ch 25 acid base fluids
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
Body Fluid Percentage
Human body fluid ranges from 45% to 75%.
Intracellular Fluid (ICF)
Fluid within cells, two-thirds of total body fluid.
Extracellular Fluid (ECF)
Fluid outside cells, includes interstitial fluid and plasma.
Interstitial Fluid (IF)
Fluid surrounding cells, two-thirds of ECF.
Blood Plasma
ECF within blood vessels, more permeable than ICF.
Adipose Tissue Water Content
Adipose tissue contains about 20% water.
Skeletal Muscle Water Content
Skeletal muscle contains about 75% water.
Fluid Intake
Addition of water to the body, 2500 mL/day.
Metabolic Water
Water produced from cellular respiration, 200 mL/day.
Fluid Output
Loss of water from body, 2500 mL/day.
Sensible Water Loss
Measurable loss through feces and urine.
Insensible Water Loss
Not measurable; includes expired air and sweat.
Obligatory Water Loss
Water loss that always occurs, essential for waste.
Facultative Water Loss
Controlled loss, dependent on hydration and hormones.
Volume Depletion
Isotonic fluid loss exceeds isotonic fluid gain.
Volume Excess
Isotonic fluid gain exceeds isotonic fluid loss.
Dehydration
Water loss exceeds solute loss, blood plasma hypertonic.
Hypotonic Hydration
Excess water retention, plasma becomes hypotonic.
Fluid Sequestration
Normal total body fluid, abnormal distribution.
Thirst Center Regulation
Stimulated by decreased blood volume and pressure.
Electrolytes
Dissociate in solution, conduct electrical current.
Sodium Ion (Na+)
Principal cation in ECF, regulates osmotic pressure.
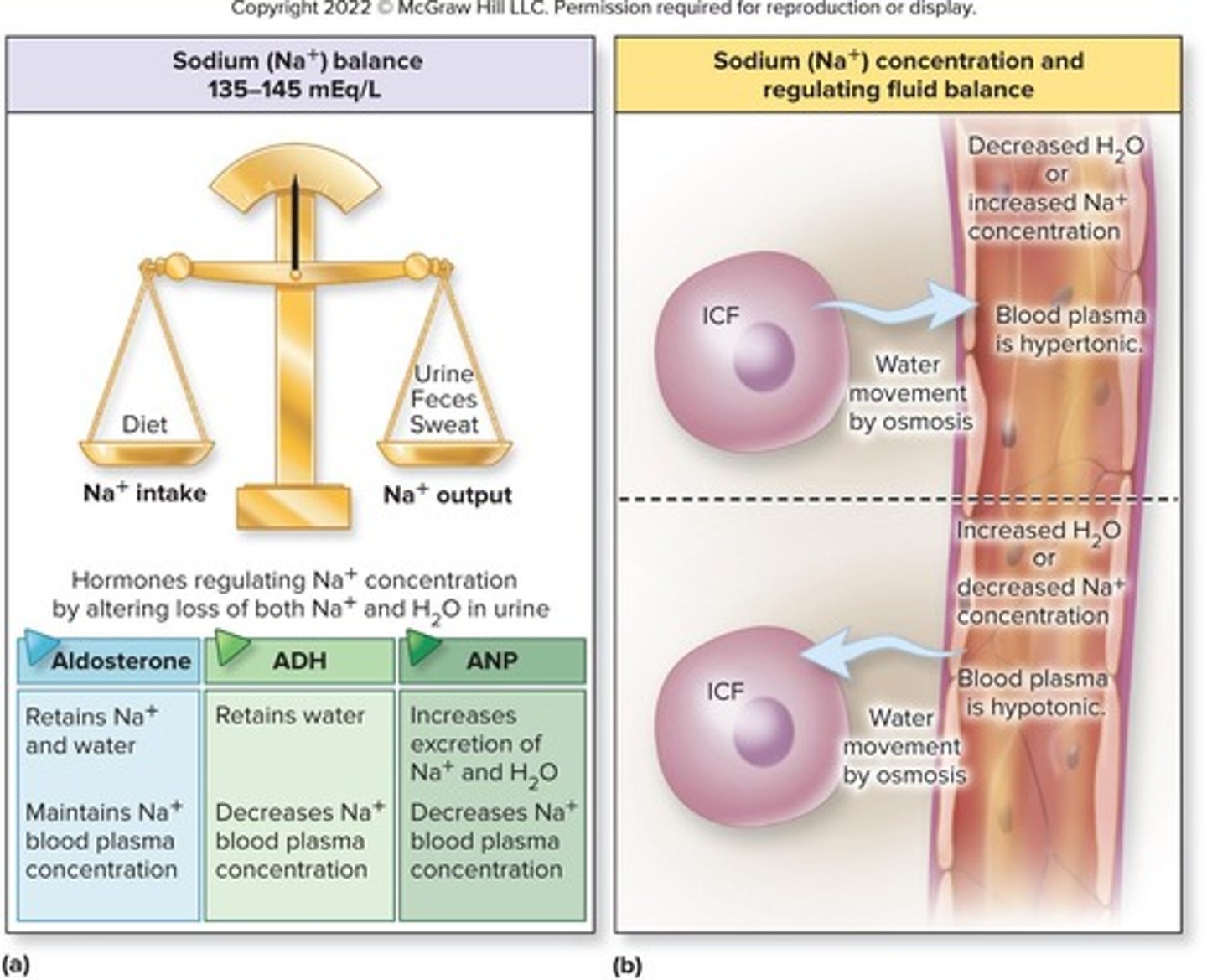
Sodium Balance
Normal concentration 135-145 mEq/L, daily intake 2g.
