ASTR Exam 2
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
The more massive a main sequence star is the more.…
Luminous it is
Stars in the upper-right regin of H-R Diagram
Stars have low temperature and high luminosity.
There are also some stars in the lower-left corner of the diagram, which have high temperature and low luminosity. If they have high surface temperatures, each square meter on that star puts out a lot of energy. How then can the overall star be dim? It must be that it has a very small total surface area; such stars are known as white dwarfs (white because, at these high temperatures, the colors of the electromagnetic radiation that they emit blend together to make them look bluish-white). We will say more about these puzzling objects in a moment.
What stellar temperature is the hottest?
Blue
What stellar temperature is the coolest?
Red
Each of these methods allows you to measure the distance to stars. Which method has the farthest range?
Cepheid stars
If a star is 20 parsecs away, its parallax must be
1/20th of an arcsecond
Where on the H-R Diagram would we find stars that look red when seen through a telescope?
only on the right side of the diagram and never on the left
Measurements show a certain star has a very high luminosity (100,000 x the Sun's) while its temperature is quite cool (3500 K). How can this be?
it must be quite large in size
For what type of star can astronomers measure the diameter with relative ease?
eclipsing binary stars
I am measuring the spectrum of the stars in a spectroscopic binary system. When one of the stars is moving toward the Earth in its orbit, we observe
that the lines in its spectrum show a blue-shift
Which of the following characteristics of a single star (one that moves through space alone) is it difficult to measure directly?
its mass
In recent decades, astronomers discovered stars even cooler than the traditional spectral type M stars recently. Astronomers gave these cool stars a new spectral type, L. If you wanted to go out and find more such type L stars, what kind of instrument would it be smart to use?
a sensitive infra-red telescope
Which of the following looks the brightest in the sky?
a star with magnitude -1
Two stars have the same luminosity, but star B is three times farther away from us than star A. Compared to star A, star B will look
nine times fainter
M-type star
Includes the smallest stars
Ex: Betelgeuse
O-type star
The most massive stars
→Strong absorption lines showing ionized helium
Brown Dwarf Stars
No sustained fusion in core (technically not a star)
→ Between 13-80 Jupiter masses
G-type star
The sun
→ yellowish most of its lifetime
M class stars (smallest, reddest stars that are very dim) are the most….
Common
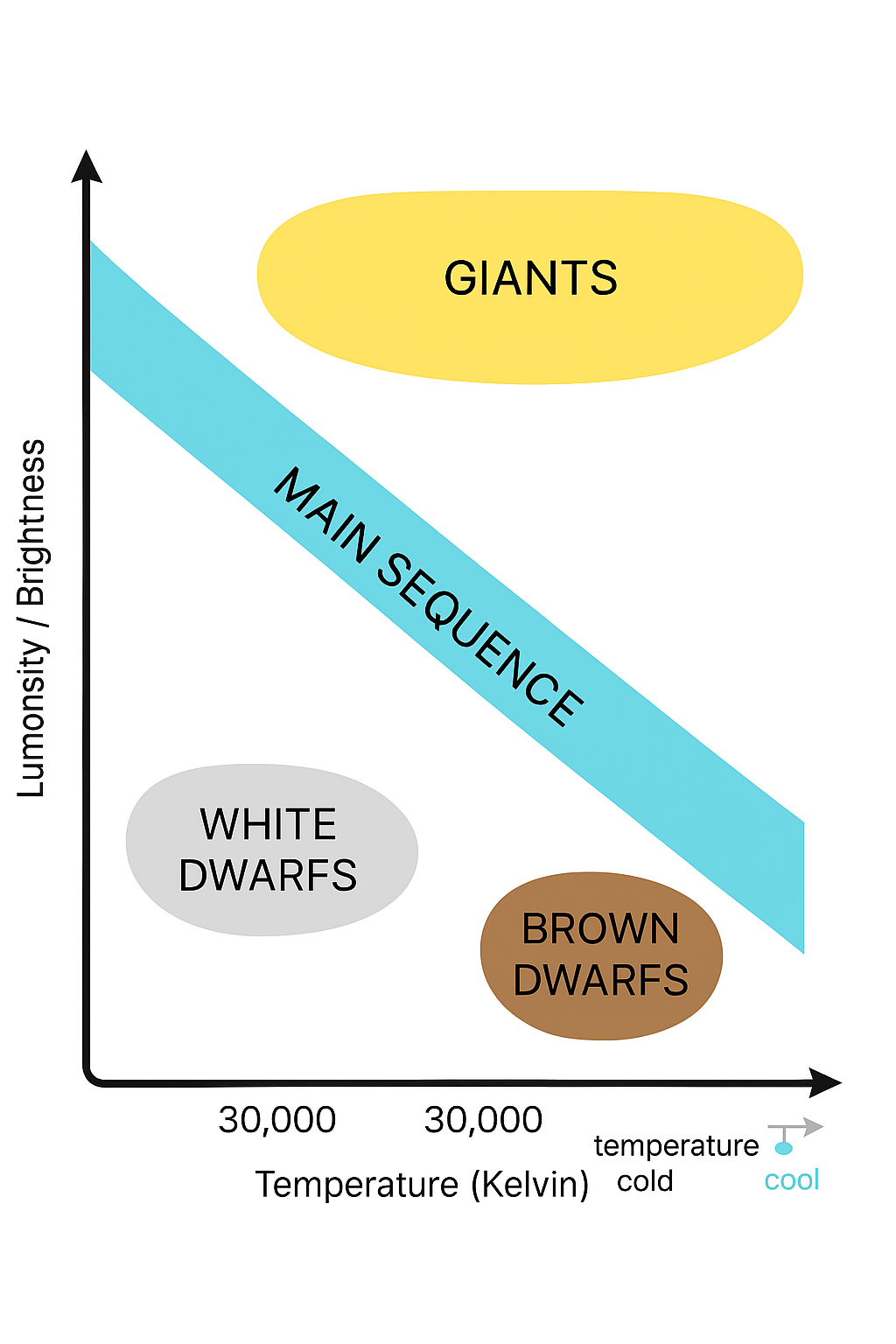
Where are brown dwarfs on the H-R Diagram?
Bottom right
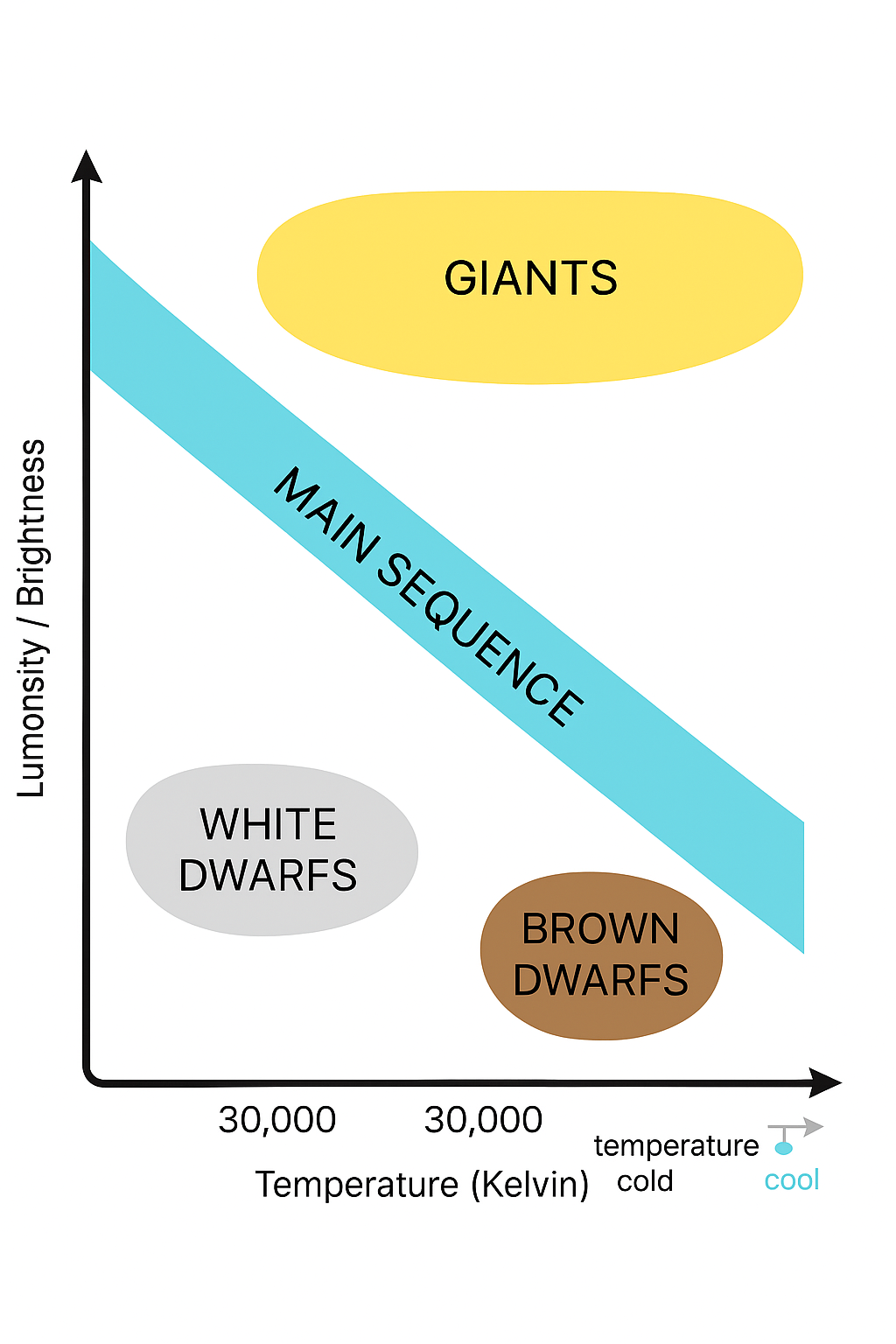
where are giants on the H-R diagram?
