BIO 181 Exam 3 Set
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
"Did King Phillip Come Over For Gay Sex" Taxonomic Levels
➷ Domain
➷ Kingdom
➷ Phylum
➷ Class
➷ Order
➷ Family
➷ Genus
➷ Species
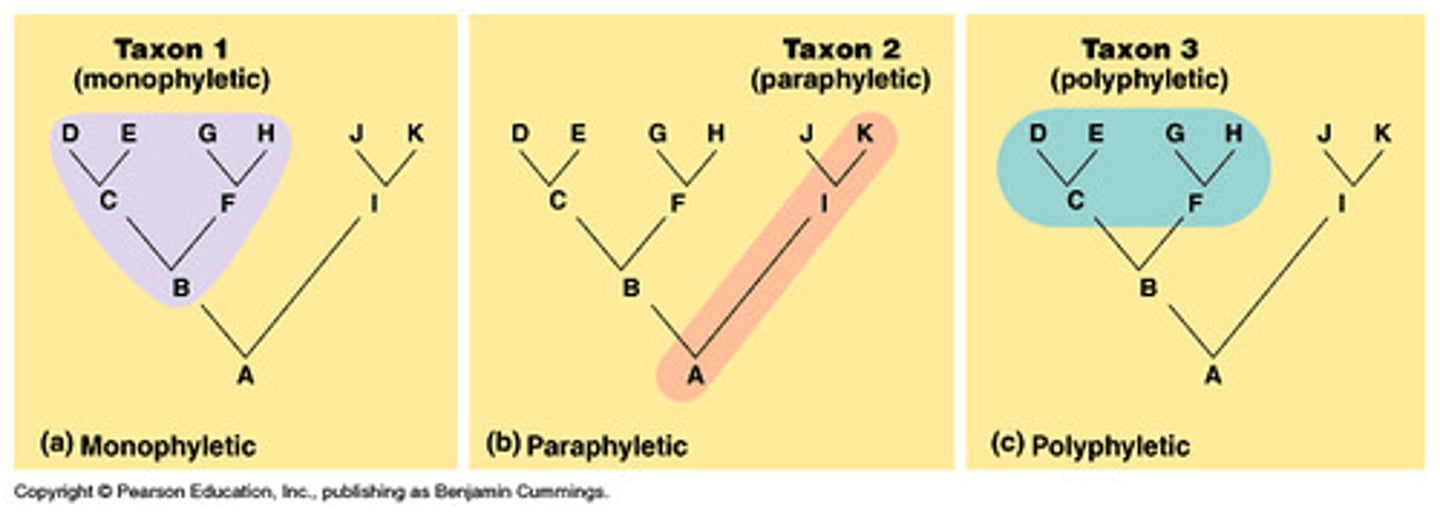
Monophyletic
➷ Ancestor and ALL descendants
➷ preferred (one phylogeny)
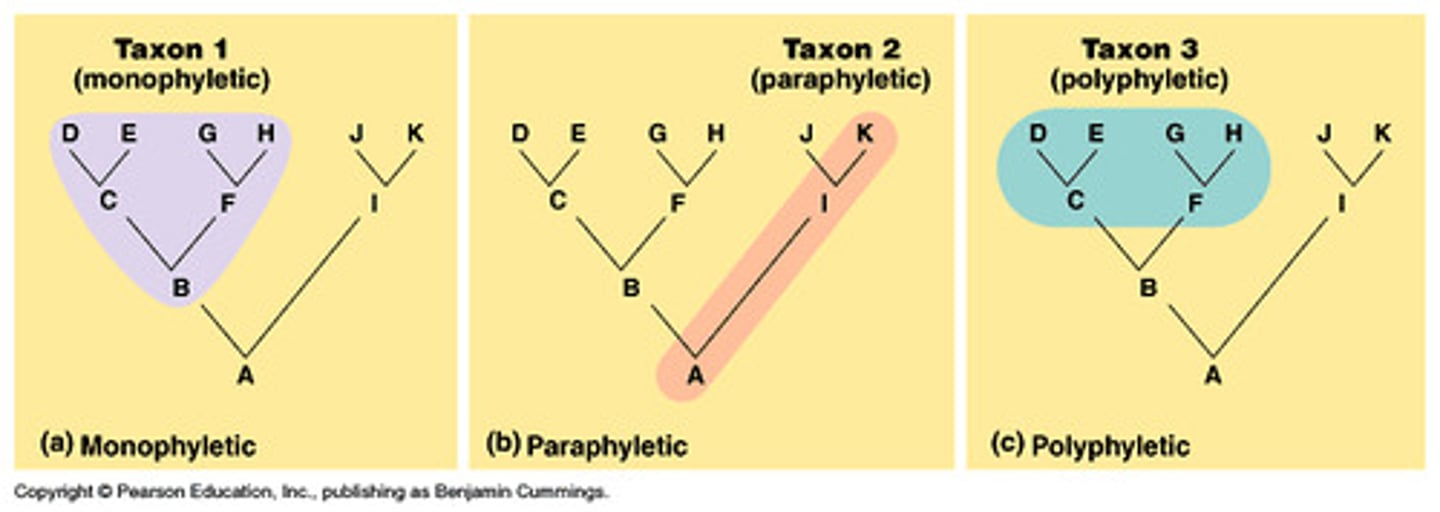
Polyphyletic
➷ Many phylogenies/descendants but no ancestor