Hypernatremia
Above normal sodium levels in blood.
Hyponatremia
Below normal sodium levels in blood.
Osmolarity Changes
Altered by sodium concentration, affects fluid movement.
Fluid Movement
Occurs by osmosis in response to osmolarity changes.
Fluid Compartments
Intracellular and extracellular compartments are chemically distinct.
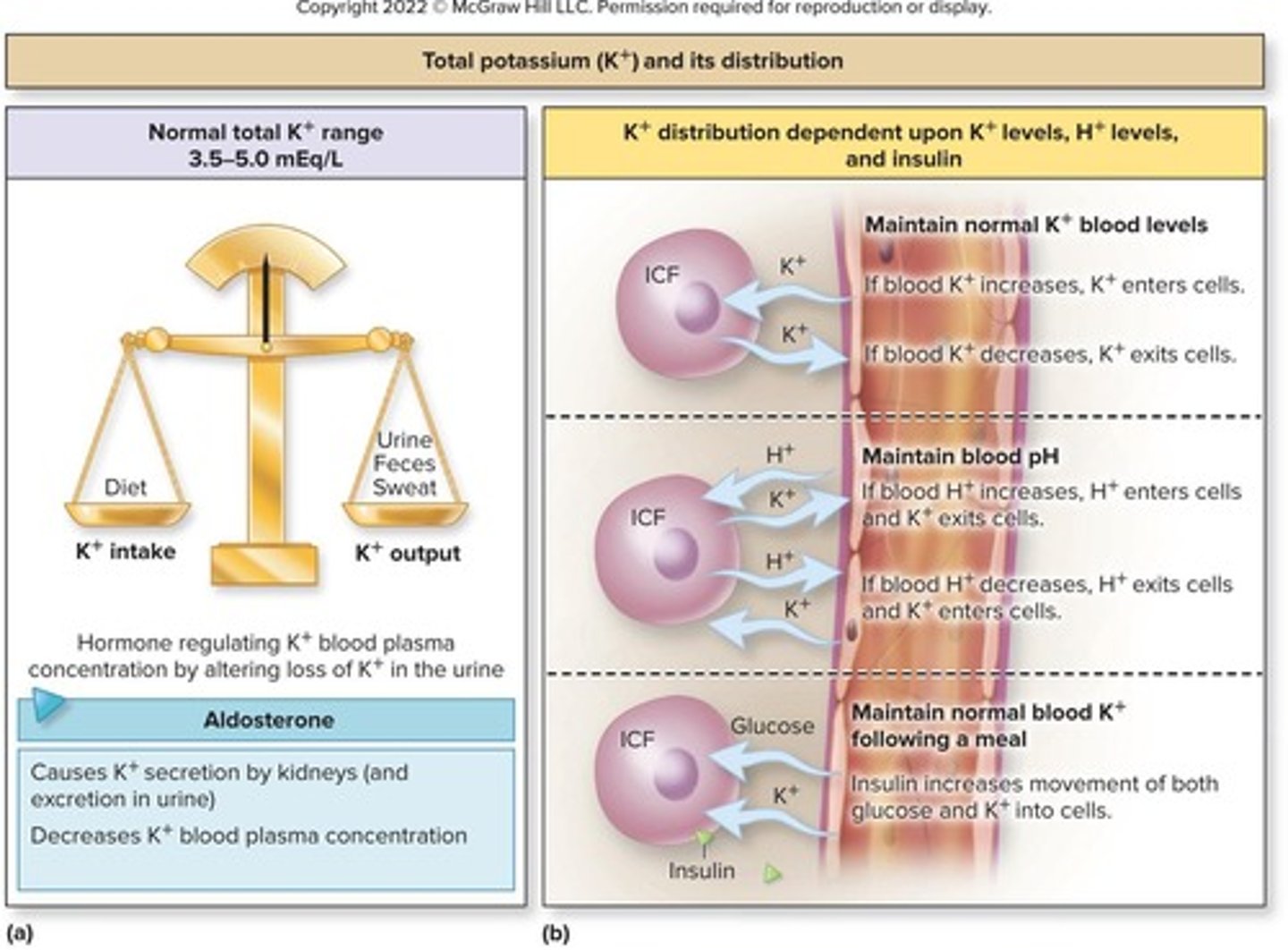
Potassium (K+)
Essential for maintaining electrochemical gradients in cells.
