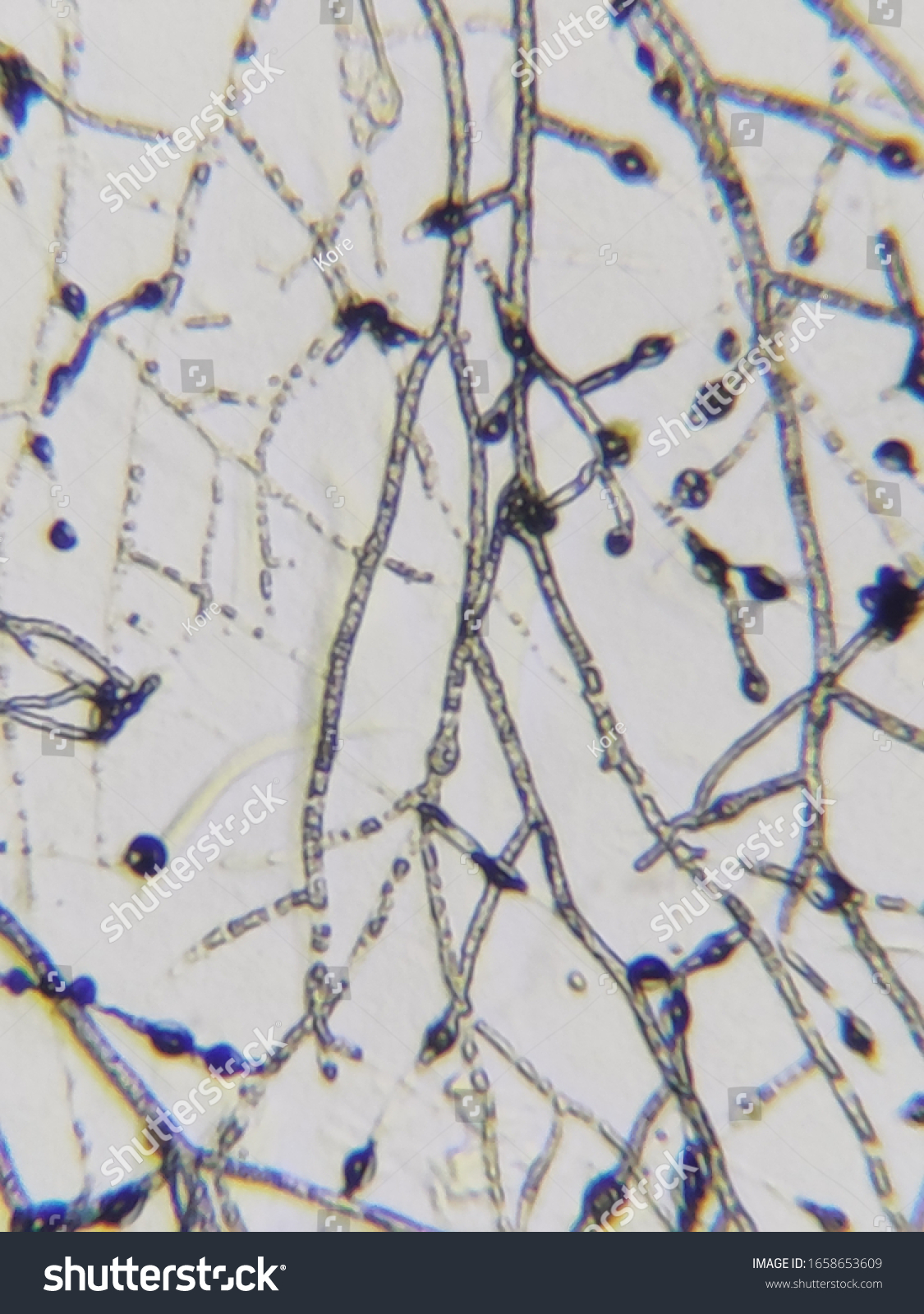

what microbe is this
fungi
what characteristic might fungi have
hyphae
which microbe requires a host cell to replicate their genomes
viruses
which microbes may be multicellular
fungi
which ones have a cell wall
bacteria (peptidoglycan) and fungi (chitin)
which ones have organelles
protozoa and fungi
what is procedure for streaking for isolation
label cultures
mix the broth culture by flicking the eppendorf tube with your finger several times
Flame your inoculating loop, then aseptically remove a loopful from the broth culture tube labeled “MIX”; streak the loopful in a line (going back and forth), then streak across the first quadrant of the TSA plate to the next to connect them
(just barely)between each quadrant flame the loop and continue to streak plate as did in 3 (DO NOT GET MORE culture)
do until all 4 quadrents are done (do not connect quadrant 4 and 1)
flame loop
why do we streak for isolation
to isolate a cell (by diluting the sample that creates a lawn)
define a colony
a group of genetically identical cells that are derived from the same mother cell
what does a fungi colony look like
hairy
what does a bacteria colony look like
perfectly circular
The ability to prepare and maintain cultures that are completely pure and contamination-free requires what