➷ Shows analogous creatures
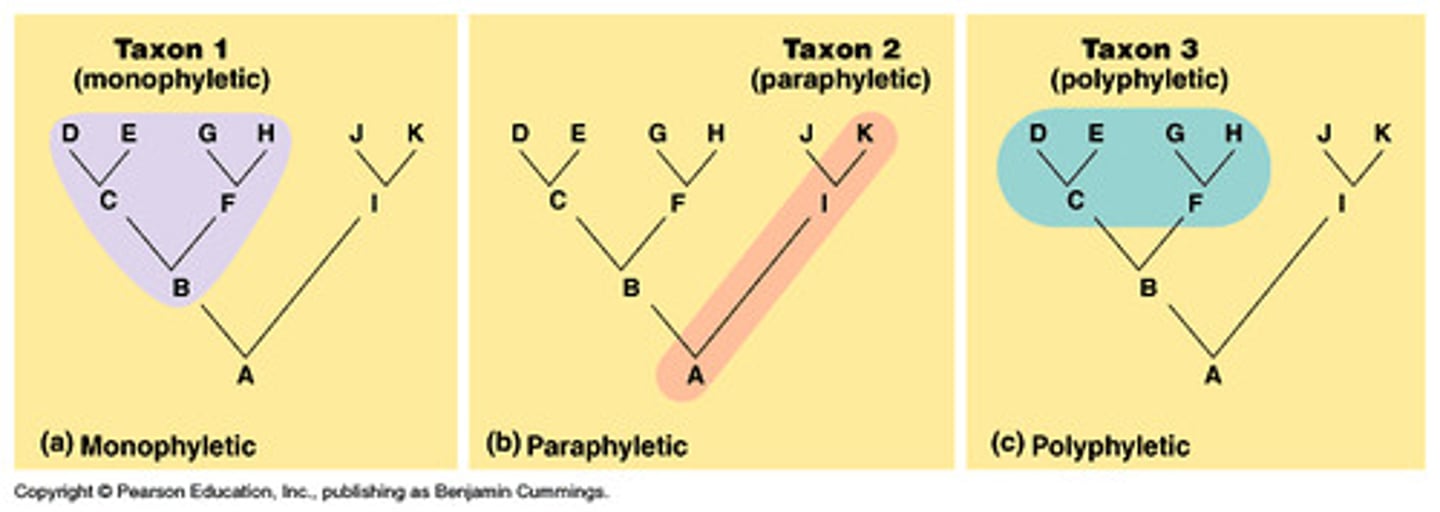
Paraphyletic
➷ Includes CA but not all the descendants
"parallel"
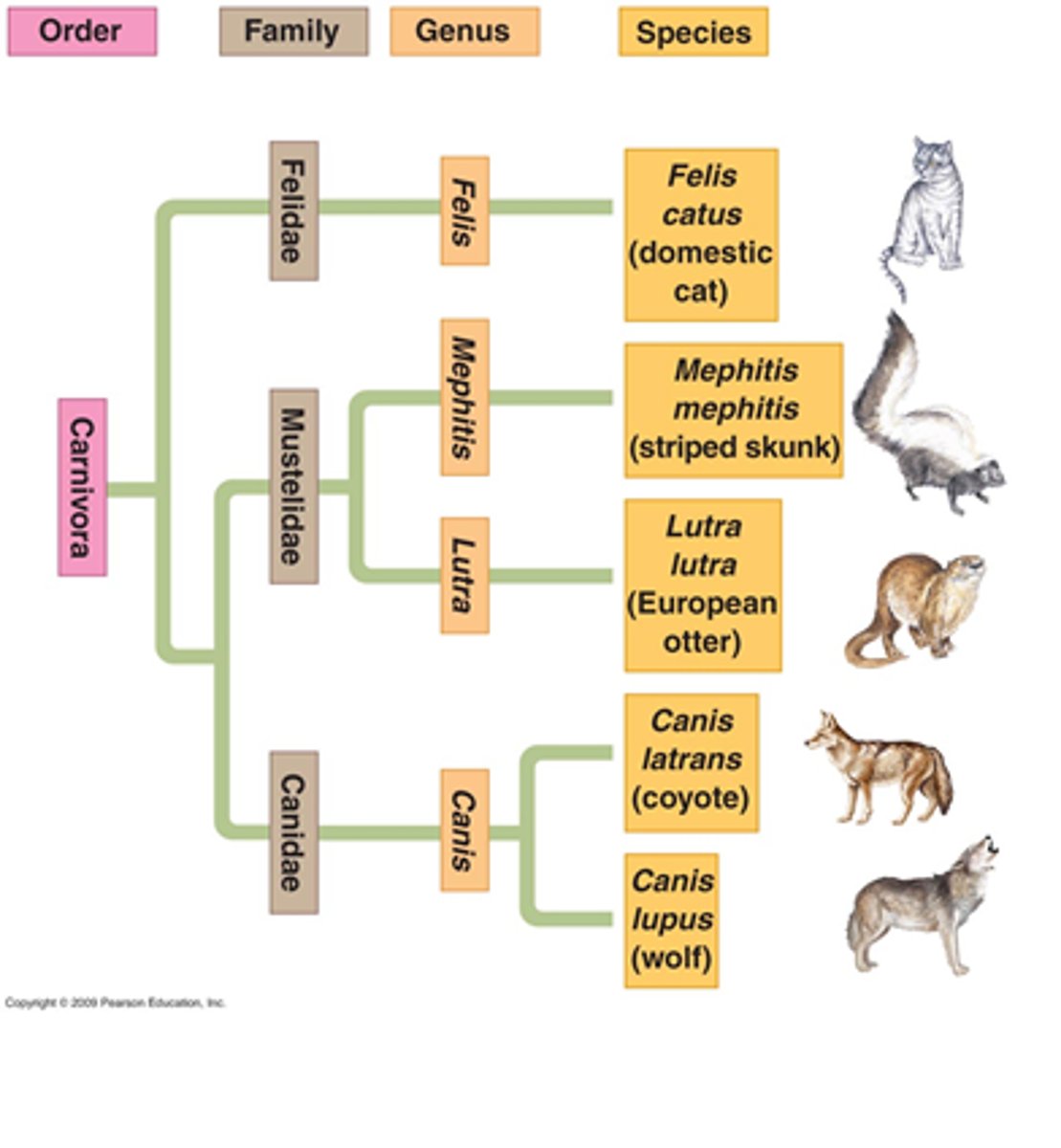
Life Classification based on ...