Hyperkalemia
Elevated potassium levels in the blood.
Hypokalemia
Decreased potassium levels in the blood.
Chloride ion (Cl−)
Most abundant anion in extracellular fluid (ECF).
Hyperchloremia
Increased chloride levels in the blood.
Hypochloremia
Decreased chloride levels in the blood.
Calcium ion (Ca2+)
Most abundant electrolyte in bones and teeth.
Hypercalcemia
Elevated calcium levels in the blood.
Hypocalcemia
Decreased calcium levels in the blood.
Phosphate ion
Most abundant anion in intracellular fluid (ICF).
Magnesium ion (Mg2+)
Second most abundant cation in intracellular fluid.
Renin
Enzyme released by kidneys to regulate blood pressure.
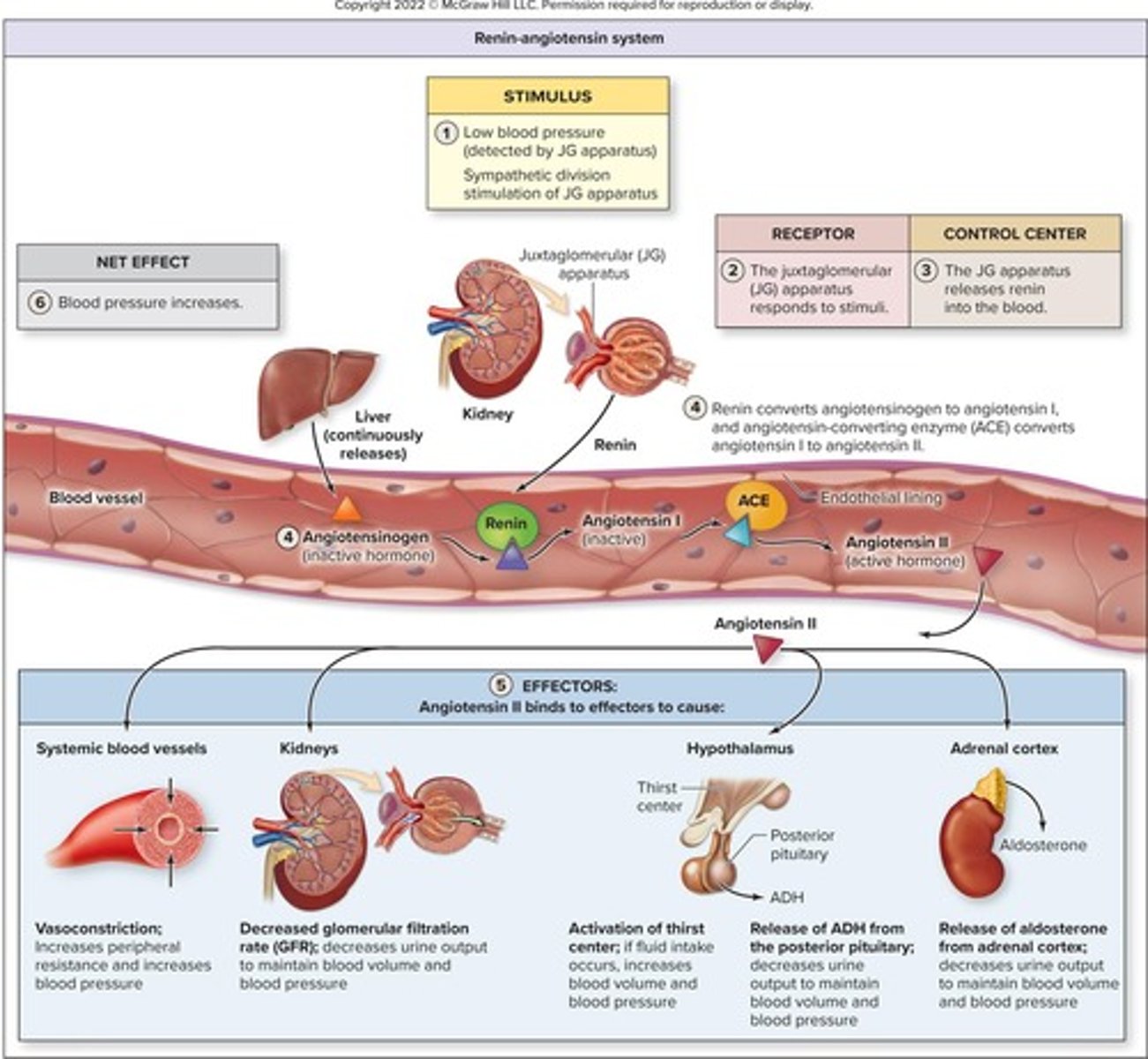
Angiotensin II
Hormone that constricts blood vessels and increases blood pressure.