Good aseptic technique, Correct streaking for isolation, Proper flaming of your loop
which gram stain has LPS/which color
gram negative, red
which gram stain has LTS/which color
gram positive, purple
what cell wall do gram negative bacteria have
thin and multiple
what cell wall do gram positive bacteria have
thick, 1 wall
what do cocci look like
circles
what doe bacilli look like
pills, long cylindrical
what do vibrio look like
c or comma shapped
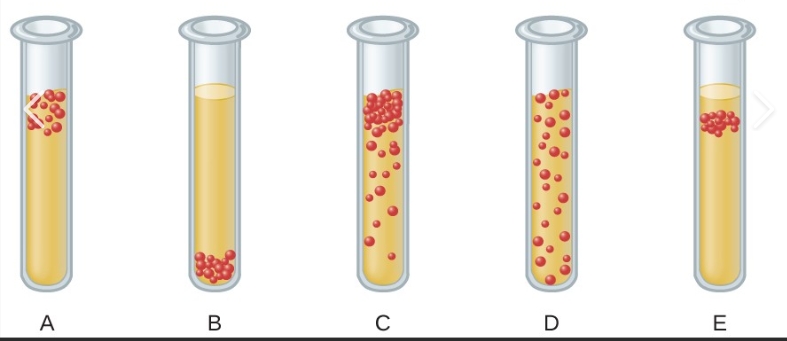
which is obligate aerobe
a

which is obligate anaerobe
b
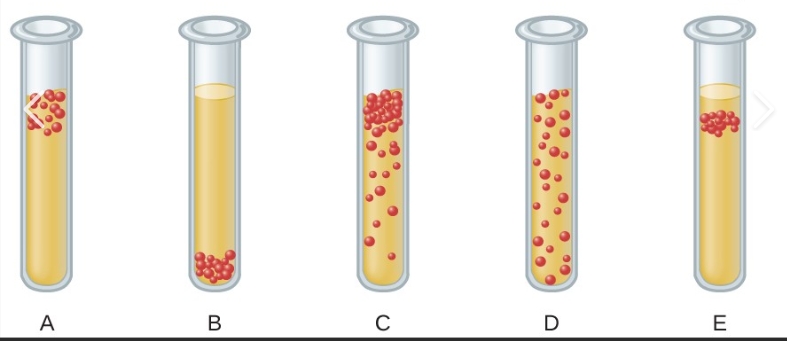
which is facultative anaerobe
c
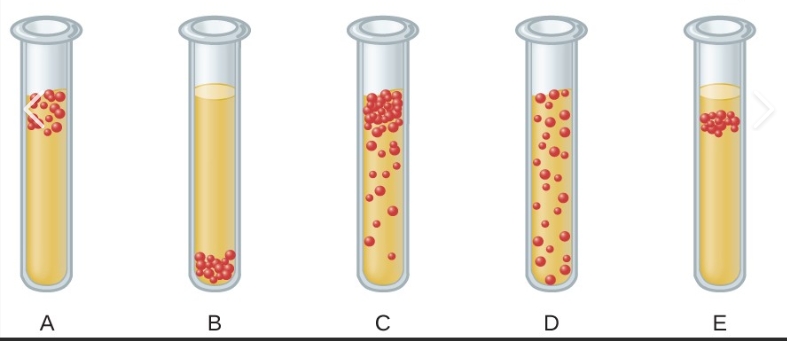
which is aerotolerant anaerobe
d
what does obligate aerobe mean
cannot grow if no O2
what does facultative anaerobe mean
can grow with out without O2 but do better with O2
what does aerotolerant anaerobe mean
O2 has no effect on growth
what does obligate anaerobe mean
cannot grow if there is O2

which ones can produce gas within the agar
2, 3, 4
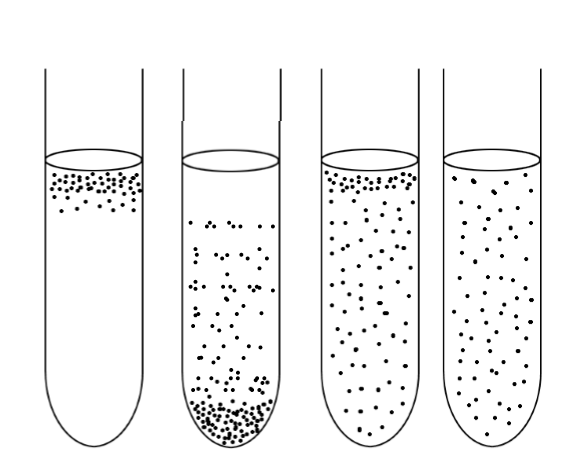
which one is a facultative anaerobe
3
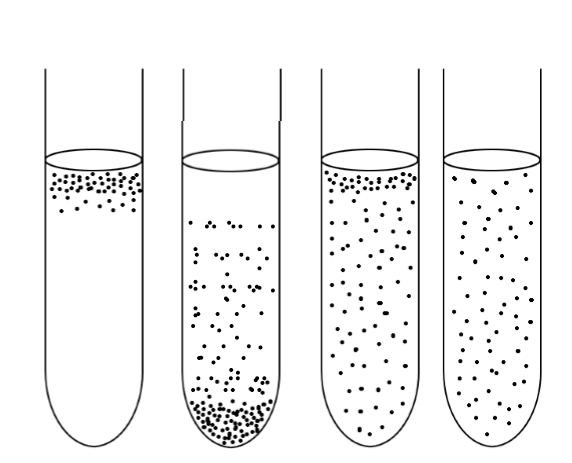
which one will die if exposed to O2
2
what is a countable plate (for bacteria)
has 20-200 colonies

which plate is countable
40

how many CFU/ml are in original inoculum