➷ Ray (defined species)
➷ Linnaeus (father of taxonomy)
Taxonomy
➷ Naming a group of any rank (e.g. species/class)
➷ Taxon - plural
➷ Taxa - singular
Phylogeny
➷ Evolutionary history and relationship of organisms
➷ Genetics of a phylum
Cladogram
➷ Diagram showing evolutionary relationships among organisms
- picture of evolutionary relationships
➷ Clade
- group of evolutionary ancestors and descendants of common ancestor
➷ Sister clades
- share immediate common ancestor; each other's closest relative
Phylogenetic Trees and their Anatomy
➷ Cladogram with bells and whistles
- branches can be proportional to change or time
➷ Root
- where tree begins
➷ Nodes
- split where speciation event occurs; could mean an extinction
➷ Branch
- literally a tree branch
Symplesiomorphy
➷ (shared) Ancestral trait
➷ trait in group's CA that could be kept or changed in descendants
➷ "please remember your ancestors"
Synamorphy
➷ Derived trait
➷ trait that differs from ancestral form; an evolutionary novelty
➷ derived = "just arrived" on the scene!
Homoplasy
➷ Analogous trait
➷ "plasy" = plastic -- it's malleable
Principle of Parsimony
➷ Best explanation of observed data is simplest explanation
➷ A succinct phylogenetic tree is favored
Three Domain System "AEB"
➷ Archaea
➷ Eukarya
➷ Bacteria
Characteristics to Classify Organisms "STEEL"
➷ Skull types
➷ Temperature regulation
➷ Excretory product
➷ Extraembryonic membranes
➷ Life cycles
Haploid vs Diploid
➷ Haploid - one set of chromosomes (n)
➷ Diploid - two sets of chromosomes (2n)
Gametophyte vs Sporophyte