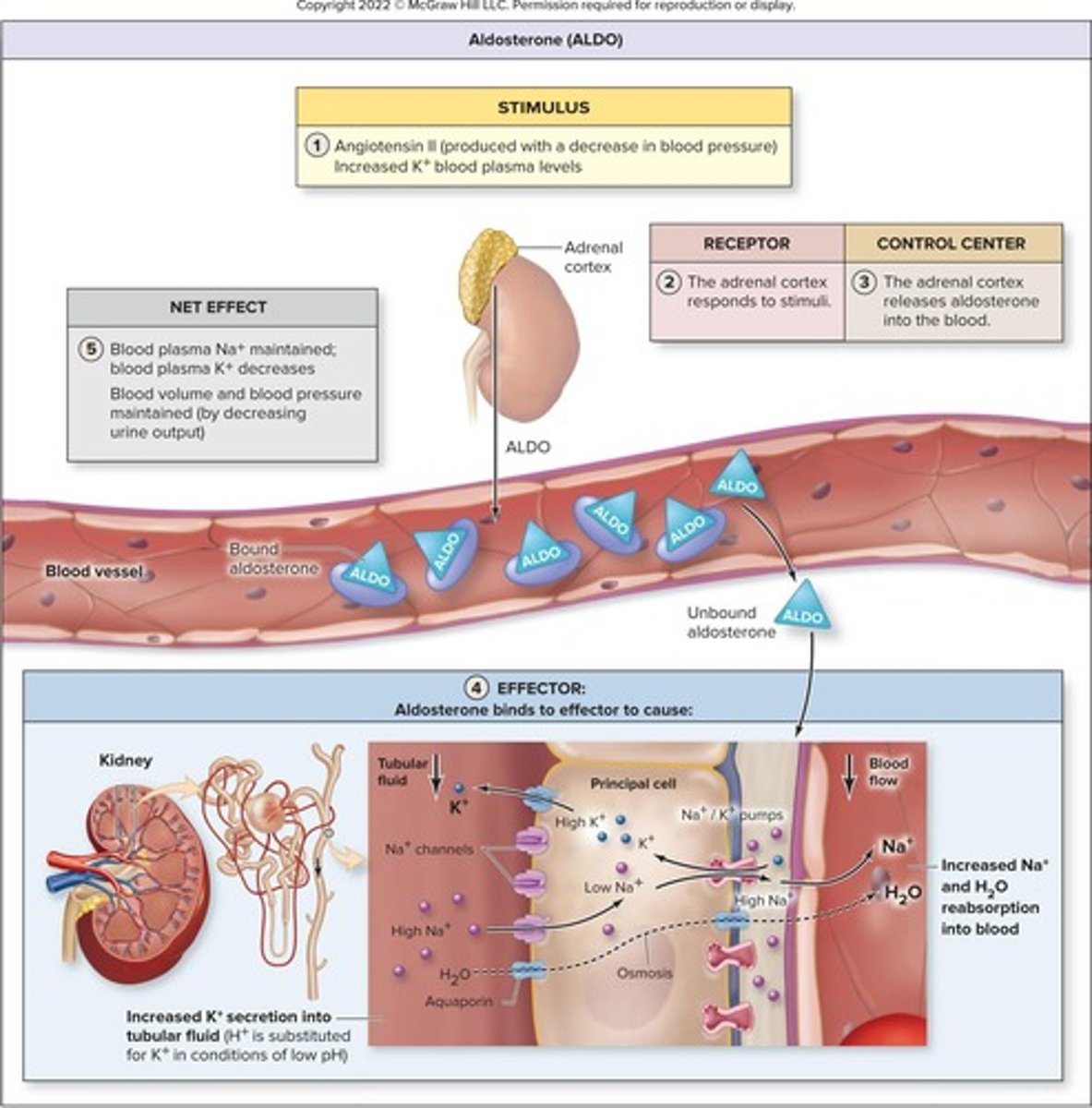
Aldosterone
Hormone that decreases urine output to increase blood volume.