4×10^6 CFU/ml
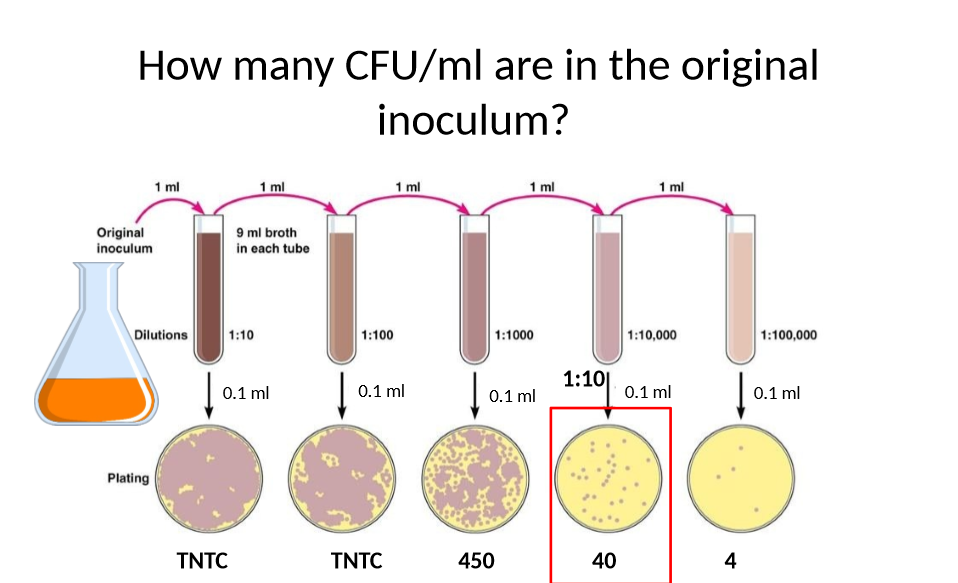
How do you get how many CFU/ml are in original inoculum
put 40 in scientific notation: 4×10^1
then for each vial add to the 1, including the origianl beaker
so since 5 in this example, add 5+1=6
final answer: 4×10^6 CFU/ml
what are viruses
nonliving, packages of protein and genetic material, requiring host cells for their replication
what genetic material do viruses use
DNA or RNA
what is a capsid
shell made of interlocking proteins
what are optional components in viruses
envelope: membrane on outside of capsid, not all viruses have one (no envelope=naked)
enzymes: packaged with viruses ex RT or RDRP
what are different capsid symmetry/shapes
helical
icosahedral
are there any clinically relevant naked helical viruses
no
what is this viruses shape/envelope status
enveloped icosahedral

what is this viruses shape/envelope status
helical enveloped

what is this viruses shape/envelope status
naked icosahedral
what does the genome in viruses look like (all different ways it can exist)
DNA or RNA
linear or circular
segmented or non-segmented
single or double stranded
negative or positive sense
what is RDRP enzyme
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, necessary for production of virus genome and proteins in negative sense viruses
