Intro to Biogeography
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biogeography
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Define biogeography
Scientific study of spatial patterns of biological diversity.
Biogeographers ask questions relating to:
Why are ____ as they are?
What ___ were involved?
What factors affect ____ and overall ___ of organisms?
Why are organisms distributed as they are?
What processes were involved?
What factors affect species diversity and overall abundance of organisms?
Thus, studying:
Patterns of _____ and ____ , and
The ____ affected the ____ (ex: continental drift extinction)
Patterns of distribution and abundance, and
The processes affected the patterns (ex: continental drift extinction)
This information can be applied toward predicting ______ and the ______ of organisms to various changes.
This information can be applied toward predicting future changes and the adaptability of organisms to various changes.
Scientific Study of Biogeography:
Biogeography is very much an ____ and ___ science.
Biogeography is primarily dependent on observational data.
Why does it mostly use ____ data?
Biogeography is very much an integrated and synthetic science.
Biogeography is primarily dependent on observational data.
Why does it mostly use observational data?
Scope of Course:
Focus on the factors affecting _____ of organisms.
In doing so, learn some of the _____.
Focus on the factors affecting distributions of organisms.
In doing so, learn some of the biogeographical patterns.
What processes influence the distribution of organisms?
extinction
dispersal
speciation
plate tectonics
glacial cycles
Factors affecting _____ are a combination of ____ and ____factors, both _____ and ____.
Factors affecting distribution are a combination of biotic (living) and abiotic (nonliving) factors, both historical and present.
Types of biogeographical study:
a. Ecological biogeography
b. Historical biogeography:
b1. Vicariance biogeography
b2. dispersalist biogeography
a. Ecological biogeography
Primarily deals with current distribution patterns in relation to ecological conditions.
b. Historical biogeography
Historical biogeography = paleobiogeography
Primarily deals with distributions of past organisms, including how past taxa originated and dispersed.
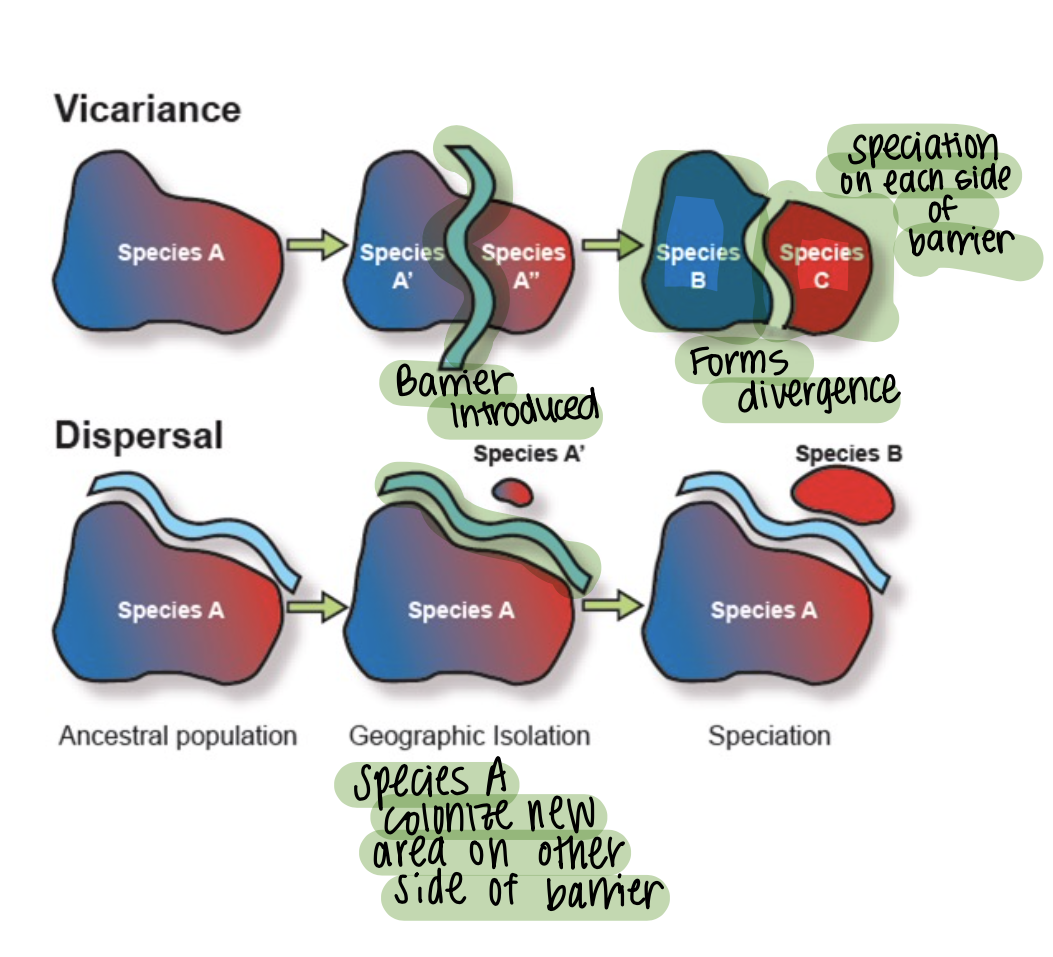
b1. Vicariance biogeography
Emphasis is on new barriers separating previously connected populations. (allopatric speciation)
(“Barrier placed in the middle which creates two different species”)
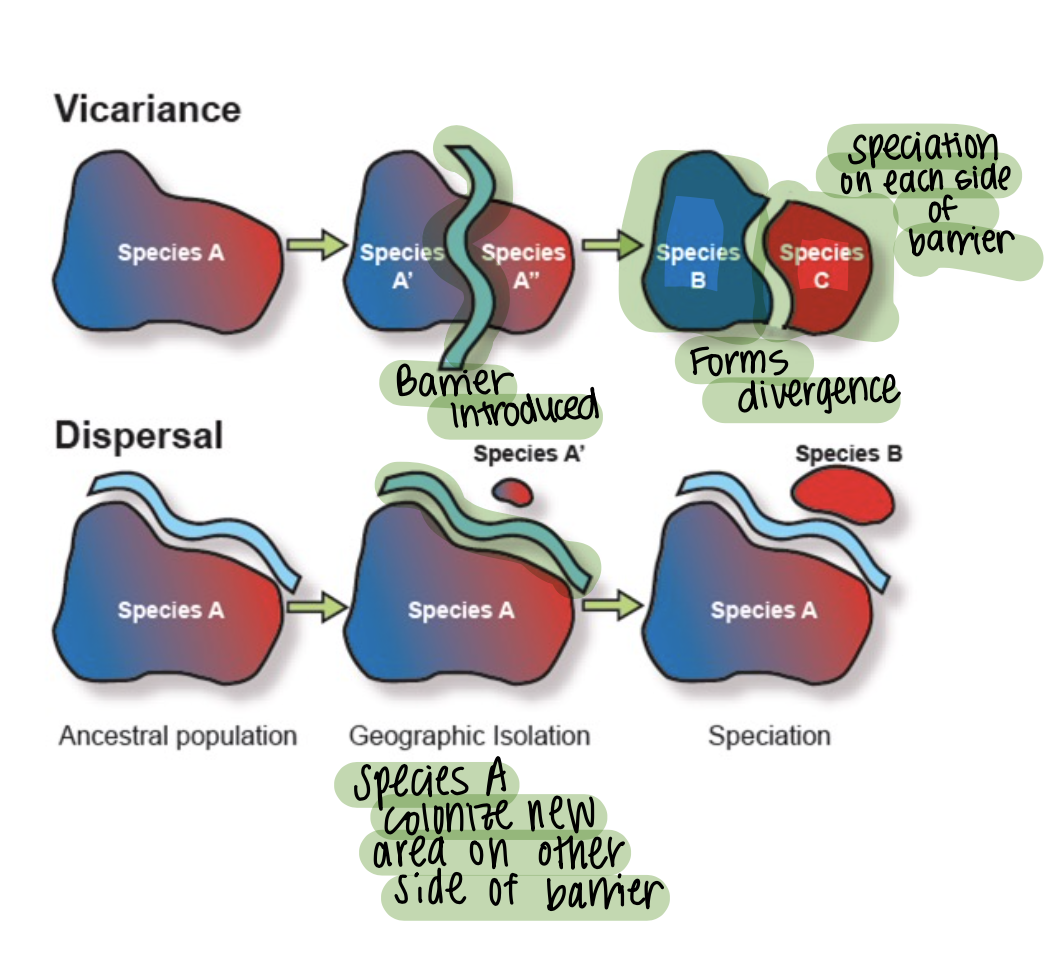
b2. Dispersalist biogeography
Dispersalist biogeography = migrationist biogeography
Emphasis is on species dispersing across a “barrier”.
(“Species move across a barrier.”)
Taxon =
Taxa =
Taxon = looking at one focal groups
Taxa = looking at two or more focal groups