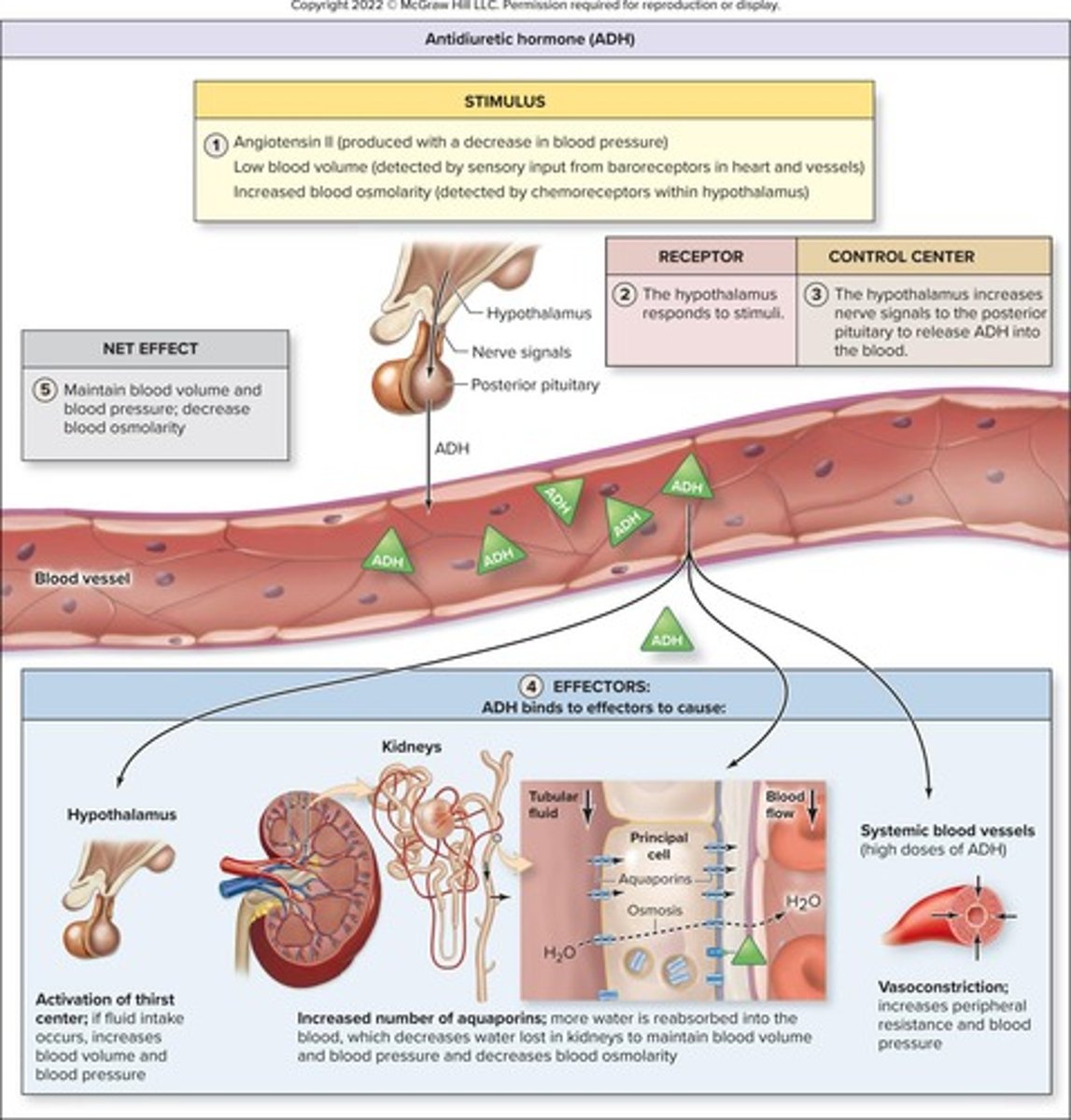
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Hormone that promotes water retention in kidneys.
