bio igcse
1/201
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
202 Terms
nucleus
controls activities of the cell
cytoplasm
where chemical reactions accur
contains organelles
chroroplast
contains chlorophyll and essential enzymes to produce glucose by photosinthesis
cell wall
supports and protects the cell
cell membrane
controls movement of substances in and out of cell
vacuole
contains cell sap
presses out on the cell wall to mantain shape
ribosomes
synthesiste proteins
mitochondria
site of aerobic respiration to release energy
ciliated cells (specialised cells)
function: movement of mucus in the trachea
specialisation: layer of tiny hairs to move the mucus
root hair cells (specialised cells)
function: absorption of water and ions in roots of plants
specilisation: long extensions to increase surface area
xylem vessels (specialised cells)
function: transport water and support the plant
specialisation: no cytoplasm or end wall, water can move freely
nerve cells (specilised cells)
function: conduction of nerve impulses - reflex
specialisation: many branched endings to pass the signal quickly to many other nerve cells
red blood cells (specialised)
function: transport of oxygen
specialisation: no nucleus and biconcave, more room for heamoglobiin and oxygen
sperm cells (specialised)
function: reproduction
specialisation: tail for swimming, lots of mitochondria for energy
egg cells (specialised)
function: reproduction
specialisation: large size, energy stores and chemicals to prevent multiple sperm entering
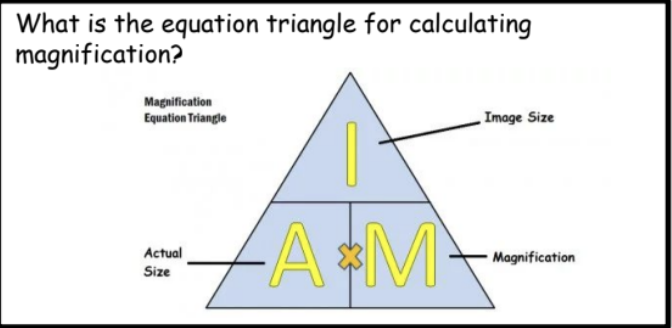
equation for calculating magnificatioon
M= I ÷ A
A = I ÷ M
I = M X A
diffusion definition
the net movement of particles form a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration down a concentration gradient, as a result of their random movement
what causes particles to diffuse
kinetic energy of random movement of molecules and ions
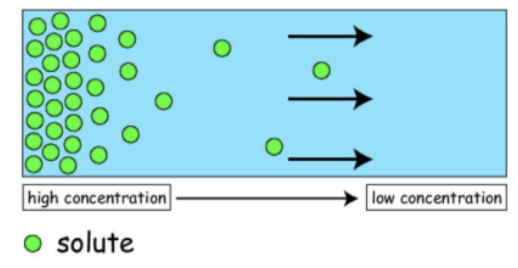
how is diffusion important for organisms
gas change in alevoli
uptake od nutrients in digestion
active transport - definition
the movement of particles through a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration using energy from respiration
2 examples of active transport
ion uptake by root hairs
glucose uptake in villi and kidney tuboles
affecting factors on the rate of movement - diffusion
surface area - larger surface are increases the rate of diffusion
temperature - rate increases as temperature inceases as molecules have more kinetic energy, they move faster and collide more often
conc. gradient - mantaining a conc. gradient increases the rate
distance - the rate is faster if there is less distance to travel
osmosis - definition
the diffusion of water through a partially permeable membrane
the net movement of water molecules form a region of high concenrtration to lower concentration through a partially permeable membrane
importance of osmosis to plants
ensures water is always being drawn in the plant
test for starch - IODINE
place food to be tested on spotting tile
2-3 drops of IODINE SOLUTION
positive result for starch = from yellow to blue black
test for protein - BIURET SOLUTION
place food to be tested in test tube
5-6 drops of BIURET solution
positive result = from blue to purple
test for glucose - BENEDICT SOLUTION
place food sample in boiling tube
add equal amount of BENEDICTS solution
plaice boiling tube in hot water bath
positive result = from blue to red
test for lipids - ETHANOL
cut and place food sample in test tube
cover with ethanol
add stopper and shake
add distilled water to half fill the test tube
shake again
positive result = cloudy white emulsion forms
simple and complex carbs common factors
used for energy
simple carbs
soluble in water
small
eg. glucose
complex carbs
insoluble
large (made of many simple carbs joined together )
eg. starch
balanced diet - deifintion
an adequate intake of the nutrients and energy needed to sustain the body and ensure health
components of a balanced diet
carbs
proteins
fats
vitamins
minerals
water
fibre
dietary needs - age
children have a greater energy requirement from adults becauswe they are still growing
elderly people have lower energy and protein needs
dietary needs - gender
females have a lower energy requirement than men due to a more stored fat in their body
dietary needs - pregnancy
pregnant women need more calcium for the fetuses bones
more iron to make more blood cells
carbs for energy to move a heavier body
more protein to provide amino acids to develop more tissues
dietary needs - brestfeeding
calcium, fats, proteins needed for milk prodution
malnutrition - definition
having too much, too little or an imbalance of the nutrients essential to remain free of health issues