➷ Gametophyte - gamete (sex cell)-producing structure
➷ Sporophyte - spore (haploid "seed")-producing structure
➷ Plants have alteration of generation between gametophytes and sporophyte
Extraembryonic Membranes
➷ Non-amniotes - eggs laid in water, no special water-filled enclosure (fish & amphibians)
➷ Amniotes - reptiles and birds (shelled eggs) and mammals (uteruses)
Excretory Product
➷ Ammonia - (Aquaman!) most aquatic animals, including many fish
➷ Urea - (U!) mammals, amphibians, sharks, some bony fish
➷ Uric acid - (birds!) birds, insects, many reptiles, land snails
Temperature Regulation
➷ Endotherms - heat from inside (us)
➷ Exotherms - heat from outside (l i z a r d)
➷ Homeotherms - body temp can fluctuate (us)
➷ Heterotherms - body temp constant (fish)
Skull Types
➷ Synapsis - one temporal fenestrae; mammals
➷ Sauropsids -
- anapsids - no temporal fenestrae (turtle)
- diapsids - two temporal fenestrae
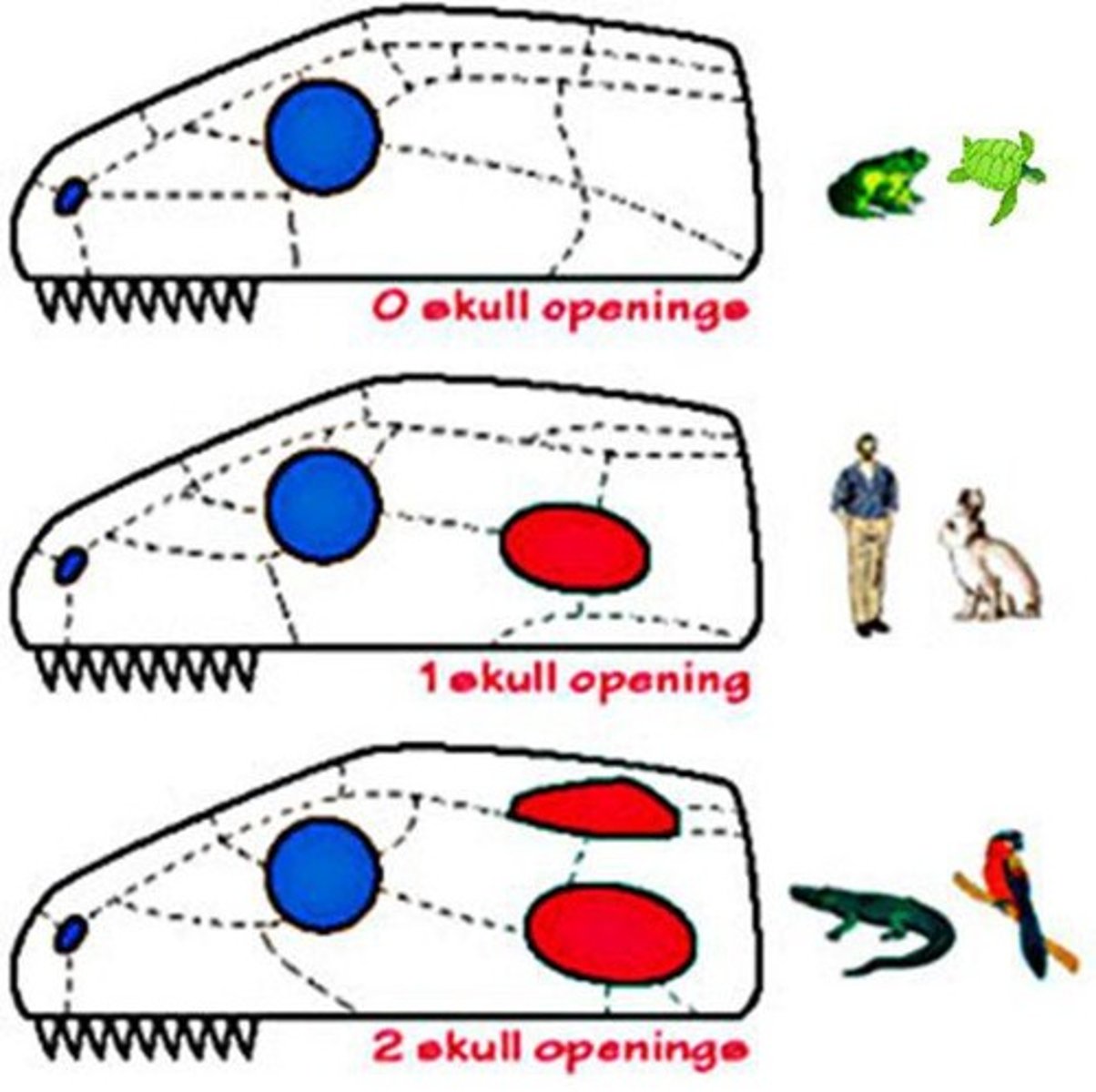
"Tiny Snakes Check Cozy Dens"
➷ Tiny - Tissues
➷ Snakes - Symmetry
➷ Check - Cephalization
➷ Cozy - Cavity
➷ Dens - Development
Basic Body Plan of Animals
1) # of TISSUE TYPES in embryos
2) BODY SYMMETRY
3) Degree of CEPHALIZATION
4) Presence/absence of FLUID-FILLED CAVITY
5) How EARLY DEVELOPMENT proceeds
Tissues
➷ Only sponges lack tissues (cells not organized)
- sponges = parazoans
➷ All other animals have tissues
- eumetazoans ("truly among animals")
- diploblasts ("two germ layers), (jellyfish!)
1) ectoderms
2) endoderms
- triploblasts ("three germ layers"), (us!)