Top right
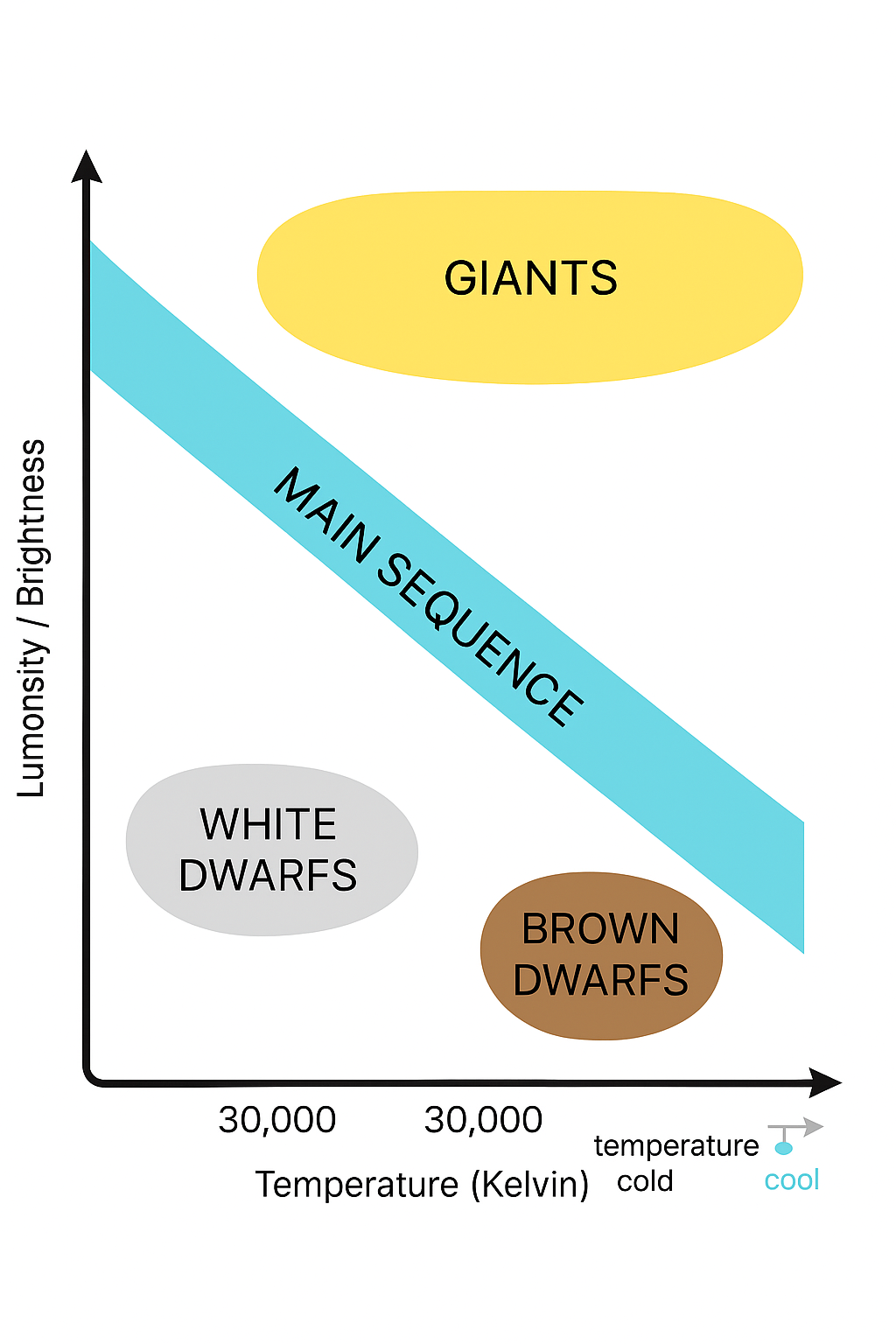
Where are white dwarfs on the H-R Diagram?