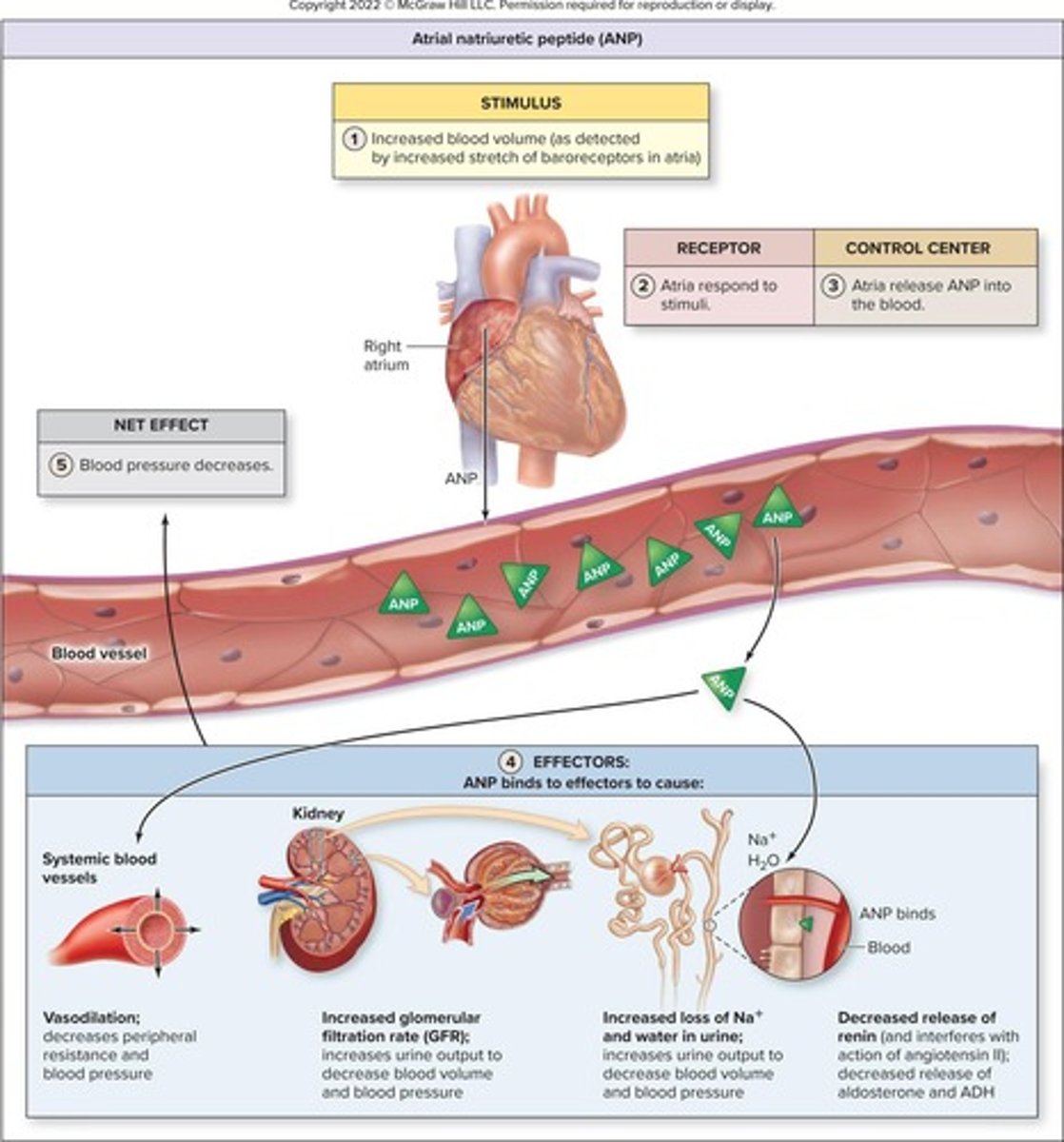
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
Hormone that increases urine output to reduce blood volume.
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Organelle that stores calcium in muscle cells.
Na+/K+ pump
Transporter that moves sodium out and potassium into cells.
Electrolyte balance
Maintaining proper levels of ions in body fluids.
Intracellular buffer
Substance that helps maintain pH within cells.
Extracellular fluid (ECF)
Fluid outside of cells, rich in sodium and chloride.
Intracellular fluid (ICF)
Fluid within cells, rich in potassium and phosphate.
Angiotensin II
Stimulates aldosterone and ADH release for blood pressure.
Aldosterone
Hormone increasing sodium retention and potassium excretion.
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Hormone promoting water reabsorption in kidneys.
Renin-Angiotensin System
Hormonal pathway regulating blood pressure and volume.
Sodium Retention
Increased sodium in blood raises blood volume.
Potassium Excretion
Aldosterone causes kidneys to release potassium.
Blood Volume
Total amount of blood in circulation.
Blood Pressure
Force exerted by circulating blood on vessel walls.
Fluid Intake
Increased drinking raises blood volume and pressure.
Aquaporins
Channels that facilitate water reabsorption in kidneys.
Vasoconstriction
Narrowing of blood vessels increases blood pressure.
Peripheral Resistance
Resistance in systemic circulation affecting blood pressure.
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)
Hormone reducing blood volume and pressure from heart.
Vasodilation
Widening of blood vessels decreases blood pressure.
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
Rate of blood filtration in kidneys.
Nephron Tubules
Kidney structures involved in urine formation.
Fluid Loss
Decreased water retention leads to increased urine output.
Renin
Enzyme initiating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
Osmolarity
Concentration of solutes in blood affecting fluid balance.
Principal Cells
Kidney cells responsive to aldosterone for sodium reabsorption.
Stretch Response
Heart's reaction to increased blood volume and pressure.
