Cell Theory
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
spontaneous generation
a theory in where people believe that living organisms could spontaneously arise from non-living matter
Francesco Redi
in the 17th century, he conducted a simple yet powerful experiment using meat and jars. he placed the meat into two set of jars, one covered and one open. where flies appeared and left magots in the open jar.
Lazzaro Spallanzani
In the 18th century he experimented by boiling broth in sealed containers. No microorganisms appeared in the sealed broth, proving that boiling killed the life forms and that new ones didn’t just arise from the broth
Biogenesis
In Spallanzani’s work, this was highly hinted. It also means that life comes from pre existing life, what terminology was this?
Louis Pasteur
In the 19th century, He used a special flask with a curved neck that allowed air in but prevented dust and microbes from reaching the broth inside. The broth remained free of microorganisms until the flask was tilted, allowing dust to reach the broth, which then became contaminated.
Louis Pasteur
Whose experiment showed that clearly showed that microorganisms came from other microorganisms in the air, not from the broth itself?
All organisms are composed of one or more cells.
Cells are the smallest and basic units of structure and function in organisms.
Cells arise only from previously existing cells
what were the first three postulates / tenets involved in the cell theory?
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
He is the first to see living organisms under the microscope, he termed this organisms “animalcules”
Schleiden and Schwann
Who developed the first two tenets of the cell theory?
Rudolf Virchow
He discovered the third tenet of the cell theory.
4
How many tenets were added to the modern cell theory?
All energy flow occurs within the cell
Cells contain genetic material passed to daughter cells during cell division
All cells are similar in their chemical composition
Activities of the organism are a result of combined actions of individual cells
What were the four other tenets added to the cell theory?
All energy flow occurs within the cell
This postulate emphasizes that all the biochemical processes that provide energy and build the cellular components—collectively known as metabolism—occur within the cells.
Cells
are the sites of energy conversion and usage, such as in cellular respiration and photosynthesis.
Cells contain genetic material passed to daughter cells during cell division
This tenet says that cells contain DNA that is responsible for hereditary information. This is then passed from parent cells to daughter cells, to ensure the continuity of life.
All cells are similar in their chemical composition
This postulate asserts that while there is vast diversity in cell types and organisms, the chemical composition of cells is fundamentally similar. Cells across different species share basic molecular components like nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates, indicating a common origin of life.
Activities of the organism are a result of combined actions of individual cells
This postulate highlights that the functions and activities of a multicellular organism result from the collective activities of its individual cells. Each cell's performance contributes to the organism’s overall health, growth and function.
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
He discovered bacteria, and was the first to observe it along with protists.
Robert Hooke
He initiated the study of cell structure.
Free Cell Formation
What theory of Schleiden was rejected?
Carl Zeiss and Ernst Abbe
They developed modern compound microscope with improved optics and revolutionized cell study.
Camillo Golgi
They discovered “golgi apparatus”
Golgi Apparatus
This is an organelle involved in cellular transport and secretion.
Santiago Ramón y Cajal
he pioneered the neuron theory that showed that the nervous system consists of discrete individual cells (neurons)
Robert Brown
They identified the cell nucleus, which is essential for housing genetic materials in eukaryotic cells.
James Watson and Francis Crick
it is known that there are four people who contributed to the double helix structure of the DNA, however- who were the actual first two pioneers?
Lynn Margulis
They proposed the endosymbiotic theory, which suggests that certain organelles, like mitochondria, originated from symbiotic bacteria engulfed by eukarotyic cells.
Rita Levi-Montalcini
Discovered nerve growth factor (NGF) showing that cells produce specific molecules to regulate cell growth and differentiation.
Shinya Yamanaka and John Gurdon
Discovered cellular reprogramming which proved that specialized cells can be converted back into stem cells, eventually opening up new possibilities in regenerative medicine.
unicellular organism
what type of cell depends upon just one cell for all of its functions
multicellular organism
what type of cell has cells specialized to perform different functions that collectively support the organism
Unicellular organisms
this type of cell, the _____ include bacteria, protists, and yeast.
Unicellular organisms
form the base of food chains and are crucial for nutrient cycling.
Phytoplankton
what perform photosynthesis in aquatic environments, and soil bacteria, which decompose organic matter?
Unicellular organisms
Beneficial ____ aid in digestion, vitamin synthesis, and immune system support. An example of this is e-coli (Escherichia coli) which helps for digestion in the human gut.
fermentation
Unicellular organisms are used in industrial processes like ____ and in the production of pharmaceuticals.
False, unicellular.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast) is a type of multicellular organism which is commonly used in baking, brewing and such. it is also the bacteria needed in producing insulin. true or false?
True
Unicellular organisms contribute to oxygen production and the breakdown of pollutants. An example of this is the cyanobacteria. true or false?
True
Some unicellular organisms are pathogens, which help in studying disease mechanisms and developing treatments. True or false?
Multicellular organisms
These cells are composed of more than one cell, with groups of cells differentiating to take on specialized functions.
labour
The division of ____ is seen in multicellular organisms. These cells are differentiated in the earlier stage of cell division.
Nerve cells
These cells have appendages called dendrites and axons that connect with other nerve cells to move muscles, send signals to glands, or register sensory stimuli.
Outer skin cells
This cells form flattened stacks that protect the body from the environment.
Muscle cells
these cells are slender fibers that bundle together for muscle contraction.
unicellular organism
with the descriptions in the table, can you tell which cell organism is it?

multicellular organism
with the descriptions in the table, can you tell which cell organism is it?