bottom left
What is the main medium of heat exchange in near total vaccums?
Photons
What is the majority of gas made up of?
atomic hydrogen and helium
What’s the temperature of space if you block out the sun?
2 Kelvin
How does atomic hydrogen release energy?
Release of photons
Where are most stars formed?
Collapsing giant molecular clouds
What’s the most common type of molecule in the ISM?
Molecular Hydrogen H(2)
B or A stars
O III lines
O star
C IV
A star whose temperature is increasing but whose luminosity is roughly constant moves in what direction on the H-R diagram?
to the left
Which of the following types of stars will spend the longest time (the greatest number of years) on the main sequence?
K
Which of the following types of stars are the shortest lived?
O
Which of the following types of stars have the highest mass?
O
Stars in the upper right of the HR Diagram..
High luminosity, large radius, low surface temperature
Star A is a magnitide 7.1 star and Star B is a magnitide 8.6 star. What is the brightness of Star A divided by the brightness of Star B?
Star A is 42 times brighter than Star B. What is the magnitude of Star A minus the Magnitude of Star B.
What is the radius of a main sequence star in solar radii that is 11.16 times as luminous as the sun and has 0.71 times the sun's surface temperature?
When gravity and pressure are balanced, a star is in..
hydrostatic equilibrium
Our sun is a
G class star
The biggest stars are
O
The smallest stars are
M
What’s resosnance?
when stars pulse in and out overtime over the equilibrium point
When does fusion occur?
When density and temperature increase.
The Instability Strip-
narrow band of temps and luminosities, chemical changes cause the star to go in and out in resonance
Classical Cepheids -
stars within the instability strip with a relationship between their period and their luminosity that are also used to calculate distance.
Where do stars spend 90% of their lifetime?
In the main sequence
What are stars doing on the main sequence?
fusing hydrogen into helium
Why would a star be white?
A star is white because...
all colors of light are added together, making it appear white.
If a star has a high mass, it has a ____ luminosity.
high
What’s the rarest type of star?
O type
high mass stars run out of _____ first
fuel
The sun turns _____ into helium
hydrogen
What is interstellar medium (ISM)?
the entire collection of interstellar matter
the space between the stars is filled with gas and dust
Composition:
~99% gas (mostly hydrogen, with helium and trace heavier elements).
~1% dust (tiny solid grains of carbon, silicates, and ices).
Also includes cosmic rays and interstellar radiation fields.
Parallax
method of measuring the distance to an object by measuring a parallax angle from two different observation points
What is the distance between the observation points in parallax?
baseline
Why is a longer baseline better?
if you make the baseline between two observations twice as long, you can measure distances that are twice as far away
smaller parallax angle =
greater distance
If star A has ¼ the parallax angle of star B, star A is ____ times as far away as star B
4
d = 1/p
d = distance (parsec)
1 = 1 AU
p = parallax angle (arcseconds (“))
The stars emitting the most energy are ____ stars
blue
____ mass stars emit the most energy
high
The stars with the longest lifetimes are ___ mass stars
low
___ stars have the longest lifetime
red
A star that has ten times more mass than another star mass lives
much less than 1/10 as long
In general, the more massive stars emit
more energy
In general, the more massive stars have
shorter life spans
More massive stars are _____ temperature in general
higher
Lumonosity of a star is almost directly proportional to the mass of the star raised to the 4th power
L = m^4
lumonosity = mass^4
What property represents how much “fuel” a star has?
→ mass,
bc how much hydrogen it has to fuse
What property represents how quickly a star is consuming its “fuel”?
→luminosity
bc luminosity represents how much energy a star is emitting