3) mesoderm (between the two)
Body Symmetry
➷ All animals are bilateral except starfish (echinoderms) and coral polyps (radial symmetry)
- sponges don't count either way because they're "besides animals"
Cephalization
➷ In the Chordata phylum:
- notochord (cartelagenous & rod-like)
- also a dorsal, hallow nerve chord
- pharyngeal slits/clefs (used to filter food)
- muscular, post-anal tail
- 3 subphyla:
* vertebrata
* urochordata
* cephalochordata
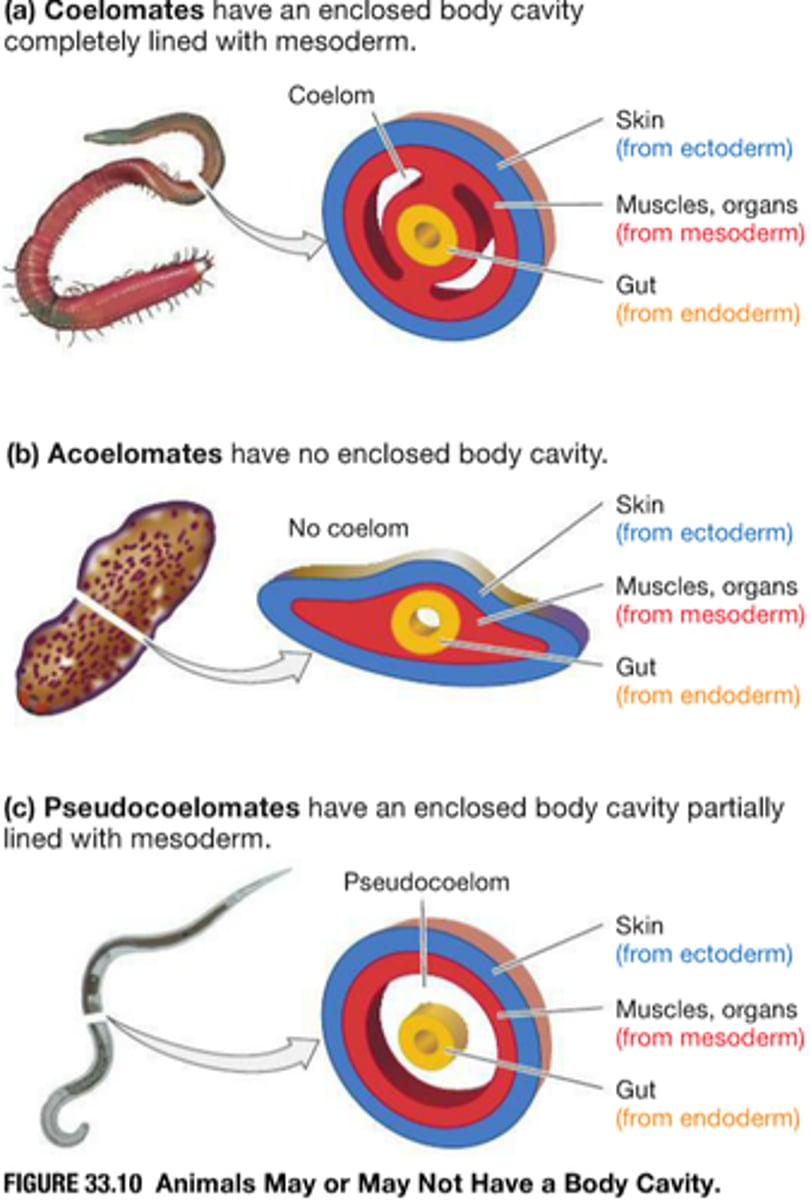
Body Cavity
➷ Coelom - fluid-filled space separating digestive tract from outer body wall
- found in tripoblasts because it's derived from the mesoderm
- cushions internal organs and allows them to grow independently of each other
- acoelomates have no coelom (flatworms, tapeworms, etc.)
Early Development
➷ Protosomes ("first opening/hole")
- mouth develops first
- arthropods (spiders, insects, crustaceans)
➷ Deuterosomes ("doody)
- anus develops first
- Chordata phylum (us) and echinoderms (starfish)
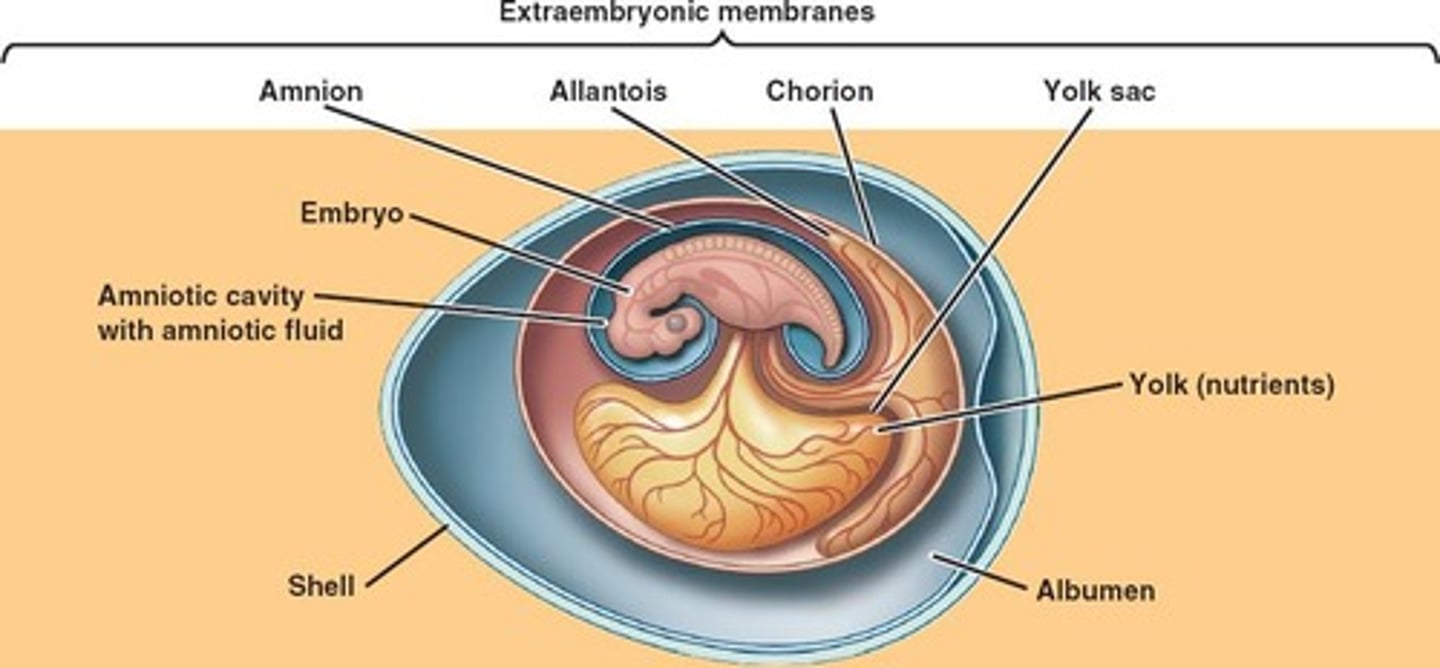
Anatomy of an Egg
➷ Yolk sac - food source
➷ Amnion - like amniotic fluid
➷ Allantois - stores metabolic waste (uric acid)
➷ Chorion - lines the inner surface of the shell, which is permeable to gas, and exchanges O2-CO2 between embryo and outside air
Sponge Phylum
➷ Porifera
Diploblasta
➷ Cnidaria and Ctenophora
Domain Eukarya: Fungi
➷ Single-celled: yeasts
➷ Multicellular, filamentous: mycelia/mycelium
- made of hyphae (strand-like structures in mycelia) that help fungi grow
- have cell walls
- mainly of chitin
Specialized Hyphae
➷ Haustoria - appendage of parasitic fungus that penetrates hosts' tissue and draws nutrients from it
- "haus" = "host!"
- "HA! I gotta STORY for you!" = haustoria
Fungal Lifestyle
➷ Incredibly diverse
➷ heterotrophs
➷ extracellular digestion
- enzymes break stuff down outside of cell so cell can absorb it
➷ decomposers (saprobes)
- absorm nutrients from dead organisms
➷ can be parasitic, pathogenic, or mutualistic
Important Fungal Roles
➷ Decomposers
➷ Consumption and food (yeasts!)