vitamin a
source: milk, eggs
fhnction: good eyesight
vitamin c
source: organges
function: repair of skin tissue
vitamin d
source: seafood, nuts
function: bone growth
calcium
source: milk
function: strong bones / teeth
iron
source: meat, spinach
function: healthy blood
water
source: fruit, water
function: part of all body processes
fibre
source: fruit, vegetables
function: moving food along the alimentary canal
deficiency diseses
rickets - lack of sunlight, soft bones, legs bow outwards
anemia / iron deficiency - lack of iron, tiredness, lack of energy
scurvy - lack of vit C, sore arms and legs, tooth loss
ingestion
taking in substances, into the body through the mouth
absorption
movement of small food molecules and ions through the wall of the intestine into the blood
egestion
passing out of food that has not been absorbed or digested, as feces, through the anus
cholera
disease caused by badcteria transferred in contamined water / food
causes diarrhea and dehydration
amylase - enzyme
secreted from - salivary glands AND pancreas
acts in - mouth & small intestine
protease - enzyme
secreted from: stomach & pancreas
acts in: stomach & small intestine
lipase - enzyme
secreted from: pancreas
acts in: small intestine
where bile is produced and stored
produced: liver
stored: gallbladder
2 roles of bile
neutralisation: neutralises acidic mixture of food and gastric juices enterinf the duodenum from the stomach. Provides a suitable pH for the enzymes in the ileum
emulsification: breaks down fat globules of fat into smaller ones, increases surface area to allow fats to be better digested by lipases
enzyme - definition
proteins that function as biological catalysts, speeding up reaction in cells
catalyst definition
a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction and is not changed by the reaction
why enzymes are important to living organisms
they increase the speed of reactions in cells like respiration / photosynthesis , necessaty to sustain life
enzyme substrate specificity - definition
the active site of an enxyme has a complementary shape to fit just one specific substrate to form one type of product
investigate the effect of ph on enzyme activity
Add 2ml of amylase to a test tube
2. Add 1ml of pH2 buffer solution and leave for 5 minutes
3. Add iodine to the wells of a spotting tile
4. After 5 minutes add 2ml of 1% starch solution to the enzyme and
start a stopwatch
5. Every 10 seconds pipette some of the solution and add a few drops to
one well of iodine
6. Record the time it takes for the iodine to remain orange (not change
to black). This shows when the starch has all been broken down by
the amylase
7. Repeat this two more times
8. Repeat using buffer solutions for pH4, pH6, pH 8 and pH10
small intestine function
a region for the absorption of digested food into the bloodstream
2 places wherew water is absorbed in the alimentary canal
small intestine ( absorbs more water)
colon of large intestine
how are villi adapted for their function
thin lining: short distance for food molecules to diffuse
large surface area: folded to increase the surface area on which diffusion occurs. Microvilli to increase the surface area further
role of capillaries in villi
take absorbed food away quickly to manitain a concentration gradient to ensure more molecules diffuse across
take absorbed food cells where they are assimilated
adaptations of alveoli
spherical shape gives a large surface area for diffusion
this surface reduces the distance of diffusion
good blood supply mantains a concentration gradient
moinst surface allows gases to dissolve increasing the rate of diffusion
practical to investigate the effect of excercise on breathing
record number of breaths per minute at rest
complete one minute of intense excercise
record breathing rate right after excercise
repeat two more times and take an average for 2 / 3 minutes of excercise
IV - minutes of excercise
DV - breathing rate
CVs - type of excercise, individual completing the excercise
effects of physical activity on the rate / depth of breathing
during physical activity the rate + depth of breathing increase
physical activity increases amount of CO2 in the blood
this is deteced by the brain which sends a signal to the brreathing system to increase the rate of breathing
this increases the amount of CO2 that can be removed from the body
aerobic respiration - definition
the chemical reactions in cells that use oxygen to break down nutrient molecules to release energy
aerobic respiration - equation
glucose + oxygen ➡ carbon dioxide + water
C6H12O6+6O2 ➡ 6CO2 + 6H2O
anaerobic respiration - definition
the chemical reactions in cell that break down nutrient molecules to release energy without using oxygen