Prokaryotes
are unicellular organisms without a true nucleus or membranebound organelles. (Bacteria and Archaea)
Eukaryotes
have a true nucleus containing the cell's DNA and possess membrane-bound organelles. (Plant cells, animal cells, fungi, and protists.)
Prokaryotic Cells
They have a Cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm, ribosomes, nucleoid region (DNA). What type of cell is this?
Eukaryotic Cells
This type of cell contains Nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, chloroplasts (in plant cells), and more complex cytoskeleton.
Prokaryotes
They typically reproduce through binary fission, a simple form of asexual reproduction.
Eukaryotes
They Can reproduce asexually through mitosis or sexually through meiosis, involving complex processes and cell division.
Prokaryotes
They generally have a single, circular DNA molecule located in the nucleoid.
Eukaryotes
They have multiple, linear chromosomes contained within a membrane-bound nucleus.
Prokaryotes
They exhibit a wide range of metabolic activities, including photosynthesis, nitrogen fixation, and anaerobic respiration.
Eukaryotes
They are more specialized in their metabolic processes, often relying on organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts for energy production
Prokaryotes
Their role in ecological applications are mainly nitrogen fixation, decomposition, and as pathogens or symbionts.
Eukaryotes
They function in complex organisms, ecosystems, and applications in biotechnology and medicine.
plant cell
what kind of cell is this?
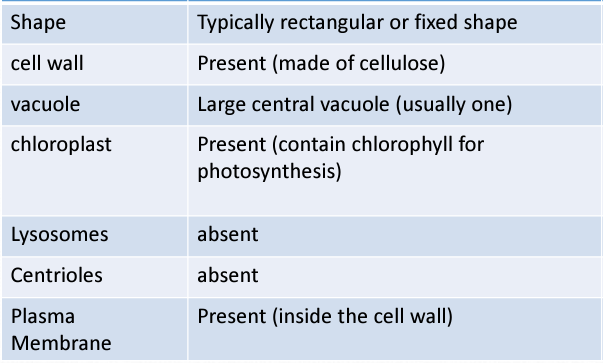
animal cell
what kind of cell is this?
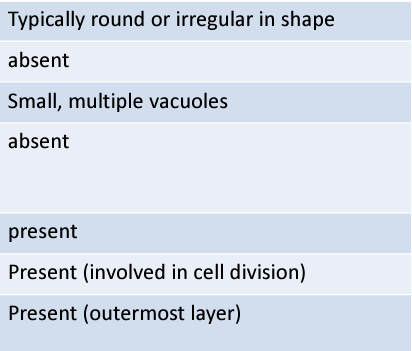
plant cell
what cell is this?
animal cell
what cell is this?

Specialized Cells
Your body contains over 200 different types of this. Each type is adapted to do a particular job well and has developed special features to do it.
Muscle Cells
key function-contraction.
long fibres, 1–40 mm long
Many mitochondria for high energy demands
up to 100 nuclei
contain special cylindrical organelles called myofibrils that are involved in contraction.
Sperm Cells
These cells are specialized for reproduction and their function is to transport the male DNA to the egg
egg cell
The function of this is to carry the female DNA and to provide nourishment to the embryo during the first stages of pregnancy.
Nerve cells
The function of the nerve cell is to carry nerve impulses around your body.
Root Hair Cell
The function of the this is to absorb minerals and water from the soil.
It has:
A large surface area to absorb lots of water
Thin cell wall to allow water to pass through easily
Doesn't contain any chloroplasts
Red Blood Cell
The function of this is to carry oxygen from the lungs to the body.
It has:
• A large surface area to volume ratio
• Contains haemoglobin which carries oxygen
• Has no nucleus to make room for more oxygen
Ciliated Epithelial Cell
The function of these is to line the surface of organs. These cells move substances in one direction. These can be found along the lining of the airways. They move mucus.
Palisade Cell
Their function is to carry out photosynthesis. They are found at the top surface of a leaf.
Palisade Cell
Tall and has a large surface area to catch as much sunlight as possible, Packed with chloroplasts to absorb sunlight. What specialized cell is this?
Cell Differentiation
These are cells developing into different cell types.
DNA
This determines what the cell will be.