what is RT enzyme
reverse transcriptase, necessary for formation of DNA from RNA in retroviruses
why do some viruses have no enzymes
they don’t need them, ex: positive sense viruses
what is an acute viral infection
rapid and self-limiting, virus causes symptoms quickly after infection but is recognized and cleared by immune system (ex: influenza virus)
what is a persistent viral infection
initial infection is not cleared by immune system, and low viral numbers remain in body, can last months or years at low levels, then another infection occurs later in life, characterized by high viral numbers (ex: HIV)
what is a latent viral infection
virus infects host and is cleared, but its genome remains within host cells, months/years later, second infection occurs and is characterized by high viral numbers (ex: Herpes/cold sores)
what is the central dogma theorem
DNA→ RNA→ Protein
what is Transcription
DNA to RNA
DNA bases: A, T, C, G
RNA: all same but U instead of T
promoter
terminator
What is translation
mRNA to protein
ribosome: translates 5’ to 3’
start codon (5’AUG3’)
stop codon (5’UAA/UGA/UAG3’)

how many operons
how many promoters/terminators
how many genes
how many start/stop codons
3
4
8
8
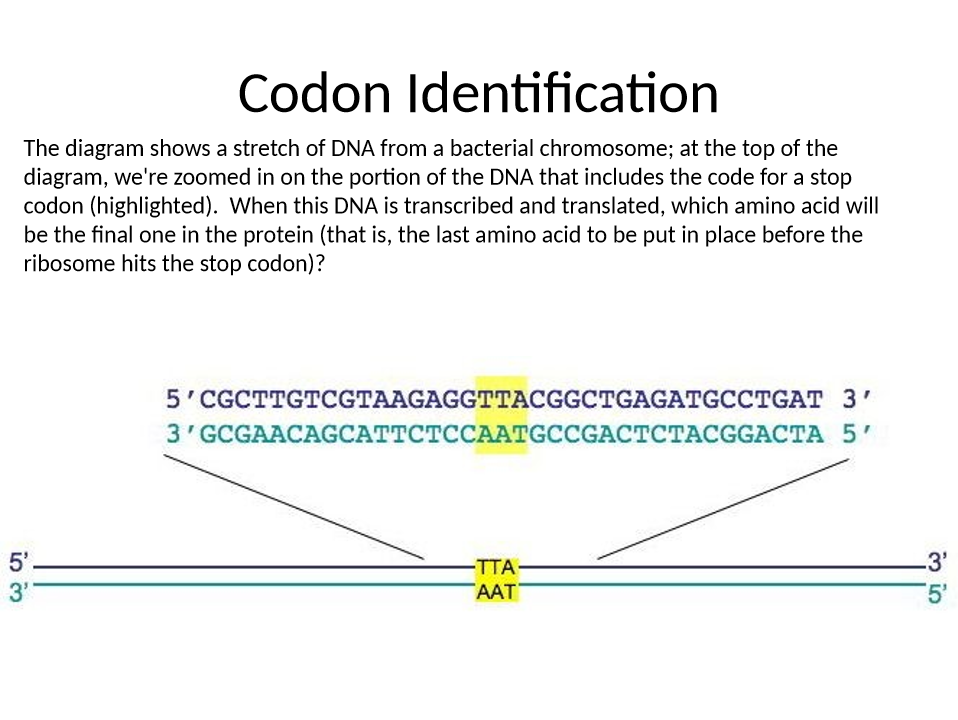
which amnio acid will be the final one in the protein?