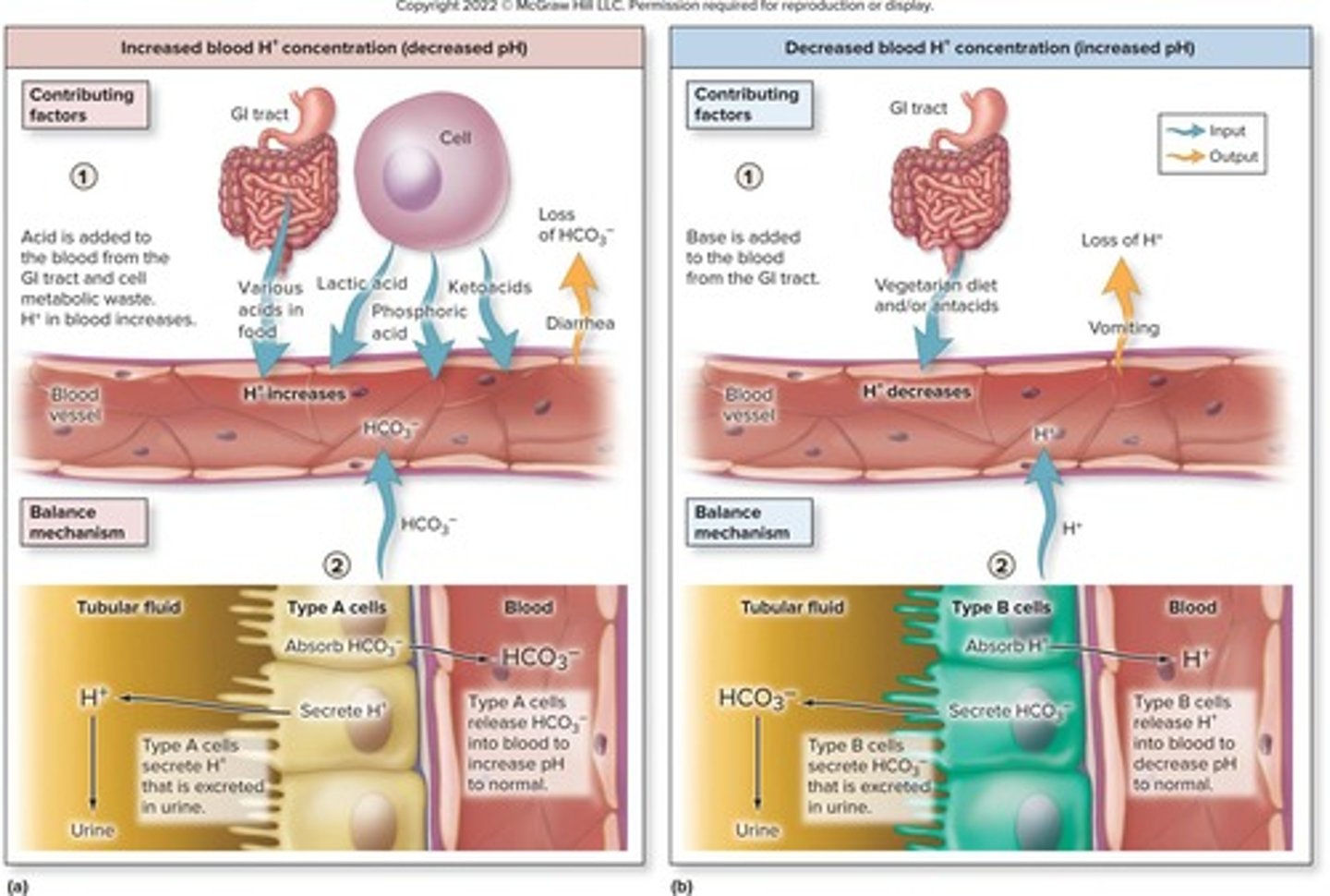
Acid-base balance
Regulation of hydrogen ion concentration in blood.
Normal pH range
Normal blood pH is 7.35 to 7.45.

Hydrogen ion (H+)
Concentration affects acid-base balance in body.
Fixed acid
Nonvolatile acids produced from metabolic processes.