➷ Antibiotics (pennicillin)
➷ Pathogens -> fungal infections (mycosis)
➷ Mostly infects plants
➷ Symbionts
- helps herbivores digest tough plant material
- food for leaf-cutting ants
Mycorrhizae
➷ "Fungus roots"
➷ Hyphae of certain fungi <-> roots of most seed plants
➷ Feed land plants (helps get more P)
- optimize plant production so both can grow big and strong
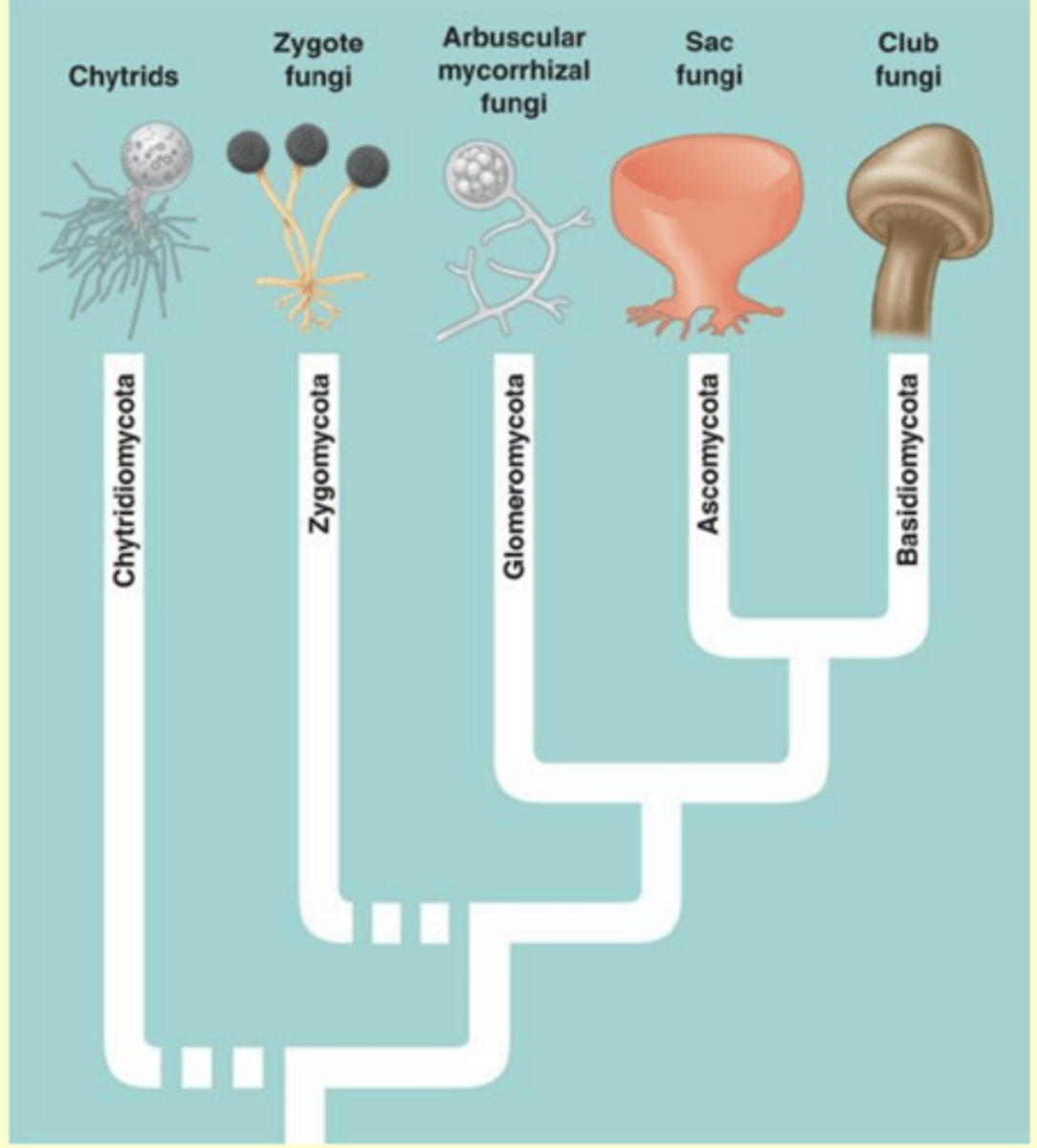
Phylogeny of Fungi
➷ memorize it
- Chytrids (Chtridiomychota)
- Zygote fungi (Zygomycota)
- Mycorrhizal fungi (Glomeromychota)
- Sac fungi (Ascomychota)
- Club fungi (Basidiomychota)
Domain Eukarya: Plants
➷ Nonvascular plants - no vascular tissue to transport water or provide support
➷ Seedless plants - have vascular tissue but don't make seeds
➷ Spermatophytes - have both vascular tissue and seeds
Nonvascular plants
➷ Bryophytes - moss, liverwort, hornwort
- cuticle provides covering to prevent moisture evaporation
➷ "Bryan really loves water and likes to manicure cuticles"

Seedless plants