CCG
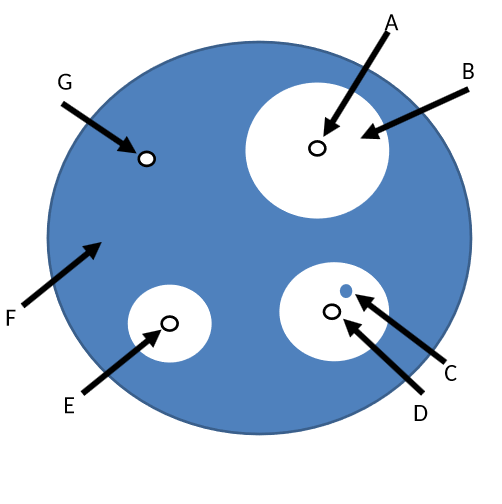
what is the zone of inhibition
B
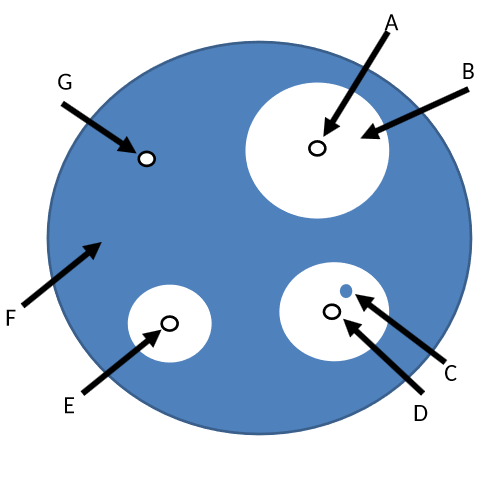
what is the disk with the lowest concentration of triclosan
G

what can you tell about colony C (of triclosan)? and why
it is triclosan resistant, because it is growing inside the zone of inhibition
what is a point mutation
a single nucleotide is changed to a different nucleotide (ex: silent, missense, and nonsense)
what is a silent mutation
new codon codes for same amino acid (protein functions normally)
what is a missense mutation
new codon codes for new amino acid (protein may or may not function properly)
what is a nonsense mutation
new codon codes for a stop codon ends protein early (protein will not function properly)
what is frameshift mutation
a base is added to or deleted from the sequence, changing reading frame so every amino acid that follows is incorrect (protein will NOT function properly)
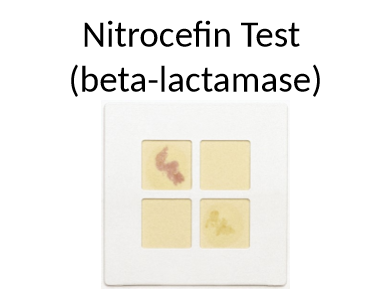
what does the yellow and pink tell us
yellow: negative for beta-lactamase
pink: positive for enzyme

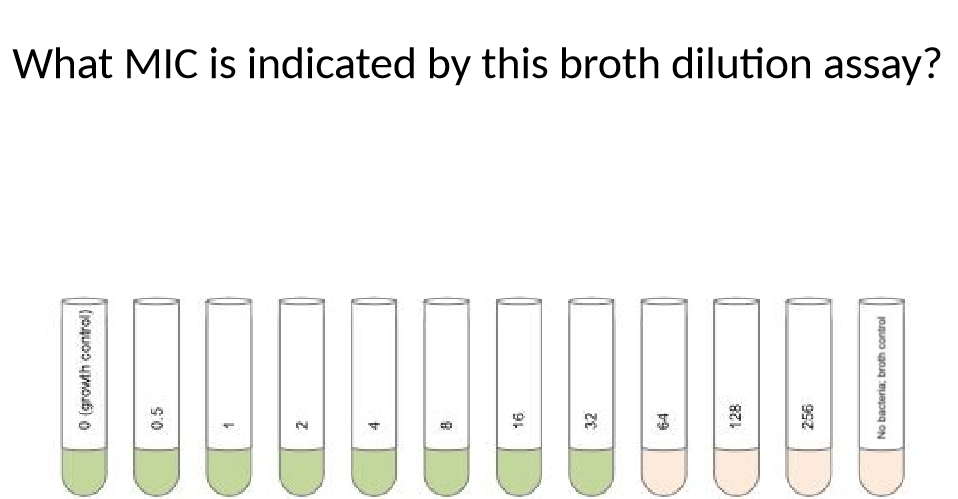