anaerobic respiration - equation
anaerobic respiration in animals : glucose ➡ lactic acid
anaerobic respiration in yeast: glucose ➡ ethanol + carbon dioxide
symbol eq anaerobic respiration in yeast: C6H12O6 ➡ 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
oxygen debt
lactic acid builds up in muscles and blood after vigorous excercise, this requires oxygen to be broken down, the amount required is oxygen debt
removal of oxygen debt
Continued raised heart rate after exercise transports lactic acid from muscles to the
liver. Continued raised breathing rate provides oxygen for the aerobic respiration of
lactic acid in the liver, breaking it down to water and carbon dioxide
role of anaerobic respiration in yeast and bread making
yeast concumes glucose in the bread mix and secretes ethanol and carbon dioxide
carbon dioxide makes the dough rise
ethanol evaporates them the heat of the oven
circulatory system - definition
a system of blood vessels with a pump and valves to ensure one way blood flow
lymphatic system - what is it
circulatory system for tissue fluid and lumphocytes, separate to the one for blood
functions of the lymphatic system
recycles tissue fluid by returning it to the vena cava near the heart
contain stores of lympgoytes in the lymph nodes that help protect the body from infection
function of shunt vessel
links an artery directly to a vein
constriction or dialation regulates hear loss
function of arteriole
subdivision of arteries that carry blood to capillaries
can regilate blood pressuee
artery - structure, function, adaptations
structure: narrow lumen, thick elastic and muscular walls
function: carry blood at high pressure away from the heart
adaptations: muscular and elastic walls to withstand high presssure
vein - structure, function, adaptations
structure: wider lumen, less muscular or leastic walls, valves
function: carry blood back to the heart
adaptations: valves to prevent blood flowing backwards
capilllary - structure, function, adaptation
structure: very narrow, one cell thick
function: allow exchange of substances in blood with body’s cells
adaptation: thin to allow substances to pass easly to and from the blood
impartance of the septum - heart
prevents deoxygenated blood on the right side from mixing with oxygenated blood on the left side
thickness of muscle wall of left and right ventricles
left has more muscle as it has to pump blood around the whole body
thickness of muscle wall of ventricles and atria
ventricles have more muscle as theu pump blood at a higher pressure
how the heart functions
atria and ventricles contract at the same time
during relaxation semilinar and atrioventricular valves are shut to prevent backflow of blood
blood flows into the atria from veins
when atria contract the pressuse opens and the atrioventricular valves and blood moves into the ventricles
ventricles contract opening semilunar valves allowing blood to leave in arteries
coronary heart disease
caused by a blockage of the coronary arteries that cupply the heart muscle cells with glucose and oxygen
if no glucose reaaches the hart cells no aerobic respiration accurs
without energy the heart cells die leading to heart attack
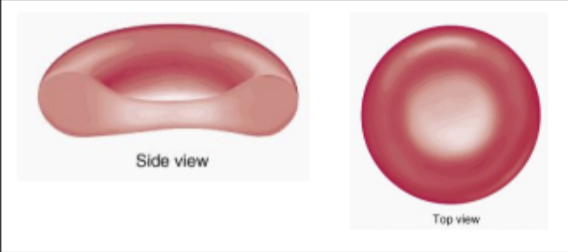
red blood cells - function
transport oxygen for respiration to the cells of the body
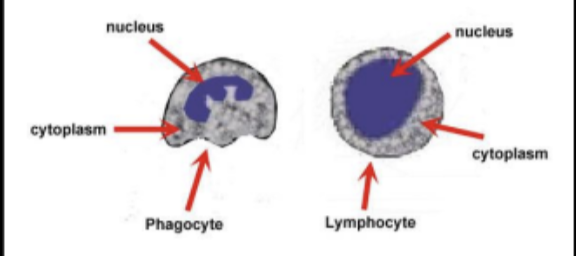
white blood cells
fight pathogens that cause disease
lymphocytes - produce antibodies (large central nucleus)
phagocytes - phagocytosis ( irregular shaped nucleus )
platelets - function
fragments of cells that cause the blood to clot
plasma - function
liquid to transport the other blood components
transports soluble nutrients, hormones, co2
how are red blood cells specialised
contain heamoglobin ( protein that carries oxygen)
biconcave shape to increase surface area
no nucleus, more space fir oxygen
heamoglobin
protein that carries oxygen
role of blood clotting
prevents blood loss and entry of pathogens
blood clotting process
platelets release a substance that converts the soluble plasma protein into the insoluble protein
forming a mesh of fibres around the cut, which hardens forming a scab
with time the skin heals and the scab falls off
pathogen
a disease causing organism
eg. hiv, influenza
transmissible disease
a disease in which the pathogen can be passed from one host to another
eg. aids, flu
direct ways a pathogen can be transmitted
through blood from cuts in the skin
unprotected sex
indirect ways a pathogen can be transmitted
contaminated food
droplets in the air
vaccination - definition
injections to enhance the bodys defence against pathogens
can be injections of antibodies for a specific diease or weakened versions of the disease