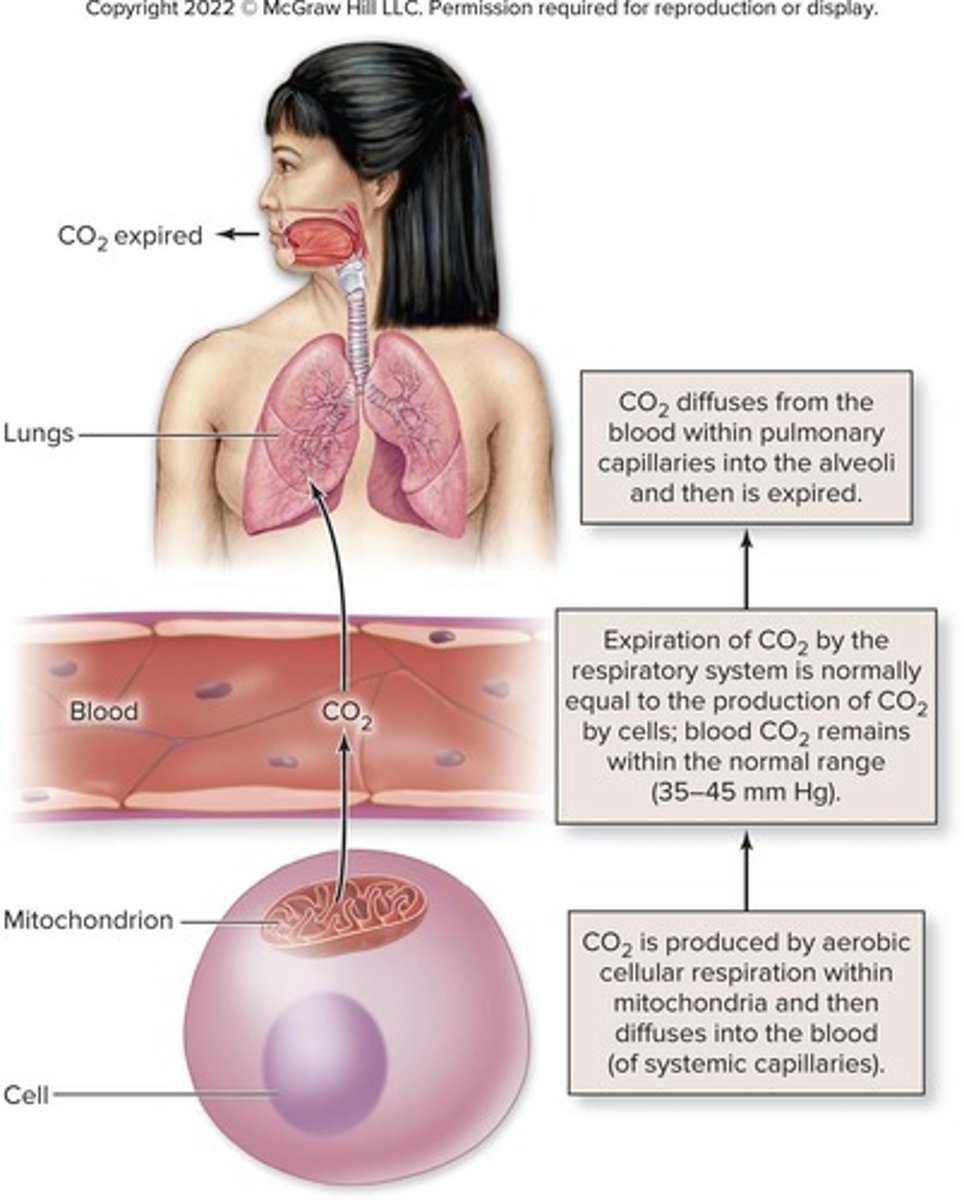
Volatile acid
Carbonic acid formed from CO2 and water.
Carbonic anhydrase
Enzyme facilitating carbonic acid formation.
Kidney function
Regulates fixed acids and maintains pH balance.
Lactic acid
Produced during glycolysis, a fixed acid.
Phosphoric acid
Generated from nucleic acid metabolism, a fixed acid.
Ketoacids
Produced from fat metabolism, a fixed acid.
Respiratory rate
Influences acid-base balance through CO2 elimination.
HCO3− (Bicarbonate)
Buffer reabsorbed by kidneys to maintain pH.
Acid input sources
Includes nutrients from GI tract and metabolic waste.
Antacid ingestion
Can decrease blood H+ concentration, affecting pH.
Renal tubules
Adjust bicarbonate and hydrogen ion reabsorption.
Physiologic buffering system
Kidneys eliminate excess acid or base over hours.
Chemoreceptors
Detect changes in CO2, H+, and O2 levels.
Respiration center
Regulates breathing rate based on blood gas levels.
Carbonic acid regulation
Dependent on CO2 levels in the body.
Acid-base balance importance
Critical for proper body functions and homeostasis.
Diarrhea effect
Can increase blood H+ concentration due to loss.
Chemical buffering systems
Prevent pH changes within minutes using molecules.
H+ binding
Chemical buffers can bind and release H+ quickly.
Weak base
Can bind excess H+ to minimize acidity.
Weak acid
Can release H+ to counteract alkalinity.
Physiologic buffering systems
Kidneys eliminate excess acid or base long-term.
Protein buffering system
Accounts for 75% of body fluid buffering.
Intracellular proteins
Proteins inside cells that buffer pH changes.
Plasma proteins
Proteins in blood plasma aiding in buffering.