what MIC is indicated by this broth dilution assay
64
if the isolate has a MIC of 5 which tubes will still show bacterial growth
0-4
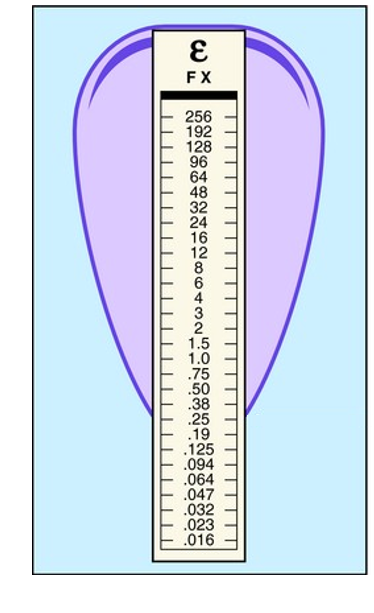
what is the MIC indicated by this E-test
0.25
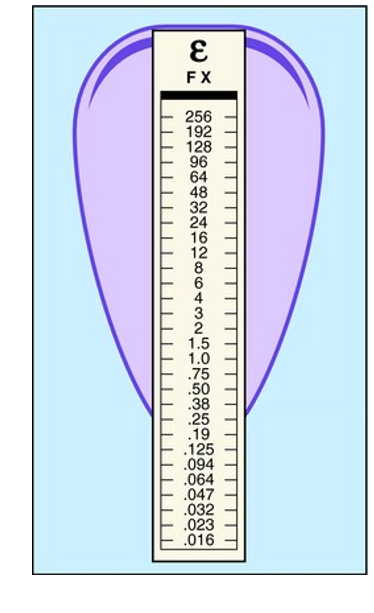
Standards for this organism consider less than or equal to 0.5 to be sensitive and greater than 0.5 to be resistant, is it likely that this patient can be successfully treated with ampicillin?
yes, MIC is below 0.5
what does kirby-bauer test for
susceptibility to antibiotics based on inhibition zone diameter
(antibiotics act on specific bacterial components, antibiotics are used to treat an infected host)
what do disinfectants do
disinfectants can be analyzed by zone of inhibition (kirby-bauer)
disinfectants act non-specifically on a large group of components (such as lipids of plasma membranes)
disinfectants are used to control organisms before host entry
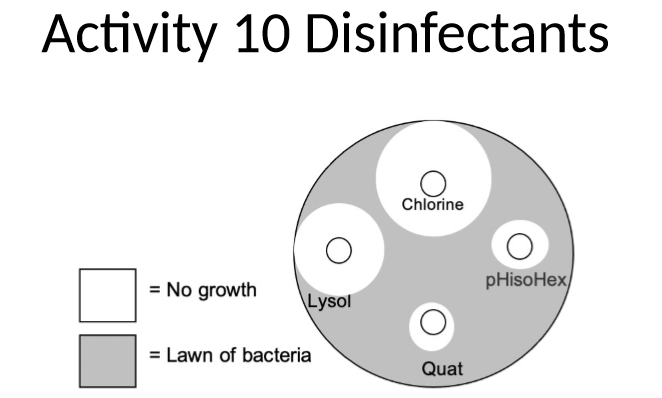
which disinfectant is most effective against this organism
chlorine
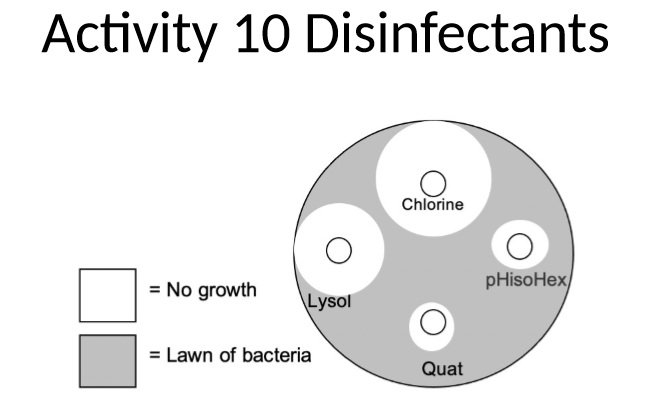
which disinfectant is least effective against this organism
quats